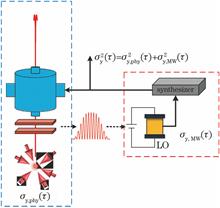
We have developed a low-noise microwave frequency synthesizer for the world's first 85Rb fountain clock. The setup is based on the techniques of low phase-noise frequency synthesis and phase-locking, which can realize the clock frequency signal output with low phase noise. When the output frequency is about 3.035 GHz and the frequency resolution is 0.7 μHz, the single-sideband phase noise densities at 1 Hz, 100 Hz, and 10 kHz Fourier frequency are -97 dBc·Hz -1, -127 dBc·Hz -1, and -130 dBc·Hz -1 , respectively. Moreover, the residual phase noise of the microwave frequency synthesizer is lower by 20 dB than that of the local oscillator. By comparing the contributions of quantum project noise and Dick effect, we show that the stability of the 85Rb fountain clock is comparable to those of 87Rb clock and 133Cs clock, where the noise from a microwave system is the main noise source. The stability caused by the microwave source for the 85Rb fountain clock is estimated as 2.9×10 -13τ-1/2(τ is integration time), among which the contribution of the residual phase noise from the frequency synthesizer is 1.2×10 -14τ-1/2. The synthesizer is helpful to realize the operation of the 85Rb fountain clock with high stability and is expected to be the basis of the future improvement in clock performances.
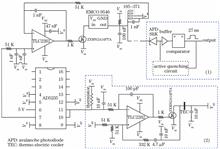
In this work, the temperature characteristics of a single-photon avalanche diode working in Geiger mode are studied. The experimental results show that the avalanche voltage of the avalanche diode linearly decreases with the decrease in temperature and the voltage temperature coefficient is 0.42 V/K. When the avalanche diode works at an avalanche voltage of more than 13 V, the dark count rate decreases exponentially with the decrease in temperature. In addition, the dark count rate decreases by half for each 8.58 K decrease in temperature. Furthermore, when the temperature drops from 274 K to 192 K, the dark count rate of the avalanche diode also decreases from 13900 Hz to 14 Hz. The single-photon avalanche diode with an operating temperature of 260 K and a dark count rate of 58 Hz is cooled to 192 K. The bias voltage at both ends of the diode is adjusted to ensure that the dark count rate is reduced to 0.064 Hz and the after-pulse probability is 6.7% when the detection efficiency is 50% at wavelength of 852 nm. Thus, the performance of the single-photon detector is significantly improved. Moreover, the single-photon detector with an ultra-low dark count rate has significant applications in quantum communication and weak light detection.
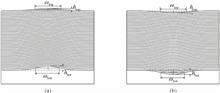
This paper proposed a new method for profile reconstruction of phase defects in extreme ultraviolet lithography mask multilayer films. Three-dimensional profiles of phase defects were characterized using the top and bottom profile parameters. The top profile parameters of defects were measured using an atomic force microscope. Moreover, Fourier ptychography technology was used to retrieve the complex amplitudes of aerial images of the defected mask blanks. Using deep learning models, the bottom profile parameter reconstruction model of defects was constructed by determining the relationship between the amplitudes/phases of aerial images and the bottom profile parameters of defects. The deep learning models used herein include a convolutional neural network and multilayer perceptron. The bottom profile parameters of defects can be reconstructed from the amplitudes/phases of the aerial images using the trained models. The simulation results show that the trained models can accurately reconstruct the bottom profile parameters of phase defects. The root-mean-square errors of bottom full-width-half-maximum reconstruction results of bump and pit defects are 0.51 and 0.43 nm, respectively. The root-mean-square errors of bottom height reconstruction results are 3.35 and 1.73 nm, respectively. The proposed method is immune to the deposition conditions because it captures aerial images as an information carrier.
Herein, a filterless 24-tupling frequency millimeter-wave generator based on polarization multiplexing was proposed. The generator cascaded a three-parallel Mach-Zehnder modulator structure and a single Mach-Zehnder modulator. Further, the generator used the polarization multiplexing structure to filter out all redundant optical sidebands, leaving only 12th order optical sideband signals. The scheme can produce a 24-tupling frequency millimeter-wave signal without any optical or electrical filter. Moreover, combined with the theoretical study of the system, the feasibility of the generator was verified via simulation. The system performance was analyzed and the effects of modulation depth, extinction ratio, phase difference, bias voltage, and line width of the laser on system performance under non-ideal conditions were discussed. The research results show that the value of the optical sideband suppression ratio and radio frequency stray suppression ratio can reach 40 dB and nearly 30 dB, respectively. The system maintains good transmission performance for 150-km transmission distance. The system does not require any auxiliary filter. This system demonstrates the advantages of a high-frequency multiplier and good spectrum quality, thus providing important reference values for research of filterless millimeter-wave generator.
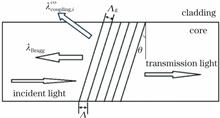
Stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS) is one of the primary factors that limit the output power and stability of narrow-linewidth high-power fiber laser systems. Backward scattered Stokes light would damage the seed and preamplifier system; therefore, suppressing SBS or filtering the Stokes light is a key problem that needs to be addressed. In this study, we design and prepare a matched tilted fiber Bragg grating (TFBG) using an ultraviolet laser and phase masks in a single mode fiber based on the operating wavelength and the tiny frequency shift of SBS, and perform an SBS signal filtering verification experiment. Experimental results show that the average filtering rate of the TFBG to the backward SBS signal is more than 16 dB, which can well protect the front system and help stabilize the system.
In this study, the temperature sensing system performances of a fiber loop ring-down cavity with a fiber Bragg grating (FBG) are investigated by analyzing the spectral response of an FBG and the dynamic variation of an exponential decay. A theoretical FBG loop ring-down cavity model is established to investigate the relationships of the central wavelength of the FBG transmission spectrum and the exponential decay time with temperature change as well as their dynamic evolution procedures. They are experimentally tested by building a temperature sensing system integrated with a fiber loop ring-down cavity with an FBG and 1551.13 nm pulsed laser. The mathematical simulation results agree well with the experimental results, which show that the proposed system has perfect repeatability and stability under the low temperature conditions of -40 ℃. Specifically, the measurement resolution achieved is 0.05 ℃, the sensitivity of temperature is 0.0025/(μs·℃), and the sensitivity of FBG central wavelength is 0.00248/(μs·pm).
Aiming at the risks arising from the static keys in an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing passive optical network (OFDM-PON), this study proposes a physical-layer chaotic encryption scheme using channel phase information as dynamic keys. In the coherence time, the initial values of chaotic keys can be extracted from the uplink and downlink channel phases, which are estimated using communication sides. The downlink data is encrypted and decoded by applying XOR operations with the chaotic key stream generated by a one-dimensional chaotic system. The dynamic key obtained using the proposed scheme can be continuously updated with the change of time, further improving the security performance of the physical layer. The experimental results demonstrate that the keys of both communication sides have a good consistency subsequent to the 16-quadrature-amplitude-modulation (16QAM) optical OFDM signal with a speed of 3.625 Gb/s passing through the standard single-mode fiber (SSMF) with a length of 25 km. The key space of the proposed encryption scheme reaches 10 15, enhancing the security of system transmission and effectively preventing illegal users from eavesdropping.
In this study, we propose an improved U-Net retinal vascular image segmentation algorithm by introducing some modules, such as inception, hole convolution, and attention mechanism, into the U-Net network to solve the problem of low segmentation accuracy caused by the small blood vessels in the retinal image. Initially, the inception module was added during the encoding stage, and convolution kernels of different scales were used to extract the image features to obtain multiscale information from the image. Subsequently, a cascaded hole convolution module was added to the bottom of the U-Net network for expanding the receptive field of the convolution operation without increasing the network parameters. Finally, an attention mechanism was designed for the deconvolution operation during the decoding phase. The problem of weight dispersion can be solved by focusing on the target features under the combination of the attention mechanism and jump connection mode. The experimental results obtained using the standard image set DRIVE denote that the average accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity of the proposed algorithm are 1.15%, 6.15%, and 0.67% higher than those of the traditional U-Net algorithm, respectively, and that the proposed algorithm outperforms other traditional segmentation algorithms.
Signal crosstalk can produce significant fringing effects on the observed images in a focal plane channel. Based on the earth and lunar observation data, the on-orbit detection of the crosstalk effects of all bands of the medium resolution spectral imager (MERSI-II) as FY-3D core load, and the preliminary correction tests also done. The detection results indicate that there are significant signal crosstalk phenomena of bands in some MERSI-II focal planes, among which the band 5 and band 6 of short-wave infrared focal plane and the bands 20, 21, 22, and 23 of mid and long wave infrared focal plane are suffered most obviously, manifested as inter-band and inter-detector characteristics, respectively. Based on the lunar point source imaging characteristics, the crosstalk coefficient is calculated using the linear approximation correction algorithm. Moreover, this correction algorithm is preliminarily verified through band 20. The results show that crosstalk correction can effectively remove the crosstalk signals of lunar images and significantly improve the fringe phenomena of earth observation images, implying that the proposed algorithm has good applicability.
An optical coherence tomography system will inevitably introduce additional aberration into scanning imaging. Thus, image details are lost, and the high definition requirements of medical imaging cannot be satisfied. In this study, we proposed an aberration correction method based on the particle swarm optimization algorithm. The aberration correction method was modeled as a filtering process based on a linear combination of the Zernike polynomials. The particle swarm optimization algorithm was used to iteratively estimate the optimal coefficient value of the polynomials by considering the image information entropy or sharpness as the optimization index. Further, the resolution plate was used as the simulation target image to load the defocused and low-order mixed wavefront aberrations. The image information entropy and sharpness were considered to be the evaluation functions. The root mean square error values of the restoration results were less than 0.1λ, so the clear imaging can be obtained. For the experimentally collected onion cells, the information entropy was considered to be the evaluation index, which decreased by 18% after aberration correction. However, for the collected grape tissue image, sharpness was considered to be the evaluation index, which increased by 36% after aberration correction.
A novel Smith-Purcell free-electron laser based on T-shaped grating is proposed herein. The influences of grating shape on the output characteristics of the Smith-Purcell free electron laser are discussed through theoretical analysis and Particle-in-Cell (PIC) simulation calculation. Through the theoretical analysis, it is found that the beam-wave interaction of the Smith-Purcell free electron laser based on the T-shaped grating and the bunching of electron beam are strong. Accordingly, the beam-wave conversion efficiency is strong, and the output power is high. Through the PIC simulation calculation, it is found that the Smith-Purcell free electron laser based on the T-shaped grating can increase the radiation power. Results indicate that a continuous-wave terahertz radiation at 0.753949 THz with a peak output power of approximately 2 kW can be obtained for a grating of period D=0.3 mm operating at a beam energy of E=50 keV and beam current i=10 A in this novel device. However, in the Smith-Purcell free electron laser based on rectangular grating, continuous-wave terahertz radiation at 0.723397 THz with a peak output power of approximately 0.3 kW can only be generated by the same electron beam (energy E=50 keV and beam current i=10 A) passing through the grating with the same size (D=0.3 mm).
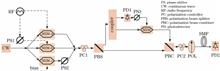
Coherent polarization beam combination (CPBC) is an effective method to obtain the high-brightness laser with linear polarization. This paper proposed an optical phase modulation method to transform the phase difference between two laser beams into amplitude modulation. Using optical heterodyne phase detection and linear phase-locked control, the polarization beam combination of two laser beams with the same frequency was realized. Further, the mathematical models of optical heterodyne polarization phase detection and linear phase-locked control loop were theoretically analyzed in detail for optimizing the system parameters. After phase locking, the polarization extinction ratio of the combined beam achieves 17.67 dB with the combined power of 352.4 mW, while the control bandwidth is nearly 66.1 kHz. The residual phase noise is 1×10 -4 rad·Hz -1/2(1 Hz) and 3×10 -6 rad·Hz -1/2(>100 Hz). Compared with other CPBC phase-locking methods, the proposed method can significantly improve polarization extinction ratio and control bandwidth, and effectively suppress phase noise.
Generally speaking, the optical radiation safety analysis of an adaptive optics (AO) retinal imaging system does not currently consider the spectral bandwidth and superposition effect of imaging and beacon lights. To solve these problems, we propose a radiation safety analysis method that conforms to the international commission on non-ionizing radiation protection (ICNIRP) standard. First, the radiance calculation method is determined when a broadband spectral beam irradiates retina. Then, the maximum permissible exposure (MPE) is analyzed when retina is irradiated by two beams. The exposure safety analysis process is finally developed from the obtained retinal radiance and MPE. An AO swept-source optical coherence tomography imaging system, which covers the illumination conditions of various human retinal imaging systems, is considered as an example to calculate the radiance as well as the maximum radiance. The validity of the proposed method is verified by comparing with other methods. The proposed method is suitable for various human retinal imaging systems with and without AO technology, and it can provide a reference for calculating the safety level of human eye exposure to radiation.
To improve the uniformity and controllability of the multifocal array in laser parallel fabrication, a vector iterative optimization phase algorithm is proposed based on the property of the vector Fourier transform in an objective focusing system. Based on this iterative algorithm, a multifocal array with high uniformity can be produced and the position of each focal spot can be precisely controlled. The numerical simulation and experimental results show that the optimized phase can be utilized to generate a multifocal array with high uniformity. Furthermore, applying the homemade femtosecond laser fabrication system based on a spatial light modulator and taking gold films as the sample, we confirm the validity of laser parallel fabrication. The experimental results demonstrate that using the proposed algorithm, one can achieve the laser parallel fabrication based on multifocal array with an arbitrary arrangement structure. In addition, the dynamic scanning laser fabrication can also be realized by dynamically loading phase patterns.
Resultsshow that the root mean square errors for coordinates and poses are 0.352 mm and 0.0145 rad at field of view of 690 mm×520 mm, respectively. Unlike the traditional edge extraction algorithm, the proposed algorithm is robust with respect to defective data and noisy data and can obtain precise localization for valve center at a wide field of view.
In the aerial image of unmanned aerial vehicle(UAV), the target is usually small, and the shooting angle and height are variable. To address the problems, we proposed an adaptive drone object detection algorithm based on the multi-scale feature fusion. First, lightweight feature extraction network was established using the advantages of deep separable convolution and residual learning. Second, a multi-scale adaptive candidate region generation network was constructed, and feature maps with the same spatial size were weighted and merged based on the channel dimensions, which enhance the feature expression ability to objects. Based on these multi-scale featured maps, the use of semantic features to generate target candidate frames can be more matchable with real objects. Moreover, simulation experiments demonstrate that this algorithm can effectively improve the accuracy of UAV detection and have better robustness.
To obtain a continuous range of clear vision in pseudophakia, an intraocular lens (IOL) with a dual-area aspheric surface and an extended depth of focus was proposed. The IOL was optimized based on a model of aphakia, and its optical performance was analyzed using Zemax. The modulation transfer function (MTF) values remained >0.30 at 50 cycles·mm -1 for eyes with a pupil diameter of 2.5 mm and object distance ranging from 0.75 m to infinity at a full field of view of ±4° and wavelength of 550 nm. Monte Carlo analysis showed that the MTF value at 50 cycles·mm -1 was >0.29, with a probability of 90% for eyes with anterior corneal asphericity ranging from -0.70 to 0.60 when the object distance ranged from 0.75 m to infinity. In addition, theoretical analysis showed that the optical performance remained stable at different pupil diameters and in polychromatic light.
Through electro-static discharge (ESD) strike, we investigate the electro-static discharge failure phenomenon and study the failure evolution process of a vertical structure GaN-based light emitting diode (LED) thin film chip integrated with Ag mirrors through electro-static discharge (ESD) strike. Results show that a black spot appears inside the chip subsequent to the application of ESD strike. With the increase of ESD voltage, the ESD black spot gradually develops into an electro-static hole. Based on the focused ion beam etching, the cause of ESD black spot is clarified as the reduction in the reflectivity of Ag mirrors occurring when the p-GaN and Ag mirrors in the LED chip are melted by the high temperature generated during the electro-static breakdown. During the electro-static failure evolution process of the LED thin film chip, the GaN coarsened hexagonal cone structure around the ESD black spot becomes smaller and denser. This is closely related to the degree of electro-static breakdown. Therefore, the high temperature generated by electro-static breakdown influences the crystal quality of surface GaN materials.
From the design perspective of an optical multi-dimensional information acquired device with small scale, simplicity, and easy integration, we analyze the principle of polarization and phase control of metalens, and design a metalens which can simultaneously focus Si-based orthogonal circularly polarized light based on geometry and transmission phases. The working wavelength of this metalens is 800 nm. It can simultaneously obtain two orthogonal circularly polarized light intensities of a target. The similarity between x/y polarized light rectangular structures is used to simplify the design process and reduce the design time consumption. From design perspective, we select the elementary structure with small depth-width ratio and large scale tolerance to reduce the processing difficulty. The finite difference time-domain (FDTD) simulation tool is used to verify the device function of polarization splitting and focusing imaging. The focusing efficiency is 56.2% when the numerical aperture of this metalens is 0.45.
Taking Nanjing as an example, using the geo-social data combined with optical remote sensing information from the Landsat8 and nighttime light satellites, we design the characterization parameters of the local detection environment within the 2 km buffer around the observation site, such as the anthropogenic factors (population density and anthropogenic heat flux), geometric parameters (area ratio of land use type and altitude), and physical optical parameters (area ratio of impervious surface and vegetation index), and investigate their impacts on the air temperature (AT) observations. The results indicate that under the same weather background, when the vegetation index and area ratio of water body increase and the area ratio of impervious surface decreases, the AT decreases. The quantitative regression model between the vegetation index, area ratio of impervious surface, and area ratio of water body around the observation site and AT is given, and passes over the 99.9% significance level. The proposed method can be used to quantitatively evaluate the air temperature distribution at some region with high resolution.
By placing a pair of linear electrodes at the focal point of a femtosecond laser, the plasma generated through the laser-ionized air is placed in the bias direct-current (DC) field generated by the linear electrode. We observe the terahertz characteristics of plasma in the bias-electric field in this case. By scanning the linear electrodes and observing the terahertz wave intensity, we obtain the optimal electrode position for enhancing the amplitude of terahertz wave. Results suggest that as the laser power increases, the optimal position moves in the direction of light propagation. This work not only studies the characteristics of terahertz signal generated through plasma under the modulation of linear electrodes, but also reveals the physical characteristics of plasma.
Owing to the serious interference of soil moisture content in the detection techniques such as X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy (XRF) method, a support vector regression (SVR) correction prediction model is proposed based on the grey wolf optimization (GWO) algorithm. Subsequent to the preprocess of spectral data, a quantitative analysis model for determining the relationship among net peak area, moisture content, and cadmium content is established based on GWO-SVR. The GWO-SVR model is compared with other models. The results show that the SVR nonlinear model has a better decision coefficient and smaller errors than the linear regression model. Moreover, under the GWO optimization, each model index is improved. Compared with other optimization algorithms, GWO-SVR has less iterations, better fitting effect, and smaller prediction errors. The proposed model can provide an effective reference for the prediction of other heavy metals in soils and the correction of moisture content.
A method for improving the spatial resolution of an infrared scene projector chip is proposed by making in-plane microstructures. By establishing a simplified two-dimensional heat conduction model, the spatial resolution of the chip with periodical microstructure is calculated. On this basis, the influences of contact area ratio and filling factor of microstructure on the spatial resolution of this infrared scene projector chip are studied and the optimization design of periodical microstructure is realized. The theoretical calculation shows that by fabricating the microstructure with a contact area ratio of 0.18 and a filling factor of 0.52, the spatial resolution can be improved to 10.3 lp·mm -1 at an MTF of 0.3, twice that of the chip without microstructure. Two kinds of infrared scene projector chips with different contact area ratios and filling factors are fabricated. The diameter of the chip is 7.62 cm and the thickness is about 800 nm. Using the non-contact steady-state infrared imaging method, the spatial resolutions of these two chips are measured. When the MTF value is 0.3, the spatial resolutions of the chips with contact area ratios of 0.20 and 0.46 are 11.2 lp·mm -1 and 6.6 lp·mm -1, respectively. Our experimental results coincide well with those of the theoretical calculation, indicating that the proposed method is effective and practical for spatial resolution improvement.
Mo/Si multilayer coating process is one of the key technologies for extreme ultraviolet lithography. In order to optimize the coating process of Mo/Si multilayers, we study the influences of environment pressure and target-substrate distance on the surface roughness of Mo/Si multilayer coating. A model of atomic deposition is established based on the physical process of magnetron sputtering. The variations of incident angle and the energy distribution of depositing atoms with environment pressure and target-substrate distance are investigated. Moreover, the experiments are performed to fabricate Mo/Si multilayer coating samples using a direct current magnetron sputtering coating machine, and the evolutions of the surface roughness and power spectral density with environment pressure and target-substrate distance are studied. The conclusion obtained from the model agrees well with that from the experiments, and the proposed model can provide a theoretical explanation for the results measured by the experiments.
A pulse-dilation X-ray diodes (XRD) is developed and also tested using a femtosecond laser. A time-dependent ramp waveform is applied to a photocathode (PC) to introduce a time-dependent electric field between PC and mesh. This electric field leads to an axial speed dispersion of the photoelectron signal. The electrons generated earlier move faster than those later. The photoelectrons transiting a drift region are stretched before reaching a microchannel plate (MCP), and are then amplified and read out with a digital oscilloscope. The detector's time response is enhanced by 11 times with the usage of pulse-dilation technique.