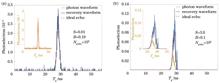
Single-photon light detection and ranging (LiDAR) is constrained by the first photon bias effect, which requires the use of low photon flux to avoid signal distortion. This results in longer detection times, and requirements for rapid detection and imaging are not met. In this study, we propose a single-photon array imaging reconstruction algorithm based on photon waveform recovery. By leveraging the principles of high-flux photon signal distortion and incorporating a high-flux photon detection probability model, we effectively mitigate the imaging distortion issues typically encountered in high-flux single-photon LiDAR. Simulations demonstrate the algorithm's capability to extract highly accurate distance and intensity information. Our analysis reveals that even when the signal flux is increased from the traditional 0.05 to 7 photons, the distance error remains <1 cm, while the intensity error remains <0.13. Furthermore, experiments on high-flux array imaging reveal that at a flux level of 3, the average distance error is 0.476 cm and the intensity error is 0.081, achieving a 5-fold improvement in intensity dynamic range. The proposed algorithm eliminates the dependency on low flux for photon imaging, effectively enabling precise imaging with single-photon LiDAR within complex scenes featuring multiple reflectivity levels and targets at various depths.
This study proposes a simple and robust adaptive fringe projection method for the 3D measurement of highlighted surfaces. The method initially projects a uniform white pattern to help identify overexposed regions and extract boundaries. These boundaries are then mapped to a projector pixel coordinate system. The pixel intensities within the boundaries are reduced to regenerate new fringe maps with brightness distributions adapted to the sample. Finally, this process is repeated until no overexposed regions remain in the acquired images. Conventional methods use multiple exposures and adaptive projection, have complicated operations and calculations, and must capture a large number of fringe images. By contrast, the proposed method just needs to capture fewer patterns and is easier to implement. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method can accurately measure the highlighted surface of biological tissue and reconstruct complete and high-precision 3D profiles.
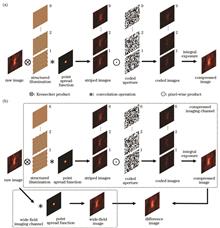
Superposition compression of different phase-shift structured illumination images in compressed imaging-based structured illumination super-resolution microscopy (CISIM) technique reduces the proportion of spectral modulation components, thereby affecting image reconstruction quality. To address this issue, a differential CISIM (DCISIM) technique is developed. This technique utilizes the reference difference between the compressed structured illumination and wide-field images to enhance the information content of high-frequency components and improve the quality of reconstructed images. In this study, the advantages of DCISIM technique are verified through simulation experiments, its performance under different noise levels is tested, and its characteristics and development prospects are briefly discussed. Results indicate that DCISIM technique can improve the accuracy and detailed resolution of reconstructed images and can provide a better super-resolution imaging effect under the condition of low noise intensity.
The rapid advancement of modern technology has made the detection of"low-slow-small"targets crucial in both civilian and military applications. With ongoing industrial upgrades and transformations, the widespread use of low-altitude, slow-moving, and small targets presents new challenges, especially in long-range detection. Long-range detection of"low-slow-small"targets using traditional detection technologies such as sonar, radar, radio, visible light, infrared, and lidar still faces many limitations. Single-photon lidar technology, with its excellent temporal and spatial resolutions, high sensitivity, and long-range detection capability, offers promising solutions to these technical challenges. This paper provides an in-depth analysis of the difficulties associated with long-range detection of"low-slow-small" targets and systematically reviews and compares existing traditional detection technologies. Furthermore, this study explores the application prospects and technical challenges of single-photon lidar technology in the future detection field of"low-slow-small"targets, providing support and guidance for enhancing detection system performance and advancing related technologies.
Point cloud data obtained and preprocessed using LiDAR serve as foundational data in various fields, such as satellite remote sensing, autonomous driving, and military navigation. With continuous advancements in deep learning algorithms and models, LiDAR point cloud processing has also progressed toward intelligence. However, due to the higher dimensionality of point cloud data, deep learning networks require more computational and inferential resources in their design and processing than two-dimensional data processing. This limits the direct deployment of point cloud processing deep learning models on many edge devices. Therefore, compressing point cloud processing deep learning models and achieving hardware-accelerated deployment have emerged as popular research directions. To comprehensively analyze current research progress on compressing and deploying point cloud processing deep learning models, we presented the first comprehensive review focusing on the compression of these models both domestically and internationally. First, we classified compression methods for point cloud processing deep learning models and outlined general approaches used in the compression process. Second, we summarized and compared relevant literature on compression techniques for point cloud processing deep learning model across five aspects: model pruning, quantization, distillation, tensor decomposition, and compactness. Additionally, we discussed methods for hardware acceleration of point cloud processing deep learning models and explored the synergy between software and hardware acceleration. Finally, we provided insights and conclusions about the future prospects of compressing and deploying point cloud processing deep learning models.
Comparing the space situational awareness capabilities of aerospace powers, such as the United States, Russia, the European Union, and Japan as the research background, in this study, the development status and trends of space situational awareness systems are analyzed worldwide. Key space situational awareness equipment, including satellite-based, ground-based, optical, and radar systems, focusing on major aerospace powers are focusing on are outlined. Additionally, the study highlights demonstration and verification projects promoted by various aviation powers and the technological capabilities. Based on the analysis and assessment of key technological capabilities in space situational awareness and in conjunction with the current development status in China, this study identifies the gaps in the current space situational awareness system, perception capabilities, and technological reserves between China and other aerospace powers. Furthermore, the development direction for the Chinese space situational awareness field is identified, and suggestions for effectively supporting the Chinese space situational awareness system and capacity building are provided.
To solve the problem wherein the structure of a two-dimensional (2D) grating is single and does not match the actual structure, a 2D metal-medium grating is proposed that has excellent polarization independence and high diffraction efficiency and wherein the grating structure is more consistent with the actual topography. Based on the intensity distribution of a two-beam orthogonal exposure single-period interference field, a 2D grating structure based on a light intensity profile is constructed, and the grating is optimized using a Fourier mode method and particle swarm optimization algorithm. Results show that, under optimal parameters, the transverse electric and transverse magnetic polarized light diffraction efficiencies are greater than 95% when the designed 2D grating is incident at the Littrow angle at a 780-nm wavelength, and it exhibits excellent polarization independence and large preparation tolerance. In addition, a comparison of the diffraction efficiencies of traditional round and prism gratings with the same structural parameters reveal that a small change in the grating structure significantly affects the diffraction efficiency of the 2D grating. Finally, the designed structure based on a light intensity profile can effectively improve the matching degree between the design and actual grating. This research provides a theoretical basis for the development of high precision 2D grating in the displacement measurement field.
Single-pixel cameras, characterized by low imaging costs and high detection sensitivity of single-pixel detectors in specialized bands, offer significant advantages in low-light conditions and special-band applications. These cameras hold promising prospects in fields like security monitoring, remote sensing, and medical imaging. This study proposes a co-aperture single-pixel imaging system capable of visible light full-color and near-infrared imaging. Utilizing the operational characteristics of the digital micromirror array, this design incorporates a symmetrical double optical path splitting structure to achieve a compact single-pixel imaging system with high energy efficiency. The integration of these components not only minimizes the system's volume but also enhances its stability and resistance to interference. Employing a standard Nikon lens, the system captures spectral and spatial information through four detectors, facilitating simultaneous full-color and near-infrared imaging. Experimental results confirm the system's capability to fulfill its intended functions and achieve the anticipated performance. This study marks a significant advancement in single-pixel imaging technology and establishes a foundation for its future industrial application.
Among the numerous semiconductors available, HgTe colloidal quantum dots (CQDs) have the advantages of widely adjustable band gap within the infrared spectrum, low production cost, and ease of integration with silicon-based readout circuits. Consequently, photoelectric devices based on HgTe CQDs exhibit significant potential for infrared detection and large-scale focal plane array (FPA) imaging applications. This review discusses recent advancements in the synthesis of HgTe CQD materials and improvements in the electrical property of CQD solids, which have contributed to the enhancement of device performance. Additionally, it summarizes the current research on HgTe CQD device structure design and FPA infrared detection technology, and provides an outlook on future development directions.
Herein, a cubic-vortex phase mask (CVPM) coding imaging system is proposed to solve the problem of the relatively weak laser blinding protection capability of the cubic phase mask (CPM) and vortex phase mask (VPM) coding imaging systems over 1 km. The imaging quality and laser protection performance of the proposed CVPM coding imaging system are quantitatively analyzed via numerical simulations. Combined with the Wiener filter decoding algorithm, the CVPM coding imaging system can image clearly, with its imaging quality being close to those of the CPM and VPM coding imaging systems. Furthermore, a blinding laser is modulated using the CVPM, and the light spot on the photodetector surface has a butterfly-shaped distribution, enabling the CVPM to exhibit stronger power dispersion than the CPM and VPM coding imaging systems. When the laser source is more than 10 km away from the CVPM coding imaging system, the power density suppression ratio remains at ~33, which is about more than twice as those of the CPM and VPM coding imaging systems. Results show that the CVPM coding imaging system exhibits excellent long-distance laser blinding protection performance under the premise of ensuring the imaging quality. Therefore, the proposed CVPM coding imaging system can be applied to the laser blinding protection scene of aerospace and aviation optical reconnaissance.
To address the problems of inadequate adaptability and poor visual quality in existing infrared and visible image fusion methods under varying luminance conditions, this paper proposes a fusion method based on Retinex theory. First, the dimension of visible light images is enhanced using an encoder, followed by the decomposition of these images into reflectance and illuminance feature maps, which is consistent with Retinex theory. Second, the reflectance feature is combined with the infrared image feature obtained via the encoder,which enhanced using a structure tensor representation. In addition, convolution kernels with varying sizes are employed to extract multiscale features, which enriches the image's hierarchical information. Finally, the decoder reduces the feature map's dimensionality, and a learnable gamma transform layer is introduced to improve the contrast of the fused image. The model's performance is validated using multiple evaluation metrics on the LLVIP public dataset. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method enables adaptive fusion of visible and infrared images under different luminance environments, achieving superior fusion results in terms of both visual perception and quantitative assessment.
The maturity level and appearance defects of apples are crucial criteria for determining their quality. To automate the removal of immature and defective apples in picking tasks, a lightweight multi-task maturity classification model (L-MTCNN) is proposed. This model comprises two sub networks, D-Net and M-Net, for multi-task classification of apple appearance defects and maturity level. Furthermore, it uses a backbone network to extract feature information, which is then applied to D-Net and M-Net, thereby improving feature utilization and reducing overall recognition computation time. Introducing Triplet loss as the loss function for M-Net increases the separation between different maturity levels while reducing the variance within the same level. Additionally, based on industry standards, the study examines the appearance changes in various apple ripening processes and constructs an apple maturity dataset. A brightness-based color restoration algorithm is proposed to address the inconsistencies between collected apple images and their actual appearance, caused by varying lighting conditions during image acquisition. This algorithm restores the color restoration of the collected images and facilitates the creation of a reliable on apple maturity dataset. Experimental results indicate that D-Net and M-Net substantially improve average accuracy compared to AlexNet, ResNet18, ResNet34, and VGG16. Furthermore, in terms of recall rate, precision rate, and F1 score, the proposed model outperforms existing models in classifying maturity levels and defect statuses. This demonstrates that the model can achieve high-accuracy maturity level judgments for different types of apples, providing valuable insights for developing integrated operation robots.
The contradiction between the field of view (FOV) and spatial resolution of imaging systems cannot be solved easily via the conventional single-aperture imaging, primarily because an optical system with a large FOV presents significant distortion, which severely affects the angular resolution at the edge of the FOV. In this study, a parallel compound-eye and secondary-imaging-system structure is adopted, and a multi-aperture lens array is used to image the spatial scene once. Sub-eye image planes are pieced together, integrated using an infrared fiber bundle, and then coupled with a detector through a relay system. Experimental results show that an optical detection system based on this technology can achieve the same imaging distortion (less than 2%) between splicing large and sub-eye FOVs as well as a uniform angular resolution under all FOV angles, thus effectively achieving high-resolution mid-infrared imaging with small distortion in a large FOV.
Currently, road surface smoothness in China is typically measured using manual detection methods, which are time-consuming, labor intensive, and risky. In addition, these methods do not provide real-time measurements during road construction. To address these issues, we propose a road surface smoothness detection method based on line lasers. This method uses a custom-built line-laser system to achieve high-precision three-dimensional (3D) measurements with millimeter-level accuracy. The issue of deviations in the detection results caused by equipment vibrations during operation is optimized using a wavelet transform algorithm. The comparative experimental results show that the proposed method has over 85% similarity with the flatness detection results obtained from a laser section analyzer on the same road section, with a Euclidean distance of approximately 2. This line-laser-based method can capture the 3D morphology of a road surface, reduce cost losses, and enhance the detection capabilities of roads. The proposed method also provides a comprehensive, accurate, and multidimensional approach to road surface flatness detection for road construction in China.
To capture images of the internal surface vascular tissue of the human body under small cavity conditions, accurately present the state of vascular tissue, and address issues related to the large size of conventional image detectors, poor imaging quality under uneven lighting conditions, and low contrast of vascular imaging, an electronic endoscopic image acquisition system is designed. This system uses an OV6946 ultra-small image detector with a 300?1100 nm-wide spectrum imaging capability and is driven by a domestic Pangu FPGA. By improving the contrast-constrained adaptive histogram equalization (CLAHE) algorithm, vascular images on the surface of small cavity tissues in human can be effectively enhanced. The proposed system provides superior imaging performance for tissue imaging within small cavities under nonuniform illumination. The improved CLAHE image enhancement algorithm significantly enhances the contrast of vascular tissue imaging, providing an effective technical solution for advancing medical ultrafine electronic endoscopic systems or broadband image enhancement systems with similar requirements.
The laser active detection technology based on the cat's eye effect has been widely used in fields such as rapid reconnaissance and target information acquisition. This article analyzes the theory of the cat's eye effect in optical systems, its application in the field of laser active detection, the development trend of this technology, and the feasibility of implementing long-distance target laser active detection. First, the working principle of the laser active detection system based on the cat's eye effect is described. Second, three methods for laser active detection using the cat's eye effect, i.e., geometric optics, physical optics, and angular spectrum propagation, are compared. Then, the characteristics and processing methods of cat eye target echo data are analyzed. Finally, the main difficulties and issues of the current technology are identified, and the development trend of the technology is analyzed according to engineering requirements.
Light-sheet microscopy has become a pivotal tool in life sciences, offering benefits such as high-throughput 3D tomography and suitability for long-term in vivo imaging. Despite these advantages, the impact of light scattering on imaging performance across different optical microscopes in scattering media remains poorly understood. This study addresses this knowledge gap by considering the electric field at the back focal plane of objective. It employs the fractal propagation method to derive the light propagation in heterogeneous scattering media and utilizes the adjoint method to develop a dual objective simulation architecture for optical microscopy. By integrating various scanning and detection strategies from different optical microscopes, the image formation process was elaborated, facilitating three-dimensional imaging simulations across four distinct types of optical microscopes. The study reveals that the capability of light-sheet microscopy to retain image quality is correlated with the confocal properties of the microscope and the thickness of the light sheet, rather than the size of the slit and the detection end exhibits greater susceptibility to scattering effects than the illumination end.
The clinical applications of optical coherence tomography (OCT) have expanded beyond ophthalmology to include imaging of various body cavities, functional imaging, diagnostic integration, and surgical robotics. Consequently, there is an increasing need to enhance the resolution of OCT to analyze biological tissues at the cellular level and beyond. However, enhancing OCT's lateral resolution typically results in a reduced depth of focus, which complicates the acquisition of a consistent point spread function throughout the imaging range. To address this issue, researchers have developed various strategies for extending the depth of focus, including using Bessel beams, phase masks, dispersion effects, synthetic apertures, computational imaging, multimode interference, and dynamic focusing. Each method employs distinct principles to improve the depth and quality of OCT imaging. This study thoroughly examines the principles, implementation methods, benefits, and limitations of these techniques. In addition, this study compares the performances of different depth-of-focus extension methods in the contexts of free-space and endoscopic OCT. Finally, this paper offers insights into future developments in depth-of-focus extension techniques for OCT, highlighting promising research directions and potential challenges.
The mid-infrared band holds important application value in frontier fields such as environmental remote sensing, astronomical observation, biomedical diagnosis, and molecular spectroscopy. High-performance mid-infrared detection technology is crucial for realizing these applications. Advances in narrow-bandgap semiconductors and heat-sensitive material technologies have greatly improved the performance of mid-infrared detectors. Despite this progress, mid-infrared detectors still lag behind InGaAs/Si-based detectors functioning in adjacent bands, particularly in avalanche/counting and planar array configurations. The frequency up-conversion of mid-infrared light using mature near-infrared and visible light devices to achieve high-level analysis and sensing has emerged as a new indirect detection paradigm that effectively complements traditional direct detection methods. This paper reviews the development history of mid-infrared frequency up-conversion detection technology both domestically and internationally, classifies the "four elements" of a detection system (i.e., a nonlinear crystal, a probe light source, a mid-infrared target, and an optical detection terminal), and summarizes the key advances in mid-infrared single photon detection, spectral analysis, and imaging applications. The paper also discusses future directions for advancements in detection technology.
The scattering phenomena prevents traditional optical systems from directly observing the target object behind a random medium, allowing only the collection of speckle images. The quality of a target recovered from speckle images is limited not only by algorithm parameters, but also by scattering distance and the employed optical imaging system. To improve the quality of speckle image restoration, this paper relates the image restoration quality to focal length and object length and proposes an optimal imaging-parameter model. Clear speckle images are collected after changing the lens focal length and adjusting the target spectrum information obtained by the camera. Applying the speckle correlation principle and a phase restoration algorithm, objects passing through a scattering medium are restored in the speckle image. The simulation and experimental results show that when the scattering distance is 0.5 m and the focal length is increased from 18 mm to 55 mm, the effective aperture of the lens enlarges and more complete spectral information of the object is preserved. The similarity of the target object structure increases from 0.3824 to 0.7829, enhancing the recovery effect. Adjusting the algorithm parameters optimizes the quality of speckle reconstruction at short focal lengths. At a focal length of 45 mm, the structural similarity increases from 0.6341 to 0.7626 but the restoration effect is non-ideal. After increasing the scattering distance, the image reconstruction effect decreases and the scattering medium can be imaged using longer focal length lenses.
Understanding the point spread function (PSF) in scattering media is crucial in various fields such as biomedical imaging, atmospheric science, and optical communication. This study delves into the characteristics of PSF and elucidates the relationship between PSF and different wavelengths in scattering media through theoretical derivation and experimental verification of the light field function. The correlation of PSF at different wavelengths is mainly controlled by the scaling factor and the equivalent phase mask. By analyzing and predicting the equivalent phase mask, this article proposes a weighted average algorithm that successfully estimates PSF under unknown wavelength conditions, thereby improving the quality of image reconstruction compared to traditional algorithms. This work reveals the relationship between PSF and wavelength, providing valuable insights into optimizing imaging quality in scattering environments and analysis of spectral signal characteristics.
The super-resolution fluorescence imaging method can observe the nanoscale structure of different subcellular organelles, and its specificity comes from fluorescence labeling. The label free imaging method avoids the possible impact of staining process on the sample itself, but loses specificity. Therefore, the two have complementary properties, each with its unique advantages and application scope. Integrating two different imaging technologies into the same instrument can broaden its application scenarios. A dual-mode microscopy imaging system was constructed by combining structured light illumination super-resolution microscopy (SIM) and rotational coherent scattering microscopy imaging (ROCS), which can switch between the two modes at will. The system was tested with fluorescent microsphere standard sample and PANC-1 pancreatic cancer cell sample. The spatial resolution of 111 nm and 145 nm were obtained in SIM and ROCS channels respectively, and the imaging speed could reach about 100 Hz. This system has high spatiotemporal resolution fluorescence and label free imaging functions, providing more convenience and possibilities for the research of cell biology.
Shape-from-focus (SFF) is a technology that can capture the three-dimensional features of objects through a monocular camera. Using focus measure operators to calculate image clarity is a crucial step in this technique. Addressing the issue of focus evaluation operators heavily relying on the surface texture of the measured object, a method of actively projecting patterns in microscopy is proposed in this paper. Through optical system design, the proposed method achieves co-focusing of the projected pattern and the object texture to enhance image texture. However, it is observed in experiments that this method faces challenges such as the non-coincidence of the focus plane of the projected pattern with the camera's focus plane and the curvature of the projected pattern field. To solve these problems, this paper proposes a method to adjust the height of the camera's focus plane and provide depth compensation to correct errors. The effectiveness of this method is validated through experimentation. Comparative experiments on objects with and without active projected patterns demonstrate that the proposed method significantly improves the accuracy and completeness of three-dimensional reconstruction for smooth surfaces. Based on the conclusions drawn, the paper introduces the applicable scenarios of this method.
A novel phase-unwrapping method is proposed to improve the speed of three-dimensional measurement by reducing the number of fringe images required for projection and acquisition in phase-shifting profilometry. First, an additional cosine-coded image with a fixed position frequency jump is projected under a three-step phase-shifting mode. The cosine truth value is calculated from four captured images. Second, the cosine relationship between the absolute phase and cosine truth value at different frequencies within different periods is utilized. Phase discontinuity points are obtained, whereby phase unwrapping is performed through an iterative interpolation method. Finally, the order jump errors that occur near the discontinuity points are corrected using a three-phase method. In line with the experimental results, the proposed method required only four images for temporal phase unwrapping in multi-frequency mode and was unaffected by phase interruptions. When the number of phase-shifting image period was 15, the phase calculation results were consistent with the multi-frequency progressive method.
Correlated imaging and interference is currently a topic of intense research interest. However, research based on interference is limited. This study introduces the basic theory of second-order correlation imaging based on the properties of correlation functions and simulates the ghost imaging of double-slit interference. In addition, when the incident wavelengths of the two optical paths are different, the ghost imaging of double-slit interference exhibits more regular behavior. This observation indicates that the wavelength in the reference optical path significantly impacts correlation information. In contrast, the selected wavelength in the signal optical path has a relatively small impact on the correlation results. This provides a reference for selecting lighting sources for ghost imaging experiments. Finally, the second-order correlation function's correlation characteristics were studied, and interference behavior occurred in double-slit ghost imaging after second-order correlation, laying a good foundation for applications in imaging resolution and other aspects.
In most traditional head-surgery navigation systems, a binocular infrared camera is used to track retroreflective markers fixed on the human head, registering the 3D medical image data of the head to the human body. Generally, the registration markers are manually installed at specific positions. As the marker positions affect the accuracy of registration, they must be carefully installed, which extends the preparation time and may cause invasive damage to the patient. Meanwhile, when the navigation system uses a screen display, surgeons must repeatedly move their gaze between the surgical site and screen. The screen display is non-intuitive and imposes a cognitive burden on the surgeon. To resolve these problems, we propose markerless registration method using a structured light camera that registers 3D medical image data to the human body. The structured light camera obtains a point cloud of the patient's face. The precise head pose of the patient is obtained through a fast and accurate registration pipeline comprising coarse and fine registration algorithms. The registration method is combined with an optically transparent head-mounted display to build an augmented reality system. During multi-user experiments, the average accuracy of target registration was determined as (2.61 ± 0.55) mm, the average Dice similarity coefficient between the virtual and real models was 0.9548, and the average time of the registration algorithm was 0.47 s. Experimental results demonstrate that proposed method quickly and accurately automates the registration process. The proposed method can provide physicians with accurate target spatial information while meeting the accuracy and time requirements of surgery navigation. Moreover, proposed method can be further developed for applications in clinical settings.
The aim of this study is to comprehensively explore the impact of novel fiber optic X-ray grids on imaging quality and to evaluate their potential applications in medical imaging. Using experimental analysis and comprehensive evaluation, we systematically investigated the effects of the source image distance, product of tube current and time, tube voltage, and filter grid array area on the performance of these fiber optic X-ray grids in the imaging process. Further, we comprehensively analyzed the performance of fiber optic X-ray grids by measuring the transmission of primary radiation, scattered radiation, and total radiation and image quality.Results show that under the exposure conditions of 60 kV, 40 mAs; 80 kV, 40 mAs; and 120 kV, 20 mAs, the 80-, 100-, and 120-μm novel fiber optic X-ray grids show good scattering suppression effects, which improve the quality and clarity of X-ray imaging. Additionally, the 100-μm fiber optic X-ray grids exhibit better performance in balancing the transmissions of total radiation and scattered radiation compared with the 80- and 120-μm fiber optic X-ray grids. The experimental results indicate that fiber optic X-ray grids have great potential for considerably reducing scattered radiation and improving image quality and contrast. Thus, this study offers new possibilities for diagnosis and treatment in the field of precision medicine.