View fulltext
View fulltext
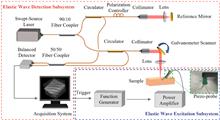
Optical coherence elastography (OCE) can quantitatively obtain the viscoelasticity of tissues using rheological models and is widely applied to the clinical diagnosis of diseases. However, commonly used rheological models in OCE do not account for the distinctive dependence of high-frequency storage and loss moduli on frequency in tissues, which results in the rheological models failing to accurately measure the viscoelastic properties of tissues. In this paper, a modified Kelvin-Voigt fractional derivative model is presented based on the power-law behavior of soft tissues and the dependence of high-frequency complex shear modulus on frequency in living cells. In the rheometer and OCE tests, the modified model can provide the prediction of the power-law relationship between the low-frequency shear viscosity and frequency; compared with the Kelvin-Voigt and Kelvin-Voigt fractional derivative models, the modified model has a higher goodness-of-fit (accuracy >96%) for the high-frequency storage moduli of gelatin phantoms. Furthermore, the proposed model can reduce the root mean square error of fit by approximately 83% for the high-frequency (1–128 kHz) storage modulus of the polydimethylsiloxane phantoms obtained from publicly available data. Overall, the modified model accurately predicts the mechanical properties of biomimetic materials over a wide frequency range, with the potential to more accurately reflect pathological changes in tissues.
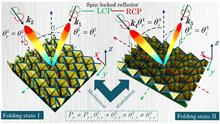
The retroreflector based on a gradient metasurface can reflect electromagnetic (EM) waves to the source, and it is small in size and lightweight. However, even if the previous retroreflectors can be used for angle adaptation, the working efficiency declines sharply at large angles. In this paper, a retroreflector is designed based on a reconfigurable origami two-dimensional (2D) metagrating for efficient spin-locked retroreflection and for suppressing unwanted Floquet diffraction channels. After the retroreflection, the handedness of the wave remains consistent with the incident. By changing the folding state of the origami metagrating, the adaptive tangential momentum can be transferred to the incident wave, providing high-performance retroreflection over a continuous incidence angle range of 30°–45.8° (x-direction) and 30°–81° (y-direction). As proof of concept, an electric metagrating-based retroreflector is fabricated in the microwave frequency band, and the simulation and experimental results are consistent. This adaptive origami spin-locked metasurface has promising applications in spin-optics devices, communication systems, remote sensing, and radar cross-section (RCS) enhancement.
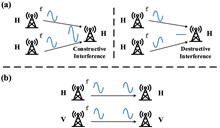
We experimentally demonstrate the transmission of discrete multi-tone (DMT) millimeter-wave (mm-wave) signals over a 1.2-km distance at the D-band (110–170 GHz) in a cost-effective intensity-modulation and direct-detection (IM/DD) communication system. In the experiment, we successfully achieve the transmission of DMT-QPSK and DMT-16QAM mm-wave signals over multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) links. After the 1.2-km free-space transmission, the bit error rate (BER) of the DMT-16QAM is below the 25% soft decision forward error correction (25% SD-FEC) threshold of 4 × 10-2, with a maximum net bit rate of 24.62 Gbit/s achieved in this system.
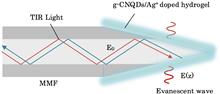
We conducted an experimental study on an off-on fluorescence optical fiber probe utilizing graphitic carbon nitride quantum dots (g-CNQDs) -doped hydrogel for chloride ion detection. It resulted in fluorescence quenching after g-CNQDs were modulated by silver ions (Ag+). The chloride ion sensing probe was obtained by wrapping the tapper fiber tip with the composite fluorescent material of g-CNQDs/Ag+ mixed with chitosan hydrogel. Within the concentration range of 1–9 µM chloride ions, the fluorescence intensity of the prepared optical fiber probe exhibits a robust linear correlation with chloride ion concentration, and the detection limit is 0.037 µM.
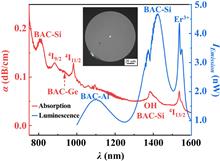
The photobleaching (PB) effect of bismuth active center (BAC)-related silicon (BAC-Si) in the bismuth- and erbium-codoped optical fiber (BEDF) under repeated pumping was studied. The results demonstrated that the irreversible PB could be eliminated after repeated pumping, while the rest of the PB could be decreased and remained stable in the subsequent pumping. The mechanism was also discussed using electron transferring theory and the distribution function concept of activation energy. Moreover, the results also demonstrated that BAC-Si could further become stable, reversible, and irreversible after PB, and new standards can be established for the BEDF to evaluate its quality.
We propose a multi-tap look-up-table (LUT)-based error-tracking decision feedback equalizer with partial unrolling (ET-DFE-PU) algorithm to improve log-likelihood ratio (LLR) quality with error propagation. We introduce an error-tracking model to obtain the probabilities of different error states, which are input into the decoder to obtain more accurate LLRs. We also use LUTs to reduce the computation complexity of ET-DFE-PU. Moreover, we adopt a low-complexity partially unrolled architecture to relax the feedback timing constraint. We conduct experiments to transmit 170-Gb/s 4-ary pulse amplitude modulation signal in intensity modulation and direct-detection system at C-band. The results show that the proposed method can achieve 3-dB receiver sensitivity improvement at the same post-forward error correction bit error ratio compared with the conventional DFE.
Computational ghost holography is a single-pixel imaging technique that has garnered significant attention for its ability to simultaneously acquire both the amplitude and phase images of objects. Typically, single-pixel imaging schemes rely on real-value orthogonal bases, such as Hadamard, Fourier, and wavelet bases. In this Letter, we introduce a novel computational ghost holography scheme with Laguerre–Gaussian (LG) modes as the complex orthogonal basis. It is different from the traditional methods that require the number of imaging pixels to exactly match the number of modulation modes. Our method utilizes 4128 distinct LG modes for illumination. By employing the second-order correlation (SOC) and TVAL3 compressed sensing (CS) algorithms, we have successfully reconstructed the amplitude and phase images of complex objects, and the actual spatial resolution obtained by the experiments is about 70 µm. Due to the symmetry of the LG modes, objects with rotational symmetry can be recognized and imaged using fewer modes. The difference between bucket detection and zero-frequency detection is analyzed theoretically and verified experimentally. Moreover, in the process of object reconstruction, the advanced image processing function can be seamlessly integrated via the preprocessing of the LG modes. As such, it may find a wide range of applications in biomedical diagnostics and target recognition.
A highly sensitive temperature sensor was developed using a thin-walled SiO2 hollow microrod resonator (SHMR) to excite Lorentz resonance and Fano resonance. The SHMR has a high Q factor (3.16 × 107) and concise resonance modes. Moreover, the SHMR has a small wall thickness, which can effectively improve the sensitivity of the temperature sensor. The experimental results show that the sensitivity reaches 24.78 pm/°C under Lorentz resonance and further improves to 31.28 pm/°C under Fano resonance. By further reducing the wall thickness of the SHMR, the sensitivity under Lorentz resonance is increased to 34.34 pm/°C. The sensor in this study has the advantages of low cost, simple structure, high sensitivity, and satisfactory repeatability.
A novel Mach–Zehnder interferometer (MZI) sensor based on multiple supermode interferences that can be used for dual-parameter measurements of temperature and strain is proposed and demonstrated. The MZI is made by splicing a coupled four-core sapphire-derived fiber (FSDF) between two single-mode fibers, utilizing the differences in temperature response and strain response of different supermodes in the FSDF to realize the simultaneous measurement of the two parameters. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed MZI can achieve up to 1600 µε and 1000°C measurements with a temperature-strain cross-sensitivity of approximately 0.075°C/με.
Coherent lidar (CL) addresses existing constraints in CL data products by enabling simultaneous observation of multiple meteorological parameters such as cloud height, extinction coefficient, aerosol concentration, and wind field evaluation. A detailed analysis of CL echo signals was performed at a wavelength of 1550 nm, enabling accurate measurements of cloud height and aerosol concentration. Extensive data analyses and validation tests were conducted, aligning them with a 532 nm direct aerosol lidar (AL). The assessments of the aerosol extinction coefficient demonstrated notable consistency. This underscores the potential of advanced CL for providing prolonged and consistent observations across diverse meteorological conditions.
A diode-pumped mode-locked (ML) Tm,La:CaF2 crystal laser is reported in this paper. This laser system delivers stable continuous-wave ML pulses, achieving a maximum output power of 143 mW at a fundamental frequency of 96.2 MHz. Moreover, the signal-to-noise ratio in the stabilized single-pulse regime reaches as high as 75 dB. The central wavelengths of the laser are located at 1886.5 and 1886.7 nm, which further advances the development of ultrafast lasers in the water absorption band of 1.8–1.9 µm.
Ultrastable continuous-wave lasers are one of the important elements for space-based gravitational wave detection. Here we present a Pound–Drever–Hall laser frequency-locked system based on a field-programmable gate array, demonstrating its potential to achieve 10-16 levels of frequency stability for space applications. The system is employed to lock a space-qualified 1064-nm neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet laser to a laboratory-operated 20-cm ultrastable optical cavity. Major noise contributors are identified as laser intensity fluctuation and residual amplitude modulation. The heterodyne beat measurement shows that the frequency noise spectral density of a single laser is reduced to 2.5 Hz/√Hz at a Fourier frequency of 1 mHz, and the frequency instability is 2.1 × 10-16 at 1 s and remains below 3.5 × 10-16 up to 6000 s.
We demonstrated a divided pulse amplification of burst pulse trains. The intraburst rate is 1 GHz, and the burst rate ranges from 1.5 kHz to 15 MHz. Under the pump power of 100 W, the burst pulse energy is adjustable from 2.2 µJ to 22 mJ. The pulse width of combined and compressed pulses is 275 fs with beam quality M2 of 1.2.
In this paper, a digital laser with a dual-cavity configuration for the pattern control of a Q-switched pulsed laser is presented. The dynamic pattern control of the pulsed laser from the primary cavity is generated and controlled by simply manipulating the projected phase of the spatial light modulator (SLM) in the secondary cavity. The proposed digital laser design provides a solution for a flexible pulsed laser source while preventing damage to the SLM from high-peak light pulse flux density, benefiting structured laser applications that require high-peak laser power.
We propose a novel automatic phase-matching method for generating optical frequency combs using cascaded electro-optic modulators. By analyzing the power changes of different spectral lines, our method enables real-time monitoring and dynamic adjustment to achieve precise phase matching. Experiments have confirmed the fast phase matching and the adjustable spacing of a flat electro-optic frequency comb and its long-term stability. This method provides flexible and efficient light source solutions for optical communications, spectral analysis, and optical measurements.
Orbital angular momentum (OAM) waveguides are critical for multi-channel photonic-on-chip applications. However, current large-mode-area waveguides pose a challenge for OAM device miniaturization. Here, a novel hybrid plasmonic waveguide is theoretically proposed to decrease the OAM mode area by two orders of magnitude. Benefiting from the Ag-As2S3-SiO2-As2S3-Ag five-layer cylindrical structure, the guided OAM mode realizes a larger figure of merit of 88. Based on this waveguide, an OAM coupler with a record-breaking small footprint (0.68 µm × 5.7 µm) is designed. The proposed waveguide enables subwavelength OAM light transmission, which provides a key building block for high-density OAM photonics circuits.
Recently, polarization conversion based on the equivalent magnetic field of Weyl semimetals (WSMs) has gained significant attention. Based on a twin WSM-layer structure, we transplant the concept of twist from Twistronics to obtain a dynamically tunable polarization converter with multifunctions and nonreciprocity. One-way conversion of linear polarization to its orthogonal state can be obtained and tuned by twisting the converter. Moreover, nonreciprocal conversion from linear polarization to elliptical polarization (with ellipticity linearly tuned from -1 to 1 by twisting the converter) in one way and to quasi-linear polarization in the other way can be obtained. Calculations show that the converter achieves 95% efficiency, high optical isolation (100 dB), and low insertion loss (<2 dB). The proposal may find applications in tunable and nonreciprocal devices for integrated photonics.
Lithium-niobate-on-insulator (LNOI) chips have shown outstanding performance in various photonic devices including modulators, lasers, nonlinear converters, and quantum sources. LNOI-based edge couplers are quite important for further promotion of the above devices in practical applications, especially for large-scale multiport photonic uses, where efficient and mode-selective coupling between chips and fibers is of necessity. Previously, several LNOI edge couplers have been demonstrated, but they mainly focus on achieving high coupling efficiency of the fundamental mode, and sub-wavelength etched lithium-niobate (LN) structures are normally needed, which increases fabrication complexity. Here we propose a new type of edge coupler with direct mode-selective excitation ability, using only SiON cladding grating structures without additional etching of LN. By introducing a cladding waveguide with periodic structures on the uniform LNOI waveguide, high-efficiency excitation of multiple modes can be realized directly with easier fabrication. For a specific simulation here, TE00, TM00, and TE10 core modes can be excited, respectively, at optimized periods and grating lengths with a tunable central wavelength, at the launch of the TM cladding mode. The periods of the needed SiON gratings are all over 2 µm, which is feasible with i-line UV lithography. Our results provide a low-cost edge coupler for LNOI photonic circuits with the ability of flexible spatial mode selectivity, which may promote LNOI devices in large-scale multiport photonic integrated circuits in the future.
The development of nonlinear optical materials with strong multiphoton absorption (MPA) is crucial for the design of ultrafast nonlinear optical devices, such as optical limiters and all-optical switchers. In this study, we present the wavelength-dependent coefficients of two-photon absorption (2PA) and three-photon absorption (3PA) in a GaS film across a broad range of wavelengths from 540 to 1600 nm. The observed dispersions in the 2PA and 3PA coefficients align well with the widely used two-band approximation model applied to direct bandgap semiconductors. Notably, the GaS film exhibits exceptional MPA properties with a maximum 2PA coefficient of 19.89 cm/GW at 620 nm and a maximum 3PA coefficient of 4.88 cm3/GW2 at 1500 nm. The GaS film surpasses those found in traditional wide-bandgap semiconductors like β-Ga2O3, GaN, ZnO, and ZnS while remaining comparable to monolayer MoS2, CsPbBr3, and (C4H9NH3)2PbBr4 perovskites. By employing a simplified two-energy-level model analysis, our results indicate that these large MPA coefficients are primarily determined by the remarkable absorption cross sections, which are approximately 4.82 × 10-52·cm4·s·photon-1 at 620 nm for 2PA and 8.17 × 10-80·cm6·s2·photon-2 at 1500 nm for 3PA. Our findings demonstrate significant potential for utilizing GaS films in nonlinear optical applications.
We experimentally demonstrate a continuous-wave (CW) injection-seeded cascaded optical parametric amplifier (OPA) for generating femtosecond pulses in the NIR-I spectral region. Utilizing a cascaded two-stage configuration, our system achieves an output of 347 mW of NIR radiation centered at 792 nm, combined with a pulse duration of 171 fs at a repetition rate of 50 MHz. The CW seeding intrinsically ensures superior pulse-to-pulse and long-term power stability. Our measurements indicate a relative intensity noise (RIN) of 2.2% root mean square (RMS) (integrated from 3.3 Hz to 2.5 MHz) and an RMS power stability as low as 0.63% over a duration of 90 min. Moreover, the beam quality of the output beam is near-diffraction-limited, with M2 factors of MX2 = 1.11 and MY2 = 1.29. We believe that this type of laser source is capable of delivering stable femtosecond pulses within the NIR-I spectral range and can serve as an ideal solution for various applications including biophotonics, microscopy, and laser processing.
Zinc sulfide (ZnS) has promising linear and nonlinear optical properties and has shown important applications in military and modern devices. In this work, coupled with the chemical vapor deposition (CVD) method and hot isostatic pressing (HIP), we successfully grew a high-transmittance and low-absorption-coefficient polycrystalline ZnS with a size of 1 m × 2 m and a thickness of 20 mm. The linear optical properties, including the UV-vis-NIR transmission spectrum, infrared spectrum, and refractive index, were systematically characterized, which shows that the present ZnS polycrystal exhibits a wide transmission range from 0.34 to 15.00 µm, covering two important atmospheric windows. Moreover, its Sellmeier equation was achieved and fitted as a modification of previous studies. According to the refractive index and transmission spectrum, optical loss was calculated to be < 3.5% from 1 to 10 µm. All the results indicate that the present sample has comparable properties with the single crystals and should have potential applications as a functional material.
We propose a promising method to develop flexible, compact, and tunable light-activated film diffractive optical elements (FDOEs) with exceptional diffraction efficiency, by integrating liquid crystal (LC) geometric phase-based diffractive optical elements (DOEs) with a specifically designed light-activated LC polymer (LCP) film. Arbitrary film bending induced by UV/Vis irradiation is realized through precise mesogens arrangement within the LCP film, enabling 1D and 2D beam steering, as well as dynamic and reversible switching between structured and Gaussian lights after cooperating with the DOE design. Furthermore, remarkable fatigue resistance, solvent resistance, and thermal stability are demonstrated, providing a solid material platform for advanced optical applications.
Under a specified loss condition, the resonant mode in a three-turn lossy microfiber coil resonator exhibits periodic evolution among normal resonance, white-light cavity effect, and resonance mode splitting in response to alterations in the phase shift and coupling state. It exhibits normal resonance when the coupling state exceeds a threshold with specific loss. The white-light cavity effect is activated when the coupling state matches loss. The resonant phase bifurcates as the coupling state falls below the threshold. The excitation conditions for each resonant mode have been derived, and the critical coupling conditions exist for both normal resonance and mode splitting in the case of relatively small losses.
For bicolor regulation in laser protection compatible with visible light stealth, a metal–dielectric–enhanced reflection asymmetric Fabry–Perot structure is proposed that has high reflectance at the laser wavelength and the color control of the visible spectrum. The six-layer reflection enhancement unit is composed of an Al metal mirror, SiO2, Ta2O5, and an ultrathin Nb metal layer. The synergistic relationship between the background color and laser wavelength reflectance was analyzed and simulated. Six different colors from blue to red with high reflectance at 1064 nm laser wavelength up to 97.84% were prepared. The thin films can withstand 2535 W cm-2 power density continuous irradiation for 60 s without being destroyed. Moreover, a symmetrical structure presents the spectrum consistency from both directions, which makes the potential to be applied to the laser protective coatings. The blue symmetrical microreflector sample was prepared and sprayed on the nonplanar models to demonstrate the actual application effect. This simple and efficient scheme provides an innovative technical approach in the field of surface laser protection.