View fulltext
View fulltext
Device-independence is the ultimate goal of the realistic security of quantum information, but violating Bell inequality is difficult and complex. We have implemented the first on-chip SDI-QRNG in the whole DI/SDI field, paving the way for large-scale secure utilization of the quantum resources at room temperature. See Lang Li et al., pp. 1379.
Towards next-generation intelligent display devices, it is urgent to find a cheap and convenient dynamic optical control method. Conventional gratings are widely used as cheap diffractive elements due to their effective optical control capabilities. However, they are limited within multi-function or complex optical modulation due to the lack of accurate control of the amplitude/phase at pixel-level. Here, a metasurface-assisted grating-modulation system is originally proposed to achieve switchable multi-fold meta-holographic dynamics. By incorporating metasurfaces with traditional gratings and tuning their relative coupling positions, the modulation system gains the optical modulation capability to realize complex optical functionalities. Specifically, by varying the grating periods/positions relative to the metasurface, 2–8 holographic image channels are programmed to be dynamically exhibited and switched. The proposed metasurface-assisted grating-modulation approach enjoys cost-effective convenience, strong encoding freedom, and facile operation, which promises programmable optical displays, optical sensors, optical information encryption/storage, etc.
The COVID-19 pandemic continues to significantly impact people’s lives worldwide, emphasizing the critical need for effective detection methods. Many existing deep learning-based approaches for COVID-19 detection offer high accuracy but demand substantial computing resources, time, and energy. In this study, we introduce an optical diffractive neural network (ODNN-COVID), which is characterized by low power consumption, efficient parallelization, and fast computing speed for COVID-19 detection. In addition, we explore how the physical parameters of ODNN-COVID affect its diagnostic performance. We identify the F number as a key parameter for evaluating the overall detection capabilities. Through an assessment of the connectivity of the diffractive network, we established an optimized range of F number, offering guidance for constructing optical diffractive neural networks. In the numerical simulations, a three-layer system achieves an impressive overall accuracy of 92.64% and 88.89% in binary- and three-classification diagnostic tasks. For a single-layer system, the simulation accuracy of 84.17% and the experimental accuracy of 80.83% can be obtained with the same configuration for the binary-classification task, and the simulation accuracy is 80.19% and the experimental accuracy is 74.44% for the three-classification task. Both simulations and experiments validate that the proposed optical diffractive neural network serves as a passive optical processor for effective COVID-19 diagnosis, featuring low power consumption, high parallelization, and fast computing capabilities. Furthermore, ODNN-COVID exhibits versatility, making it adaptable to various image analysis and object classification tasks related to medical fields owing to its general architecture.
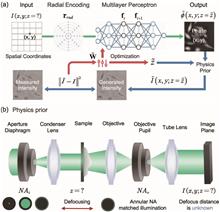
The transport-of-intensity equation (TIE) enables quantitative phase imaging (QPI) under partially coherent illumination by measuring the through-focus intensities combined with a linearized inverse reconstruction algorithm. However, overcoming its sensitivity to imaging settings remains a challenging problem because of the difficulty in tuning the optical parameters of the imaging system accurately and because of the instability to long-time measurements. To address these limitations, we propose and experimentally validate a solution called neural-field-assisted transport-of-intensity phase microscopy (NFTPM) by introducing a tunable defocus parameter into neural field. Without weak object approximation, NFTPM incorporates the physical prior of partially coherent image formation to constrain the neural field and learns the continuous representation of phase object without the need for training. Simulation and experimental results of HeLa cells demonstrate that NFTPM can achieve accurate, partially coherent QPI under unknown defocus distances, providing new possibilities for extending applications in live cell biology.
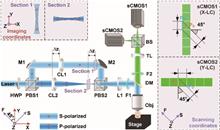
Using an on-the-fly scanning scheme, line confocal microscopy can obtain complex structures of large biological tissues with high throughput. Yet, it suffers from lateral imaging asymmetry and thus introduces the potential deformations of the observation results. Here, we propose cross-line illumination microscopy (cLIM) that acquires the imaging data of two perpendicular directions simultaneously through the same objective lens in a line scanning and utilizes two-direction deconvolution fusion to achieve lateral symmetric imaging performance. Imaging fluorescence beads indicates that cLIM reduces lateral resolution asymmetry from 46.1% to 2.5% and improves lateral resolution by 31.0%, compared with traditional line-scanning imaging. Compared with commercial point-confocal microscopy, the cLIM has a 25.84× increase in imaging speed and 1.93× better background-suppressing ability when imaging an 11,306 μm×7783 μm×100 μm mouse kidney slice. We also show the advantages of the cLIM in observing direction-sensitive texture features by imaging a muscular tissue slice. cLIM offers a novel solution to achieve laterally symmetric line-scanning imaging with simple modifications while maintaining high throughput and accuracy for imaging large-scale samples.
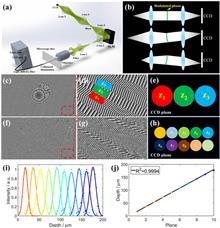
3D imaging technology is pivotal in monitoring the functional dynamics and morphological alterations in living cells and tissues. However, conventional volumetric imaging associated with mechanical z-scanning encounters challenges in limited 3D imaging speed with inertial artifact. Here, we present a unique phase-modulated multi-foci microscopy (PM3) technique to achieve snapshot 3D imaging with the advantages of extended imaging depths and adjustable imaging intervals between each focus in a rapid fashion. To accomplish the tasks, we utilize a spatial light modulator (SLM) to encode the phases of the scattered or fluorescence light emanating from a volumetric sample and then project the multiple-depth images of the sample onto a single charge-coupled device camera for rapid 3D imaging. We demonstrate that the PM3 technique provides ∼55-fold improvement in imaging depth in polystyrene beads phantom compared to the depth of field of the objective lens used. PM3 also enables the real-time monitoring of Brownian motion of fluorescent beads in water at a 15 Hz volume rate. By precisely manipulating the phase of scattered light on the SLM, PM3 can pinpoint the specific depth information in living zebrafish and rapidly observe the 3D dynamic processes of blood flow in the zebrafish trunk. This work shows that the PM3 technique developed is robust and versatile for fast 3D dynamic imaging in biological and biomedical systems.
The decomposition and identification of signals are crucial for flow vector acquisition in a multi-dimensional measurement. Here, we proposed a two-dimensional (2D) flow vector measurement system based on all-fiber laser feedback frequency-shifted multiplexing technology. The reliable performance of the system is characterized by experimental verification and numerical simulation. An orthogonal dual-beam structure is employed to eliminate the impact of an unknown incident angle in the practical application. Meanwhile, the vector velocity signals in 2D can be decomposed into one-dimensional (1D) scalar signals by adopting the frequency-shifted multiplexing, which makes it easy to obtain the vector information and velocity distribution of fluid motion through the self-mixing interference frequency spectrum. Moreover, the measured flow rates present a high linearity with syringe pump speeds ranging from 200 to 2000 μL/min, and the velocity information of the different incidence angles is easily obtained with high precision. This work may pave the way for the acquisition and processing of multi-dimensional flow vector signals, with potential applications in biomedical monitoring and microflow velocity sensing.
In recent years, terahertz (THz) technology has made significant progress in numerous applications; however, the highly sensitive, room-temperature THz detectors are still rare, which is one of the bottlenecks in THz research. In this paper, we proposed a room-temperature electrometry method for THz detection by laser spectroscopy of cesium (Cs133) Rydberg atoms, and conducted a comprehensive investigation of the five-level system involving electromagnetically induced transparency (EIT), electromagnetically induced absorption (EIA), and Autler–Townes (AT) splitting in Cs133 cascades. By solving the Lindblad master equation, we found that the influence of the THz electric field, probe laser, dressing laser, and Rydberg laser on the ground state atomic population as well as the coherence between the ground state and the Rydberg state, plays a crucial role in the transformation and amplitude of the EIT and EIA signals. Temperature and the atomic vapor cell’s dimensions affect the number of Cs133 atoms involved in the detection, and ultimately determine the sensitivity. We predicted the proposed quantum coherence THz detection method has a remarkable sensitivity of as low as 10-9 V m-1 Hz-1/2. This research offers a valuable theoretical basis for implementing and optimizing quantum coherence effects based on Rydberg atoms for THz wave detection with high sensitivity and room-temperature operation.
Breathers are localized structures that undergo a periodic oscillation in their duration and amplitude. Optical microresonators, benefiting from their high-quality factor, provide an ideal test bench for studying breathing phenomena. In a monochromatically pumped microresonator system, intrinsic breathing instabilities are widely observed in the form of temporal dissipative Kerr solitons which only exist in the effectively red-detuned regime. Here, we demonstrate a novel bichromatic pumping scheme to create compulsive breathing microcombs via respectively distributing two pump lasers at the effectively blue- and red-detuned sides of a single resonance. We experimentally discover the artificial cnoidal wave breathers and molecular crystal-like breathers in a photonic chip-based silicon nitride microresonator and theoretically describe their intriguing temporal dynamics based on the bichromatic pumping Lugiato–Lefever equation. In particular, the corresponding breathing microcombs exhibit diverse comb line spacing ranging from 2 to 17 times the free spectral range of the microresonator. Our discovery not only provides a simple yet robust method to harness microcombs with reconfigurable comb line spacing but also reveals a new class of breathing waves in driven dissipative nonlinear systems.
The increasing demand for diverse portable high-precision spectral analysis applications has driven the rapid development of spectrometer miniaturization. However, the resolutions of existing miniaturized spectrometers mostly remain at the nanometer level, posing a challenge for further enhancement towards achieving picometer-level precision. Here, we propose an integrated reconstructive spectrometer that utilizes Mach–Zehnder interferometers and a tunable diffraction network. Through random tuning in the time domain and disordered diffraction in the space domain, the random speckle patterns closely related to wavelength information are obtained to construct the transmission matrix. Experimentally, we achieve a high resolution of 100 pm and precisely reconstruct multiple narrowband and broadband spectra. Moreover, the proposed spectrometer features a simple structure, strong portability, and fast sampling speed, which has great potential in the practical application of high-precision portable spectral analysis.
In this paper, we present a detector-integrated vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser (VCSEL) with a movable high-contrast grating (HCG) mirror in an n-i-p-i-n manner. The detector-integrated VCSEL with a movable HCG can achieve three functions, including wavelength tuning, power monitoring, and resonant-cavity-enhanced (RCE) photon detection. Currently, the device can achieve a wavelength tuning range of 27 nm at room temperature when the suspended HCG is driven by the reverse-bias voltage. The n-i-p structure located at the upper part of the device can serve as an intra-cavity photodiode to monitor the output power due to the defect absorption. The RCE photon detection function of the detector-integrated VCSEL with a movable HCG is measured, and it has a peak responsivity at about 926 nm. This detector-integrated VCSEL with a movable HCG will be useful for sensing and imaging.
Metasurfaces have demonstrated rich electromagnetic control capabilities and degrees of freedom in past years. As is well known, for passive metasurfaces, their functionalities cannot be further expanded accordingly once prototypes are established. Therefore, reconfigurable metasurfaces, utilizing active devices to replace geometric changes in passive structures, have received widespread attention, especially with the development of wireless communication recently. In reconfigurable metasurfaces, artificial meta-atoms are composed of active devices and passive structures combined together. However, these two modules are usually utilized as a whole due to the tight coupling of the active devices and the passive structures, which results in passive structures not receiving sufficient attention and being utilized as independent degrees of freedom. In this article, we propose the concept of weakly coupled reconfigurable metasurfaces in transmissive systems, enabling independent control of active and passive modules through weak coupling. As the proof of concept, a simple weakly coupled system is proposed, which can realize the transmission wavefront engineering through the geometric changes of meta-structures in passive mode, while achieving switching between transmission and reflection states in active mode, respectively. Our exploration lies in making use of the physical structure, which is easily neglected in traditional reconfigurable metasurface design, emphasizing the collaborative work of active and passive modules, exploring more available variables within the same aperture, and providing a potential solution for balancing functionality and resource consumption in practical applications.
Programmable metasurfaces have received a great deal of attention due to their ability to dynamically manipulate electromagnetic (EM) waves. Despite the rapid growth, most of the existing metasurfaces require manual control to switch among different functionalities, which poses severe limitations on practical applications. Here, we put forth an intelligent metasurface that has self-adaptive EM functionality switching in broadband without human participation. It is equipped with polarization discrimination antennas (PDAs) and feedback components to automatically adjust functionalities for the different incident polarization information. The PDA module can first perceive the polarization of incident EM waves, e.g., linear or circular polarization, and then provide the feedback signal to the controlling platform for switching the EM functionality. As exemplary demonstrations, a series of functionalities in the 9–22 GHz band has been realized, including beam scanning for x-polarization, specular reflection for y-polarization, diffuse scattering for left-handed circular polarization (LCP), and vortex beam generation for right-handed circular polarization (RCP) waves. Experiments verify the good self-adaptive reaction capability of the intelligent metasurface and are in good agreement with the designs. Our strategy provides an avenue toward future unmanned devices that are consistent with the ambient environment.
The realization of a high numerical aperture (NA) fiber lens is critical for achieving high imaging resolution in endoscopes, enabling subwavelength operation in optical tweezers and high efficiency coupling between optical fibers and photonic chips. However, it remains challenging with conventional design and fabrication. Here we propose an ultrathin (400 nm) graphene oxide (GO) film lens fabricated in situ on a standard single-mode fiber facet using the femtosecond laser direct writing technique. An extremely high NA of 0.89 is achieved with a near diffraction-limited focal spot (FWHM=0.68λ), which is verified theoretically and experimentally. The diameter of the fabricated fiber GO lens is as small as 12 μm with no beam expansion structure. The proposed fiber GO lens is promising for applications such as super-resolution imaging, compact optical tweezers, medical endoscopes, and on-chip integration.
Microlens arrays have been widely used in the fields of micro-optics and micro- and nanofabrication. Traditional preparation methods utilize commercial photoresists and thermosetting materials, thereby restricting the optical properties of microlenses. In recent years, significant advancements have been achieved in near-field super-resolution imaging by utilizing microspheres and forming arrays of microsphere lenses via self-assembly. However, self-assembly approaches lack flexibility in terms of pattern selection. This study proposes a method that utilizes electrohydrodynamic jet (E-jet) printing to code ultraviolet (UV)-curable adhesives and assist in the assembly of patterned microsphere-lens arrays. Simulation results demonstrate that the UV-curable adhesive has little impact on the optical properties of the microsphere lens. Moreover, the microsphere lens exhibits a superior imaging resolution compared with traditional microlenses. A projection-lithography system is developed to achieve an accurate alignment between the focal plane of the microsphere lenses and the plane of the photoresist, facilitating the fabrication of patterned nanostructures. The lithographic nanostructures have a minimum feature size of 850 nm. This method enables the fabrication of arrays of microsphere lenses with arbitrary patterns and presents an inexpensive and simple strategy for fabricating micro- and nanostructure arrays with submicrometer features.
Quasi-bound states in the continuum (QBIC), with exceptionally high-Q factors and the local field enhancement effect, have found potential applications in matter sensing. Introducing the QBIC mechanism into terahertz (THz) metasurfaces can significantly enhance the interaction between incident THz waves and matter, providing a feasible platform for the detection of biochemical substances. Currently, most experimental studies on terahertz QBIC metasurfaces utilize metallic structures. By contrast, research on terahertz all-dielectric QBIC metasurfaces generally remains at the simulation stage due to the high fabrication process requirements, and transitioning to the experimental stage still poses many challenges. In this paper, a hollow-structured all-silicon metasurface supporting THz QBIC is proposed. The resonance of THz QBIC is excited via a simple hollow structure and observed in experiment. Simulations and experimental results demonstrated that the designed THz QBIC metasurface can achieve sensing of Auramine O. Notably, it is the first study, to our knowledge, to employ a metasurface to sense Auramine O. Additionally, the sensing performance maintains good stability under different humidity and temperature conditions. This study provides new references and insights for the design and implementation of THz QBIC, and also opens a new pathway for the detection of Auramine O.
We present an innovative approach for the simultaneous agile manipulation of high-refractive-index (HRI) and low-refractive-index (LRI) particles. Our method involves introducing a dual-curvilinear optical vortex beam (DC-OVB) generated by superimposing a pair of curved beams: HRI and LRI particles are controlled by the bright curve and the dark channel between the two curves, respectively. The proposed DC-OVB provides customizable motion paths and velocities for both LRI and HRI particles. Each curve of the DC-OVB can support a distinct orbital flow density (OFD), enabling the application of torques to HRI and LRI particles, guiding them to orbit along specified trajectories and prompting them to execute various curvilinear motions simultaneously, including curvilinear movement, revolution, and rotation.
The topic of optical precise displacement measurement has garnered significant attention and generated widespread interest recently. The use of optical singularity offers a potential solution for this purpose, although effectively manipulating the singularity in an ideal manner remains challenging. In this work, we propose a theoretical approach to achieve controllable position modulation of the C-point in the focal plane, whose spatial position can be easily modulated by adjusting the relative offset factor β and the offset angle α of an azimuthal polarization beam (APB), while the interval and orientation of the C-points can be flexibly regulated. Notably, the chiral polarization state undergoes a distinct reversal along the link-line connecting the two C-points, thereby providing a promising approach for accurate displacement sensing. To evaluate its sensing characteristics, the varying pattern of the scattered field intensity is monitored when sweeping a gold helix and nanoparticle along the link-line. The results of simulation quality index Q verify that the equilibrium factor of the scattering field possesses an obvious linear relationship with the displacement, signifying a precise sub-nanometric sensitivity. This research introduces new methods for the flexible control of polarization singularities in tightly focused fields, thereby enhancing the utilization of circular polarization properties near C-points for displacement sensing. These findings not only enrich the field of nanometer measurement technology but also pave the way for new avenues of research in this domain.
Quantum resources offer intrinsic randomness that is valuable for applications such as cryptography, scientific simulation, and computing. Silicon-based photonics chips present an excellent platform for the cost-effective deployment of next-generation quantum systems on a large scale, even at room temperature. Nevertheless, the potential susceptibility of these chips to hacker control poses a challenge in ensuring security for on-chip quantum random number generation, which is crucial for enabling extensive utilization of quantum resources. Here, we introduce and implement an on-chip source-device-independent quantum random number generator (SDI-QRNG). The randomness of this generator is achieved through distortion-free on-chip detection of quantum resources, effectively eliminating classical noise interference. The security of the system is ensured by employing on-chip criteria for estimating security entropy in a practical chip environment. By incorporating a photoelectric package, the SDI-QRNG chip achieves a secure bit rate of 146.2 Mbps and a bare chip rate of 248.47 Gbps, with all extracted secure bits successfully passing the randomness test. Our experimental demonstration of this chip-level SDI-QRNG shows significant advantages in practical applications, paving the way for the widespread and cost-effective implementation of room-temperature secure QRNG, which marks a milestone in the field of QRNG chips.
The conventional Gaussian-modulated coherent-state quantum key distribution (QKD) protocol requires the sender to perform active modulations based on a true random number generator. Compared with it, the passive-state-preparation (PSP) continuous-variable quantum key distribution (CVQKD) equivalently performs modulations passively by exploring the intrinsic field fluctuations of a thermal source, which offers the prospect of chip integration QKD with low cost. In this paper, we propose and experimentally demonstrate a high-rate PSP-CVQKD scheme within an access-network area using high-bandwidth detectors in a continuous wave encoding and decoding way. By proposing effective methods for suppressing the noises during the PSP process and polarization multiplexing to decrease the photon leakage noises, we realize the high-intensity local oscillator transmission, thereby achieving coherent detection with high efficiency, low noise, and high bandwidth. The secure key rates over transmission distance of 5.005 km with and without consideration of the finite-size effect are 273.25 Mbps and 1.09 Gbps. The use of the PSP method boosts the asymptotic secret key rate of CVQKD to Gbps level for the first time, to our knowledge, within the range of the access network, which provides an effective and secure key distribution strategy for high-speed quantum cryptography access communication.
Ultra-compact multifunctional integrated photonic modules have great practical significance to photonic integrated circuits (PICs). However, the design effect and efficiency of the existing mainstream inverse design algorithms are incompetent when designing these modules. We analyze their shortcomings in this task, and propose a new, to our knowledge, inverse design algorithm named polygon search (PS) algorithm to address these problems. We utilize the PS algorithm to design an integrated dual-channel mode-conversion-crossing waveguide module. This module integrates three functions: interconversion between TE0 and TE1, interconversion between TE0 and TE2, and channel crossing within only a 4 μm×4 μm footprint, and its performance is verified by experimental testing. It not only greatly reduces the total footprint of many PICs but also greatly improves their fabricating robustness. Furthermore, we propose a PS-designed mode mixer and a PS-designed bending waveguide, and connect them with the integrated modules to form a four-channel crossing-mode-division-multiplexing system. This system can provide multiple modes on the basis of channel crossing and transmit the output signal in the same direction in parallel within a single output waveguide, which significantly increases the communication bandwidth and decreases the footprint of PICs. At last, we demonstrate the effect and efficiency advantages of the PS algorithm over several mainstream inverse design algorithms by a comprehensive contrast experiment and explain these advantages in theory from several perspectives.
The terahertz (THz) absorption spectrum is a powerful method to identify substances. The improvement focuses on sensitivity and recovery ability. Here, we demonstrate enhanced THz vibrational absorption spectroscopy based on an on-chip THz whispering gallery mode resonator (THz-WGMR). A THz-WGMR with high Q can store energy and enhance the interaction between the THz waves and the target substances to capture the unique absorption fingerprint information. Therefore, it possesses significant sensitivity to identify trace amounts of substances. As a proof of concept, lactose powder and glucose powder are applied to demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach in recovering fingerprint absorption spectroscopy. Compared with a straight waveguide, the high sensitivity of the THz-WGMR is illustrated. The change of the transmissivity caused by the lactose reaches 7.8 dB around 532 GHz for the THz-WGMR, while only 1.4 dB for the straight waveguide, demonstrating the state-of-the-art sensing performance in fingerprint absorption recovery. We believe the proposed integrated THz-WGMR will promote the THz identification of tiny fingerprint substances.
The consumption of contaminated food may cause serious illnesses, and traditional methods to detect Escherichia coli are still associated with long waiting times and high costs given the necessity to transport samples to specialized laboratories. There is a need to develop new technologies that allow cheap, fast, and direct monitoring at the site of interest. Thus, in this work, we developed optical immunosensors for the selective detection of E. coli, based on liquid crystal technology, whose molecules can align in different manners depending on the boundary conditions (such as substrates) as well as the environment that they experience. Each glass substrate was functionalized with anti-E. coli antibody using cysteamine as an intermediate, and a vertical alignment was imposed on the liquid crystal molecules by using DMOAP during functionalization. The presence of bacteria disrupts the alignment of the liquid crystal molecules, changing the intensity of light emerging between cross polarizers, measured using a polarized optical microscope and a monochromator. It was possible to detect E. coli in suspensions in the concentration range from 2.8 cells/mL to 2.8×109 cells/mL. Selectivity was also evaluated, and the sensors were used to analyze contaminated water samples. A prototype was developed to allow faster, in-situ, and easier analysis avoiding bulky instruments.