View fulltext
View fulltext
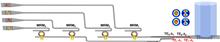
In this Letter, a four-channel silicon photonic mode-division-multiplexing (MDM) and wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM) transmitter chiplet is proposed over a 1.65 mm2 footprint, utilizing add-drop micro-ring modulators to simultaneously achieve electro-optic modulation and two-wavelength multiplexing. A dual-mode grating coupler with a side-distributed Bragg reflector for equalized two-mode coupling is realized with high chip-to-fiber coupling efficiency, so as to support the MDM optical fiber interface. A high data rate of up to 4 × 56 Gbps signaling is experimentally demonstrated, featuring applications like 200G quad small form-factor pluggable (QSFP) transceivers and indicating significant potential for high-density and large-capacity 3D co-packaged optical interconnects through flip-chip-based electronic-photonic packaging.
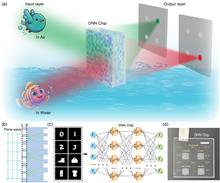
Research in the ocean places high demands on chips’ robustness, speed, and energy consumption. Diffractive neural networks (DNNs) enable direct optical image processing at light speed, with great potential for underwater applications. Here, we experimentally demonstrate a compact DNN chip capable of operating directly in both water and air by multi-objective training and initial training value optimization. The two layers of DNNs are integrated on the two surfaces of a quartz plate, respectively. The chip achieved high accuracies above 90% in recognition tasks for handwritten digits and fashion products. The architecture and material ensure the chip’s high stability for long-term underwater use.
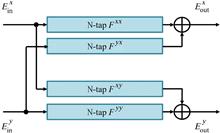
A multiplier-simplified adaptive channel equalization scheme is proposed for short-reach digital coherent optical transmission. The data processing is based on hardware-efficient logic, such as a shifter and adder unit, rather than a conventional multiplier. Through the offline experiment, the performances of 64 Gbaud polarization division multiplexed (PDM) quadrature phase shift keying (QPSK), 16-quadrature amplitude modulation (16QAM), and 64-quadrature amplitude modulation (64QAM) are verified. Typically, in 10.8 km standard single-mode fiber transmission, the 64 Gbaud PDM-16QAM performance penalty can be limited to less than 0.2 dB by the proposed adaptive channel equalization, compared with the conventional method. Furthermore, based on our 10 Gb/s real-time coherent optical transceiver, we demonstrate the feasibility of a field-programmable gate array. Using a reasonable number of logical units, the performance of the proposed scheme is shown to be close to that of the conventional method.
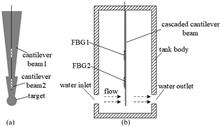
We propose a novel target-type fiber Bragg grating (FBG) flowmeter based on a cascaded cantilever beam with a simple structure in this paper. Such a cascaded cantilever beam consists of two sections with constant strength but different dimensions, where two FBGs connected in series are glued on the surface of the two sections. Bending occurs when the target of the beam is rushed by a flow, which results in different strain-induced wavelength shifts for the two FBGs. Because the two FBGs have the same responses to ambient temperature and pressure changes, a differential wavelength shift that is insensitive to the ambient influences can be simply realized by monitoring the wavelength separation change of the FBGs. So that temperature- and pressure-independent flow rate sensing can be performed. Finally, we experimentally validate that ambient temperature and pressure fluctuations do not affect the proposed FBG flowmeter, where a sensing accuracy of 0.015 m3/h and a measurement range from 0 to 1 m3/h are achieved. Based on its simple structure and low cost, this flowmeter has broad application prospects in the industrial field.
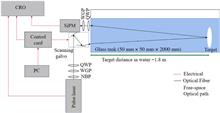
In this work, we demonstrate a single-photon lidar based on a polarization suppression underwater backscatter method. The system adds polarization modules at the transmitter and receiver, which increases the full width at half-maximum of the system response function by about 5 times, improving the signal-to-background ratio, ranging accuracy, and imaging effect. Meanwhile, we optimize a sparsity adaptive matching pursuit algorithm that achieves the reconstruction of target images with a 7.3 attenuation length between the system and the target. The depth resolution of the system under different scattering conditions is studied. This work provides a new method for underwater imaging.
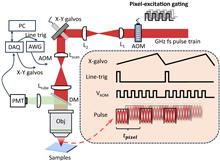
In this Letter, we propose a pixel-excitation-gating technology for high-sensitivity nonlinear imaging excited by femtosecond pulses at a GHz repetition rate, which can enhance the signal quality of nonlinear imaging. To validate this technology, we apply it to a customized two-photon excitation (TPE) fluorescence microscope that uses a GHz femtosecond pulse fiber laser as the excitation source. Compared with the excitation using a continuous GHz pulse train, up to ∼4-fold enhancement of fluorescence signal can be obtained when the excitation pulse train is gated with a 25% duty cycle of the pixel dwell time, under constant average power. It is anticipated that pixel-level-excitation gating can be an add-on solution for fluorescence signal enhancement in nonlinear imaging systems that are excited by GHz femtosecond pulses. Moreover, the pixel-level excitation control would allow more flexible excitation.
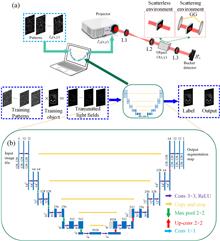
It is difficult to extract targets under strong environmental disturbance in practice. Ghost imaging (GI) is an innovative anti-interference imaging technology. In this paper, we propose a scheme for target extraction based on characteristic-enhanced pseudo-thermal GI. Unlike traditional GI which relies on training the detected signals or imaging results, our scheme trains the illuminating light fields using a deep learning network to enhance the target’s characteristic response. The simulation and experimental results prove that our imaging scheme is sufficient to perform single- and multiple-target extraction at low measurements. In addition, the effect of a strong scattering environment is discussed, and the results show that the scattering disturbance hardly affects the target extraction effect. The proposed scheme presents the potential application in target extraction through scattering media.
Free manipulation of electromagnetic waves in the terahertz (THz) band based on metasurface functional devices has been the focus of research in recent years. Among these devices, active metasurfaces have generated extensive research interest due to their reconfigurability. In this work, we demonstrate a mechanically reconfigurable THz polarization converter that consists of two parallel transmissive metasurfaces with a tunable spacing. By mechanically adjusting the coupling strength between the metasurfaces, the orthogonal polarization conversion of the incident linearly polarized THz waves can be tuned. Specifically, the device can be tuned from efficient dual-frequency orthogonal polarization conversion to efficient single-frequency orthogonal polarization conversion. After a gradual decrease in efficiency, it is finally changed to a low transmission state as the gap distance increases from 150 to 800 µm. We theoretically analyze the tuning process under different spacings and experimentally verify it using a vector network analyzer. Our proposed design is straightforward and robust, with the potential to find wide applications in THz science and technology.
We propose a high-sensitivity spin polarization detection scheme based on optical amplitude modulation in atomic co-magnetometers, which is different from the traditional configuration. A linearly polarized laser with intensity modulation interacts with electron spins, generating optical rotation angles. Through differential amplification and demodulation, atomic spin polarization information is extracted with high precision. The effectiveness of the proposed method is verified by applying external perturbations during testing. Compared to traditional detection methods, the proposed approach effectively enhances inertial measurement sensitivity. Specifically, at 1 Hz, the measurement sensitivity has improved from 9.7 × 10-6 to 3.25 × 10-6 deg/(s Hz1/2). Furthermore, the proposed scheme is easily integrable and conducive to future research on miniaturizing co-magnetometers and can also be applied to many other related fields.
Chirped Bragg grating is a powerful dispersion compensator. It has the advantages of a broad working bandwidth, a simple structure, and a compact footprint. However, previously reported integrated silicon chirped Bragg gratings relying on the transverse electric (TE) modes fail to achieve a large time delay because the TE modes are hypersensitive to sidewall roughness and fabrication errors. Here, we propose and demonstrate a dispersion compensator utilizing a transverse magnetic (TM) type silicon chirped multimode waveguide grating (CMWG), which exhibits a broad working bandwidth of 30.3 nm, an extensive dispersion of 25.1 ps/nm, and a recorded large group delay of 812.6 ps.
In this work, polarization mode dispersion (PMD) in polarization-maintaining (PM) fibers, to the best of our knowledge, is first proposed and experimentally proved to be responsible for severe spectral modulations in ultrafast PM fiber amplifiers, the introduction of which can give reasonable explanation for the dense spectral ripples imposed on the spectra of amplified lasers from the commonly used all-PM-fiber or hybrid “PM-fiber + bulk crystal” amplifiers, including both high-power amplifiers with remarkable nonlinear effects (self-phase modulation, SPM) and even low-power amplifiers with negligible nonlinear effects.
Statistical properties of the erbium-doped random fiber laser (ERFL) play an important role in studying its physical attributes and advancing profound applications. Thus, there is an obvious need for thorough characterization and effective tailoring. Here, we investigate the full-bandwidth time-domain statistical properties of ERFL and achieve its tailoring through the aspect of fiber dispersion. Particularly, a narrowband ERFL is delicately designed to guarantee full-bandwidth measurement. The intensity probability density function (PDF) employed to analyze time-domain characteristics exhibits an inward deviation from the exponential distribution, indicating that correlations exist among different wavelength components. Furthermore, the effect of fiber dispersion on the temporal characteristics of ERFL is explored. The results demonstrate that dispersion accumulation breaks correlations among wavelength components, making its time-domain characteristics closer to the amplified spontaneous emission source. Conversely, dispersion compensation makes the PDF distribution converge further, leading to a more stable temporal output compared to the ERFL seed source. This work reveals the intrinsic time-domain dynamics of ERFL and provides new insights into tailoring demand-oriented temporal characteristics.
A hybrid cavity structure based on individual laser diode integrating coherent beam combining (CBC) and spectral beam combining (SBC) is demonstrated. The CBC structure is used to enhance laser output power while optimizing beam quality, and the SBC structure is employed to further increase laser output power. An output power of 1.42 W was obtained at 0.55 A, with a high combining efficiency of 87.2%. Additionally, the brightness of this structure is 58.65 MW·cm-2·sr-1, which is 3.66 times that of a single laser diode. The entire structure provides a new approach for increasing the output power and optimizing the beam quality of the laser diode.
We experimentally demonstrate a Yb-doped all-fiber mode-locked laser based on the Mamyshev mechanism. The entire experimental setup operates only by injecting pump powers and adjusting polarization controllers (PCs), which realizes self-starting. Two types of pulse patterns are observed at different pump powers and polarization states, including single pulses and up to eight-pulse bound-state pulses. The operating wavelength of single-pulse mode-locking switching between 1072.3 and 1043.1 nm can be realized by increasing the pump power while keeping the PCs in a fixed state. The design can provide an attractive experimental model for all-fiber and self-starting Mamyshev oscillators.
A mode-switchable femtosecond vortex laser is innovatively developed in a Yb:KGW-based resonator. The unique structure is designed to achieve a transition between different transverse modes. In a normal cavity, 416 fs TEM00 mode is obtained. With a 50 µm defect spot mirror, the resonator delivers LG0,1 mode with a pulse duration of 476 fs. Under off-axis pumping, LG0,1 mode is switched to a two-vortex array. The pulse width of the two-vortex array is as short as 520 fs. The maximum output power is 401 mW with a pulse energy of 4.15 nJ. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first realization of a femtosecond vortex array from resonators.
In this paper, we experimentally investigate the tuning characteristics of laser modes for an ultrahigh-Q Er3+-doped microbottle resonator (MBR) based on the whispering gallery mode (WGM). Thanks to the optimized Er3+ doping technique, the laser threshold could be as low as 70 µW. Benefiting from the abundant axial modes and radial modes of the MBR, our experiments demonstrate that the number of laser modes can be flexibly controlled by varying the pump power, adjusting the coupling positions along the axis of the MBR, as well as modifying the coupling diameter of the tapered fiber. The laser mode switching is performed from single-mode to multimodes. Furthermore, different from the traditional external tuning method, we propose a simple and stable approach for continuous wavelength tuning of the laser mode based on the thermal effect associated with the high Q MBR. By precisely adjusting the pump laser wavelength, the emitted laser wavelength can be tuned over a range of 0.102 nm with a high linearity of 99.96%. The engineering of laser mode switching and precise wavelength tuning of the Er3+-doped MBR is expected to have promising applications in miniature tunable single-mode lasers, laser precision measurement, and so on.
In this Letter, we demonstrate the transmission of fifth-generation new radio (5G NR) signals over a fiber-millimeter-wave (mmWave)-fiber mobile fronthaul system in the 75–110 GHz band for an ultra-dense small cell network. The system employs a simple all-optical conversion technology, including mmWave signal generation using an optical heterodyne and a photonics-enabled receiver based on different modulator schemes. As a proof-of-concept demonstration, we successfully transmit 400 MHz 64QAM/256QAM at 3.5 and 4.9 GHz. The proposed system can provide a simple solution for facilitating the deployment of ultra-dense small cells in high-frequency bands for 5G mmWave/intermediate-frequency-over-fiber networks.
We theoretically demonstrate electrically controlled light focusing using a tunable metasurface employing thin film lithium niobate (TFLN). The designed metasurface features a high-quality factor guided-mode resonance with an electrically controllable resonant wavelength, resulting in a high extinction ratio of transmittance at the operational wavelength by changing the applied voltage. A reconfigurable one-dimensional Fresnel zone plate with a focusing efficiency of around 15% has been realized through spatial modulation of transmitted light intensity, whose focal position can be electrically tunable in both longitudinal and lateral directions. Our approach reveals the great potential of metasurfaces using TFLN for electrically controlled light focusing.
A designed arrangement of nanometer-sized holes in a thin dielectric film is presented to create a gradient-index plasmonic metasurface Gutman lens (PMGL) for controlling surface plasmon polaritons. We introduce two distinct designs for PMGL: one features a periodic rectangular hole array and the other features a dodecagonal quasicrystal array. Upon comparing their focusing properties, we find that, despite the superior rotational symmetry of the dodecagonal structure, the rectangular array outperforms in terms of the focusing properties of the Gutman lens.
The fundamental understanding of exciton physics and the anisotropic behavior of excitons and charge carriers in perovskite materials are pivotal to controlling the orientation of emission dipoles and the polarization of photocurrents to enhance the efficiency of light-emitting diodes (LEDs) and polarization photodetectors. However, it is not easy to clarify these fundamental physics and optoelectronic properties in traditional inorganic 3D perovskite polycrystalline thin films. Here, we found three narrow emission peaks with one broad peak from neutral excitons at 78 K in hybrid perovskite PEA2PbI4 single crystals. The out-of-plane electric field can induce the dissociation of the excitons with a larger decrease in the emission intensity of the exciton with a higher out-of-plane component. Moreover, the photocurrent can be greatly increased up to a maximum of 11 times with the tuning of excitation polarization from 90° to 0°. These results deepen our understanding of the anisotropic exciton and charge carrier physics of perovskite materials to promote the development of highly efficient LEDs and polarization photodetectors.
The lightwave field possesses several dimensional properties, including amplitude, spectrum, phase, and polarization. Multi-dimensional measurements of lightwaves have diverse applications ranging from remote sensing to analytical chemistry. However, achieving high-resolution simultaneous multi-dimensional measurement of lightwaves remains challenging. In this work, we demonstrate an all-fiber spectropolarimeter based on a speckle pattern obtained from the end of a multi-mode fiber. The proposed system simultaneously achieves a spectral resolution of 100 pm and a polarization resolution of 0.001437. The polarization measurement errors for three Stokes parameters are 3.37%, 1.01%, and 0.84%, respectively, with a mean squared error of 5.3 × 10-5. This work provides novel potential for high-resolution and accurate multi-dimensional lightwave field measurements.