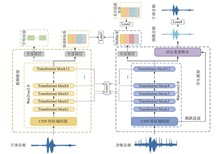
Aiming at the research hotspots of speech emotion recognition in human-computer intelligent interaction, noisy speech emotion recognition based on the multi-task constrained teacher-student model is designed as a research-oriented teaching experiment. In this experiment, the guiding role of the teacher model, the learning process of the student model and the constraining force of multi-level enhanced loss are observed. The design is based on the Wav2vec 2.0 teacher-student model and the multi-level enhanced loss mechanism. A speech enhancement auxiliary task is introduced into the student model, enabling it to acquire the feature representation ability of the teacher model through learning. In the testing phase, the student model directly extracts key emotional features from noisy speech for emotion classification. Finally, a large number of experiments are conducted to analyze the performance and robustness of the emotion recognition system. The experimental design based on the teacher-student model helps to improve students’ thinking ability, scientific research innovation and exploration awareness.
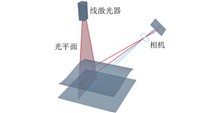
To facilitate the advancement of the project-oriented optical experiment teaching reform, a meticulously designed three-dimensional reconstruction experiment utilizing monocular-line laser technology is presented. A laser triangulation system is established based on the pinhole imaging model, incorporating a monocular camera, line laser, stepping screw, and Raspberry Pi. The calibration parameters encompassing internal and external camera parameters as well as distortion parameters are accurately determined through checkerboard calibration, and the method of threshold segmentation is employed to extract the center of the laser light bar for acquiring point cloud data representing the target object surface. By using the algorithms of the manual registration and the nearest point iteration to register the point clouds and reconstruct the surfaces, three-dimensional reconstruction of the target object can be implemented. This experiment emphasizes interdisciplinary integration, which helps stimulate students’ interest in scientific research, foster innovation awareness, and enhance their ability to apply professional knowledge to solve practical problems.
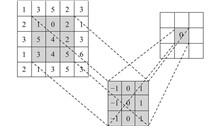
In order to cultivate students’ ability of development and application practice, an experimental case for strawberry distortion recognition based on multi-scale convolutional neural networks is designed, according to the curriculum experiment setup, to facilitate students’ learning and hands-on practice. An algorithm for recognizing distorted strawberry images is implemented using multi-scale convolutional neural network to improve the recognition capability for distorted strawberry images. The experimental results show that the algorithm possesses accurate recognition ability for distorted strawberry images and effectively reduces the impact of factors such as illumination and background. Through this experimental case, students’ understanding of artificial intelligence knowledge is deepened, their interest in learning artificial intelligence is cultivated, and their ability to develop and apply artificial intelligence projects is improved.
There are some problems in the teaching experiment of yeast alcohol dehydrogenase (YADH) extraction and purification. In order to obtain YADH with high purity, high activity, and high recovery, a single factor experiment is applied to optimize the separation and purification process of enzyme protein, including hot extraction, thermal denaturation precipitation, and organic solvent precipitation, which will improve the extraction and purification efficiency of YADH. The results show that the best effect of separation and purification is achieved when the solid-liquid ratio is 1∶6, the crude extraction temperature is 25 ℃, the crude extraction time is 1.5 h, the thermal denaturation temperature is 65 ℃, the thermal denaturation time is 15 min, the organic solvent precipitant is ethanol, the adding proportion of precipitated impure protein is 0.5 times of the supernatant, and the adding proportion of precipitated enzyme protein is 0.45 times of the supernatant. Through the optimization of the above conditions, the effect of teaching experiment is improved. It is also helpful to exercise students’ practical skills, innovative thinking, and scientific research abilities.
To enhance students’ biochemical experimental operation and analysis skills, a comprehensive design and exploration is conducted on the competitive inhibition of succinate dehydrogenase. This involves improving the enzyme extraction method, optimizing the reaction system, determining the enzymatic reaction conditions, and adding experimental controls. The result show that using muscle homogenate obtained by grinding muscle and removing red blood cells as the improved crude enzyme extract eliminated color interference make the phenomenon of competitive inhibition more apparent. The ratio of crude enzyme extract, succinic acid and methylene blue is fixed in the enzymatic reaction system. The reaction is carried out at pH 7.4 and 37℃ for 15 min, with the addition of a succinate-free control. This results in good experimental repeatability. The comprehensive design of the experiment is beneficial for students to understand the principles and characteristics of competitive inhibition of enzymes, as well as the factors that affect enzyme activity.
To meet the teaching and research requirements related to the comprehensive application of control theory to complex engineering problems in the context of motor control, a semi-physical simulation experiment system for permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSM) based on VxWorks has been designed. To address the issue of coupling between the d and q axis currents in the rotating coordinate system of PMSMs, the control strategy based on complex vector decoupling is adopted to decouple the current loop; meanwhile, a disturbance observer is combined to observe and compensate for parameter variations and external disturbances during the actual operation of the motor, thereby improving decoupling performance. The load experiment results indicate that the complex vector decoupling control strategy reduces the d-axis current fluctuation by approximately 39.6% and the q-axis current fluctuation by approximately 15.4%, maintaining a better decoupling effect even in the case of mismatch of inductance parameters. Tracking control experiments further demonstrate the favorable dynamic tracking performance of the proposed decoupling control strategy. The experimental system can be flexibly applied to the experiments of various professional courses and the comprehensive course design of automation, laying a foundation for improving students’ professional and technical abilities.
Regarding the design problem of heliostat field in the tower solar thermal power system, the corresponding efficiency calculation and parameter optimization models are established based on planar optical laws and layout strategies. Firstly, the Monte Carlo method is employed to establish computational models for shadow occlusion efficiency and truncation efficiency, thus obtaining the computational model for the optical efficiency of heliostat field. After comparing different optimization strategies for heliostat field layout, the occlusion-free layout is chosen as the optimization strategy. An optimization model for heliostat field parameters meeting the output power requirements is then proposed. The variable step size search algorithm is employed to estimate the heliostat field parameter values. Finally, based on the model calculation, the optimized heliostat field achieves an average annual optical efficiency of 63%, an average annual shadow occlusion efficiency of 94.9%, an average annual cutoff efficiency of 78.17%, and an average annual thermal output power per unit heliostat area of 0.7312 kW/m2. Compared with the performance of the heliostat field before parameter optimization, the performance is significantly improved. For instance, the average annual thermal output power after optimization is 60.2933 MW, which represents an increase of 91.57% compared to the pre-optimization level.
Rock thin section identification is applied in the field of geology, possessing advantages such as simple, economical, and rapid identification methods. However, in practical work, traditional rock naming and the further classification of plagioclase, amphibole, and pyroxene are still determined through manual calculation and plotting methods, which are cumbersome and inefficient. The Rock Thin Section Identification Assistant System combines traditional naming and plotting methods with computers. Based on the measurement and identification methods proposed in relevant textbooks and papers, it uses the VB 6.0 programming language to achieve human-computer interactive operation. It features straightforward operation and intuitive display, improving work efficiency and identification accuracy, and holding significant practical value for rock thin section identification.
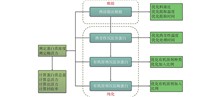
To address the shortcomings of traditional experimental teaching, such as inadequate pre-class preparation and a lack of training in experimental design thinking, the Experimental Teaching Center has developed a biological scientific research training platform using virtual simulation and information technology. This platform comprises five modules: creating mind maps for experimental design, constructing virtual experimental procedures, collecting data from hands-on experiments, collating and compiling experimental reports, as well as reviewing and learning from excellent experimental projects. This platform enables the comprehensive life-cycle management of biological experimental projects, representing a novel attempt to reform the traditional biological experimental teaching model. By integrating online and offline approaches, it enhances the effectiveness of biological experimental teaching and project management efficiency, while strengthening the cultivation of students’ scientific research and innovative thinking abilities.
Fundamentals of thermal engineering is a subject that studies the law and application of the conversion of heat energy and other forms of energy. This course is highly theoretical, abstruse and difficult to learn. In order to improve students’ learning efficiency, based on finite element method and COMSOL simulation APP, thermal engineering basic virtual simulation experiment platform is developed, and the packaging of APP is realized. Students can numerically simulate heat transfer problems of three types of boundary conditions in thermal engineering foundation through the APP interface, and realize visual display of simulation results. The work reported in this paper is a beneficial attempt to enhance students’ interest in learning, reduce their learning difficulty, and deepen students’ understanding of basic concepts of basic thermal engineering.
Combined with the “Internet + Education” technology, an information-based teaching resource platform, named interactive virtual experiment platform including web program and Wechat applet, is developed independently for mechanics theory courses. This platform solves the problems such as the reduction of experimental class hours in theoretical mechanics, vibration mechanics and other mechanics theory courses, as well as the difficulty for students to combine theories with phenomena and explore mechanical phenomena independently. Based on this interactive virtual experiment platform, the exploratory and progressive teaching modes with student deep participation are proposed to promote the cultivation of students’ scientific thinking and ability. The practice shows that the interactive virtual experiment platform effectively promotes the students’ understanding and applications of theories, expands the breadth and depth of theoretical teaching, promotes the students’ participation and teacher-student interaction in class, and improves the learning effect and quality of theoretical course teaching as well.
The traditional bending-torsion combination experimental teaching has limitations in time and space, making it challenging for students to learn in depth. To solve these problems, a bending-torsion combination virtual simulation experimental platform is developed using UG NX10.0 and Unity3D software. The platform adopts a service-oriented software architecture design. It is designed with reference to the layout of the Mechanics Laboratory of Xinjiang University. Moreover, it provides two types of strain rosette virtual simulation experiments at 45° and 60°. The system module design is more intelligent. The application results show that the development of this platform expands research angles and operational forms of the experiment and meets the requirements of controllable cost, safety, flexibility, intelligence and innovation education. It also offers new perspectives for the development of other engineering virtual simulation experiments.
The application and exploration of the virtual reality technology in tourism experimental teaching is explored, and its important role is elaborated by analyzing its characteristics and advantages. This technology provides students with immersive learning experiences, and enhances their understanding and mastery of professional knowledge about tourism. Moreover, it effectively reduces the costs and safety risks in traditional tourism experimental teaching. Finally, corresponding optimization strategies and suggestions are proposed, and the future development trends of the virtual reality technology in the field of tourism experimental teaching is looked ahead, aiming to provide useful references for promoting the innovative development of tourism education.
To deepen the reform of undergraduate teaching, a comprehensive experiment on “the adsorption and decolorization effects of Pleurotus ostreatus strains on dyes” in the environmental microbiology experiment course is proposed. After completing the cultivation of Nameko mushroom strains in the previous experiment, the mycelia formed are weighed to carry out the dye decolorization experiment. The adsorption and decolorization process are analyzed, which involve measuring the absorbance and Zeta potential of the dye solution as well as observing color changes on the mycelial surface/cross-section. The results show that the decolorization effects of Nameko mushroom strains on different dyes are significantly different, and the removal rate for 10 mg/L BL blue dye reach 93.06%. By comparing the mycelial surface/cross-section images at different treatment times, the adsorption and diffusion processes of the dye inside the mycelia are intuitively presented. Dyes with high electronegativity are more tightly bound to the mycelia and exhibit better decolorization effects. This experimental design can not only cultivate students’ basic operational skills, but also enable students to fully understand the application of microorganisms in water treatment. It is of great significance for cultivating senior professionals with both scientific research spirit and practical ability.
In the physical optics course, a learning-centered teaching innovation is proposed, and a three-tiered progressive teaching design of “problem-oriented interactive classroom, immersive exploratory teaching, research-oriented project design”, and a five-ring constructive teaching method of “phenomenon-problem-theory-method-capability” is developed. As a common data storage medium in daily life, the optical disc is also a reflective diffraction grating, exhibiting obvious grating diffraction phenomena that are easy to observe. The paper takes the project-based design experiment on measuring the operating laser wavelength and the track spacing of optical discs using diffraction gratings, as an example, to explore the teaching reform practice of research-oriented project design in the physical optics course. The proposed experimental method is straightforwardly designed with strong repeatability, combining the grating diffraction theory with actual diffraction phenomena organically, which is helpful for deepening the understanding of the Fraunhofer diffraction effect.
The experimental course teaching is an important part of college teaching, and an effective way to cultivate students’ professional quality and improve students’ practice ability. Under the outcome-based education(OBE)concept, the teachers of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Teaching and Research Section of the College of Life Sciences at Inner Mongolia University have carried out a teaching practice for Large-scale Biotechnology Experiment based on the already constructed and established Comprehensive Large-Scale Experiment Course for Undergraduate Biotechnology, with the aim of cultivating high-quality innovative talents. A mature experimental teaching model has been established to effectively stimulate students’ enthusiasm for experiments and initiative in experimental learning, and enhance their ability in independent exploration and practical problem-solving. Meanwhile, this teaching model can also further improve students’ comprehensive literacy and ability, thereby effectively improving teaching quality. These outcomes positively contribute to the cultivation of high-quality innovative talents.
In the context of deepening the construction of “Double First Class”, in order to cultivate students’ innovative spirit and practical ability, an astronomical practice innovation platform for innovative talent cultivation is introduced. Detailed explanations and research explorations have been made from the importance of platform construction, practical construction situation, and practical mode exploration. By combining the cutting-edge astronomical technology to develop and design innovative experiments, building an open experimental platform, and carrying out practical base construction, opportunities of independent design and operation for students are provided. This platform has played a positive role in cultivating astronomical innovative talents.
The role of data analysis and mining applications in the supply chain field is increasingly prominent in the digital economy era, and improving data analysis capabilities is a new social requirement for training logistics professionals. In order to better adapt to the demand for logistics professionals in the era of big data, it is necessary to reform the existing curriculum and teaching system, and the construction of data analysis experiments is an important part of teaching reform. The article integrates the teaching practice of the “Logistics Information System” course to explore the construction and practice of data analysis experiments in the course. Based on the product detail page data of e-commerce platforms, five experiments are designed covering aspects such as data collection, preprocessing, analysis of qualified suppliers and logistics service quality in the supply chain, data visualization, as well as data analysis report writing. Based on the characteristics of the experiments, targeted experimental teaching and assessment models are proposed. Teaching practice has shown that experiments help students develop initial practical skills in collecting, processing and analyzing data as well as exploring applications, thereby enhancing their practical abilities in logistics research and innovation.
With the development of artificial intelligence, ultrasonic ranging plays a pivotal role in both industry and daily life. To achieve industry-education integration, an ultrasonic ranging experimental system was designed for the Engineering Test Technology course. Module circuits for the ultrasonic ranging transmitter and receiver were designed and simulated in Multisim; a physical system was then built on an NI ELVIS III breadboard, and the actual circuits were debugged by connecting ultrasonic transducers, with the results compared to the simulation waveforms; upper-level computer software was developed by using LabVIEW to accomplish functions such as signal acquisition, data processing, and graphical display. Through the concrete implementation of this experimental project, students gained a deeper understanding of the system architecture of engineering testing technology and a more thorough comprehension of the key knowledge points in the course. This lays a solid foundation for the future development of high-precision, large-scale testing systems targeting complex industrial environments, demonstrating considerable practical value.
The management of experimental consumables in colleges and universities is demanding and difficult to supervise, and involves many functional departments and internal control risk points. By applying COSO internal control framework, the experimental consumables management business of Shandong University is examined, its internal control environment and related risks of business management are analyzed, and an internal control management model based on risk assessment is developed, covering organizational structure, system construction, process management, information system, and other aspects. Furtherly, the internal control management from the perspective of service is optimized and evaluated from the perspective of supervision, and the improvement of internal control is continuously promoted. Through the combined interaction of control objectives, risk assessment, and control activities, a virtuous cycle of internal control, risk management, and university governance can be achieved, thereby enhancing the supporting role of experimental consumables management in university talent training and scientific research.
With the rapid development of the woodworking industry, the demand for woodworking talents is increasing. To cultivate high-quality woodworking talents with practical abilities and innovative spirit, a project-driven approach for building a woodworking practice teaching platform is proposed. Firstly, the background and significance of establishing the woodworking practice teaching platform are analyzed, clarifying its crucial role in fostering students’ practical skills, innovation, and comprehensive qualities. Building on this, the construction path for the woodworking practice teaching platform is introduced. Furtherly, the key issues and solutions encountered during its construction are summarized, and the platform’s significant effects in enhancing students’ practical and innovative abilities are verified. Finally, the future development of the woodworking practice teaching platform is looked forward, proposing suggestions to further optimize its functions, expand practical teaching resources, and improve the practical teaching system. Through an in-depth analysis of the connotation, constituent elements, and construction path of the woodworking practice teaching platform, the paper provides theoretical guidance and practical reference for the reform of woodworking practice teaching in China.
Taking the background of “new liberal arts” as the starting point, focusing on the seven cores of “teaching, management, practice, training, communication, wisdom and support”, the “seven dimensions” development path of “teaching mode, management mode, project practice, teacher training, international exchange, intelligent interconnection and spatial support” is created. Meanwhile, a road of development of virtual simulation laboratories of the new liberal arts with distinctive characteristics on the basis of practice is gradually created, aiming at breaking through the bottleneck of the development of virtual simulation laboratories of colleges and universities and offering a new way of thinking about the construction and development of virtual simulation laboratories of colleges and universities under the background of the “new liberal arts”. The construction of virtual simulation laboratories will promote reform of the mode of teaching experiments of the “new liberal arts” and practically upgrade the quality and level of the teaching of experimental courses of the “new liberal arts”.
The electron beam lithography system plays an indispensable role in teaching and research of semiconductor physics and devices in universities. Building an electron beam lithography system based on the existing scanning electron microscope of the university has lower cost and multiple applications. By building a complete training system, including theoretical knowledge training, classification practical training, and supplementary training on difficult points, the efficiency and effectiveness of the use of instrument have been improved. Instrument users and managers work together to maintain and conserve the instrument, extending its service life.