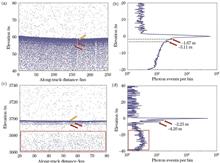
The ICESat-2 satellite carries the world's first photon-counting system LiDAR system, i.e., the advanced topographic laser altimeter system (ATLAS), whose high repetition frequency and multibeam design can provide water-profile data with high spatial resolutions. However, the water-profile signals acquired by the ATLAS exhibits "after pulse" which restricts the application of the observation data and must be corrected using an inverse convolution algorithm, where an appropriate system impulse-response function is the core of the inverse convolution algorithm. In this study, the possible sources of "after pulse" are first identified, based on which the requirements of the system impulse-response function in the deconvolution are clarified through theoretical derivation, and a data-quality control algorithm is proposed on this basis, and the system impulse-response function is established using salt-marsh and desert data. Based on an analysis of ex-Gaussian fitting results, the pulse widths of the system impulse-response functions established using the desert and salt-marsh data are 0.095 and 0.142, a difference of 0.047, which can be reduced to 0.002 using quality-control methods. Subsequently, the system impulse-response functions generated from the two types of surface data are used to back-convolute the water body signals and invert the backward scattering coefficients of the water body and particulate matter. Finally, the inversion results show that in the Black Sea waters, without quality control, the inversion error of the system impulse-response function based on salt-marsh data is smaller, whereas after quality control, the inversion results using desert and salt-marsh data as the system impulse response-function indicate similar errors.
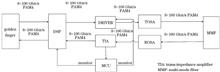
The rapid advancement of artificial intelligence models has increased the demand for faster, higher-bandwidth data transmission technologies in modern data centers to manage growing data volumes. Fiber optic communication, with its large capacity and low-loss characteristics, has become the preferred transmission method in such environments. At the core of these systems, optical transceiver modules enable photoelectric signal conversion, directly influencing the stability and efficiency of the communication networks. This paper explores the principles underlying 800 Gbit/s optical transceiver modules and evaluates their practical performance through a comprehensive development and testing process. This study first outlines the fundamental components of an 800 Gbit/s optical transceiver module: transmission unit, reception unit, management unit, and digital processing chip. The article then delves into advanced technologies and design strategies implemented to ensure stable performance in high-speed transmission scenarios. The 800 Gbit/s OSFP 2×DR4 optical transceiver module was developed and tested to verify whether its primary performance metrics met the required standards. Results from rigorous testing indicate that the module's main indicators align with anticipated benchmarks, demonstrating the 800 Gbit/s transceiver module's high performance and suitability for contemporary data center demands.
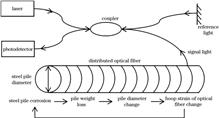
Offshore wind turbines are exposed to long-lasting harsh marine environments with high humidity and salt spray. With an increase in service time, accidents such as corrosion fatigue of basic steel pipes and fan collapse, can occur. Therefore, it is important to monitor the corrosion of steel piles. In this study, the application of distributed optical fiber sensing technology to the corrosion monitoring of steel piles is explored in a simulated marine environment. By wrapping distributed optical fibers around the surface of the steel piles, the strain changes in the steel piles due to corrosion products in the atmospheric zone, water level fluctuation zone, and immersion zone are monitored. Based on this, a relationship between the circumferential strain and mass loss of the steel pile is established. The corrosion areas of the steel piles are visualized using color cloud images. The research results show that distributed optical fiber sensing technology can be used for the online monitoring of steel pile surface corrosion and can locate the corrosion area and quantify the degree of corrosion, which provides technical support and assurance for the early warning and maintenance of offshore wind turbine steel structures.
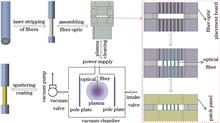
With the increasing costs of heavy-metal wastewater treatment and stricter requirements of environmental legislation, traditional chemical and electroplating methods are expected to be replaced by magnetron sputtering, which is gradually becoming a common technique for preparing the metal coatings on optical fibers. Magnetron sputtering processing parameters have a significant impact on the mechanical properties of fibers. This study investigates the influence of the magnetron sputtering process on the tensile properties of metal-coated fibers, to optimize the relevant process parameters. Prior to the formal preparation of metal coatings, pre-treatments such as laser stripping, fiber assembly, and plasma cleaning were employed. The microstructures of metal coating were characterized using scanning electron microscopy, and the tensile strength of metal-coated fibers was tested using a universal testing machine. The results reveal that pre-treatment has minimal effect on the tensile strength of fibers. However, variations in sputtering power, gas pressure, and deposition time (thickness) significantly affect tensile properties of fibers. Additionally, fibers coated with metals having elastic moduli close to SiO2 exhibit higher tensile strength. In summary, the magnetron sputtering process has a crucial impact on the tensile properties of metal-coated fibers, and the optimization of process parameters can improve the mechanical performance of fibers, providing foundational support for their stability and reliability in various applications.
The laser field can be effectively reconstructed using phase retrieval methods by measuring intensity distributions on two planes perpendicular to the beam propagation direction. To address the phase retrieval challenge in laser beams, an initial phase estimation strategy based on ray mapping is proposed, which provides a rapid and accurate initial phase distribution. A more precise phase distribution is achieved by superimposing radial basis function components onto this initial phase and determining their weights through the gradient descent method. The spatial intensity distribution of the laser is then calculated using the angular spectrum method, with the beam width fitted using the second-moment method and the least squares method. This approach facilitates the calculation of the beam quality factor (M2). Simulations of single-mode and multimode laser beams and experimental results from a helium-neon laser demonstrate that the proposed method enables high-precision laser phase reconstruction, leading to the effective calculation of M2.
The light screen projectile velocity measurement system is widely used in the field of flying object velocity measurement and weapon testing, but its velocity measurement accuracy is largely limited by the timing accuracy of the system. This paper proposes and builds an light screen projectile velocity measurement system based on field programmable gate array and multi-phase clock time-to-digital converter. Its timing resolution reaches 312.5 ps, timing accuracy reaches 125.6 ps, and the maximum timing range reaches 1.342 s. At the same time, in view of the limitations of the existing simulation test scheme of light screen velocity measurement system with less sampling and slow response, this paper designs a simulation test scheme of high speed response based on picosecond pulse laser, and obtains that the time measurement accuracy of this velocity measurement system is better than 85 ns. When the projectile velocity is 1000 m/s, the theoretical measurement accuracy of the velocity measurement system can reach 0.085‰. In addition, the working state of the system is verified by the projectile firing test. The results show that the system has simple structure, low cost, high timing accuracy, and high scalability, which provides a feasible scheme for improving the measurement accuracy of the light screen velocity measurement system.
Laser ranging based on single-photon detection (single-photon ranging) usually employs pulse time-of-flight method, whereby the target distance is obtained by measuring the time of emission of the laser pulse and time of arrival of the echo photon. To achieve high ranging precision, a narrow-pulse laser with low timing jitter, a high-precision detector, and an event timer are required, which significantly increases the system cost. In this paper, we introduce a low-cost single-photon laser ranging method and propose a cross-correlation algorithm for moving-window accumulation, thereby effectively improving the ranging precision of larger timing jitter systems. In the experiment, a laser diode light source with a pulse width of 2.18 ns and a silicon avalanche photodiode single-photon detector with a timing jitter of 0.80 ns were used. The photon time-of-flight measurement precision improved to 0.13 ns, and the unidirectional ranging precision reached 4.0 cm, using the cross-correlation algorithm.
Ultrashort pulsed lasers operating in the deep ultraviolet (UV) spectrum, with high energy and peak power, are crucial for a wide range of advanced applications. In this study, we successfully developed a high-power, mode-locked Nd∶YVO4 laser operating at 1064 nm, achieving an average output power of 9.32 W, a pulse repetition rate of 78.12 MHz, and a pulse width of 13.9 ps. The 1064 nm picosecond laser was subsequently used as a seed in a regenerative amplifier, where a stable pulsed laser was obtained at 200 kHz with a maximum average output power of 26.7 W and a pulse width of 16.3 ps. Furthermore, we generated a green laser at 532 nm and a deep UV laser at 266 nm through two stages of nonlinear frequency doubling. The green laser exhibited an average output power of 14.24 W and a pulse width of 12.6 ps, whereas the deep UV laser achieved an output power of 3.94 W and a pulse width of approximately 14.3 ps. The 266 nm laser delivered a single pulse energy of 19.7 μJ and a peak power of 1.37 MW.
This study theoretically investigates a dynamic process of periodic structures formed on a gold surface through a single-pulse laser, to discuss the transient changes during the formation of laser-induced periodic surface structure (LIPSS). We employ the two-temperature model to calculate the electron and lattice temperatures of the gold surface and use the excited-state dielectric constant to determine the transient optical properties after laser irradiation. We explore the relationships between the refractive index, extinction coefficient, scattering frequency, and LIPSS period. Results reveal fluctuations in the optical properties, electron-electron scattering frequency, electron-phonon scattering frequency, and LIPSS period following laser action. The theoretical predictions align closely with experimental observations reported in the literature. Notably, the extinction coefficient and electron-electron scattering frequency significantly influence the LIPSS period compared to the refractive index and electron-phonon scattering frequency. The time evolution of the LIPSS period after femtosecond laser action is accurately predicted by the surface plasmon polaritons model based on the excited-state dielectric constant.
The recycling of carbon fiber reinforced plastics (CFRP) waste has become an inevitable trend in the development of science and technology and industry. In this paper, a method of recycling carbon fiber is introduced. Ultraviolet picosecond laser is used to vaporize the resin on the surface of CFRP, which can realize the recycling of surface carbon fiber. Based on the difficulty of carbon fiber extraction and the performance of recycled carbon fiber, the influence of recycling process parameter window and laser parameters on recycled carbon fiber is studied. The results show that with the increase of laser power, the parameter range of recycled carbon fiber becomes narrower. When the laser power is too high, the graphitization degree of carbon fiber will become serious. The graphitization degree of recycled carbon fiber is significantly affected by laser irradiation. Compared with the original fiber without laser irradiation, laser-induced graphitization improves the tensile modulus of the recycled carbon fiber, but reduces its tensile strength. The tensile strength of the recycled carbon fiber can reach 75% of the original fiber, and the tensile modulus can be increased by 14%. By controlling the laser processing parameters, the regenerated carbon fiber with good performance can be obtained.
To improve the laser ablation quality of polycrystalline diamond composite materials, a predictive model for each response indicator was established using the response surface methodology with laser power, scanning speed, and repetition frequency as influencing factors and ablation depth and surface roughness as response indicators. The impact patterns of the interactions of the three laser parameters on the response indicators were analyzed. Maximization of ablation depth and minimization of surface roughness were set as optimization objectives. This led to an optimized parameter combination of laser power at 94 W, scanning speed at 63 mm/s, and repetition frequency at 1490 kHz, and thereby, corresponding predicted values for the two response indicators were obtained. Subsequent secondary laser ablation experiments were conducted using the optimized parameter combination, resulting in measured errors of 1.272 μm for ablation depth and 0.134 μm for surface roughness when compared to the predicted values. The error rates between measured and predicted values were 1.59% and 17.68%, respectively, all within the specified tolerance range. This partially validates the accuracy of the model and reliability of the optimized process parameters.
Noise characteristic analysis is conducive to a deeper understanding of the dynamic features for semiconductor laser arrays, which are crucial in various fields such as optical communication, optical sensing, precision measurement. This study analyzes the effects of injection current, source-area radius, light-output aperture, and cavity length on the relative intensity noise and phase noise of a vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser array with an external cavity feedback using the optical feedback L-K rate equation. Results indicate that increasing the injection current and light-output aperture are benefitial to achieve coherent coupling and low-noise output while still maintaining the fundamental optical mode output. Moreover, increasing the source-area radius helps to increase the relative intensity noise. However, no evident relationship exists between the phase noise and source-area radius. In addition, excessively large or excessively small external cavity length considerably increased the relative intensity noise and phase noise .
A laser diode (LD) corner-pumped Nd∶YAG electro-optical Q-switched laser with high efficiency and high stability that generates a 1.06-μm pulse laser output is designed and experimentally verified. Amplified spontaneous emission and parasitic oscillation are suppressed by using a low-doped Nd∶YAG crystal as a gain medium and a bonding Sm∶YAG crystal on both sides. The angular pump direct pumping method is used to increase the pump absorption optical path and thus increase the pump absorption efficiency of the gain crystal, and a zig-zag structure is used to improve the thermal effect. Under the conditions of a pump pulse energy of 383 mJ, repetition frequency of 20 Hz, and pump pulse width of 230 μs, laser output with a single pulse energy of 97.5 mJ and pulse width of 7 ns is obtained. The dynamic-to-static ratio of the output energy is 95.3%, the optical-to-optical conversion efficiency is 25.43%, the beam quality factors in two directions are Mx2 = 4.31 and My2 = 4.67, the change in Q-switched output energy within 140 s is less than 2%, and the energy instability of three consecutive working cycles is also less than 2%. The individual output energy attenuations are 1.59% and 2.11%, and the total output energy attenuation is 3.67%.
Triply periodic minimal surfaces (TPMS) exhibit the advantages of excessive smoothness, high specific surface area, and good internal interconnectivity. In this study, the porous structure of TPMS with varying porosity, cell size, gradient density, and gradient size is prepared via selective laser melting (SLM). The effects of these parameters on mechanical properties and failure forms of the structures are examined via compression tests and finite element simulation. The elastic modulus of TPMS lattice structures ranges from 3.0?5.5 GPa and the yield strength ranges from 54?159 MPa. This matches the mechanical properties of human bone tissue. The experimental results show that the porosity is the key factor affecting the mechanical properties of the structure, and the cell size has a slight effect. The compressive stiffness of Gyroid structures is higher than that of Primitive structures. The gradient structure further reduces the elastic modulus of the structure and shows different deformations and failure forms when compared to the single structure.
High-strength aluminum alloy has the advantages of high specific strength, corrosion resistance, and weldability. By combining it with laser selective melting (SLM) technology, it is expected to improve the performance of aerospace structural components. However, the pore defects generated during the forming process limit its further application. Laser in-situ remelting is currently being introduced into the SLM forming process to explore the effectiveness of this process in eliminating pore defects and its impact on mechanical properties. Research has found that laser in-situ remelting technology can eliminate the pore defects formed during the SLM forming process and effectively improve the density. By exploring different laser in-situ remelting scanning speeds and the density and pore distribution of the sample after laser remelting, the optimal process window was obtained, where the laser power and scanning speed were the same as the SLM forming parameters (that is, 390 W and 2250 mm/s, respectively). Under this process, the density of the sample reaches the highest value of 99.87%, and the pore size is less than 5 μm with no irregular defects. Weak impurity peaks are observed in the X-ray diffractometer spectrum of the Al3Sc and Al6Mn phases, and all other elements are dissolved in the aluminum matrix. The microstructure exhibits a good bimodal structure, with an average grain size of 2.22 μm. No grain coarsening is observed in the samples that had not undergone laser in-situ remelting test. The tensile strength is 545 MPa, which is 18.5% higher than that of the sample without laser in-situ remelting test. The fracture mode is brittle intergranular fracture. This study is of great significance for improving the printability of high-strength aluminum alloy SLM to obtain low defect and high-performance parts with stable quality.
The TA1/304L dissimilar joint needs to undergo a high temperature environment of about 800 ℃ during colinear continuous rolling of titanium and steel. This article first uses V as the intermediate layer for laser welding to obtain a TA1/304L joint (JV) with partially melted V as the intermediate isolation layer. Its room temperature tensile strength is equivalent to that of the TA1 base material, but after insulation at 800 ℃ for 30 minutes, the JV joint directly cracks and fractures in the weld zone (FZSV) between 304L and V. Further laser welding is carried out using V+Cu as the intermediate layer to obtain a TA1/304L joint (JVC) with a composite intermediate layer. V partially melts and acts as an isolation layer, while Cu completely melts into the FZSV region. The tensile strength of the welded JVC joint reaches 0.92% that of the TA1 base material, and after insulation at 800 ℃ for 30 minutes, the tensile strength of the JVC joint is about 79% that of the TA1 base material. In both cases, the specimen fractures in the weld zone between V and TA1 (FZVT). The analysis results indicate that after insulation at 800 ℃ for 30 minutes, a large amount of FeV brittle phases are generated in the FZSV weld zone of the JV joint. When Cu+V is used as the intermediate layer, Cu entering FZSV can effectively suppress the generation of FeV brittle phases in the FZSV region during the heating process, thereby improving the tensile strength of TA1/304L joint after heating.
This study proposes a tunable ultrawideband metamaterial absorber based on a graphene-vanadium dioxide composite metamaterial structure. Ultrawideband flexible and adjustable functions are realized using the electrically tunable properties of graphene and the phase-transition properties of vanadium dioxide. Under the premise that the absorption rate exceeds 90%, the absorption bandwidth of the absorber reaches 7.003 THz in the frequency range of 5.4491?12.4521 THz, and the relative bandwidth is 78.24%. The effects of the Fermi level of graphene, vanadium dioxide conductivity, incidence angle, and polarization angle on the absorption rate are also analyzed. Analytical results show that the proposed absorber has an ultrawideband, is insensitive to the incidence angle and polarization, and exhibits flexible tunability. The study also finds that the optimization of the performance of metamaterial absorbers is of great significance.
Coding metamaterials have attracted significant attention for their ability to flexibly modulate electromagnetic waves and provide a high degree of freedom for coding sequences to manipulate electromagnetic waves in the frequency domain. A dynamically absorbing 2-bit coding metasurface based on the phase transition properties of vanadium dioxide is presented. In this study, the insulating state of vanadium dioxide is defined as code "0", and the metallic state of vanadium dioxide is defined as code"1". When the state of vanadium dioxide changes due to changes in external conditions such as temperature, light, and electricity, the coding state of the coding particles also changes. A 30×30 coding array of four coding particles integrated two by two can display the desired pattern in the near-field in the frequency range of 0.5‒2.5 THz. The novel design in this study can dynamically adjust the display content by using the absorption of the metasurface when the frequency of the electromagnetic wave changes, which provides a effective method for electromagnetic wave manipulation in the fields of frequency selector and signal encryption.
To enhance the accuracy of downward light sensors used for measuring solar downward radiation, a radiation transmission model for cosine correctors is developed based on the principles of radiation transfer on material surfaces. An analytical equation is established for the structural parameters of the shadow ring in a plate-type cosine corrector, and a structural optimization design method is proposed. For designing of a cosine corrector intended for a small unmanned aerial vehicle downlink optical sensor, a genetic algorithm is employed to determine the optimal structural parameters based from the analytical expression, with the model verifies through optical simulation. Results indicate that the cosine corrector with optimized structural parameters exhibits the minimal cosine correction global weighting error across an incident angle range of 0°?90°. The cosine response characteristics of a prototype cosine corrector with a 10 mm radius are then test in the laboratory. Findings reveal that the global weighted error in cosine correction is 4.62% within the incident angle range of 0°?90°, consistent with the simulation results. These findings confirm the accuracy of the analytical equation for the shadow ring's structural parameters and provides a valuable reference for further structural optimization and error analysis of cosine correctors.
As one of the core components of an aero-engine, turbine blades operate in high temperature, high pressure, strong vibration, and other multi-physical field coupling for long periods of time. Hence, the stability of its manufacturing and service process has a direct impact on the service life of the entire engine. In this study, the design of an endoscopic probe with high resolution, small diameter, and wide temperature range is proposed. Coupled with traditional digital image correlation methods, it enables non-contact synchronous measurement of stress and temperature fields of engine blades during operation. This system features a design incorporating multiple coaxial optical paths, with a front-end optical aperture of less than 10 mm and an image plane size exceeding 25 mm. At a cut-off frequency of 40 lp/mm, the modulation transfer function exceeds 0.4 within 70% of the maximum field of view, and the maximum distortion is less than 0.1%. After undergoing non-thermalization design, this system can produce clear images within the temperature range of 20?250 ℃. The design is equally informative for other non-contact measurements in high-temperature environments.
Based on the semiconductor technology, an electromagnetic scanning micromirror of microelectromechanical system (MEMS) for application in the field of microspectrometry is designed and fabricated. By integrating a gold-silicon grating narrowband optical filtering structure onto the mirror surface, spectral separation and detection functions without external detectors are achieved. This is based on the characteristics of its narrowband filtering wavelength varying with the incident light angle, as well as the absorption of incident light through surface plasmon resonance, which generates a photocurrent. Next, an aluminum plating is applied to the back of the micromirror to form ohmic contact and is bonded to a printed circuit board (PCB) to generate a photocurrent. Two sets of current circuits of drive and photocurrent are then designed on the micromirror, where the integration of optical signal detection and electrical signal reading is realized. Compared with a MEMS scanning grating micromirror based on the dispersive splitting principle, the optical path is shortened and system integration is improved. When driven by an 89.2 mA current, the measured device can reach a mechanical angle range of ±11.4°. The I-V characteristic curve shows that the photocurrent loop has obvious Schottky rectification characteristics. The photocurrent response function curve of the incident light angle from 10°?17° is selected for testing. With an increase in the incident angle, the photocurrent response summit gradually moves in the shortwave direction, and the photocurrent response is accompanied by an increase in a photocurrent response. The resonance filtering wavelength has a good linear change relationship with the incident angle, and the resonance wavelength offset of the device is approximately 15.7 nm for every 1° change in the incident light angle.
Aiming at the problem that the characteristics of fast steering mirror and the external environment change constantly during the working process, a control strategy combining the fuzzy control theory and the traditional proportional-integral-derivative (PID) control, namely fuzzy PID control, is proposed. According to the mechanical structure and motion characteristics of the fast steering mirror, the dynamic model of the fast steering mirror is established and the fuzzy PID controller of the fast steering mirror is designed. The simulation model is built in Matlab/Simulink and the simulation results of angle control between traditional PID control and fuzzy PID control are analyzed and compared. The experimental results show that the fuzzy PID controller realizes the stable control of the fast steering mirror, and the time for the fast steering mirror to reach stability is 0.13 s, and the overshoot phenomenon is effectively eliminated.
In practical engineering problems such as the optimal design of filter antennas, the optimization of large-scale variables is usually involved, and there are complex associations between variables, which will lead to slow convergence speed, low solution accuracy, and poor population diversity. To solve this problem, an improved non-dominant sorting gray wolf optimization algorithm is proposed. In order to achieve effective dimensionality reduction and decoupling of large-scale variables, a multi-objective differential grouping method is proposed, which is applied to the original non-dominant sorting gray wolf optimization algorithm, which divides the search space into multiple subspaces and finds the optimal solution in each subspace. In addition, in order to improve the uniformity of the distribution of the initial population in the search space, the Tent chaotic map and K-means clustering algorithm are used for population initialization. In order to improve the exploration ability of the algorithm, the golden sine strategy is used to update the position of the gray wolf, and an adaptive nonlinear control parameter is proposed. The performance of the algorithm is verified on the ZDT test set, and the proposed algorithm is better than the comparison algorithm in both inverse generative distance (IGD) and hypervolume (HV). The proposed algorithm is applied to the optimization design of the filter antenna, and the experimental results show that the optimization solution of the filter antenna can be found quickly, and compared with the original NSGWO algorithm, the average value of the S11 parameters of the optimized filter antenna is reduced by 36.4%, and the average gain is increased by 41.4%; Compared with the NSWOA* algorithm, the average value of the S11 parameters is reduced by 24.0%, and the average gain is increased by 33.5%.
Based on a tight-binding approximation electronic structure model and incorporation of the dynamic evolution method of the time-dependent density matrix equation, in this study, the ultrafast photo-current generation process is theoretically investigated from the topological material Bi2Se3 driven by few-cycle femtosecond laser pulse. The research results demonstrate that the light current is highly sensitive to change in the carrier waveform of the electric field, exhibiting a strong dependence on the carrier envelope phase (CEP) of the laser pulse. As the driving laser intensity increases, the electron dynamics enter a strong field interaction regime, and the ultrafast current shows significantly different variations with changes in CEP, reflecting distinct optical response phenomena of topological materials on ultrafast time scales. Specifically, it is crucial that the significant CEP-dependent light current can also be generated in the direction perpendicular to the polarization direction of the driving light. Further analysis shows that this phenomenon is closely related to topological surface states and cannot be observed in bulk states of topological materials. The research results can aid in exploring the ultrafast electron motion characteristics of surface states of topological insulators and offer theoretical guidance for the future design of optical devices operating at optical frequencies.
This paper proposes the implementation of a neighboring coupling network of three identical oscillators in a cavity optomechanical system using optomechanical interactions. The objective is to investigate the irreversible dynamics characteristics of nonequilibrium transient heat transport driven by different temperature gradients and optomechanical couplings, eventually converging to a nonequilibrium steady state. A theoretical framework of entropy assessment, based on the quantum phase space approach, is used to evaluate the entropy dynamics applicable to transient processes. The study explores the transition of entropy dynamics from monotonic to oscillatory behavior under symmetric temperature thermal reservoirs from the weak coupling regime into strong coupling regime, further investigating the entropy dynamics under asymmetric temperature thermal reservoirs, where the strong coupling leads to non-regular oscillatory behavior. The analytical results show that the evolution of system entropy and thermodynamic irreversible behavior are significantly affected by the internal coupling and thermal reservoir temperatures. Furthermore, the results offer a guide for accurately measuring the evolution of irreversible dynamics in nonequilibrium transient processes in experiments, providing new ideas for the development of thermal management devices via cavity optomechanical manipulation.
Optical fiber has remarkable advantages such as excellent anti electromagnetic interference in monitoring gas insulated switchgear (GIS), showing unique stability and reliability in high voltage environment. In addition, the weak grating array technology based on fiber enables the large-scale deployment of fiber sensors, which has high flexibility and ductility. Therefore, this paper combines weak fiber Bragg grating (WFBG) static leveling instruments and strain sensing optical fibers, to achieve the safety monitoring of GIS. The former realizes settlement monitoring in the vertical direction, whereas the latter achieves displacement monitoring in the horizontal direction. Both the static leveling instrument and strain sensing optical fiber employ weak fiber Bragg gratings as sensitive components and are interconnected using time-division multiplexing, to achieve long-term real-time settlement monitoring of ultra-long GIS equipment foundations. This system is applied to the monitoring of GIS foundation settlement in a ±800 kV ultra-high voltage converter station, comprising 33 WFBG static levels and 325 WFBG strain sensors. The monitoring data obtained over a two-month period align with manual observation data, indicating its excellent practical value in relevant structural monitoring.
Extreme ultraviolet (EUV) multilayer are crucial components of EUV lithography optical systems. During the operation of lithography systems, the performance of EUV multilayer mirrors can be affected significantly by surface contaminants, thus resulting in reduced light-source output power and decreased overall system lifespan. Understanding the contamination of EUV multilayer mirrors and developing targeted control technologies can enhance the stability and longevity of EUV lithography systems. This paper reviews the research progress on the contamination control of EUV multilayer mirrors, with emphasis on the causes of surface contamination and cleaning technologies. It provides a detailed overview of the main contaminants and formation mechanisms of multilayer mirrors in EUV lithography systems, as well as prevention, suppression, and cleaning techniques for different contamination types.
2?3 μm mid-infrared lasers have important applications in medical, environmental monitoring, and military fields. The Cr∶ZnSe and Cr∶ZnS laser crystals have the advantages such as wide absorption and emission spectrum, large absorption and emission cross-sections at room temperature, and their applications in 2?3 μm mid-infrared lasers have received widespread attention. The characteristics of Cr∶ZnSe and Cr∶ZnS laser crystals and the research progress of their corresponding mid-infrared lasers are introduced, and the perspectives and future development are also proposed.
Frequency-modulated continuous wave (FMCW) laser measurement exhibits the advantages of high precision, wide range, good sensitivity, and strong anti-interference ability, enabling the noncontact measurements of high dynamic targets. This measurement technique has an important value in the large-scale precision measurement and machining and manufacturing fields and has become a hot spot in the laser precision and absolute measurements. Herein, the principle of FMCW laser measurement is introduced, current application requirements of long-distance measurements are analyzed, and key points of FMCW laser measurement at home and abroad are highlighted. In this study, an FMCW laser measurement system is developed based on high-sensitive coherent detection technology, which realizes the meter-level ranging of diffuse reflection targets at 10 km. Results provide an important reference for the future long-distance, high-precision FMCW laser measurement at home.
Quantum microwave-to-optical wave conversion is a key technology for establishing quantum networks and a driving force behind advances in quantum science. This technology has remarkable potential in areas such as distributed quantum computing, remote quantum sensing, and quantum precision measurements. This article provides a systematic overview of the four main experimental platforms for microwave-to-optical wave conversion: electro-optic, atomic, optomechanical, and magneton systems. This article also reviews the physical principles and models underlying these platforms, summarizes the experimental approaches and research advancements achieved using these platforms, and compares their performance based on the photon conversion efficiency, conversion bandwidth, and specific experimental conditions required. Finally, the current challenges and future trends in microwave-to-optical conversion are discussed, along with key issues that must be addressed for applications in quantum information systems.
Raman spectroscopy is a non-elastic light scattering, non-destructive spectroscopic detection method based on the interaction between laser and matter. It finds applications in modern battlefields, industrial production, social security, and the detection of hazardous or prohibited goods. Compared to visible light and near-infrared Raman spectroscopy, solar-blind ultraviolet (UV) Raman spectroscopy offers advantages such as reduced environmental interference, higher scattering intensity, and safety for human eyes. These characteristics make it suitable for detecting explosive substances and enabling remote sensing of samples in natural environments. However, solar-blind UV Raman spectroscopy faces several challenges that affect qualitative and quantitative analyses: 1) at equivalent spectral resolution, the Raman shift (wavenumber) resolution of UV Raman spectroscopy is lower than that of visible and infrared spectroscopies; 2) due to the cost and material limitations of UV glass and coating materials, developing optical lenses with large apertures and high transmittance is challenging, this is particularly problematic in telemetry scenarios where UV Raman spectroscopy signals are prone to significant noise; 3) UV fluorescence resonance is stronger than other bands, which can interfere significantly with Raman spectroscopy signals. To address these issues, the characterization capabilities of Raman spectra should be enhanced through noise filtering and baseline spectral processing methods. This study analyzes the principles of solar-blind UV Raman spectroscopy detection in natural environments and reviews global advancements in noise reduction and baseline correction algorithms for solar-blind UV Raman spectroscopy. Furthermore, it examines the potential of this technology in areas such as counter-terrorism, drug control, and food safety. The study also provides an outlook on the development trends of solar-blind UV Raman spectroscopy processing technologies in natural environments.
A 2 μm tunable narrow-linewidth fiber laser has valuable applications in fields such as atmospheric detection, LiDAR, and medical detection. First, four common wavelength-tuning techniques are introduced, including diffraction grating filter tuning, volume Bragg grating filter tuning, acousto-optic filter tuning, and fiber Fabry-Perot filter tuning. Then, the advantages and disadvantages of these techniques are compared and analyzed. Next, we demonstrate three structures of narrow-linewidth lasers: linear cavity, ring cavity, and compound cavity, and compare their advantages and disadvantages. Subsequently, the current research results and technical challenges of narrow-linewidth, high power, and tunable fiber lasers in the 2 μm waveband are introduced. Finally, the technical development trends of tunable narrow-linewidth fiber lasers in the 2 μm waveband are prospected.
This article comprehensively reviews the advancements in infrared spectroscopy technology for detecting components in gasoline, diesel, and jet fuels. First, the basic structure and detection principles of two commonly used infrared spectroscopy instruments are outlined. Next, the article elaborates on the data modeling and predictive analysis methods relevant to fuel component analysis. The application of infrared spectroscopy in determining gasoline octane number and methanol and ethanol content, as well as the cetane number of diesel, is discussed. The infrared spectroscopy measurement methods for key physical properties of jet fuel, such as flash point, distillation range, density, and initial boiling point, are also introduced. Additionally, the effectiveness of various modeling methods and optimization algorithms is evaluated, highlighting the potential of infrared spectroscopy to enhance fuel quality and environmental performance. Infrared spectroscopy enables rapid detection of multiple fuel components. In the future, the integration of infrared spectroscopy with artificial intelligence is anticipated to improve prediction accuracy and broaden the predictive capabilities of the method, indicating significant development prospects.
Terahertz spectroscopy, a noninvasive, low-energy detection technique that enables coherent measurements, can accurately monitor the dynamic processes of particles and quasiparticles, such as charge carriers, phonons, and excitons, within materials after optical pumping and reveal their interactions. These processes and interactions directly influence the functional performance of devices. Recently, halide perovskite materials have shown considerable potential in various optoelectronic applications, including solar cells, light-emitting diodes, and lasers. A deep understanding of the dynamic characteristics of charge carriers and other low-energy excited quasiparticles in these devices is crucial for revealing the physical principles controlling device performance. Terahertz spectroscopy can precisely measure charge carrier mobility in halide perovskite materials, study the origins of high/low photoelectric conversion efficiencies, investigate phase transitions through changes in phonon mode frequencies, and explore the polaron formation process by monitoring changes in the effective mass of charge carriers. This study aims to review several key research achievements, highlighting the substantial role and benefits of terahertz spectroscopy in these materials.
Distributed fiber optic sensing technology based on Brillouin scattering is gradually being applied in engineering monitoring in fields such as infrastructure, rail transit, and submarine cables. The attenuation and noise effects of the photoelectric signal in the Brillouin demodulation system lead to a decrease in the signal-to-noise ratio of long-distance sensing, which limits measurement accuracy. Researchers improve signal-to-noise ratio through methods such as optical pulse coding and Raman amplification, achieving good results while also increasing system complexity and equipment costs. Improving system performance through backend signal processing could reduce hardware costs and facilitate iterative upgrades. This paper reviews the methods of using signal processing methods to improve signal-to-noise ratio in optical fiber sensing systems based on Brillouin scattering both domestically and internationally in the past decade, including one-dimensional signal denoising, image and video denoising, and deep learning denoising technologies. These technologies are discussed and analyzed, and the performance improvement effects of each technology on the system are compared. Finally, the development prospects of signal-to-noise ratio improvement technology in distributed fiber optic sensing system based on Brillouin scattering are discussed.
High-precision measurement of geomagnetic field is important in many applications, including geology and geomagnetic-matching navigation. A single atomic magnetometer cannot simultaneously realize high-precision measurements of the magnitude and direction of geomagnetic field. A promising solution of magnetic field vector measurement is a type of atomic magnetometer based on coherent population trapping (CPT) effect. Firstly, the principle of measuring magnetic field vector based on the CPT effect is introduced. Then, two types of methods for measuring magnetic field vector with or without auxiliary coils are discussed, and three key technologies for measuring magnetic field vector based on CPT effect are discussed, including accurate measurement of gradient magnetic field, continuous real-time measurement of magnetic field vector, closed-loop control of measurement system, and interference suppression. Finally, the application prospects of CPT-based magnetic field vector measurement methods are explored from three aspects: calibration and compensation of heading error, reduction of the effect of magnetic field gradient with micro-electromechanical system atomic vapor cell technology, and elimination of optical power fluctuations with an optical power compensation algorithm.
In recent years, infrared spectroscopy technology has been rapidly developed and widely used in forensic science. However, data analysis is complicated, and traditional algorithms are no longer applicable. Therefore, it is necessary to combine chemometrics to improve the accuracy and scientificity of material evidence analysis. In this paper, infrared spectroscopy and chemometrics are introduced and summarized in detail, and the application progress of the combination of the two in the field of trace evidence, food and drug ring evidence, biological evidence and document material evidence analysis is reviewed. At the same time, its future development direction and application prospect are also discussed.
Two types of “cherry rain” quartzite jade were analyzed using standard gemological tests, X-ray fluorescence spectrometer, infrared spectroscopy, and laser Raman spectroscopy. The white-base part of both minerals is quartz, while the pink component of one variety is rhodonite and for the other one, it is elbaite. The infrared spectrum exhibits Si—O stretching vibration absorption peaks at 1078 cm-1, 962 cm-1, and 911 cm-1, the Si—O bending vibration absorption peaks at five places in the range of 750?550 cm-1, and cationic coordination octahedral absorption peaks in the range of 550?400 cm-1. The laser Raman spectrum primarily shows the [SiO4] tetrahedral vibration Raman displacement peaks at 669 cm-1, 975 cm-1, and 1000 cm-1. In the infrared spectrum, notable peaks were observed, including the [BO3]3- stretching vibration peaks at 1359 cm-1 and 1306 cm-1, Si—O—Si asymmetric stretching vibration peak at 1115 cm-1, O—Si—O asymmetric stretching vibration peak at 1033 cm-1, O—Si—O symmetric stretching vibration peak at 998 cm-1, Si—O—Si symmetric stretching vibration peaks at 796 cm-1, 721 cm-1, and 601 cm-1, and the Si—O bending vibration or [BO3]3- group vibration absorption peak near 507 cm-1. The laser Raman spectra reveal vibration displacement peaks of the [Si6O18]12- group hexagonal ring at 224 cm-1 and 376 cm-1, a [BO3]3- vibration displacement peak around 710 cm-1, and a stretching vibration displacement peak of Si—O (non-bridging oxygen) near 1089 cm-1. This indicates that the mineral composition of the aggregate is elbaite quartzite jade. The gemological characteristics of these two mineral aggregates are crucial for the identification and classification of "cherry rain" quartzite jade.
To achieve rapid identification of Ganoderma lucidum medicinal materials from different places of production and cultivation methods, a high-sensitivity X-ray fluorescence spectrometer is used to determine 52 Ganoderma lucidum medicinal materials. 52 samples can be divided into 5 categories through systematic clustering method. Based on this, a Gaussian mixture model is used to verify and analyze the clustering categories, and a multi-layer perceptron is used to train the classification model. Results show that the detection accuracies of both training and test sets by the multi-layer perceptron are 100%. The combination of high sensitivity X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy and chemometric methods can quickly and effectively classify and test Ganoderma lucidum medicinal materials, providing a technical method for rapid testing of food, drugs, and environment cases using Ganoderma lucidum as evidence.
Palladium nanoparticles boast large specific surface area, high catalytic efficiency, and excellent electrochemical performance, making them highly promising for applications in photocatalysis and light sensing. Improving the interaction among these nanoparticles and the light field is crucial for enhancing optical device performance. In this study, palladium nanoparticle superlattice thin films were prepared using a self-assembly method. The superlattice polariton mode, which is based on excitation enhancement, significantly improved the concentration of light field energy on the palladium nanoparticle structure. Both experimental and calculated transmittance/reflectance spectra indicated that the as-prepared palladium nanoparticle superlattice effectively excites polariton modes. As the number of superlattice film layers increases, the same order polariton modes experience a redshift, while higher-order polariton modes are generated. Notably, this superlattice structure creates enhanced local fields at the intervals between nanoparticles. Compared to discrete palladium nanoparticles, the local field enhancement factor of the superlattice structure is approximately doubled, achieving more effective focusing of incident field energy. This study offers valuable insights for designing high-performance photocatalytic and light sensing devices.