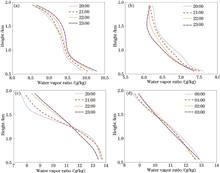
Water vapor plays an important role in the earth-atmosphere system, and the change of water vapor is an important reference for the change of weather and climate. Raman lidar has outstanding performance and is widely used in water vapor detection. It is very important to determine the calibration constant term in the inversion of water vapor mixing ratio detected by Raman lidar. It is common to use the radiosonde data to determine the calibration constant. However, the cost of simultaneous release of sounding balloons is high, and the radiosonde data of the global radiosonde network is limited in time and space. Compared with radiosonde data, ERA5 reanalysis data has higher spatiotemporal resolution and wider coverage. Many scholars analyze and apply ERA5 reanalysis data, which verifies that ERA5 reanalysis data is in good agreement with radiosonde data. Therefore, this paper proposes to use ERA5 reanalysis data to determine the calibration constant at the place and time without radiosonde data. The calibration constant of water vapor inversion with Raman lidar is determined by ERA5 water vapor data in Hefei. In the altitude range of 0.5?2 km, the calibration constant changes with time and altitude, which is considered to be caused by data deviation, interpolation calculation and lidar system error. The relative error between the inversion results and ERA5 data is mostly within ±10% by substituting the mean profile of the adjacent time calibration constants.
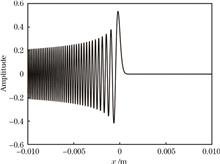
To address problems of a high loss of optical beam energy, weak optical beam quality, and weak communication performance in underwater wireless optical communication, an experimental system is setup to carry out comparative experiments of the transmission for Airy beam and ordinary Gaussian beam in water channel, as well as comparative experiments of the single-photon detection communication in an 80-meter water channel. Experimental results show that the abilities of the Airy beam to maintain beam quality and to resist beam dithering in water channel are evidently superior to those of the Gaussian beam. Compared to the Gaussian beam, the adoption of the Airy beam in communication can increase the effective frame ratio by ~11.15% and reduce the error rate by ~42.52%. Results prove the superior performance of the Airy beam to the Gaussian beam in underwater optical communication, thus providing a possibility for long distance and high performance underwater optical communication.
Electromagnetically induced transparency (EIT) is the basis of measuring microwave by Rydberg atom, and the spectral characteristics of EIT affect the measurement accuracy of microwave field directly. The effects of the Rabi frequency of a coupling laser, Rabi frequency of a probe laser, and temperature of an atomic chamber on the electromagnetically induced transparency spectral characteristics of cesium atoms were investigated experimentally in this study. The causes for the variations in optical bistability, atomic collisions, and atomic density are investigated. The research results indicate that as the Rabi frequency of the coupling laser increases, both the width and the degree of asymmetry of the EIT spectrum first increase and then stabilize. In addition, as the Rabi frequency of the probe laser increases, the width of the EIT spectrum increases monotonically. The fitting slope initially increases and then stabilizes as the Rabi frequency of the coupling laser increases, whereas the degree of asymmetry has two trends: increasing, decreasing, and increasing, decreasing, increasing; as the temperature of the atomic chamber increases, both of them first increase and then decrease. This study is beneficial for optimizing the experimental parameters of quantum microwave measurement, improving the sensitivity of microwave measurement, and facilitating the practical application of the technology for quantum microwave measurement.
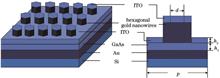
This study constructs a metal-semiconductor-metal photodetector based on a hexagonal gold nanowire structure for enhancing the light absorption capability and responsivity of photodetectors at specific wavelengths. An tin indium oxide layer, which exhibiting excellent optical transparency and electrical conductivity, is coated onto this structure. Multiple models are established using the finite element simulation software COMSOL to conduct comparative simulations. Following parameter optimization, the overall light absorptivity of the device reaches 90% in the wavelength range of 700?1500 nm. The responsivity of device reaches 0.39 A/W under a bias voltage of 5 V and an incident light power of 10 mW. Furthermore, the thickness of GaAs layer, diameter of hexagonal gold nanowires, and angle of incident light affect the performance of the device.
To address the challenge of low-altitude path planning for clusters of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) in military electromagnetic denial environments, a novel approach using ultraviolet light is proposed. This method takes advantage of ultraviolet light's low background noise and all-weather wide field of view, enabling non-line-of-sight communication and maintaining links between UAV clusters by combining a hemispherical multi-input multi-output structure. An improved moderate random particle swarm optimization (MRPSO) algorithm that incorporates dynamic weights is proposed, alongside strategies like antiroulette wheel selection, chaotic distribution factors, and the Metropolis criterion, to enhance global search capabilities and optimize path planning. The simulation results demonstrate that MRPSO outperforms traditional PSO, hybrid inertial traction PSO, and spherical PSO by increasing the success rate of path breakthroughs in radar-free environments by 7.65%, 7.68%, and 29.71%, respectively. In complex radar environments, improvements are more evident, with increases of 18.19%, 14.86%, and 43.99%, respectively. When the algorithm converges, it exhibits low fitness values and notable advantages in convergence rate and optimization stability, demonstrating its effectiveness and versatility across different application scenarios. This study offers a notable contribution for enhancing low-altitude breakthrough path planning of UAVs in electromagnetic denial environments.
The external cavity time-delay signature (TDS) is a critical parameter influencing the application of chaotic lasers. This study presents a method for enhancing the TDS of chaotic light output from a semiconductor laser with loop feedback by injecting it into a whispering-gallery mode microcavity. By utilizing the storage effect, attributed to the long photon lifetime in the whispering-gallery mode, and the extraction of coherent signal components through the coupling process, significant enhancement of the chaotic light signal's TDS was achieved. An experimental setup was constructed to first explore the influence of the coupling state of the whispering-gallery mode microcavity on the chaotic TDS enhancement. Then, the effect of this approach on the chaotic signal TDS generated under different feedback strengths was studied. The experimental results confirm that this method significantly enhances the TDS of chaotic signals across different feedback strengths, with the enhancement being more significant under critical coupling conditions and low bandwidth. The compact structure and low cost of this scheme offer a convenient solution for the development and application of chaotic TDS-related devices.
The existing leakage detection systems have challenges in identification and localization for pinhole leakage in long-distance gas transmission pipelines due to high costs and difficulty. This paper presents a model test for gas transmission pipeline leakage monitoring based on distributed acoustic sensing (DAS) technology. The optical sensing cable with a spiral structure effectively enhances the capability to identify leakage events. A method utilizing fast Fourier transform for pipeline leakage signal identification and precise localization is proposed. By analyzing the vibration of fiber in both time and frequency domains, the generation of leakage signals can be accurately detected. Preliminary localization of leakage points is achieved by observing the spectral average amplitude changes in each sensing channel. Additionally, a precise localization method based on cross-correlation algorithm is introduced, which improves the positioning accuracy of the optical sensing cable with a spiral structure from ~0.74 m to 0.24 m.
Identifying, monitoring, and locating the loss of bolt preload for bolted steel members in corrosive conditions is difficult. Hence, this study investigates the strain distribution on the surface of the cover plate of bolted member based on optical frequency domain reflectance (OFDR) technology. Fiber optic calibration tests, corrosion tests of bolted steel members, and numerical simulations using ANSYS software are conducted. The test and numerical simulation results show that when the bolt preload is 100 kN, a preload loss exceeding 10% in the identified bolt can be accurately detected and localized. Using the longitudinal pasting method, and excluding errors from the fiber optic paste tip effect, a comparative analysis is performed on the distributed optical fiber strain loss rate before and after corrosion. The results show strain loss rates of 10.6%, 16.7%, and 28.1%. Additionally, the strain distribution patterns from the test and simulation results coincide, demonstrating that OFDR technology can be used to identify and localize bolt preload loss in bolted specimens under corrosive conditions.
In order to quantitatively evaluate the impact of the overall migration process on the ancient buildings, a method for monitoring the migration of ancient buildings based on ultra-weak fiber Bragg grating (UW-FBG) arrays is proposed. The principle of strain and nonuniform settlement monitoring of UW-FBG sensor array is analyzed. A UW-FBG strain sensing cable with twisted steel cables is designed and its sensing characteristics are calibrated, which center wavelengths are 1530 nm, 1542 nm, and 1552 nm. The fiber optic cable has a resolution spacing of 0.2 m, a strain sensitivity of 1.10 pm/με, and a temperature sensitivity of ~22.4 pm/℃. The fiber optical cable is pre-buried into the pallets of an ancient building in Jing'an District, Shanghai, and an automatic monitoring system based on UW-FBG is constructed to monitor the lifting, migration and placement of buildings in real time. Results indicate that the maximum strain during the relocation of the ancient building is ~110 με, which is less than the pallet strain design threshold of 500 με, and the maximum nonuniform settlement is ~8 mm, of which the lifting process produces the greatest strain impact. The proposed method can realize multi-point, wide-range and high-precision monitoring of the strain field of pallet beams, and obtain the nonuniform settlement of pallet beams in real time, which provides a basis for optimizing the relocation of ancient buildings.
The workshop measurement and positioning system realize coordinate measurement based on the principle of multistation observation and intersection, and the accurate calibration of the pose parameters of the measuring instrument is the premise of high-precision measurement of the system. In the process of system orientation, multiple observation equations are established based on instrumental observations and geometric constraint information to construct an orientation network, and its structural strength reflects the calibration accuracy of pose parameters. In this study, based on the mathematical model of the implicit function of the system and the orientation principle, the uncertainty of the pose parameters of is derived, and the structural strength evaluation model of the directional network is proposed. The evaluation index of the structural strength of the directional network is formed based on the structural coefficients calculated by the model. The structural strength of the directional network with different configurations is compared and verified numerically and experimentally to verify the correctness of the model. Through the analysis of the influencing factors of the structural coefficients, some guiding suggestions for the layout and structural optimization of the directional network is proposed.
This study proposes a low-cost, high-efficiency calibration method for motion axes using a measurement system that combines line lasers and five axes. By scanning the surface of a standard sphere and performing an optimization search, the method achieves step-by-step calibration of displacement and rotation axes. Compared with existing calibration methods for motion axes, this method requires only the participation of the measurement system itself and a standard sphere, with simple steps, lower calibration costs, and higher efficiency. The proposed method is simulated and practically implemented with a line-laser five-axis system under calibration and measurement experiments. Experimental results indicate that after calibration, the surface peak-to-valley (PV) of the standard sphere measured by the system is 10.98 μm, with a standard deviation of 0.199 μm for repeated measurements of the surface PV of the standard sphere. The system also has integrated 3D measurement capabilities for various sizes and structurally complex devices, thus demonstrating the practical performance and application value of the proposed method.
A scanning error correction method is proposed to eliminate phase errors in white light scanning interferometry, addressing the limited measurement accuracy caused by inexact phase shift. Adding a monochromatic light interference signal detection device to a white light scanning interferometer allows the collected monochromatic signal to share the same phase error as the white light signal. The phase error obtained from the monochromatic light interference signal was used to correct the white light signal. The effectiveness of the scanning error correction method was verified through simulations and experiments on the roughness of a measurement surface and the repeatability of multiple measurements. This method further improves measurement accuracy based on the wavenumber domain phase compensation method proposed by our research group and enables the white light interferometer to adapt to noisy working environments.
This paper proposes a new method for measuring film thickness that combines frequency-domain white-light interference and reflection spectroscopy. In addition to the film to be measured, this method considers air as a medium layer to construct a multilayer-film-structure model. The nonlinear phase is reconstructed using white-light frequency-domain interference fringes generated by the reflection of the multilayer film structure, and the film thickness is obtained via fitting. To solve the local optimal solution problem that occurs during fitting, the thickness obtained via reflection spectroscopy is used to limit the fitting range. In this study, theoretical derivation and numerical simulation are performed to examine the process of measuring the thickness of the film to be measured using a multilayer-film-structure model. Subsequently, a fiber-optic measuring system is constructed to verify the feasibility of this method by experimentally measuring the thickness of a single-layer silica film.
We developed an efficient acoustic monitoring system that uses the speckle method with a Fresnel lens for light collection and applied it to long-range line-of-sight acoustic surveillance (up to 100 m). The proposed system can effectively capture and reconstruct speech from a human target 100 m away. The reconstructed speech demonstrates a high degree of real-time performance, with a measurement error of less than 0.15%, making it suitable for a variety of applications.
The uniformity of the light source in contact angle measurement systems directly influences the accuracy of droplet image acquisition, which subsequently impacts the reliability of contact angle measurements. However, systematic studies and designs aimed at achieving optimal light source configurations in domestic contact angle equipment are currently insufficient. This study aims to achieve high uniformity and low cost by employing the particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm. Through practical analysis, an optimal arrangement of light source modules and control systems is developed. Using a contact angle standard plate, the variance, mean square error, and relative error are calculated as 30°, 60°, 90° and 120°, and the gray scale of the picture is obtained. Compared with the data measured by other methods, the results demonstrate that the design is reliable and can be used to measure the light source of portable contact angle equipment within the industry.
To meet the requirements of high-speed and high-sensitivity detection of surface defects of transparent optics, and to solve the problems of the low scanning efficiency of the dark field scattering point confocal imaging and the cross-talk of the line confocal imaging, a “point-to-line” confocal collection device for dark field scattering light is designed by partially breaking the object-image conjugacy constraint of the objective. It breaks through the bottleneck of mutual restriction between numerical aperture and field of view, and greatly increases the line field of view from “millimeter” to “hundred millimeter”. A high-speed laser line scanning strategy is designed to illuminate the tested surface with only one laser spot every moment, avoiding the cross-talk of the scattering light of defects. On this basis, a “point-to-line” confocal dark field laser scattering probe with optical sectioning capability is developed. The probe shows the ability of separation of the scattering light from the front and back surfaces of transparent optics. The experiments show that the effective line field of view of the probe reaches 100 mm and the scattering light collection uniformity is 80.7%. For a transparent optical element with a thickness of 2 mm, the signal-to-noise ratio for suppressing back-surface scattered light is up to 14.1 dB. The system has a scanning efficiency of 800 mm2/s at a scan speed of 8 mm/s, a lateral resolution of 20 μm, a signal-to-noise ratio of the scattering signal of 10.9 dB for a fine scratch with a width of 1.16 μm, and a figure of merit of 6.9 cm-2·s-1·μm-1.
This study investigates an optical fiber Mach-Zehnder interferometric measurement system for measuring the micro-displacement of a target object. The Mach-Zehnder interferometer structure is used to build a heterodyne laser interferometric optical path. In addition, an acousto-optic frequency shifter is used to modulate the frequency of the reference light, and a photodetector is used to interfere with the measurement light containing the displacement information of the object. To solve the problem of frequency drift of the acousto-optic modulator, the radio-frequency (RF) signal of the modulator is taken as the reference signal. Next, a frequency drift is introduced into the measured and reference signals to give them the same frequency shift error. During phase demodulation of the two signals, the frequency shift errors cancel each other out. The signal demodulation uses a correlation phase identification algorithm that can determine the lead-lag relationship of the signals, and the displacement and direction information of the object is obtained. Experimental results show that in the displacement range of ±25 μm, the maximum and minimum relative errors of displacement are 0.78% and 0.145%, respectively, the fitting coefficient for the linear fit R2 is 0.9999, and the displacement consistency error is less than 0.033 μm. The experiments show that the measurement system has good measurement accuracy and stability.
To introduce the ISO10110-5 evaluation index into detecting the surface deviations of optical components, this study uses a plano-convex lens with a large curvature radius as an example, and presents a new method for measuring the surface roundness error of the lens based on the principle of equal-thickness interference. By combining the plano-convex lens with the optical flat to form a Newton's ring instrument, using the eyepiece cross hair of the reading microscope for visual positioning of the plano-convex lens to be measured, and integrating the new reading method of the double-micrometer screw device, the radius variation of each uniform distribution point on the circular interference fringes relative to the starting point is obtained, and the roundness error of the surface cross section of the tested lens is evaluated using the least squares method. The experimental results indicate that the relative uncertainty is approximately 6.5%. The optical techniques used to locate the plano-convex lens can effectively reduce the eccentricity error, and the new reading method also overcomes the limitation of the traditional reading microscope in that the microscope tube can only move in one direction to eliminate space differences. The measurement system does not require special measuring instruments and is simple, practical, low cost, non-contact, and widely applicable.
Broadband extreme ultraviolet (EUV) radiation has shown significant advantages in advanced-node semiconductor metrology. To meet the high-volume manufacturing demands of advanced nodes, the conversion efficiency of a laser-plasma broadband EUV source was studied. First, the wavelength and spectral intensity of the EUV spectrometer were calibrated and used to characterize the total conversion efficiency (CE) from laser to EUV radiation at 10?20 nm. Subsequently, an in-situ second pulse was applied to a solid Sn target using a 1 μm laser, thereby achieving a broadband EUV conversion efficiency of 52.5% in the 10?20 nm range, which is the highest CE reported so far. The main reason for this is that the curved surface formed by the ablation of the first laser pulse caused spatial constraints on the tin plasma. These spatial constraints were induced by the subsequent laser pulse and resulted in a significant increase in EUV emission. This study provides a new approach for generating a broadband EUV light source with high CE, presenting a novel method of semiconductor microchip metrology for advanced technology nodes of the future.
In order to solve the problem that the surface traceability and anti-counterfeiting data matrix (DM) code of industrial pure titanium alloy (TA1) is easy to wear, the coating is prepared on the surface of TA1 using low-power laser nitriding process to achieve surface strengthening in a closed nitrogen environment. The effects of laser power on the microstructure, microhardness, and friction and wear properties of TA1 nitride layer are investigated. The research results show that the nitride layer is mainly composed of TiN phases and a small number of α-Ti and β-Ti phases, indicating that the process can effectively achieve laser nitriding on the surface of TA1. When the laser power is 16 W, the scanning distance is 0.03 mm, the frequency is 40 Hz, the scanning speed is 25 mm/s, and the compensation factor is 0.04 mm, the surface microhardness of the nitride layer is increased by 1.7 times, the wear volume is reduced by 98%, and the width and depth of the wear mark are reduced by 83% and 82%, respectively. In addition, under the optimal laser nitriding parameters, the DM code is laser-marked in atmospheric and nitrogen environments, and the wear resistance of the DM code is evaluated through a friction experiment. The results show that the average friction coefficient of the DM code is reduced by 44.4%, the width of the wear mark is reduced by 55%, and the contrast is increased by 25%. The DM code reading grade is level A in the nitrogen environment and level C in the atmospheric environment. The results show that the laser nitriding marking process substantially improves the hardness and wear resistance of the DM code on the basis of ensuring the reading grade of the DM code.
To investigate the forming quality of selective laser melting (SLM) in an aerobic environment, Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu (SAC305) alloy with a low melting point was selected. An orthogonal experiment scheme involving three process parameters (laser power, scanning speed, and hatch spacing) was designed to investigate the effects of different process parameters on the density of a sample formed via SLM in an air environment. Additionally, the surface morphology, micromorphology, and mechanical properties of samples with different densities were analyzed. The results indicate that laser power affected the density of the samples the most, whereas the other parameters exerted insignificant effects. The density of the samples increased with the energy density. For samples with lower densities, the main internal defects are holes and non-fusion defects. As the density increases, non-fusion defects disappear gradually and the number and size of holes decrease. The mechanical properties of the specimen formed in an aerobic environment are primarily affected by the residual large-sized spatters inside the sample. The failure of spatters to fuse with the substrate reduced the cross-section area of the sample and decreased its tensile strength. Compared with samples formed with protective gas, the abovementioned sample shows only a slight increase in oxygen content, although the oxidized spatters affect the forming quality.
To address the low convergence speed and the challenge of selecting an optimal iterative step size in the stochastic parallel gradient descent (SPGD) algorithm, an adaptive SPGD algorithm based on energy feedback adaptation is proposed. This improved algorithm adjusts the step size adaptively based on the energy feedback value of the far-field spot, thereby accelerating convergence. Instead of requiring a specific initial step size, it only needs a defined convergence interval, allowing the initial step size to be chosen freely within this range. The proposed algorithm resolves the difficulty of initial step size selection. Simulations of 3-way, 19-way, and 37-way beam combinations demonstrate improved convergence speeds by 7.14%, 33.33%, and 42.78%, respectively, and enhanced convergence accuracy by 0.0018, 0.0016, and 0.0075, respectively, compared to the traditional algorithm. A 3-way beam combination experiment further confirms these findings, showing increases of 57.69% and 0.0297 in the convergence speed and convergence accuracy, respectively, with a final voltage increase of 0.052 V. The feasibility of the improved algorithm is validated through simulations and experiments comparing it to the traditional approach. The proposed algorithm effectively reduces system convergence time and increases beam energy, contributing valuable insights to multibeam synthesis technology.
In this study, we propose to construct topological photonic crystal resonant cavities in both horizontal and vertical directions simultaneously to obtain low-threshold and high-robustness novel lasers that provide topological protection in both directions. In the vertical direction, we designed resonant cavities based on one-dimensional topological photonic crystals: the supported longitudinal topological protection mode realizes the Zak phase flip on the topological boundaries, which creates an effective cavity feedback at the topological edge. In the horizontal direction, we designed a resonant cavity based on a two-dimensional topological photonic crystal, which realizes the light-field confinement effect via the flip between the topological state energy bands of the Γ-points and the energy bands of the tundish state. This not only confines the transverse modes supported by the cross-section of the laser to the inside of the topological photonic crystal but also allows the transverse modes to exhibit good anti-defect capability. The proposed topological photonic crystal laser offers the advantages of single mode and robustness, which is expected to further broaden the application of future lasers.
To satisfy the demand for multimode lasers source in chaos applications, the multimode output of a Fabry-Perot laser is used as the seed laser, and the nonlinear characteristics of an optoelectronic oscillation loop is used to generate multimode chaotic lasers in this study. Experimental results indicate that, compared with the conventional optoelectronic oscillation loop for generating chaotic laser, this scheme reduces the required loop gain by 3 dB, increases the full power spectra bandwidth by 3.3 GHz, and decreases the time-delay signature by approximately 80% while generating multimode chaotic lasers. Additionally, each mode exhibits broad and flat power spectra, and the correlation between modes significantly decreases as the mode spacing increases. This paper presents a new method for generating multimode chaos lasers.
All-optical flip-flops based on vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers (VCSEL) have the potential for a wide range of applications in all-optical signal processing. However, the relationship between the switching time and internal parameters of the laser has not yet been fully understood. To fill this research gap, this paper presents a systematic numerical simulation study on the polarization switching behavior of VCSEL induced by polarization optical injection with the a spin-flip model. The simulation analysis explores the influence mechanism of the internal parameters of the laser on the switching time of the all-optical flip-flop in depth. Based on this, the key parameters, namely the spin flip-flop rate and field decay rate, are further optimized to reduce the switching time and increase the flip-flop repetition frequency. Through parameter optimization, an all-optical flip-flop operation with a high repetition frequency can be achieved. Additionally, by introducing injection detuning and combining it with appropriate injection intensities, the repetition frequency of the all-optical flip-flops can be further improved.
A small amount of CeO2 powder is added to AlCoCrFeNi-TiC5/WC15 high-entropy alloy coating prepared on 316L substrate using laser cladding technology. After the addition of CeO2 powder, the wear and corrosion resistances of the coating are investigated under different environments. Scanning electron microscope, X-ray diffractometer (XRD), microhardness tester, friction and wear testing machine, electrochemical workstation, and other instruments are used to characterize the coating and test its performance. The research results show that cladding coating can form a variety of shapes of microstructure, such as flower, cellular, grape dendritic structure, etc., whereby the discovery of these microstructures provides a morphological basis for the formation of body-centered cubic (BCC), face-centered cubic (FCC), and other phases of cladding, which to a certain extent promote grain refining and improve the hardness of the coating. By addition of 2.0% CeO2 mass fraction of the cladding layer, the maximum hardness is attained, and the maximum Vickers hardness is 702.5 HV; in comparing the wear amount and friction coefficient, the coating with 2.0% CeO2 is found to provide the best wear resistance. In terms of corrosion resistance, the electrochemical corrosion performance of coatings in 3.5% NaCl solution, 1 mol/L NaOH solution, and 1 mol/L H2SO4 solution are compared, thereby finding that adding 2.0% CeO2 to the base AlCoCrFeNi-TiC5/WC15 coating provides the best corrosion resistance of the cladding layer.
Optical systems and photoelectric devices are easily damaged under high energy laser irradiation. Therefore, the laser protection of photoelectric devices is critical. Vanadium dioxide has unique phase transition characteristics, which can realize a reversible semiconductor-metal phase transition under heat and light stimulation. Simultaneously, vanadium dioxide has a low phase transition threshold, high damage threshold, and short response time, which are conducive to laser protection. To solve the problem of low infrared transmittance of a single-layer vanadium dioxide film in the semiconductor phase, a multilayer composite film system is designed and optimized. The photothermal coupling characteristics of the vanadium dioxide phase transition induced by laser are then analyzed using a finite element method, and variations in the vanadium dioxide refractive index with temperature are derived, where the transmittance of multilayer composite films is inverted according to these variations. The results show that the designed multilayer film has a transmittance and infrared switching rate of 66.81% and 75.43%, respectively, at a wavelength of 3 μm. This study expands the application of vanadium dioxide film in the field of laser protection in the middle infrared field.
This work investigates the temperature-responsive optical characteristics of vanadium oxide nanocrystals fabricated by plasma-enhanced atomic layer deposition (PEALD). Analysis of the films' absorption and ellipsoid spectra reveals a dual optical bandgap, linked to the evolving surface microstructure during film growth. Notably, variable-temperature absorption spectrum analysis shows these bandgaps respond differently to temperature shifts, revealing the microstructure's critical influence on optical performance. The research pioneers a novel method for tuning the optical properties of 2D vanadium oxide films through microstructural manipulation. This contributes to the scientific understanding and provides a foundation for developing functional films capable of dynamic dual-band light absorption regulation.
To improve the thermal performance of vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser arrays, reduce the temperature difference between individual emitting units within the device, and enhance the device's output power and light emission uniformity, a novel heat dissipation structure is proposed. This structure involves filling the transition heat sink with two materials with significantly different thermal conductivities. First, using finite element analysis software, a multigroove structure is introduced into a traditional silicon carbide transition heat sink and filled with copper-diamond and aluminum nitride materials. Subsequently, through thermal simulation analysis of the materials filled in multiple grooves and etching depths, the temperature variation in each unit in the array device with changing parameters is investigated. Finally, the structural parameters are optimized to design a new heat dissipation structure. Compared to traditional heat dissipation structures, the overall output power of the new structure device is increased by 14.2%. Simulation of the temperature distribution of the new structure encapsulating the array device reveals that the maximum temperature difference between individual emitting units is reduced from an initial 10.94 K to 0.15 K.
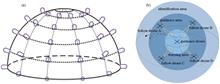
To investigate the performance of microchannel plate (MCP) image intensifiers, the electromagnetic simulation software CST Studio Suite is used to simulate and analyze the effects of changes to the parameters of MCP image enhancers on their gain and spatial resolution. Simulation results show that the working voltage of MCP has the greatest effect on MCP gain, and an increase in working voltage causes the gain to increase exponentially. Changes to the phosphor screen voltage and bias angle significantly affect spatial resolution. An increase in phosphor screen voltage significantly improves spatial resolution, but an increase in bias angle leads to a significant decrease in spatial resolution. The gain and spatial resolution of the MCP image intensifier can reach a relatively ideal theoretical simulation result when the working voltage, phosphor screen voltage, bias angle, and depth of the output electrode are 890 V, 6000 V, 5°, and 0.021 mm, respectively. These results provide a good reference for designing MCP image enhancers with better performance.
An integrated, high-precision time-of-flight (TOF) readout circuit for terahertz (THz) radar was designed to perform high-precision TOF measurements of THz radar in target detection, imaging, and other applications. Based on an in-depth analysis of the TOF readout mechanism of THz radar, a high-speed comparator circuit, time-to-digital converter circuit, and field-programmable gate array circuit were designed to realize the effective digitization of THz detector response signals, accurate time-to-digital conversion of TOF information, and efficient control and data transmission of readout circuits. A high-precision arbitrary waveform generator was utilized to calibrate the readout circuit and verify its linearity, accuracy, and stability. The experimental results show that the present readout circuit exhibits excellent linearity and stability, with a resolution of 45 ps over the measurement range of 0.1 μs to 1.5 μs and a TOF measurement accuracy that is better than 40 ps, thus satisfying the application requirements of THz radar.
Air pressure imbalance on the wingtips generates rotating airflows behind the aircraft, known as aircraft wake vortices, leading to variations in the frequency of reflected waves. The signal can be detected using Doppler lidar, but it is intrinsically weak in nature and requires new detection technologies. Hence, this paper studies the distribution and detection feasibility of aircraft wake vortices during the cruising phase. An Airbus A330 and two types of fighter jets are used as examples. The decay pattern and spatial distribution characteristics of wake vortices are also calculated. Furthermore, the wake vortex detection model discussed in this paper is based on lidar and presents the relationship between aircraft wake vortex characteristics and radar echo signals. Therefore, the identification and judgment of wake vortices are achievable. The findings of this paper provide a method and basis for the detection and identification of flight characteristics of aircraft during the cruising phase.
Tunable integrated narrow linewidth external cavity semiconductor lasers exhibit many advantages, including small size, wide tuning range, single mode, large side mode suppression ratio, and high output power. Furthermore, they have been widely used in coherent optical communications, wavelength division multiplexing systems, coherent detection, and ultrahigh-speed optical interconnects. This article introduces the development of the operating principle of narrow linewidth semiconductor external cavity lasers in detail and comparatively analyzes the performance and design ideas of integrated external cavity lasers on current mainstream platforms. Finally, we explore the development of tunable narrow linewidth semiconductor lasers based on passive external cavities and discuss their future prospects in the mid-infrared band.
Distributed fiber-optic sensing technology can detect system parameters such as temperature, strain, and vibration by demodulating the change in scattered light in optical fiber to achieve distributed measurement. The weak scattered-light signal results in low signal-to-noise ratios for a system and limited sensing performance. In recent years, researchers have focused on enhancing the performance of distributed fiber-optic sensing systems using machine learning. Herein, from the perspectives of data extraction, noise removal, and resolution enhancement, the progress of machine-learning technology in the research and development of distributed fiber-optic sensing in the past decade is described comprehensively, and an analysis and comparison with technology outlook is performed. Different types of machine-learning techniques offer different degrees of improvement to the processing speed. Among them, denoising neural networks are more effective in improving the signal-to-noise ratio, as shown by their superior noise suppression and ability to further improve the signal quality. Additionally, convolutional neural networks are outstanding in terms of improving spatial resolutions and can capture and resolve complex spatial features more accurately. These results are expected to further promote the subsequent in-depth application of machine-learning techniques to various distributed fiber-optic sensing technologies.
Photodetectors have important value in applications such as detection, communication, imaging, and guidance. In the infrared band, commonly used detectors include mercury-cadmium-telluride detectors, quantum-well detectors, and type-II superlattice detectors. However, owing to differences in the operation temperature, noise, and dark current, the development and application of various detectors are limited. Meanwhile, quantum cascade detector (QCD) can achieve the directional transport of photogenerated carriers without the need for bias voltage utilizing the principles of intersubband transition and resonant tunneling as well as the phonon ladder design concept. QCD is characterized by low dark current, excellent noise performance, outstanding high-frequency performance, and a detection wavelength range spanning from infrared to terahertz bands, offering innovative pathways for the future development of infrared and terahertz photodetectors. This article initially examines the working principles, models, and device physics of QCD. It then emphasizes on recent research developments domestically and internationally, including advancements in material systems, optical coupling optimization, active region design and optimization, and the synergistic integration of QCD with quantum cascade lasers. Furthermore, a comparative analysis of QCDs and other mainstream infrared detectors is presented. Finally, the future opportunities and challenges of QCD are summarized and discussed.
This study aims to compare the detection performances of five portable Raman spectrometers (PRSs) applied in the field of forensic science. Through an in-depth analysis of the five PRSs and a comparison with a benchtop Raman spectrometer (BRS),this study compares the performances,functional advantages,and limitations of the PRSs. The research results show significant quality differences among the five PRSs in terms of various key indicators. Products B and C have the best overall quality; however, product B has a lower output speed, and product C lacks spectral resolution. product A performs well in terms of hardware parameters. Products D and E require further optimization of instrumental performance compared to similar products. The spectral resolution of the BRS is excellent; however,the PRS is more practical in the analytical direction of this study. This study not only provides a reference for the quality supervision of related PRS products in the field of forensic science but also indicates the direction for optimizing and upgrading related products in the future.
Knives is one of the most common types of physical evidence found at crime scenes, and establishing an accurate method for classifying them is of paramount importance. In this experiment, a laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) analyzer is used to detect 138 types of knife samples, resulting in 2760 training data sets and 276 prediction data sets. After preprocessing, principal component analysis is employed to reduce the dimensionality of both the training and prediction datasets, retaining the top 400 principal components with a cumulative variance contribution rate of 81%. The dimensionality-reduced data are then fed into one-dimensional convolutional neural network (1D-CNN) model for training and prediction. After 200 iterations, the average prediction accuracy reaches 96.02%. To further improve the prediction accuracy, additional data augmentation is performed based on the spectral features of the data using methods involving normal distribution and linear combination to generate additional 40, 80, and 120 data sets for each sample. Comparative experiments are conducted to investigate the impact of different data augmentation methods and quantities on the performance of the 1D-CNN model. Finally, using the normal distribution method, the model's predictive accuracy gradually increases with the increase in synthetic data volume, reaching a maximum of 97.46%. The study demonstrates that a combination of LIBS spectroscopy, 1D-CNN models, and data augmentation using the normal distribution method can effectively achieve precise identification of knife samples, thereby providing valuable clues for investigation and case resolution.
To solve the effect of redundant information caused by high-dimensional Raman-spectrum data on the rapid and accurate identification of the aging state of transformer oil-paper insulation, a Raman-spectrum feature-extraction method for oil-paper insulation based on local linear embedding is proposed. An accelerated thermal-aging experiment was performed to obtain 100 groups of oil-paper insulation samples at different aging stages. The samples were classified into 10 categories based on the polymerization degree of the insulation paper, and Raman spectroscopy was performed on the samples. The conventional principal component analysis (PCA) and locally linear embedding (LLE) feature-extraction methods were used to extract features from the Raman spectrum. Adaboost was introduced to build a discrimination model, and the aging status of the two feature-extraction results was discriminated. Next, the subsequent discrimination accuracy of the two feature-extraction methods was compared. The results show that the discrimination accuracies of the Raman-spectrum samples after feature extraction using LLE and PCA are 98.8% and 90.2%, respectively, which proves that LLE feature extraction offers a greater discrimination accuracy and facilitates subsequent discrimination. The identified spectral information reflects the data simplification and accurate discrimination of oil-paper insulation Raman-spectrum samples via LLE feature extraction combined with the Adaboost discrimination model, which has practical engineering significance for the aging discrimination of transformer oil-paper insulation.
This paper selected yellow, yellow-green and green pyromorphite samples from Guilin, Guangxi to explore the origin of their colors. The composition and color genesis of samples are analyzed by X-ray powder diffraction, electron probe microanalysis, laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer, fluorescence spectrometer and ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometer. Results show that the main chemical components of pyromorphite are Pb, P and Cl, which have a wide range of isomorphism: Cl can be partially replaced by F; P can be substituted by Si, V, and S; Pb is easily replaced by metal cations and rare earth elements. The replacement of rare earth elements will slightly increase the cell size of samples. The ultraviolet-visible absorption spectra show that the wide absorption band at 468 nm wavelength caused by rare earth element Pr, the weak absorption peak at 644 nm wavelength caused by Er3+, and the wide and slow absorption band at 742?808 nm wavelength caused by Nd are the main reasons for the coloration of the sample. Rare earth elements Dy and Sm also have a certain influence on the color of samples. Usually, the higher the content of Dy and Sm, the easier the sample to appear yellow. Fluorescence spectra show that the rare earth element Er also has a certain influence on the color. Although Er3+ could not determine the hue of the sample, it has a certain strengthening effect on the saturation of the sample color.
To explore the effectiveness of spectral indices (SIs) combined with continuous wavelet transform (CWT) in soil organic carbon (SOC) inversion, difference indices (DI), ratio indices (RI), normalized difference indices (NDI), and re-normalized difference indices (RDI) are applied to process spectral data along with CWT for 61 soil samples from Deming Town in northeastern Germany. Through the analysis of two-dimensional correlation between these indices and wavelet coefficient and SOC content, the top 20 bands with the highest correlation in SIs and wavelet coefficients are selected. Models for SOC content inversion are constructed using input variables of original full spectrum (OR), SIs, CWT, and SIs+CWT, coupled with support vector machine (SVM), random forest (RF), and back propagation artificial neural network (BPANN) algorithms. Results indicate that after processing by SIs and CWT, spectral data have an increase in correlation coefficients by ~0.17 and ~0.14 compared to the original spectrum. Among the machine learning models, the BPANN exhibites the best model accuracy. Among the four input variables, the SIs+CWT-BPANN model demonstrates the best validation performance, whose coefficient of determination is 0.95, root mean square error is 2.13 g/kg, and relative analysis error is 4.67, indicating that the optimal feature coupling machine learning method combining SIs and CWT can improve the estimation accuracy of SOC content. This study offers a fresh perspective on accurately estimating SOC content, which holds critical significance in evaluating both soil quality and crop yield.