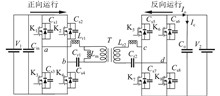
Aiming at the problems of wide frequency adjustment range and low operating efficiency of the traditional variable frequency control CLLLC resonant converter at low voltage gain, a variable mode resonant converter based on the model predictive control is designed. The control strategy can make the converter switch between the full-bridge mode and half-bridge mode flexibly in a wide range of input without additional auxiliary circuits, which can broaden the low voltage gain and keep a narrow frequency adjustment range. This strategy is beneficial to the design of magnetic components and effectively improve the operating efficiency of the converter under high input voltage. Compared with the PI control, the proposed model predictive control obviously improves the output voltage spike problem during mode switching, and increases the dynamic performance of the converter on the premise of similar steady-state performance. Simulation and experiment prove the feasibility and superiority of the designed CLLLC resonant converter and its control strategy.
A machine learning-based aging gene feature selection and classification experiment is designed as the experimental content of the “Machine Learning Basics” course for intelligent medical engineering and other majors. In this experiment, the data set is obtained by mapping aging genes to gene ontology, feature selection methods are used to deal with feature redundancy in gene ontology, and classification models such as naive Bayesian and support vector machines are used to classify aging genes. The experiment is implemented with Python language and Scikit-learn framework. In addition to the built-in methods of the framework, a hierarchical feature selection method based on the statistical properties of the data and the uniqueness of the test sample is designed to eliminate the hierarchical redundancy among features. Experimental results show that effective feature selection methods can significantly improve the results of aging gene classification.
To compare the effects of three different polishing methods on the kerf quality, inner wall surface quality and corrosion resistance of biopsy needles by laser cutting, biopsy needles are processed with optimized technological parameters. Biopsy needles are polished separately by electrolytic plasma polishing (EPP), magnetic abrasive finishing (MAF), electro-polishing (EP). The kerf quality is observed with two-dimensional image measuring instrument. The Ra and the surface morphology of the inner wall is measured and observed by the 3D measurement laser microscope. A polarization curve is plotted to verify the corrosion resistances of the biopsy needles with three different polishing treatments. Three methods namely EPP, MAF and EP can be used to completely remove the dross and oxides, reduce the Ra and improve the surface quality. The corrosion resistance of biopsy needle by magnetic abrasive finishing has been significantly improved.
The relationship model between the topography of the sea area and the layout scheme of the multi-beam survey line is established. The coverage width and overlap ratio of survey line are important indexes to measure the quality of survey line layout scheme. The calculation model of 2D and 3D sea area coverage width and overlap ratio is established by the analytical geometry method, and the basic method of measuring survey line layout scheme is obtained. At the same time, combining the survey line layout scheme with the optimization problem, the multi-objective planning model is established for the rectangular slope sea area and a real sea area to be measured respectively. The corresponding algorithm is designed to solve the model, and the optimal survey line layout scheme of the rectangular slope sea area and a feasible layout method of a real sea area to be measured are obtained. It is of reference significance to the practical multi-beam line layout problem.
The hydraulic systems of new deployed equipment are complicated and practical equipment training has the potential risks of breakdown and safety. To solve these problems, an experiment training stand is developed based on the semi-real hydraulic system and virtual models. The 3D modeling software and Unity3D are used to model the system and integrate and control the animations. The designed interface module includes the data acquisition and control card based on the core chip STM32F407IGT6, the operation control unit and the sensors, which realizes the data transformation between the semi-real system and virtual model. Taking one type of integrated gearbox hydraulic system as example, different training functions of this stand, such as constructing principles and fault diagnosis, are fulfilled and illustrated. The application shows that by using the experiment training stand based on HIL, the theory and practical training are integrated deeply, and the problems of the complicated hydraulic systems training such as obscure construction and principle and insufficient practical training are solved effectively.
To optimize the process of aseptic preparation and maintenance for BD FACSAria cell sorter to maintain long-term stable sterile sorting state, the cost of aseptic preparation, operation process and system stability are optimized. The method of monitoring the aseptic status of the fluidics system with LB medium is explored, and the aseptic sorting status and long-term culture of HCT116 cells are observed. The optimized aseptic preparation methods simplify the operation process, save the cost, and can keep the aseptic state of the instrument liquid flow pipeline for a long time. HCT116 colorectal cancer cells are sorted and cultured in antibiotic-free medium for a long time without contamination. The optimized aseptic preparation methods and maintenance procedure of BD FACSAria sorter provide a simple and feasible scheme for the operation and management of the instrument, and provide high-quality and stable aseptic sorting services for scientific research.
A hardware-in-loop visual test platform of transformers and induction motors is designed, which is mainly composed of DSP controller, MCGS touch screen, RS485 communication circuit and power module. DSP TMS320F28335 is the main controller of the test platform, which calculates the mathematical models of various transformers and induction motors under different experiments. MCGS touch screen is the upper computer, which is used to realize parameter input, waveform curve and internal magnetic field visualization of the motors. The RS485 circuit is utilized to transmit motor parameters and experimental simulation results between the controller and the touch screen. The data transmission protocol is Modbus RTU protocol. The platform has low hardware cost and good portability. Visualization of data, waveform curve and magnetic field can help students deepen their understanding of professional knowledge. The test platform meets the needs of experimental teaching and has achieved good teaching results.
Microwave measurement is an important part of microwave engineering. In order to cultivate students’ practical and engineering application abilities in microwave measurement, an “opening blind box” series of inquiry-validation experiments is designed for the course of Microwave Technology. The series experiments of “opening blind box” microwave measurement focus on measuring standing wave ratio, load impedance, two-port network S-parameters, etc. In each measurement experiment, multiple measurement objects are set without providing basic indexes, and microwave device are measured through “open blind box” method, which increases the uncertainty of the experimental results. At the same time, “hidden items” are set in the measurement objects to exercise student’s microwave engineering practical ability and problem-solving ability, which establishes a technical foundation for students to further design microwave components.
Transportation infrastructure is important to the “the Belt and Road Initiative”. The motivation of initiative sponsored by China originates from the international talent cultivation for the “New Engineering” . With the development of transportation engineering, a country with strong transportation network is an important moral education and intellectual education, and teaching designs of performance of geosynthetic-reinforced and pile-supported (GRPS) embankment as well as the mechanisms of soil arching effects are conducted. Based on the classical engineering cases of GRPS embankment, both laboratory tests and numerical simulations to model macro-micro soil arching effects are added into the multi-module international teaching course of embankment engineering, which contributes to improve the mechanical theoretical knowledge, the practical ability and the innovation education level of civil engineering students. The intellectual level and engineering attainment of civil engineering students can be promoted in order to satisfy a quick development of civil engineering and requirements of international labor market.
With the development of artificial intelligence (AI) technologies, the proportion of related courses and technological applications in university curricula has been increasing, leading to a surge in students’ demand for AI experimentation. However, the current AI experimental systems are not well-established, with most experiments being software-based and lacking hardware platforms and projects, which results in a disconnect from real-world engineering applications and industry needs. This experimental instruction integrates the CDIO (conceive, design, implement, operate) model, and to address issues such as slow inference speeds and long processing times in deep learning networks during experiments, an AI experiment based on the Huawei Ascend Atlas 200DK hardware platform is proposed, which utilizes deep learning networks to perform colorization of grayscale images. Through this experiment, students can learn about the principles of AI, the structure and inference processes of neural networks, set up software development environments, configure hardware systems, and deploy neural networks that integrate both software and hardware. The experiment also involves the completion of functional and performance testing. This hands-on experience helps students understand the operational mechanisms of neural networks from a practical application perspective, master their application methods on actual hardware platforms, and thereby enhance their overall engineering and practical skills in both software and hardware.
Combining the discipline advantages and resources of university laboratories, a series of organic optoelectronics comprehensive experimental courses have been constructed with the problem-based learning (PBL) model. With diversified teaching content and methods, the ways of cultivation talents with keen problem awareness, broad scientific perspective, flexible thinking ability and team collaboration ability have been explored. These provide theoretical support and practical guidance for the construction of comprehensive open innovation experimental courses in university laboratories, and is of great significance for promoting the improvement of higher education quality and the innovation of talent training ways.
Under the backdrop of the “Emerging Engineering Education” initiative, the student situation and course objectives is analyzed by the reform team of electrical and electronic experimental courses. They contradictions between teaching objectives and outcomes, student self-development and traditional teaching paradigms, industry advancements and teaching resources, and the integration of ideological education into practical teaching segments with course hours are adressed, and innovative approaches are proposed concerning teaching content, pedagogical methods, teaching tools, and the integration of ideological education. The curriculum's innovative reform garnered positive student feedback and results.
The comprehensive experimental design takes the “flexible Zn-air battery” as the research and development hotspot. It relies on the major of new energy to solve the problems in the air cathode catalyst of flexible Zn-air battery. The axial coordination strategy is adopted to prepare the iron phthalocyanine (FePc) and the functional MXene composite catalytic materials. Besides, the physical characterization and electrochemical performance are conducted and further evaluated. This teaching design helps students master the basic preparation method of catalytic materials and deeply understand the electrochemical theory. It is also beneficial to make students be familiar with the assembly process and testing methods of flexible zinc-air batteries as well as the basic process of scientific research. Furthermore, the students can better understand the significance of new energy courses and improve the awareness of scientific research, exploration, and independent learning ability.
Under the background of vigorously promoting the digitalization of education, the digital technology has been deeply integrated with experimental teaching through digital intelligence empowerment, constructing a blended experimental teaching model that combines online and offline approaches. This model assesses, guides, and evaluates students throughout the entire experimental process and provides personalized experimental teaching. By effectively mining and analyzing data from students’ experimental processes, teaching strategies are adjusted in a timely manner to enhance the quality of experimental teaching. Practice has proven that this teaching model can effectively stimulate students’ interest in learning, improve classroom efficiency, achieve real-time monitoring and guidance of student experiments, and meet the personalized experimental needs of students.
The shortage of integrated circuit testing talents and insufficient analysis of operational amplifier parameters in undergraduate teaching practice are two issues in current China. The experiment is a student-oriented comprehensive design experiment, including two progressive courses, namely test adapter design and automatic testing software development. The testing circuits for three typical operational amplifier parameters are provided in this article. The impact of the interaction of various parameters on measurement accuracy are analyzed and the means to reduce the impact are proposed. The design method of remote multi-parameter and multi-range switching circuit is given, for meeting the requirement of automatic test. As verified, the experimental results produced by the test system are consistent with the specified parameter range by the datasheet of the operational amplifier. The experiment includes the complete design flow of integrated circuit automatic test system, which provides the students not only the design practice for hardware circuits, embedded software and upper computer software, but also improves their system level design capability.
Given the widespread application of embedded systems in various fields, this article combines them with real-life scenarios to conduct in-depth reform and exploration of practical teaching for embedded systems. An experimental teaching system based on the embedded Android system has been designed, comprehensively covering key aspects such as underlying hardware operations, upper-level software development, hardware-software co-design, and comprehensive practical projects. This teaching system not only systematically imparts core knowledge and skills in embedded system hardware and software development but also effectively strengthens students’ practical abilities through a series of progressively challenging experimental content. It refines their thinking and approach to solving complex engineering problems and enhances their engineering literacy. Overall, this experimental teaching system is highly practical and plays a significant role in cultivating innovative and practically-minded embedded talents.
Corn straw (CS) is a resourceful adsorption material that can be prepared easily at low cost and exhibits high specific surface area. However, in the adsorption of heavy metals it has limitations, such as unstable properties and small adsorption capacity. The adsorption capacity can be enhanced by modifying surface microstructure, such as increasing functional group content or enriching specific surface and pore structure. However, the toxic reagent, complicated process, long cycle, intense reaction conditions and high preparation cost have become the limitations of modification. New economic and sustainable technologies are urgently required to convert postharvest residues into value-added products with minimal impact on the environment. A low-temperature oxidation method has been suggested as an economic and effective strategy for turning biomass into environmental remediation materials. The CS were modified in O2 and N2 atmospheres from 140 to 220 ℃, respectively, and Cu(II) was used as the heavy metal target. With the increase of modification temperature, the contents of total acid value, phenolic hydroxyl group, lactone group and total base value of CS (CS-O2-T) modified at O2 atmosphere were significantly higher than those modified by N2 (CS-N2-T). At the modified temperature of 220 ℃, the adsorption capacity of Cu(II) by CS-O2-220 is 34.5% higher than that by CS-N2-220, which is 2.2 times of original CS. The results demonstrate that acid-base functional groups on the surface of CS were increased significantly, and the adsorption capacity of Cu(II) was effectively increased after modified by oxidation. The results of SEM, BET, FTIR and XPS prove that the adsorption of Cu(II) is mainly due to the complexation and cation-π coordination of endoester group, phenolic hydroxyl group and aromatic structure by modified CS. This experiment helps students construct their theoretical knowledge such as the adsorption treatment of heavy metals in wastewater and master the experimental skills of straw modification, and it also cultivates their scientific research and innovation ability.
There are many types of related data in laboratory work, complex inter-class connections, and various types of storage, which make it difficult for data integration and data-based scientific decision-making. At present, laboratory staff only have a preliminary understanding of digital management, but there is no clear idea and method on how to carry out in daily work. Starting from the laboratory data governance, a data governance method based on the knowledge graph technology is introduced, which is guided by the top-down knowledge graph construction strategy. Firstly, a conceptual model of laboratory management business and related data sets is constructed. Then, entities and relationships between entities are extracted from the existing business data, and the storage mode is optimized according to the actual situation. Finally, data storage is performed in the graph database. Through the experiment of this method, the laboratory data management is preliminarily realized, which lays a foundation for the subsequent data-based management.
The establishment of a feasible long-term control mechanism for hazardous chemicals is the top priority to realize the normal safety of colleges and university laboratories. According to the risk of hazardous chemicals and its control requirements, in view of the actual problems of the whole process management of hazardous chemicals in laboratories, the danger source control theory is applied. On the basis of improving the management system, clarifying the responsibility system and finding out the base number, the information construction is relied. Through regulating the procurement and storage, controlling the quantity, strengthening the use management and improving the timeliness of disposal, a long-term mechanism is established for the safety control of hazardous chemicals. The education and training is strengthened in daily work as well so as to mobilize the enthusiasm of staff and implement and continuously improve the working mechanism.
The laboratory provides an important role for universities to cultivate the talents of creativity and promote the construction of “first-rate universities and disciplines”. It is necessary to establish a standardized and efficient safety management model for scientific research laboratories which is featured with diverse experimental content, complex personnel access, and overlapping safety risks. Taking the Faculty of Geographical Science of Beijing Normal University as an example, this paper comprehensively sorts out the complexity characteristics of laboratories in geographical branch, such as multiple professional directions, multiple hazards and high frequency of use, and puts forward the corresponding improvement strategies in view of the shortcomings existing in scientific research laboratory safety management, such as the lack of scientific laboratory planning and function layout, backward safety concept, weak safety awareness, professional laboratory manager shortages and weak information management. It is expected to provide references for the safety management of laboratories and create a new situation of safety management in university laboratories so as to adapt to the construction of “first-rate universities and disciplines”.
The increasing use of special equipment accompanying with the research expansion in university laboratory has become one of the important hazards threatening laboratory safety. At the same time, the management of laboratory special equipment in colleges and universities suffers from imperfect management system, few administrative staffs, and lack of process management, which has become a risk threatening the property and life safety of teachers and students in colleges and universities. Through establishing full-time and part-time management positions, setting training courses, organizing forensics examination and applying registration certificate of the “position, course, examination, and certification” safety management mode, it is proved to be of important reference significance to improve the level of college special equipment safety management and realize the life-cycle management.
Based on the achievement of the second prize of the National Science and Technology Progress Award for the new technology of rapid thermal cycling and high gloss injection molding and aimed at cultivating high-level innovative talents in the new era, a virtual simulation experimental project system for the entire process of process and equipment cognition, rapid heat cycle injection molding macro and micro integration simulation, and production simulation is designed, which mainly focuses on 42 inch LCD TV front shell steam heating rapid heat cycle injection molding production. The virtual simulation experimental course of “Rapid Heat Cycle Injection Molding Process Macro and Micro Integration Simulation and Production Simulation” is constructed, and the teaching practice is carried out, which achieves effective teaching outcomes.
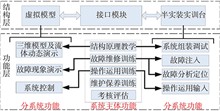
In view of the abstract design content of the control principle controller, the lack of students’ intuitive understanding of the actual control case, and the difficulty of traditional experimental teaching resources to meet the teaching needs due to the constraints of site, time, economic cost and other conditions, a design scheme of the first-order inverted pendulum virtual experiment system based on semi-physical simulation is proposed, and the key technologies of the virtual experiment system are introduced in detail, including the establishment of the physical model of the first-order inverted pendulum, the implementation of customized software and hardware, communication methods between virtual inverted pendulums and embedded targets, etc. Through the virtual experiment system, open automatic control and embedded system experimental teaching can be carried out, so as to achieve the purpose of entertaining, eliminating the boredom of learning control principles, and stimulating students’ enthusiasm for learning.
In order to solve the problems in teaching of professional background courses, such as difficulty in grasping the integration of theoretical teaching and equipment cases, difficulty in establishing the correlation between theory and practice in existing experimental plans, and singularity in evaluating the effectiveness of experimental teaching, a virtual experimental system for automatic control principles with missile control as a case background is constructed. The design concept of this virtual experimental system is based on the course of “Automatic Control Principles”, which applies the principle of constructivism and follows the idea of “intuitive introduction, layer by layer progressive, high-order synthesis”. It realizes the process of cultivating practical engineering skills through virtual experiments. By applying this experimental system to teaching practice, students are able to fully understand and proficiently apply the application technology of control theory in equipment installation through the study of equipment examples, which better cultivates their ability to transform theory into practice. The construction and application of this system have good reference value for the construction of virtual experiments in this type of professional background courses.