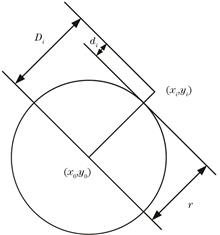
To address the problem of inaccurate identification of the receiving end caused by background light interference on the transmitting light source in underwater wireless optical communication, an underwater laser spot circle fitting center positioning algorithm is proposed based on a random sampling consensus algorithm. First, the spot image is preprocessed to obtain edge pixels. Then, a random sampling consensus algorithm is used to eliminate the interference of noisy data points, and finally, a circle fitting algorithm is used to position the spot center with high precision. Experimental verification was conducted by shooting laser spot images in water in the presence of background light interference. The results show that compared with the traditional centroid method and circle fitting algorithm, the improved algorithm significantly reduces the impact of background light on the positioning of the light source center. In the x direction, the positioning error was approximately 2 pixel, and the minimum error was only 0.49 pixel; in the y direction, the error was approximately 1 pixel, and the minimum error was only 0.04 pixel. The average coordinate deviation was 1.805 pixel, and the root mean square error for the calculated spot center coordinates was 2.2063 pixel, demonstrating the low deviation, high accuracy, and good anti-interference ability of the improved algorithm.
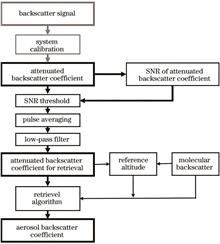
Aerosols can alter the radiation balance of the Earth's atmosphere or affect the formation of clouds as condensation nuclei, thereby affecting the global atmosphere. Aerosol optical parameters can be used to investigate this effect. Spaceborne LiDAR systems are commonly used to obtain global aerosol optical parameters. In August 2022, China successfully launched the terrestrial ecosystem carbon inventory satellite (TECIS). The main payload of the satellite is a spaceborne multibeam LiDAR, which can observe aerosol optical parameters on a global scale. This system currently requires the comparative validation of observation results. Based on the Fernald forward-integration method, we retrieve the aerosol backscatter coefficient and depolarization ratio. Data from the micro pulse LiDAR network (MPLNET), cloud aerosol LiDAR, and infrared pathfinder satellite observation (CALIPSO) are used to compare the retrieval results of the algorithm. The results show that the aerosol optical parameters retrieved by the multibeam LiDAR are highly consistent with the data and that the R2 obtained from correlation analysis is approximately 0.8. This study preliminarily verifies the observation ability of the spaceborne multibeam LiDAR system for atmospheric aerosols in the TECIS.
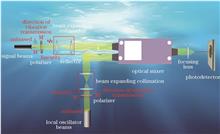
Heterodyne detection is an efficient approach for weak signal detection in underwater optical communication. Based on the generalized Huygens-Fresnel diffraction principle, a coherent detection mathematical model for the propagation of partially coherent Gaussian Schell beams in ocean turbulence is established. The model considers the transmission characteristics of partially coherent Gaussian Schell beams, and an analytical expression for the heterodyne efficiency of partially coherent Gaussian Schell beams in ocean turbulence environments is derived. The effects of the light source parameters, ocean turbulence parameters, transmission distance, and detector aperture on the heterodyne efficiency are numerically investigated. The research results show that the effects of the light source parameters on the heterodyne efficiency are negligible when compared with that of the ocean turbulence. Moreover, increasing the detector aperture does not improve the heterodyne efficiency, although selecting an appropriate detector aperture can effectively suppress the ocean turbulence effect in an environment with a specific ocean turbulence intensity. Hence, the conclusions of this study provide theoretical guidance for coherent detection systems in underwater wireless optical communication.
The quantitative calculation of pollutant transport remains challenging in air-pollution research. Based on Mie's theory, a quantitative calculation method for calculating dust flux was established using lidar-network and surface-composition observations. Subsequently, it was applied to the quantitative analysis of sand-dust flux and the investigation of the effects on the atmospheric condition during the dust process from April 10 to 14, 2023. The results show that the total net inputs of PM10 and PM2.5 in Zhejiang province are 27894 t and 5930 t during the dust process, respectively, thus indicating that the input sand-dust primarily comprised coarse particulate matter. The net input of PM10 per unit area in Hangzhou-Jiaxing-Huzhou is the largest, i.e., 0.523 to 0.598 t·km-2, followed by those of Jinhua, Quzhou, and Lishui, i.e., 0.240, 0.235, and 0.114 t·km-2, respectively. Except Quzhou with 0.083 t·km-2 and Lishui with 0.049 t·km-2, the net inputs of PM2.5 per unit area in other areas are similar, ranging from 0.050 to 0.066 t·km-2. The input of sand dust increases the atmospheric particle concentration, decreases the PM2.5/PM10 ratio, and increases the depolarization ratio. However, these effects weakened gradually owing to the sedimentation of sand dust and the binding of urban aerosols during transport. Additionally, the contents of ozone, CO2, and CH4 decreased. The volume fractions of CO2 and CH4 no longer exhibit the daily variation characteristics of high during the day and low at night, which is attributable to the effect of sand-dust on meteorological conditions such as temperature and water vapor density. In summary, sand-dust input can provide soil supplementation, affect meteorological conditions, and mitigate the greenhouse effect.
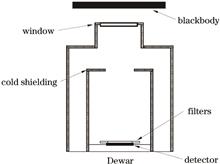
Astronomical focal-plane infrared detectors are generally installed in cryogenic Dewars. To measure the detector's dark current, all infrared backgrounds must be shielded. Hence, excluding radiations from the Dewar windows without modifying the Dewar structure is challenging. Herein, we introduce a revised method to measure the dark current by modifying the temperature of the Dewar window without disassembling and assembling the Dewar. Test results of a 512×640 near-infrared focal-plane detector show that the revised method can obtain dark currents that are 10 e-/s lower than those afforded by conventional methods without excluding the infrared background from the Dewar windows. The associated revised test procedure can be used to promptly evaluate the dark-current performance of the detector.
With the advancement of modern fiber-optic communication technology, the need for low-loss single-mode transmission optical fibers that can support high-speed optical communication with larger bandwidth and minimal transmission loss has become pressing. This study proposes a novel hollow-core anti-resonant fiber structure based on a single-ring nested design, which incorporates a small nested circle into the conventional single-ring five-tube double-nested structure. The transmission characteristics of the optical fiber are numerically simulated using the finite element method combined with perfectly matched layer boundary conditions. The numerical results show that in the range of 1400?1580 nm, the fiber achieves a higher-order mode suppression ratio exceeding 100, a confinement loss of less than 9.700×10-5 dB/m, and a bending loss of less than 1.165×10-2 dB/m at a bending radius of 5 cm. Furthermore, the dispersion is in the range of 1.020?1.222 ps/(nm·km). This hollow-core anti-resonant fiber satisfies the requirements for single-mode operation while achieving broadband low transmission loss, making it a promising candidate for applications in dense wavelength division multiplexing systems.
The interchannel delay in fiber-optic interferometric sensing systems affects the accuracy of demodulation, noise suppression, and signal information extraction, which can be suppressed by measuring the interchannel delay. This paper introduces calibration signals in the phase signal to measure the time delay using the phase difference between these signals. Through theoretical derivation and experimental verification, we analyzed factors affecting the accuracy of time delay measurement. The experimental results show that noise within the phase signal interferes with extracting the phase difference between calibration signals. Compared with the ellipse fitting algorithm, the single frequency signal extraction algorithm based on adaptive filtering offers a more significant stability and accuracy in phase difference measurement. It shows a good linear relationship (R2 = 0.99999) for measuring the length of delayed optical fibers, with a deviation range of -0.31% to 0.22%. The precise extraction of interchannel delay supports efforts to mitigate its impact on phase signal demodulation and signal processing, broadening the application scope of sensing arrays.
Cable is a vital force-transmission component of the long-span space-cable-network structure and is the core of safety operations because of the potential risk of damage and destruction. Thus, the force state of cables in real time must be elucidated. An intelligent cable with fiber Bragg grating embedded in a center wire can effectively avoid damage to a sensing unit during transportation and installation as well as realize the real-time perception of the cable force. In this study, a calibrated intelligent cable is applied to the saddle-like space cable network of the Shunde Sports Center swimming pool, and the cable force is monitored during the installation of the cable-network tension. The sensitivities of cable load monitoring and stable cable load monitoring are approximately 6.6 and 2.6 pm/KN, respectively, and the difference in the measured cable force and jack is within 5% after the tension is completed. The cable force measured by the intelligent cable is similar to the value of oil pressure. The measured cable force during the installation of the cable-network tension is consistent with the theoretical-analysis trend. The measured cable force is less than 40% of the cable breaking force. Applying intelligent cables to cable-network structures can facilitate cable-force monitoring.
We propose a high-capacity, high-speed demodulation system for fiber Bragg grating (FBG) sensor arrays using dispersion Fourier transform technology. The proposed system includes a mode-locked laser, a nonlinear amplifier module, a sensing link, a dispersive element, and a signal acquisition and processing module. The sensor capacity of the system is substantially improved by employing a nonlinear amplifier to broaden the spectrum of the mode-locked laser, enabling high-speed multiplexing and demodulation of FBG sensing arrays. The temperature demodulation experiments demonstrate that the proposed system offers high demodulation accuracy and stability, simultaneously demodulating 38 FBG sensors in real time at a demodulation rate of 16.24 MHz.
To improve the transmission performance of the radio over fiber system based on coherent detection, a scheme combining polar code with probabilistic shaping (PS) of many-to-one (MTO) mapping is proposed. The scheme uses many-to-one mapping to map 64 quadrature amplitude modulation (64QAM) signals to 44QAM signals to realize PS without extra PS redundancy; Polar code is used as forward error correction code scheme, which assigns the frozen bits of polar code to the overlapping bits of 44QAM. During decoding, the overlapping bits are implicitly pierced by successive cancellation list decoding, so that the receiver can receive the signal correctly and improve the reliability of transmission of the system. The simulation results show that at a symbol rate of 10 Gbaud, the bit error rate of the system can be increased from 2.52×10-2 to 1×10-3 compared with that of the traditional uniform (UD) signal. When lg(RBER) =-3 and the fiber length is 20 km, the received optical power of the Polar-MTO-PS signal is 2.6 dB lower than that of Polar-UD signal, and 4.6 dB lower than that of the low density parity code (LDPC)-MTO-PS signal. The optical signal-to-noise ratio of the Polar-MTO-PS signal is 3.3 dB better than that of the LDPC-MTO-PS signal.
An ultra-weak fiber Bragg grating (UW-FBG) strain rosette sensor based on SUS304 metal substrate is proposed. The working mechanism of the sensor is analyzed by theory and ANSYS simulation, and an equilateral triangular SUS304 strain rosette substrate is designed. Three UW-FBG sensing units with central wavelengths of 1536, 1542 nm, and 1548 nm are fixed to the substrate by 353ND epoxy resin glue to fabricate strain rosette sensor, and the sensors are calibrated for their temperature,tensile, and compressive properties, the proposed sensor is applied to monitor vector strain of the jacket model. Results show that the strain rosette sensor has a average temperature sensitivity of 25.4 pm/℃, with linearity of ~0.9990. The average compressive principal strain error of proposed sensor is 1.74%, with principal strain angular error of 0.51%, and a tensile principal strain error of proposed sensor is 3.22%, with principal strain angular error of 0.59%. It has a good reproducibility of experiments, which indicate that the proposed sensor can provide an excellent solution for vector strain monitoring.
To optimize virtual multicast blocking performance, an efficient algorithm combines light-trail partial path sharing, network traffic grooming, and adaptive modulation technique is proposed, which can simultaneously optimize virtual multicast mapping and light-trail selection. First, the bus architecture of light-trail is used to achieve a more flexible partial path-sharing technology. This technology allows light-trail nodes to time-share resources and transmit data to downstream nodes. Second, considering the shorter signal transmission distance of shared partial paths, an adaptive modulation technology that can flexibly choose modulation schemes based on distance is introduced to improve signal modulation efficiency. Furthermore, the support for partial path sharing greatly expands the solution space of virtual multicast node mapping. Simulation results show that the algorithm integrating adaptive modulation and any-node sharing performs the best among comparasion schemes. The improvement of adaptive modulation technique in blocking performance is particularly significant when virtual nodes have more physical node mapping options.
To address the challenges of low efficiency and heavy dependence on operator expertise in existing fiber alignment and coupling techniques, this study introduces an fiber automatic alignment coupling system that uses a spiral scanning algorithm and a dual adaptive segmented stochastic parallel gradient descent (DAS SPGD) algorithm. Coarse alignment is conducted using the spiral scanning algorithm to narrow the search scope, and fine alignment is achieved using the DAS SPGD algorithm. A fast and stable alignment process is achieved by adaptively adjusting the gain and perturbation amplitudes. The simulation and experimental results indicate that the DAS SPGD algorithm outperforms other algorithms in terms of convergence rate, stability, and reliability. Notably, in scenarios involving significant radial migration, the effective convergence range of the DAS SPGD algorithm is increased by 5 times compared with other algorithms, highlighting its practical effectiveness. These findings provide valuable insights for advancements in fiber optic communications technology.
In the semiconductor lithography process, blank masks are primitive optical flats, and nanometer precision surface profiles play an important role in improving the performance of advanced chips. To measure the surface profile and thickness variation of a blank mask, a method is proposed based on parameter time-domain estimation for wavelength phase-shifting interferometry of a blank mask. First, to ensure the validity of the measurements, the coupling relationship between the front and rear surfaces of the blank mask and thickness variation is determined according to the optical path tracing method, and the self-assessment rule for the error in wavelength phase-shifting interferometry is analyzed. Next, to avoid the influence of spectral distortion and cavity length on accuracy, the parameter time-domain estimation method is used to determine the carrier parameters. Concurrently, the initial phase is demodulated based on the weighted least-squares principle to reduce the sensitivity of the algorithm to anisotropic noise. Finally, simulations are conducted to analyze the influence of different factors on the measurements. In addition, comparison experiments are carried out at different cavity lengths, with 10-3λ0 as the magnitude of the blank mask interferometry error self-assessment index. The results show the effectiveness and stability of the proposed algorithm in measuring surface profiles and thickness variations of the blank mask, thereby providing a technical approach for advanced chip manufacturing.
In a stitching interference system, a near-zero light path is required to measure the sub-aperture face shape to minimize the effects of phase-measurement errors caused by mechanical vibrations, phase shift inaccuracies, and retrace errors on the measurement results. Therefore, a two-dimensional rotation stage based on a flexible hinge was designed to precisely adjust the measured mirror attitude. A modal analysis of the rotation stage was conducted via finite-element simulation, and the natural frequency was verified experimentally, which showed good consistency with the simulation. This rotation stage, whose angular resolution exceeds 50 nrad, was used to adjust the pitch and roll attitudes of the test mirror. The experimental results indicate good consistency between the adjustment angle of the rotation stage and the attitude change angle of the testing mirror measured using an interferometer. The measurement results of the stitching interference system matched those of the long-trace profiler for the large-aperture flat mirror. The constructed stitching interference system satisfies the preliminary measurement requirements.
The liquid-phase diffusion coefficient of L-serine is a critical parameter for studying the production processes and biological metabolism of related pharmaceuticals. To accurately determine this coefficient, our research group independently designed and fabricated a composite liquid-core cylindrical lens (SLCL-Doublet). This lens consistently demonstrated excellent refractive index resolution exceeding 0.00004 RIU while maintaining good imaging quality across various liquid samples. By leveraging the one-dimensional refractive index resolution capability of the SLCL-Doublet and applying Fick's second law, we utilized the equal-refractive-index thin-layer method to measure the liquid-phase diffusion coefficient of L-serine aqueous solutions at varying concentrations at 298.15 K. The measurement uncertainty was controlled within 0.15 × 10-6 cm2·s-1. This method offers advantages such as simple experimental operation, minimal time requirements, stable instrumentation, and high measurement accuracy, providing an effective solution for the rapid and accurate determination of liquid-phase diffusion coefficients.
To address the challenge of accurately recognizing signals in real time for space debris laser ranging, this paper proposes a deep learning-based method for real-time recognition of space debris laser ranging signals. Utilizing the long short-term memory (LSTM) network of recurrent neural networks in deep learning, the proposed method enables real-time recognition of signals that are difficult for traditional methods to detect. The LSTM network excels at capturing and maintaining long-term dependencies in time series data, effectively handling missing, noisy, or irregular sequences, while also demonstrating strong generalization capabilities. Validation using actual observational data shows that the proposed method improves the recognition rate of space debris. Compared to the echo signal correlation method, the average running time is reduced by ~8%, and the F1 score for signal recognition increases from 0.2144 to 0.6068, representing an improvement of nearly twofold. This method will play a significant role in the detection and identification of space debris and provide valuable insights for the application of deep learning techniques in space target laser ranging.
In dynamic temperature testing, the colorimetric temperature measurement method effectively reduces emissivity-related influences due to its unique temperature measurement principle, offering advantages such as fast response, wide temperature range, and non-intrusiveness. This study leverages colorimetric temperature measurement to design a dynamic temperature testing device. A comprehensive discussion is provided on the colorimetric temperature measurement principle, device configuration, dual-wavelength selection criteria, and photodetector circuit design. The device underwent static calibration using a high-temperature blackbody furnace, yielding a fitting equation between output voltage and corresponding temperature. To assess measurement accuracy, a hydrogen-oxygen water welding machine heated a stainless steel target to simulate a temperature field, and dynamic temperature measurements were simultaneously conducted using the calibrated device and a standard infrared thermometer. Experimental results indicate that the relative error of the colorimetric temperature measurement device remains below 5.4% within the 400?1200 ℃ range, demonstrating accurate dynamic temperature testing capabilities in this range.
To enable real-time adjustments of laser beam pointing in satellite laser ranging systems with bistatic units, this study proposes a method for real-time recognition of laser beam pointing key points using a deep learning model. By collecting and labeling numerous successful satellite observation laser beam images and applying data augmentation, this paper establishes a comprehensive laser beam pointing image dataset. The YOLOv8-Pose deep learning algorithm is utilized for model training, and ultimately applying the model to satellite laser observations. Compared with traditional edge extraction methods for laser beam images, the proposed algorithm demonstrates excellent adaptability, achieving an impressive mean average precision of 99.39%. In addition, the proposed algorithm addresses the challenge of accurately recognizing laser beam pointing key points in relatively poor weather conditions, paving the way for an automated satellite laser ranging system.
A picosecond laser was used to laser etch the surface of (Ce,Gd)∶YAG-Al2O3 composite-phase phosphor ceramics. The phosphor ceramics were excited using blue light-emitting diode (LED) transmission to systematically study the effect of laser etching on the surface morphology of the phosphor ceramics and the luminescence performance of the encapsulated white LED (WLED) devices. The results showed that the ablation area and depth of the phosphor ceramics increased with the number of laser treatments. An ablation structure with diameter of 46.0 μm and depth of 5.69 μm was formed on the surface of the phosphor ceramics after five laser ablation treatments. Under the same blue LED excitation conditions, the phosphor ceramics transmitting blue light and their conversion to yellow-green light intensity ratio decreased with an increase in the number of ablations. The luminous efficiency (LE) of the encapsulated WLED device increased from 83.05 lm/W to 86.88 lm/W, and the correlated color temperature (CCT) decreased from 6329 K to 5626 K. Phosphor ceramics both sides are completed laser ablation than single-side laser ablation, the color temperature of the encapsulated WLED device decreased from 5555 K to 5159 K, and the color coordinates moved from (0.3311, 0.4005) to (0.3455, 0.4226). This indicates that an effective control of the luminescence performance of phosphor ceramics can be achieved with picosecond laser ablation treatment of their surface.
To explore the physical mechanism of femtosecond laser processing, this paper discusses the mechanism of microscopic damage formation on Al2O3 ceramic materials under femtosecond laser irradiation. By combining molecular dynamics and continuous equation simulation methods, the ablation phenomenon caused by femtosecond laser on Al2O3 ceramics is analyzed. The movement of atoms on the surface of Al2O3 ceramics under femtosecond laser irradiation is compared below and above the ablation threshold, studying the changes in internal temperature, particle number, and pressure of Al2O3 ceramics. The results show that when the energy density is higher than the ablation threshold, the target material is fractured under the combined action of temperature and pressure, with the ablation and melting primarily being affected by the heat input time. The research results provide theoretical guidance for the precise processing of dielectric materials with femtosecond laser.
A copper butt welding test is conducted using laser scanning welding technology to investigate its impact on the quality, mechanical properties, and electrical conductivity of copper welded joints with varying plate thicknesses. This investigation is conducted by altering the laser scanning trajectory. The results indicate that, compared with the linear scanning trajectory, the “O”, “8”, and “∞” scanning trajectories demonstrate improved weld formations across different plate thicknesses. These improvements are accompanied by significant increases in both tensile strength and electrical conductivity. The “O” scanning trajectory shows the most significant improvement, with its optimal weld formation and good stability of its molten pool. The tensile strength and electrical conductivity reach maximum values of 226 MPa and 72.46 MS/m in the penetratedand state, while 232 MPa and 69.44 MS/m in the unpenetrated state. Compared with the linear scanning trajectory, the improvements are 24.86%, 24.63%, 15.42% and 22.21%, respectively. Therefore, selecting the appropriate scanning trajectory can effectively improve the appearance and morphology of copper welds as well as enhance the quality of welded joints, mechanical properties, and electrical conductivity.
An ultrafast Tm-doped fiber laser operating at 1.7 μm is proposed based on nonlinear polarization rotation. This laser can generate multiple solitons and noise-like pulses. As the pump power increases to 270 mW, the stable fundamental mode-locked pulses are obtained by adjusting the intra-cavity polarization state with a corresponding central wavelength of 1785.88 nm, 3 dB bandwidth of 5.16 nm, and repetition frequency of 6.14 MHz. As the pump power increases to 290 mW, a multi-soliton bunch containing six pulses is observed, and the temporal spacing among pulses varies in the hundred-picosecond range. Moreover, the number of pulses in the single multi-soliton bunch increases with further increases to the pump power. As the pump power continues to increase, the multi-soliton bunch can switch to a special mode-locked state. Real-time spectrum based on a dispersive Fourier transform technique indicates that these special mode-locked pulses are noise-like pulses that are composed of noise pulses with random and varying intensities. Exploring the nonlinear evolution process and dynamic characteristics of mode-locked pulses after reaching a stable regime not only deepens the understanding of soliton dynamics but also contributes to the optimization design of 1.7 μm ultrafast fiber lasers, thereby promoting their development and application in various fields, including ultrafast optics, short-range remote sensing, and biology.
To investigate the propagation characteristics of direct-arrival surface acoustic waves at near-surface hole defects in metals and achieve rapid defect localization, numerical simulation experiments are carried out in this study using COMSOL Multiphysics software. The near-surface propagation of surface acoustic waves excited by pulse laser on an aluminum plate surface under the thermoelastic effect is simulated. The reflection and transmission phenomena of surface acoustic waves at defects with different radii and depths are studied, and the signals are analyzed in time and frequency domains. The numerical results show that the interaction of the surface acoustic waves excited by pulse laser with hole defects leads to significant reflection and transmission phenomena. The localization of hole defects can be found accurately, with a relative error of less than 3%. In a certain range, with a variation in radius and depth of the hole defect, the reflected and transmitted waves show a regular change. This research provides a reference for the study of the propagation characteristics of surface acoustic waves at near-surface hole defects, which has potential application in quality monitoring and defect localization in metallic materials.
To expand the application range of all-solid-state single-frequency lasers and achieve high-power single-frequency laser output, this study uses dual piezoelectric ceramics (PZT) resonant detection combined with a variable reflectivity unstable cavity and side pumping module composed of a laser diode (LD) array to develop an all-solid-state, electro-optical, Q-switched, and single-frequency pulse laser with a repetition frequency of 100 Hz. This study achieves a stable, high-beam quality, high-power, and narrow-linewidth laser output. The experimental results show that when the oscillator cavity length is 300 mm, the repetition frequency is 100 Hz, pump current is 160 A, and pump pulse width is 300 μs. Thus, a stable, narrow-linewidth laser output with an average power of 10.06 W is achieved, corresponding to a pulse width of 6.6 ns, linewidth of 93.874 MHz, and beam quality factor of Mx2= 1.510, My2= 1.674. The laser can be used as a stable, narrow-linewidth pulse laser light source for detection equipment, such as Doppler wind radars.
As a crucial industrial infrastructure equipment, the durability of die-casting machines directly affects product quality and enterprise efficiency, particularly the pressure chamber in injection components. This study examines the surface modification of the pressure chamber in die-casting machines using H13 steel as the substrate material and preparing two types of Fe-based coatings on its surface using laser cladding technology. X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, microhardness testing, and an electrochemical workstation were used to analyze the phase composition, microstructure, element distribution, mechanical properties, and corrosion resistance of the H13 coating. The results indicate that the coating prepared using the laser cladding technology exhibits better hardness and corrosion resistance compared with the substrate, providing a guide for prolonging the service life of the material cylinder in the die-casting machine.
Laser cladding technology was used to prepare Ni/WC-based cladding layers with varying CeO2 contents to improve the wear and corrosion resistance of 45 steel surfaces. The effect of CeO2 addition on the properties of the cladding layer was also explored. The cladding layer was characterized using X-ray diffraction, energy-dispersive spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy, microhardness testing, friction and wear testing, and electrochemical analysis. The results indicate that an appropriate amount of CeO2 improves the forming quality of the cladding layer, reduces the pore defects, and enhances its wear and corrosion resistance. When the mass fraction of CeO2 is 2%, pore defects nearly disappear, and the cladding exhibits the highest hardness, along with the best wear and corrosion resistance. However, an excessive CeO2 content negatively influences the cladding layer's formation and performance.
The objective of this study is to investigate factors that affect the preparation of graphene via laser induction technology using DuPont plain 1500D aramid fiber as a carbon-containing precursor. Graphene coating is prepared on the surface of aramid fiber via laser induction technology, and the effects of laser power, scanning speed, and defocusing degree (the distance between the laser lens and sample) on the graphene preparation process are systematically investigated. This is expected to yield a reliable graphene coating on the surface of aramid fiber, thus enabling the in-situ detection and interface toughening of aramid-fiber laminates via the excellent electrical conductivity and microscopic pore structure of graphene. The laser-induced aramid fibers are analyzed via Raman spectroscopy and electron microscopy. Experimental results show that under 12 W of power, 300 mm/s of scanning speed, and 14 mm of defocusing degree, the Raman spectra of the products based on the surface of the aramid fiber show typical graphene characteristics. This indicates that the surface of the aramid fiber successfully yields a good structure of graphene, and that the laserpower, scanning speed, and defocusing degree affect the creation of graphene.
Dental health has a great impact on the overall health of an individual, however traditional dental treatment mostly uses a hand-held tooth whiling machine, which can cause inaccurate grinding and has a large thermal impact. The femtosecond laser has the characteristics of high precision and minimal thermal effect, displaying great potential in teeth cleaning. In this paper, we propose an experimental scheme that uses femtosecond laser to etch the tooth surface, further exploring its cleaning efficiency using gray level characterization of the tooth surface. The experimental results show that compared with the traditional drill, the femtosecond laser not only can remove dental plaque and pigmentation, but also causes no collateral damage to the surrounding healthy tissue, which greatly improves the accuracy and efficiency of treatment. In summary, the application of femtosecond laser in dental treatment has wide-ranging prospects, providing new ways and possibilities for achieving safer and more effective dental treatment.
To solve the problem of high-power consumption of high-performance infrared array readout circuit, in this study, customized low power design is conducted. Interlacing sampling technology and time-sharing gating strategy of column-level buffer are adopted to overcome the characteristics of low time utilization and high idle power consumption. In the circuit design, the input pair of capacitive feedback trans-impedance amplifier in the pixel array is biased in the subthreshold region to exchange low current for high performance. Based on the single-ended output scenario of the output buffer, a new high current efficiency asymmetrical recycling folded cascode operational amplifier structure is proposed, which significantly reduces the power consumption and area. Compared with the traditional folded cascode structure, the power consumption is reduced by 62.5% under the similar performance index. Additionally, based on SMIC 0.13 μm 1P8M digital/analog hybrid integrated circuit technology, a 1280×1024 scale area array readout circuit is designed. The post simulation results show that the overall power consumption of the readout circuit is 190 mW at a high frame rate of 120 Hz, the parallel data transfer rate of eight channels is 2×107 pixel/s, and the overall linearity exceeds 99.3%.
To solve the problem of a high string direct-current voltage in a rooftop photovoltaic (PV) system during a string-level rapid shutdown and to reduce the risk of high-voltage electric shock for firefighters working in and around the PV array, this paper introduces a rapid-shutdown system for a rooftop PV at panel level. This system includes a shutdown controller and shutdown modules installed inside each junction box of the PV modules, whose communication protocol complies with the SunSpec standard protocol. First, the shutdown controller continuously sends a cyclic code sequence using a power-line carrier. Second, the shutdown module receives the codes, decodes the frequency shift keying (FSK) signal, and controls the opening and closing of the PV modules according to the command code. Experimental results show that the voltage within the rooftop PV array is limited to that at the module level (80 V) in 30 s in the case of emergency shutdown. This solution is useful for improving the safety performance and reducing fire hazards and is more portable. Furthermore, it does not require additional wiring and significantly decreases system costs.
The development of readout circuits is shifting towards large arrays, small pixels, and advanced processes to achieve flexible adjustment of operating states and array windowing. A customized digital module for a 2560 pixel×2048 pixel infrared focal plane readout circuit, based on 55 nm complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) transistor technology, is designed. This design incorporates a configurable timing intellectual property (IP) core using a state machine with unique thermal code encoding to regulate the control timing generation circuit. This enables configurable control timing for analog circuits while enabling array windowing. An asynchronous first input first output (FIFO) is employed for bit-width conversion and cross-clock processing of quantized data, ensuring accurate data transmission. Based on the same architecture and process, the verification chip design and multi project wafer fabrication with the window size reduced to 128 pixel×128 pixel are completed. The test results demonstrate the ability of the digital module to provide configurable control timing in specific readout circuit applications, ensuring quantized data accurate transmission.
In this study, an obliquely coupled symmetrical five-cylinder metasurface structure, which can realize a broadband terahertz reflective polarization converter, is proposed. By using the finite difference time domain (FDTD) method to numerically simulate the structure, the results show that the structure can realize cross-conversion between linear polarizations in the frequency range of 2.35?4.51 THz, and the polarization conversion rate exceeds 99%. When changing the long axis parameters of the middle cylinder, the conversion between linear polarization and circular polarization can also be realized in the range of 2.42?4.83 THz, and the reflection coefficient in the conversion frequency range is higher than 0.9. The structure designed in this study can realize the switching between half wave plate and quarter wave plate by adjusting the size of the long axis parameter of the middle cylinder, and it has excellent performance, which leads to certain application prospects in the field of polarization modulation multifunctional devices.
Conventional optical absorbers based on metal and distributed Bragg reflector (DBR) structures require alteration to the device's geometric parameters to absorb light of different wavelengths, thus significantly limiting their application scenarios. Leveraging the tunable electrical conductivity of graphene, which can be modified by applying an external voltage, this study replaces conventional metals with graphene and proposes a composite structure combining two layers of graphene with a DBR. By performing finite-element analysis, the absorption characteristics of this structure in the terahertz band are investigated. The results show that at DBR periods of 6 and 15, triple optical Tamm-state absorption with rates of 91.4%, 88.3%, and 64.3% can be achieved. By adjusting the Fermi energy of graphene from 0.7 to 1.6 eV, the wavelength tuning range of the three absorption peaks can reach 0.2, 5.2, and 6.2 μm, respectively. When the Fermi levels of the two graphene layers are set to 0.8 and 1.2 eV, the absorption rates of the triple optical Tamm states enhances to 98.8%, 85.6%, and 87.2%. The findings of this study provide an effective design idea for absorbers using optical Tamm states for light absorption.
This study presents the design of a four-leaf rose-shaped coded metasurface tailored to the terahertz band with the aim of reducing radar cross section. Based on the diffuse reflection theory, the metasurface unit incorporates a built-in phase difference to create a 1-bit code. To optimize the arrangement of the metasurface coding, a genetic algorithm is integrated with the array mode. Simulation analysis shows that in the frequency range of 0.572?1.038 THz, radar cross section can be reduced by more than 10.0 dB, and the maximum can be reduced to 36.5 dB. Further research on the effect of oblique incidence shows that the performance remains stable within a range of 0?45°, although there is a weakening, but overall meet the 8 dB requirements. This coding method offers a straightforward and efficient solution for radar stealth applications, demonstrating significant potential for widespread use.
High-precision photovoltaic power prediction is one of the key technologies for the efficient use of solar power generation. To satisfy the requirements of high-precision photovoltaic power prediction, an ultra-short-term photovoltaic power generation power prediction method based on multi-feature extraction is proposed. Firstly, the relative position relationship between the sun and photovoltaic array is analyzed, and the irradiance mechanism model of the inclined surface of the photovoltaic (PV) module is established. Secondly, considering the influence of the temperature change of the PV module backsheet and attenuation of module efficiency on the photovoltaic power generation, the deep neural network and convolutional neural network are used to extract the temperature characteristics of the module backsheet at each time and slow time-varying characteristics of the photovoltaic array, respectively. Finally, considering the timing correlation of photovoltaic power generation, the long short-term memory neural network is used to extract the dynamic time series features of the data. Based on the collected historical power generation power and historical meteorological data, the input of the prediction model is constructed via the established multiple feature extraction modules, and the prediction value of photovoltaic power generation power is obtained in the next 15 min to 4 h via the multi-layer neural network. Considering a photovoltaic power station in Zhejiang province as an example for ultra-short-term photovoltaic power generation power prediction, among the prediction results of each model, the prediction accuracy of the photovoltaic power generation power prediction model based on multi-feature extraction is higher than that of other comparison models. Furthermore, the monthly average accuracy can reach 97.13%, which verifies the effectiveness of the proposed prediction method.
Based on the Rayleigh-Sommerfeld vector diffraction theory, a diffraction system combining radial gratings and an axicon is used to obtain diffraction-free petal beams with reticulated two-dimensional optical lattices. The diffraction-free petal beam generated by a radially polarized beam is analyzed theoretically in detail, and its spatial optical field distribution is numerically simulated. Based on axicon processing, the effect generated by the non-ideal axicon on a non-diffracted petal beam is analyzed in detail. The results show that the number of optical lattices of diffraction-free petal beams increases with the radial cosine grating spokes. In contrast to ideal axicons, non-ideal axicons with hyperbolic vertices produce an oscillating effect on the optical field distribution, causing the two-dimensional optical lattices to disappear or blur. In the diffraction-free zone, the range of oscillatory influence decreases with the increasing beam waist radius of radially polarized beams. Moreover, when the beam waist radius reaches 5 mm, the oscillatory phenomenon disappears, and the reticulated feature and optical lattices are restored to the ideal situation. The results of this study have a certain reference significance as reference in the fields of multiparticle capture and particle micromanipulation.
Fiber optic Fabry-Perot sensor technology offers numerous advantages for ultrasonic detection. However, demodulating the ultrasonic frequency band of the Fabry-Perot sensor is challenging, owing to complex external environments and existing technical limitations. Thus, the fast and stable demodulation of ultrasonic sensor information a key issue. First, this study introduces the development and principles of the Fabry-Perot ultrasonic sensor. Second, this study deeply analyzes the method principles, research progress, and existing problems in the demodulation process of the fiber optic Fabry-Perot ultrasonic sensor, and proposes application limitations for various demodulation methods. Finally, this study provides a prospective summary of demodulation methods for Fabry-Perot ultrasonic fibers.
Raman spectroscopy, as a powerful detection method, often faces the problem of fluorescence interference. Time-gated Raman spectroscopy can reduce fluorescence interference. This article introduces the principle and technical characteristics of time-gated Raman spectroscopy, elucidates the development trend of the technology, and introduces different detectors and applicable scenarios for the technology. On this basis, important issues pertaining to the detectors are analyzed and the future development of detectors is discussed.
Conventional spectrometers are typically large, costly, and constrained by a trade-off between spectral measurement range and spectral resolution. This paper proposes a disorder-dispersion miniature spectrometer based on deep learning. In the proposed spectrometer, mass-producible frosted glass is utilized as the spectral encoding device, significantly reducing the manufacturing cost. Further, the spectrometer employs an on-chip detection scheme that does not include any optical components. The distance between the ground glass and detector is only 2 mm, remarkably reducing the device size. Additionally, considering the accuracy and speed of spectral reconstruction, this paper presents a deep learning-based spectral reconstruction method. Experimental results indicate that the proposed spectrometer has a spectral resolution of 1.4 nm and spectral detection range of 420?700 nm. Even in noisy environments, the root-mean-square error between the reconstructed and actual spectra is 1.38×10-3, and the reconstruction time for a single spectrum is as low as 16 μs.
In industrial production and scientific research practice, the presence and transportation of hazardous chemicals are accompanied by many potential safety hazards and environmental risks. Therefore, it is crucial to adopt effective classification testing for hazardous chemicals. Raman spectroscopy technology has the advantages of non-contact, non-destructive, and fast detection. Moreover, Raman spectroscopy can accurately obtain the fingerprint spectral information of substances and has unique advantages for the identification and detection of hazardous chemicals. Owing to the significant errors concomitant with manual Raman spectroscopy analysis, combining convolutional neural networks in deep learning provides new ideas and methods for the analysis and processing of spectral data. By combining Raman spectroscopy with deep learning algorithms and introducing attention mechanism into convolutional neural network, the proposed algorithm achieves an accuracy of 99.47% in the classification of 500 hazardous chemicals.
In a 133Cs 6S1/2→6P3/2→6D5/2 (852 nm+917 nm) ladder-type atomic system, atoms are populated on the 6D5/2 excited state from the 6S1/2 ground state via step-wise excitation using two lasers with wavelengths of 852 nm and 917 nm. Subsequently, 456 nm fluorescence photons are emitted via spontaneous decay in the 7P3/2→6S1/2 transition. Thus, spectral signals between the hyperfine transition of excited states, i.e., 6P3/2F'=5→6D5/2F″=6, is obtained by detecting 456 nm fluorescence photons. Atomic excited-state spectroscopy via fluorescence detection, abbreviated as AESVFD (atomic excited-state spectroscopy via fluorescence detection) herein, is demonstrated in this study. The characteristics of AESVFD with counter-propagating (CTP) and co-propagating (CP) configurations were compared when 852 nm and 917 nm laser beams were passing through the cesium vapor cell of the spectroscopy system. Experimental results show that AESVFD in the CTP configuration yields a significantly higher signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and a narrower spectral linewidth than that in the CP configuration, which is due to the quantum coherent effect in the ladder-type atomic system. The dependencies of AESVFD on experimental parameters such as the atomic-vapor temperature, polarization, and power and frequency detuning of the pump lasers were systematically measured. Subsequently, the optimized experimental conditions for obtaining narrow linewidths and high SNRs via AESVFD were analyzed. The narrowest linewidth obtained via AESVFD is less than 5.0 MHz, which is similar to the natural linewidth of the 6P3/2 excited state at 5.2 MHz. Investigating precision spectroscopy is crucial for the further examination of atomic energy-level structures and for testing theoretical atomic models.
This study quantitatively analyzes the major elemental content in Martian-like minerals using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy combined with a feature fusion strategy. First, the spectral data are preprocessed, and the characteristic wavelength of each element is identified through qualitative analysis to determine the characteristic peak area (SK). Simultaneously, principal component analysis (PCA) and partial least squares (PLS) are combined to perform two-level feature extraction of the spectral data, yielding feature extraction variables. Finally, this variable and SK are fused and input into a genetic algorithm-optimized support vector machine regression (GA-SVR) model. Upon comparison with models established using SK, PLS, PCA alone, and the partial least squares regression (PLSR), the feature fusion (FF) -GA-SVR model shows root-mean-square errors (RMSEs) that are, on average, lower by 33.9%, 32.8%, 22.9%, and 24.1%, respectively. In addition, the model achieves an average coefficient of determination (R2) of 0.961, demonstrating its robust predictive performance. This highlights its potential as a foundational approach for rapid and accurate analyses of unknown ore sample compositions.