View fulltext
View fulltext
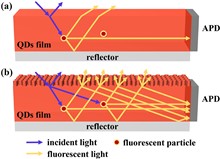
Visible light communication (VLC) is a key technology for advancing 6G networks. However, achieving both high signal gain and a wide field of view (FOV) at the receiver remains a significant challenge. To address this, we design a patterned fluorescent antenna (PFA) with microstructures fabricated via nanoimprinting technology. The microstructures modify the optical signal propagation within the fluorescent antenna, thereby enhancing its light transmission efficiency. Experimental results demonstrate that the patterned fluorescent antenna not only maintains a wide receiver FOV but also achieves high signal gain. Specifically, within the incident angle range of 0° to 60°, the average signal gains achieved by the single-sided and double-sided PFAs are 4.34 and 6.19 dB, respectively. This study provides an effective solution for enhancing signal gain in VLC systems under a wide FOV condition.
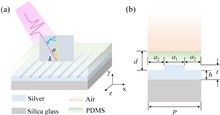
Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) sensors based on quasi-bound states in the continuum (quasi-BICs) have demonstrated extensive applications across biomedical, environmental monitoring, and industrial production sectors owing to their exceptional quality factor (Q-factor) and remarkable optical tunability. However, current research mainly focuses on the mode analysis of quasi-BICs, and insufficient attention has been paid to the relationship between quasi-BICs and the intrinsic parameters in photonic sensors such as intensity sensitivity, noise-equivalent limit of detection (LOD), and figure of merit (FOM). In this paper, a high-Q quasi-BIC is introduced into an SPR sensor, and its influence on the sensing performance, including intensity sensitivity, LOD, and FOM, is discussed in detail. The analysis shows that, compared with the traditional SPR mode, the quasi-BIC with an ultra-high and tunable Q-factor not only improves the intensity sensitivity of the device but also reduces the noise and optimizes its LOD and FOM. On this basis, we design a high-performance temperature sensor using the polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) thermo-sensitive material. The simulation results show that the temperature sensitivity of the device is as high as -0.33 nm/°C with the advantage of low noise. This theoretical analysis will provide guidance for the practical application of quasi-BICs in the field of sensing.
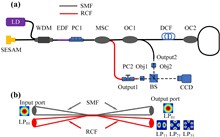
We present the dispersion-managed mode-locked pulse generation in the Er-doped fiber laser in this work. The linear cavity laser scheme is implemented with an all-fiber ring serving as the total reflection mirror and a semiconductor saturable absorber mirror (SESAM) as the mode-locker and non-transparent mirror. The dispersion compensation is applied to change the net dispersion from anomalous to normal dispersion, which integrates mode-locked regimes in the -0.495-+0.197 ps2 net-cavity-dispersion range by incorporating different lengths of the dispersion compensating fiber (DCF). The noise-like mode-locked pulse and conventional soliton are observed during the net-cavity-dispersion variation process. In addition, the homemade mode-selective couplers (MSCs) are utilized to realize high-mode-purity orbital angular momentum (OAM) outputs based on the mode superposition principle.
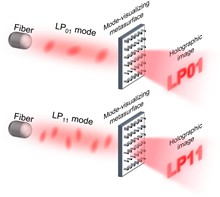
Mode-division multiplexing technology leveraging diverse spatial modes has advanced to sustain capacity expansion in fiber-optic communications. The intelligent recognition of spatial modes using ultra-compact devices and low-complexity designs is crucial for mode visualization and system miniaturization. In this work, we theoretically design and experimentally demonstrate a neural network-optimized metasurface capable of dual-mode pattern recognition through dual-channel image display. Our framework offers three key advantages: device compatibility, design flexibility, and function scalability by integrating neural networks and metasurfaces into mode-division multiplexing platforms. Our framework enhances research and applications of intelligent metasurface-driven pattern recognition and object classification, as well as information encoding and decoding.
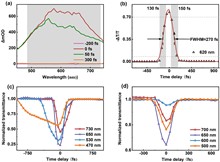
Zinc oxide (ZnO) plays a crucial role in the application of all-optical devices due to its broadband nonlinear optical response. In this work, the broadband nonlinear optical response of Ga-doped ZnO (GZO) was investigated using femtosecond transient absorption spectroscopy (450–800 nm), revealing an ultrahigh modulation depth (∼86%) and ultrafast response (∼280 fs) at a pump wavelength of 750 nm. Non-degenerate two-photon absorption (TPA) spectra corrected by dispersion revealed significantly stronger TPA in the visible range. An energy level model based on Ga-related defects explained the enhancement mechanism of TPA and the photoluminescence spectrum. This study highlights the significant potential of GZO in future broadband all-optical device applications.
This study presents a laser-based technique for fabricating nano-holes with tunable axial morphology on fused silica using ring-lens-tailored Bessel beams. Unlike conventional axicon-based Bessel methods, this approach effectively controls the beam’s axial intensity peak by simply adjusting the ring-lens radius (R). By combining theoretical simulation and experimental validation, we demonstrate that the nano-hole morphology can be precisely tuned by modulating the beam’s initial energy peak. A taper entrance can be formed, with the taper angle effectively controlled within 52° by adjusting R from 1.25 to 2.50 mm. When R exceeds 2.50 mm, the axial energy distribution becomes uniform and leads to the disappearance of the taper, resulting in a standard cylindrical hole and offering a clear process window for controlling the nano-hole morphology. This single-pulse ablation method advances precision nano-manufacturing by enabling the efficient fabrication of customized nano-holes, with potential applications in photonics, microfluidics, and other nano-engineering fields.
This study investigates the effects of laser off-nadir angles on sea surface echo dynamic range in airborne oceanic lidar. Using a dual-wavelength (486/532 nm) system with fixed off-nadir angles, varied aircraft rolls generated adjustable off-nadir angles. Experimental results reveal two to three orders of magnitude sea surface signal variations at 0°–35° off-nadir angles. A range of experimental results have shown that when the aircraft is at a lower altitude, saturation occurs at 0°–10° but is avoided at 15°–35°. Comparisons with simulations confirm that optimizing off-nadir angles reduces dynamic range occupancy and prevents saturation, enhancing lidar performance in oceanic profiling.
Scanning time-of-flight light detection and ranging (LiDAR) is the predominant technique for autonomous driving. Mainstream mechanical scanning is reliable but limited in speed and usually has blind areas. This work proposes a scanning method that uses an acousto-optic modulator to add high-frequency scanning on the slow axis of traditional automotive LiDAR linear scanning. It eliminated blind areas and enhanced the angular resolution to the size of the laser divergence angle. In experiments, this method increased the recognition probability of small targets at approximately 40 m from 70% to over 90%, providing an effective solution for future high-level autonomous driving.
Dual-comb hyperspectral digital holography (DC-HSDH) is an emerging technique employing two optical frequency combs with slightly different repetition frequencies for hyperspectral holographic imaging. Leveraging the unique capabilities of dual-comb interferometry (DCI), DC-HSDH enables the acquisition of phase maps and amplitude maps for multiple wavelengths in parallel, showcasing advantages in imaging speed and robustness. This study introduces a simplified DC-HSDH system based on spatial heterodyne DCI. It reduces the number of required optical devices in comparison to conventional DC-HSDH systems, leading to a streamlined system structure, reduced electric power consumption, and enhanced optical power efficiency. Additionally, it effectively improves the space-time bandwidth product by doubling the temporal bandwidth efficiency. Experiments were performed to validate the system. The proposed system successfully retrieved the three-dimensional profile of a stepped reflector without ambiguity, and the transmission spectrum of an absorbing gas was obtained simultaneously.
The gravimeter inclination is a significant parameter for cold atom gravimeters, and the counter-propagating Raman beams should be exactly parallel to the local vector of gravity. The tiltmeters, essential devices in cold atom gravimeters, are used to determine the optimum inclination of Raman beams and compensate for the inclination error. However, the conventional tiltmeters may lead to system errors in cold atom gravimeters due to insufficient nonlinearity and drift. In this study, we establish an optical interferometer inside the cold atom gravimeter by placing a hollow beam splitter plate in the path of the Raman beams. This optical interferometer acts as a tiltmeter to measure the inclination change of the Raman beams without influencing the gravity measurement. We prove that our optical tiltmeter (OT) works well with field assembly. Comparisons of our OT and commercial tiltmeters reveal that the nonlinearity of our OT is at least one-tenth of that of the commercial tiltmeters, and that the drift of our OT is at least 23 µrad less than that of the commercial tiltmeters over 90 h measurements. This can reduce the typical value of the atom gravimeter system error by 4 µGal. Further, a comparison of measured gravity to inclination deviation calibrated our OT and further validated that our OT outperforms commercial tiltmeters. This work enables more precise measurement of Raman beam angle variations and facilitates the calibration of installed tiltmeters, whether in the laboratory or the field.
An optical communication system based on the pulsed laser with a GHz repetition rate and multi-wavelength operation enables an increase in data transmission rate and data capacity. We propose a novel hybrid cavity with a single-mode fiber/multi-mode fiber/single-mode fiber (SMF-MMF-SMF) configuration for a GHz ultrafast laser with multi-wavelength operation. The length of each section is elaborately designed to reduce the transmission loss between the SMF and MMF, as well as to limit its total length to under 10 cm. By adopting the proposed hybrid cavity, the >1 GHz-repetition-rate fiber laser operation with four wavelength peaks is demonstrated, showing a signal-to-noise ratio of 90 dB. Furthermore, great tunability in spectra by manipulating the launched cavity parameters is also proved. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first realization of multi-wavelength operation among the GHz lasers using the SMF-MMF-SMF cavity architecture. The finding might provide a new opportunity for large-capacity high-speed optical communication systems.
Plasma shielding is a critical limiting factor in enhancing the quality and efficiency of femtosecond laser processing. This study investigates the temporal evolution of femtosecond-laser-induced plasma in water, unveiling a transient recovery window occurring between plasma recombination completion and shockwave generation. During this window, the plasma density returns to baseline levels and exerts a negligible influence on probe light transmission. Furthermore, the plasma recombination time exhibits a strong dependence on the pump pulse energy. The pump pulse energy densities of 2.15, 2.77, and 3.72 J/cm2 correspond to plasma recombination time of 231.0, 125.4, and 112.2 ps, respectively. This advancement could potentially offer a valuable reference for optimizing pulse sequences in high-repetition-rate processing.
Digital micromirror devices (DMDs) have emerged as essential spatial light modulators for holographic 3D near-eye displays due to their rapid refresh rates and precise wavefront modulation characteristics. However, since the modulation depth of DMDs is limited to binary levels, the quality of reproduced images from a binary computer-generated hologram (CGH) is often deficient. In this paper, we propose a stochastic gradient descent (SGD) based binary CGH optimization framework where a convolutional neural network (CNN) is employed to perform the differentiable hologram binarization operation. The CNN-based binary SGD optimization can significantly minimize the binary quantization noise in the generation of binary CGH, providing a superior and high-fidelity holographic display. Our proposed method is experimentally verified by displaying both high-quality 2D and true 3D images from optimized binary CGHs.
In computed tomography (CT) slip rings and similar applications, effective communication in rotating systems is critical, yet conventional slip ring methods are plagued by electromagnetic interference, low speeds, and high costs. In this work, we propose, to our knowledge, a novel fiber side-emitting communication system that employs the side-emitting fiber (SEF) as the optical transmitter to address these issues. An optical antenna with a gain of 9.6 dB enhances coupling efficiency, and a new SEF transmission model is developed. Experimental results demonstrate real-time data transfer at 1.25 Gbps with a bit error rate below 1 × 10-12, offering a robust and efficient solution for high-speed wireless communications in dynamic applications.
We comprehensively characterized the birefringence distribution of polarization-maintaining fibers (PMFs) in the fiber-optic gyroscopes using an enhanced Brillouin dynamic grating (BDG). This method enabled the quantitative analysis of the birefringence variations along the fiber, including those induced by temperature, axial strain, and transverse strain. Experimental results revealed that the birefringence coefficients of axial strain and temperature were 0.857 × 10-8/µε and -4.7 × 10-7/°C for the PMF coils, respectively. When PMFs are cross-wound in a layered configuration within the fiber-optic gyroscopes, transverse-strain will significantly impact the birefringence distribution. These findings offer valuable technical guidance for the design and manufacturing of high-precision fiber-optic gyroscopes.
This study proposes a dual-parameter sensor to simultaneously measure curvature and temperature using a 3D-printed seven-core optical fiber inscribed with a fiber Bragg grating (FBG). The seven-core fiber used was prepared by 3D-printing fiber technology of great flexibility in both structure and material. Attributed to the asymmetrical structure of this 3D-printed fiber, the sensor is capable of distinguishing the bending directions. Furthermore, the sensing characteristics and the directional recognition mechanism of the sensor are analyzed through both theoretical simulations and experimental investigations. The proposed sensor incorporates two sensing elements, specifically the Mach–Zehnder interferometer (MZI) and FBG. The combination of the MZI and FBG in the sensor enables simultaneous measurement of curvature and temperature. This vector sensor has a sensitivity of 25.782 nm/m-1 in the curvature range of 0–1.518 m-1, when the bending is applied along the defined direction of 30°. Within the temperature range of 20.0–110.0°C, the temperature sensitivity is 34 pm/°C. Experimental results validate the excellent performance of the proposed sensor, providing an efficient and scalable solution for dual-parameter sensing in future industrial and environmental applications.
Accurate liquid concentration detection is vital for medical, industrial, and environmental applications, yet conventional methods still face limitations. We propose an ultrasound probe with a self-assembled polymer whispering-gallery-mode (WGM) microcavity, leveraging the photoacoustic (PA) effect and a distributed feedback (DFB) laser tuning system for ultrasensitive quantification. The probe achieves 13.5 Pa sensitivity and 42 MHz bandwidth (–6 dB), ensuring broad applicability in diverse liquids. Overcoming traditional WGM sensors’ instability, our integrated platform demonstrates a record-low detection limit of 10-7 g/mL for crystal violet among substrate-free, real-time methods. Unifying the microcavity, laser, and electronics into a portable architecture, this system enables high-fidelity, nondestructive liquid analysis with strong anti-interference and endoscope-deployable sensing in complex environments.
Event cameras, with their significantly higher dynamic range and sensitivity to intensity variations compared to frame cameras, provide new possibilities for 3D reconstruction in high-dynamic-range (HDR) scenes. However, the binary event data stream produced by event cameras presents significant challenges for achieving high-precision and efficient 3D reconstruction. In addressing these issues, we observe that the binary projection inherent to Gray-code-based 3D reconstruction naturally aligns with the event camera’s imaging mechanism. However, achieving high-accuracy 3D reconstruction using a Gray code remains hindered by two key factors: inaccurate boundary extraction and the degradation of high-order dense Gray code patterns due to spatial blurring. For the first challenge, we propose an inverted Gray code strategy to improve region segmentation and recognition, achieving more precise and easily identifiable Gray code boundaries. For the second challenge, we introduce a spatial-shifting Gray-code encoding method. By spatially shifting Gray code patterns with lower encoding density, a combined encoding is achieved, enhancing the depth resolution and measurement accuracy. Experimental validation across general and HDR scenes demonstrates the effectiveness of the proposed methods.
Cold atoms play an important role in fundamental physics, precision timekeeping, quantum sensing, and quantum computing. The production of cold atoms requires magneto-optical traps (MOTs), but current MOTs consist of a variety of complex and bulky optical infrastructures that hamper their practical application. The development of integrated photonic circuits offers the opportunity to achieve integrated MOTs. Here, we take advantage of the ultra-low loss of the silicon nitride platform to design a grating outcoupler for coupling beams from waveguides to free space. The device operates at a wavelength of 780 nm with an experimental emission angle of 24.38°. Additionally, by appropriately designing the positions of the grating outcouplers on the chip, we propose an on-chip emission system to demonstrate the MOT application. The intersection area is about 2 mm × 2 mm at a height of 6 mm on the chip. Our work provides the possibility of realizing on-chip MOTs.
Mid-infrared (mid-IR) silicon photonic integrated circuits have drawn considerable interest to date. However, previous devices are typically designed on silicon waveguide configurations with hundreds of nanometers in thickness, hindering their application in sensing. Here, we demonstrated a suspended nanomembrane silicon (SNS) microring resonator (MRR) at 3.27 µm wavelengths with a subwavelength grating coupler. Our experimental results show that the SNS MRR showcases a quality factor of ∼3500 with a giant confinement factor of 0.89 and reduced thermal sensitivity of 0.07 nm/°C. To our knowledge, the study opens a new avenue to developing mid-IR silicon devices for sensing applications.
Photonic-crystal surface-emitting lasers (PCSELs) are considered as next-generation semiconductor lasers because they can operate in a high-power single mode. However, these devices are not suitable for low-threshold high-speed operation because they often require a long cavity length to achieve low loss. In this paper, we break this limit and demonstrate very low-threshold operation of the PCSELs for their high-speed application, using a triple-lattice photonic-crystal structure with a 100 µm cavity length. Low threshold currents of 29 mA at 10°C and 36 mA at 25°C under continuous wave (CW) operation were realized, which is comparable to the traditional high-speed distributed feedback (DFB) Bragg edge-emitting lasers. The far-field divergence angles defined by 1/e2 power were respectively 3.84° and 1.63° along the x- and y-directions. A small-signal modulation bandwidth of 5.8 GHz was obtained. By further optimizing the mesa size, the threshold current was decreased to 12 mA, which, to the best of our knowledge, is the lowest threshold current reported for PCSELs so far.
We demonstrate a quantum cascade laser (QCL) emitting at around 5.0 µm with a peak power of 4.7 W at room temperature (298 K) continuous-wave (CW) operation. The cavity length and the ridge width are 7.5 mm and 6.5 µm, respectively. The active core was grown by molecular beam epitaxy (MBE) with high-AlAs quantum barrier layers designed to suppress the current leakage. The device achieved the maximum power of 10.2 W and the maximum wall plug efficiency (WPE) of 22.7% in the pulsed mode. High beam quality is achieved by a single transverse mode (measured M2 < 1.5) with a CW power of 4 W at 298 K.
In this paper, a polarization full-feedback open-loop spectral beam combining (PFF-SBC) structure based on double-ridge stripe semiconductor parity-time-symmetric laser diodes (PTLDs) is proposed and demonstrated. The beam quality of the PTLD is optimized, and the combining efficiency is improved using the methods of polarization separation and full feedback. The maximum output power is up to 2.71 W, which leads to a spectral beam combining efficiency of 83.4% and a grating diffraction efficiency of 95.51% under continuous current operation at a current of 2.3 A. Additionally, the brightness of the SBC module is 116.2 MW·cm-2 sr-1 at a current of 1.6 A, which is 3.5 times that of a single PTLD. The PFF-SBC strategy provides, to our knowledge, a new approach for increasing the beam brightness of PTLDs.
In recent years, the perfect vortex beam with independent wavefront spiral correlation has attracted extensive attention since its beam diameter is independent of topological charge. Perfect vortex beams are expected to make significant progress in optical fiber communications, particle manipulation, quantum information, and other areas. Traditional optical devices are difficult to integrate into the system due to their large size. In this paper, we design and realize a perfect vortex beam with a high reflection efficiency of 90.17% by an all-dielectric metasurface through a Pancharatnam–Berry (PB) phase modulation structure. The cross-polarization conversion efficiency measured by experiment is 89.81%. By modulating the parameter r0 in the phase function, we can achieve flexible manipulation of topological charges and ring diameters. In addition, we also demonstrate the generation of a four-channel perfect vortex beam array based on the Dammann grating, with a beam uniformity of 40%. Our research will be of great significance for the realization of compact and multifunctional on-chip integrated photonic devices.
In this Letter, we explore the interplay between topological defects and resonant phenomena in photonic crystal slabs, focusing on quasi-flatband resonances and bound states in the continuum (BICs). We identify anisotropic quasi-flatband resonances and isotropic quasi-flatband symmetry-protected BICs that exist in coupled topological defects characterized by nontrivial 2D Zak phases, originating from monopole, dipole, and quadrupole corner modes within second-order topological insulator systems. These topological defect modes, whose band structures are described using a tight-binding model, exhibit distinctive radiative behavior due to their symmetry and multipolar characteristics. Through far-field excitation analysis, we demonstrate the robustness and accessibility of these modes in terms of angular and spectral stability. Furthermore, we investigate potential applications of the quasi-flatband resonances in light–matter interactions, including optical forces, second-harmonic generation, and strong coupling, which exhibit robust performance under varying illumination angles. These findings offer new opportunities for precise control over light–matter interactions.
We propose a heterogeneous all-dielectric photonic molecule comprising a Mie nano-resonator (MNR) and a photonic crystal nanocavity (PCNC), forming a strongly coupled system. The coupling mechanism is rigorously analyzed using the coupled mode theory, unveiling key optical phenomena, including Fano resonance, mode splitting, and Rabi oscillation. By precisely tuning the spatial position of the MNR relative to the PCNC and the structural parameters of the MNR, we achieve modulation of near-field mode interactions and far-field radiation. Performance evaluation reveals highly directional radiation and tunable spectral properties, facilitating efficient light manipulation at the nanoscale. This study establishes a versatile platform for advancing quantum optics, integrated photonics, and optical antennas, with promising applications in high-purity quantum light sources, ultra-sensitive sensing, and low-threshold nano lasers.
For the first time, to our knowledge, the cascading effects of self-phase modulation and second-harmonic generation (SPM-SHG) in a nonlinear optical medium were used to conveniently convert a near-infrared ultrafast laser with a fixed center wavelength into a visible to deep-ultraviolet (DUV) laser with a continuously tunable wavelength. When a β-BaB2O4 (BBO) crystal was used as the nonlinear optical medium, and a Ti:sapphire laser (800 nm, 38 fs) was used as the fundamental light source, the output wavelength had a tunable range of 225–460 nm, and the highest optical conversion efficiency reached 18.1% at 361 nm. For a 1030 nm fundamental light source, the shortest output wavelength was also 225 nm by one-step frequency conversion of the BBO crystal. By further frequency conversions, the tunable wavelength can extend to the vacuum ultraviolet (VUV) waveband, as short as 193 nm. These results demonstrated that SPM-SHG could be used as an extremely simple and effective frequency conversion method to obtain a wideband tunable ultraviolet laser.
We report the experimental observation of a three-dimensional abruptly autofocusing effect by synthesizing a radially distributed Airy beam with two counter-propagating Airy pulses in time. As the wave packet propagates in a dispersive medium, the radially distributed Airy beam converges inward to the center point. Two Airy pulses counter-propagate toward each other to merge to form a high-peak-power pulse. As a result, high intensity emerges abruptly as the wave packet achieves three-dimensional focusing. This autofocusing effect is believed to have potential applications such as material modification, plasma physics, and nanoparticle manipulations.
Autofocusing beams are powerful photonic tools for manipulating micro/nanoparticles. Here, we propose a special type of dislocated-superimposed swallowtail vortex beam (DSVB) and analyze its propagation properties and optical manipulating capability. By modulating the parameters of the superposition number N and the topological charge l, DSVBs show asymmetric autofocusing propagation phenomena and unconventional orbital angular momentum (OAM), especially for opposite topological charges. Furthermore, when N = |l|, DSVBs form multiple solid focuses while preserving OAM during propagation, suggesting potential applications in multi-point trapping and rotational manipulation. These results deepen the understanding of autofocusing and OAM behaviors, highlighting DSVBs’ potential as photonic tools for optical manipulation.
Structured illumination microscopy (SIM) is a pivotal technique for dynamic subcellular imaging in live cells. Conventional SIM reconstruction algorithms depend on accurately estimating the illumination pattern and can introduce artifacts when this estimation is imprecise. Although recent deep-learning-based SIM reconstruction methods have improved speed, accuracy, and robustness, they often struggle with out-of-distribution data. To address this limitation, we propose an awareness-of-light-field SIM (AL-SIM) reconstruction approach that directly estimates the actual light field to correct for errors arising from data distribution shifts. Through comprehensive experiments on both simulated filament structures and live BSC1 cells, our method demonstrates a 7% reduction in the normalized root mean square error (NRMSE) and substantially lowers reconstruction artifacts. By minimizing these artifacts and improving overall accuracy, AL-SIM broadens the applicability of SIM for complex biological systems.
Although single-pixel correlated imaging has the capability to capture images in complex environments, it still encounters challenges such as high computational complexity, limited imaging efficiency, and reduced imaging quality under low-light conditions. We innovatively propose a symmetrically related random phase-based correlated imaging method, which reduces the number of required random scattering media, enhances computational efficiency, and mitigates system noise interference. Single-pixel correlated imaging can be completed within 2 min using this approach. The experiments demonstrated that both the constructed dual-path thermal-optical correlated imaging system and the single-path computational correlated imaging system achieved high-quality imaging even under low-light conditions.
In this Letter, a quartz-enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy (QEPAS) gas sensor based on a single off-beam acoustic micro-resonator (AmR) and dual quartz tuning forks (QTFs) was demonstrated for the first time, to our knowledge. The sensor offers advantages of a compact sensing structure and high acoustic energy utilization efficiency. The key parameters of the designed off-beam AmR were optimized based on standing wave enhancement characteristics. Water vapor (H2O) in the environment was chosen as the target gas to investigate the sensor performance. Under identical experimental conditions, the reported sensor achieved 15.02 times improvement in detection sensitivity compared to the bare QTF-based sensor system, as well as a 1.53 times enhancement over the traditional off-beam QEPAS technique.
 GeneralApplicationsAtmospheric, Oceanic, Space, and Environmental OpticsAtomic and Molecular OpticsBiomedical OpticsBiophotonicsCoatings for solar cellCoherence and statistical opticsDeposition and process controlDesign and analysisDiffraction, Gratings, and HolographyDigital HolographyDuv/euv coatingsEditorialFiber Optics and Optical CommunicationsImage processingImage Processing and Machine VisionImaging Systems and Image ProcessingInfrared and Terahertz PhotonicsInstrumentation, Measurement, and Optical SensingIntegrated OpticsLasers and Laser OpticsLasers, Optical Amplifiers, and Laser OpticsLight-matter InteractionMicrowave PhotonicsMultiphoton processesNanophotonicsNanophotonics, Metamaterials, and PlasmonicsNonlinear OpticsOptical Design and FabricationOptical MaterialsOptical Sensing, Measurements, and MetrologyOptics in Computing and Optical Data StorageOptics in Interdisciplinary ResearchOptoelectronicsPhysical OpticsPlasmonics and MetamaterialsQuantum Optics and Quantum InformationReviewsSolar Energy and PhotovoltaicsSpecial Issue List: Special Issue on Structured light: fundamentals and applicationsSpecial Issue on 20th Anniversary of Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics (WNLO)Special Issue on 70th anniversary of National University of Defense TechnologySpecial Issue on Lithium Niobate Based Photonic DevicesSpecial Issue on Lithium Noibate Based Photonic DevicesSpecial Issue on Metal Halide Perovskite and Their ApplicationsSpecial issue on optical interconnect and integrated photonic chip technologies for hyper-scale computingSpecial issue on optical interconnect and integrated photonic chip technologies for hyper-scale computing systemsSpecial Issue on Optical Metasurfaces: Fundamentals and ApplicationsSpecial Issue on Quantum ImagingSpecial Issue on Structured light: fundamentals and applicationsSpecial Issue on the 20th Anniversary of Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics (WNLO)Special Issue on the 40th Anniversary of Institute of Modern Optics, Nankai UniversitySpectroscopyThin Films and Optics at SurfacesUltrafast Optics and Attosecond/High-field PhysicsUltrafast Optics: fundamentals and applicationsUnderwater Wireless Optical CommunicationVision, color, and visualVisual Optics and DisplaysX-ray OpticsAtomic and Molecular PhysicsCOHERENCE OPTICS AND STATISTICAL OPTICSFourier Optics and Signal ProcessingGeometric OpticsPhysical OpticsHolographyInstrumentation, measurement, and metrologyLasers and Laser OpticsDiffraction and GratingsOptical devicesFiber Optics and Optical CommunicationsImaging SystemsMachine VisionOptoelectronicsMedical optics and biotechnologyOptical devicesMicroscopyQuantum opticsMaterialsFiber optics and optical communicationsOptics in ComputingOPTICAL DATA STORAGEThin filmsNonlinear OpticsOptical Design and FabricationImage processingIntegrated OpticsOptics at SurfacesDetectorsRemote Sensing and SensorsScatteringSpectroscopyUltrafast OpticsVision, Color, and Visual OpticsX-ray OpticsOther Areas of OpticsAtmospheric and oceanic opticsResearch ArticlesLettersOptoelectronicsNolinear opticsGeometrical optics3d holographic displayAuto-stereography and virtual realityComputer generated hologramMedical and biological imagingOptical divcesIntegrate opticsSources and mechanisms of terahertz radiationSpectroscopy, imaging, and sensing using terahertz radiationMetamaterials, plasmon polaritons, and waveguides in terahertz regionMeasurement3d imaging and displayComputer-generated holographyHolographic reconstruction, display,and projectionIntegral imagingOptical trappingoptical computingremote sensingvision and coloroptical design and fabricationsFourier optics and optical signal processing
Special Issues
GeneralApplicationsAtmospheric, Oceanic, Space, and Environmental OpticsAtomic and Molecular OpticsBiomedical OpticsBiophotonicsCoatings for solar cellCoherence and statistical opticsDeposition and process controlDesign and analysisDiffraction, Gratings, and HolographyDigital HolographyDuv/euv coatingsEditorialFiber Optics and Optical CommunicationsImage processingImage Processing and Machine VisionImaging Systems and Image ProcessingInfrared and Terahertz PhotonicsInstrumentation, Measurement, and Optical SensingIntegrated OpticsLasers and Laser OpticsLasers, Optical Amplifiers, and Laser OpticsLight-matter InteractionMicrowave PhotonicsMultiphoton processesNanophotonicsNanophotonics, Metamaterials, and PlasmonicsNonlinear OpticsOptical Design and FabricationOptical MaterialsOptical Sensing, Measurements, and MetrologyOptics in Computing and Optical Data StorageOptics in Interdisciplinary ResearchOptoelectronicsPhysical OpticsPlasmonics and MetamaterialsQuantum Optics and Quantum InformationReviewsSolar Energy and PhotovoltaicsSpecial Issue List: Special Issue on Structured light: fundamentals and applicationsSpecial Issue on 20th Anniversary of Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics (WNLO)Special Issue on 70th anniversary of National University of Defense TechnologySpecial Issue on Lithium Niobate Based Photonic DevicesSpecial Issue on Lithium Noibate Based Photonic DevicesSpecial Issue on Metal Halide Perovskite and Their ApplicationsSpecial issue on optical interconnect and integrated photonic chip technologies for hyper-scale computingSpecial issue on optical interconnect and integrated photonic chip technologies for hyper-scale computing systemsSpecial Issue on Optical Metasurfaces: Fundamentals and ApplicationsSpecial Issue on Quantum ImagingSpecial Issue on Structured light: fundamentals and applicationsSpecial Issue on the 20th Anniversary of Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics (WNLO)Special Issue on the 40th Anniversary of Institute of Modern Optics, Nankai UniversitySpectroscopyThin Films and Optics at SurfacesUltrafast Optics and Attosecond/High-field PhysicsUltrafast Optics: fundamentals and applicationsUnderwater Wireless Optical CommunicationVision, color, and visualVisual Optics and DisplaysX-ray OpticsAtomic and Molecular PhysicsCOHERENCE OPTICS AND STATISTICAL OPTICSFourier Optics and Signal ProcessingGeometric OpticsPhysical OpticsHolographyInstrumentation, measurement, and metrologyLasers and Laser OpticsDiffraction and GratingsOptical devicesFiber Optics and Optical CommunicationsImaging SystemsMachine VisionOptoelectronicsMedical optics and biotechnologyOptical devicesMicroscopyQuantum opticsMaterialsFiber optics and optical communicationsOptics in ComputingOPTICAL DATA STORAGEThin filmsNonlinear OpticsOptical Design and FabricationImage processingIntegrated OpticsOptics at SurfacesDetectorsRemote Sensing and SensorsScatteringSpectroscopyUltrafast OpticsVision, Color, and Visual OpticsX-ray OpticsOther Areas of OpticsAtmospheric and oceanic opticsResearch ArticlesLettersOptoelectronicsNolinear opticsGeometrical optics3d holographic displayAuto-stereography and virtual realityComputer generated hologramMedical and biological imagingOptical divcesIntegrate opticsSources and mechanisms of terahertz radiationSpectroscopy, imaging, and sensing using terahertz radiationMetamaterials, plasmon polaritons, and waveguides in terahertz regionMeasurement3d imaging and displayComputer-generated holographyHolographic reconstruction, display,and projectionIntegral imagingOptical trappingoptical computingremote sensingvision and coloroptical design and fabricationsFourier optics and optical signal processing
Special Issues