View fulltext
View fulltext
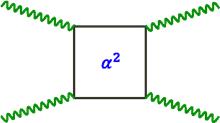
Quantum field theory predicts a nonlinear response of the vacuum to strong electromagnetic fields of macroscopic extent. This fundamental tenet has remained experimentally challenging and is yet to be tested in the laboratory. A particularly distinct signature of the resulting optical activity of the quantum vacuum is vacuum birefringence. This offers an excellent opportunity for a precision test of nonlinear quantum electrodynamics in an uncharted parameter regime. Recently, the operation of the high-intensity Relativistic Laser at the X-ray Free Electron Laser provided by the Helmholtz International Beamline for Extreme Fields has been inaugurated at the High Energy Density scientific instrument of the European X-ray Free Electron Laser. We make the case that this worldwide unique combination of an X-ray free-electron laser and an ultra-intense near-infrared laser together with recent advances in high-precision X-ray polarimetry, refinements of prospective discovery scenarios and progress in their accurate theoretical modelling have set the stage for performing an actual discovery experiment of quantum vacuum nonlinearity.
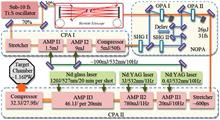
This paper provides an overview of the current status of ultrafast and ultra-intense lasers with peak powers exceeding 100 TW and examines the research activities in high-energy-density physics within China. Currently, 10 high-intensity lasers with powers over 100 TW are operational, and about 10 additional lasers are being constructed at various institutes and universities. These facilities operate either independently or are combined with one another, thereby offering substantial support for both Chinese and international research and development efforts in high-energy-density physics.
The propagation of multiple ultraintense femtosecond lasers in underdense plasmas is investigated theoretically and numerically. We find that the energy merging effect between two in-phase seed lasers can be improved by using two obliquely incident guiding lasers whose initial phase is $\pi$ and $\pi /2$ ahead of the seed laser. Particle-in-cell simulations show that due to the repulsion and energy transfer of the guiding laser, the peak intensity of the merged light is amplified by more than five times compared to the seed laser. The energy conversion efficiency from all incident lasers to the merged light is up to approximately 60 $\%$ . The results are useful for many applications, including plasma-based optical amplification, charged particle acceleration and extremely intense magnetic field generation.
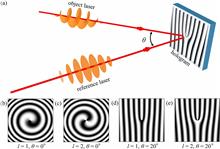
With the escalating laser peak power, modulating and detecting the intensity, duration, phase and polarization of ultra-intense laser pulses progressively becomes increasingly arduous due to the limited damage thresholds of conventional optical components. In particular, the generation and detection of ultra-intense vortex lasers pose great challenges for current laser technologies, which has limited the widely potential applications of relativistic vortex lasers in various domains. In this study, we propose to reconstruct the vortex phase and generate and amplify the relativistic vortex lasers via surface plasma holograms (SPHs). By interfering with the object laser and reference laser, SPHs are formed on the target and the phase of the interfering laser is imprinted through the modulation of surface plasma density. In particular, using the quadrature phase-shift interference, the vortex phase of the object laser can be well reconstructed. The generated vortex lasers can be focused and enhanced further by one order of magnitude, up to $1.7\times {10}^{21}$ W/cm ${}^2$ , which has been demonstrated by full three-dimensional particle-in-cell simulations. For the first time, we provide a practical way to detect the phase of relativistic vortex lasers, which can be applied in large 1–10 PW laser facilities. This will promote future experimental research of vortex-laser–plasma interaction and open a new avenue of plasma optics in the ultra-relativistic regime.
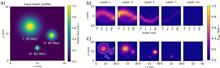
Low-density polymer foams pre-ionized by a well-controlled nanosecond pulse are excellent plasma targets to trigger direct laser acceleration (DLA) of electrons by sub-picosecond relativistic laser pulses. In this work, the influence of the nanosecond pulse on the DLA process is investigated. The density profile of plasma generated after irradiating foam with a nanosecond pulse was simulated with a two-dimensional hydrodynamic code, which takes into account the high aspect ratio of interaction and the microstructure of polymer foams. The obtained plasma density profile was used as input to the three-dimensional particle-in-cell code to simulate energy, angular distributions and charge carried by the directional fraction of DLA electrons. The modelling shows good agreement with the experiment and in general a weak dependence of the electron spectra on the plasma profiles, which contain a density up-ramp and a region of near-critical electron density. This explains the high DLA stability in pre-ionized foams, which is important for applications.
We present coherent beam combining of nanosecond pulses with 20-J energy and large beams using a Sagnac interferometer geometry based on Nd:glass rod-type amplifiers. In this study, we demonstrate that coherent beam combining is compatible with large-diameter energetic beams, presenting, therefore, an interesting and solid perspective towards the performance improvement of large-scale laser facilities, especially in terms of high-repetition-rate and high-energy operation. We demonstrate that for energy of 20 J, the coherent combination efficiency is around 92%, with high beam quality and long-term stability. A thorough temporal and spatial characterization of the system’s operation is provided to forecast the various potentialities available for large-scale facilities.
Based on a 4f system, a 0° reflector and a single laser diode side-pump amplifier, a new amplifier is designed to compensate the spherical aberration of the amplified laser generated by a single laser diode side-pump amplifier and enhance the power of the amplified laser. Furthermore, the role of the 4f system in the passive spherical aberration compensation and its effect on the amplified laser are discussed in detail. The results indicate that the amplification efficiency is enhanced by incorporating a 4f system in a double-pass amplifier and placing a 0° reflector only at the focal point of the single-pass amplified laser. This method also effectively uses the heat from the gain medium (neodymium-doped yttrium aluminium garnet) of the amplifier to compensate the spherical aberration of the amplified laser.
Time-domain characterization of ultrashort pulses is essential for studying interactions between light and matter. Here, we propose and demonstrate an all-optical pulse sampling technique based on reflected four-wave mixing with perturbation on a solid surface. In this method, a weak perturbation pulse perturbs the four-wave mixing signal generated by a strong fundamental pulse. The modulation signal of the four-wave mixing, which is detected in the reflection geometry to ensure a perfect phase-matching condition, directly reflects the temporal profile of the perturbation pulse. We successfully characterized multi-cycle and few-cycle pulses using this method. The reliability of our approach was verified by comparing it to the widely employed frequency-resolved optical gating method. This technique provides a simple and robust method for characterizing ultrashort laser pulses.
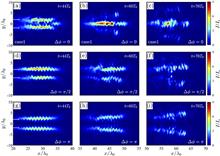
The effect of the polarizations of two counter-propagating relativistic laser pulses interacting with subwavelength thin solid-density foil is investigated. Three-dimensional particle-in-cell simulations and analytical modelling show that the interaction and resulting transverse instability depend strongly on the polarization directions as well as the intensity distribution of the resultant light field in the foil. The left- and right-handed circularly polarized laser pair with the same phase at the common focal spot in the ultrathin foil leads to the strongest distortion of the foil. The fastest growing mode and maximum growth rate depend mainly on the laser intensity. For all polarization and phase-difference combinations, the instability is weakest when the two laser pulses are exactly out of phase at the common focusing point in the foil.
We present an innovative design for a two-head, gas-cooled multi-slab high-energy, high-repetition-rate amplifier aimed at mitigating thermally induced depolarization in a wide-bandwidth neodymium-doped glass gain medium. This architecture employs two quartz rotators (QRs) with opposite-handedness, strategically positioned within each multi-slab amplifier head, to enhance depolarization compensation. Theoretical modeling of this amplifier configuration demonstrates a 20× reduction in depolarization losses for a 70 mm beam operating at the central wavelength, compared to conventional approaches that utilize a single QR positioned between the amplifier heads. In addition, for a wide bandwidth source, the integration of QRs with opposite-handedness yields a 9× improvement in depolarization losses at the spectral extremes compared to the use of two QRs exhibiting the same optical handedness in both amplifier heads.
We used the PW high-repetition laser facility VEGA-3 at Centro de Láseres Pulsados in Salamanca, with the goal of studying the generation of radioisotopes using laser-driven proton beams. Various types of targets have been irradiated, including in particular several targets containing boron to generate α-particles through the hydrogen–boron fusion reaction. We have successfully identified γ-ray lines from several radioisotopes created by irradiation using laser-generated α-particles or protons including 43Sc, 44Sc, 48Sc, 7Be, 11C and 18F. We show that radioisotope generation can be used as a diagnostic tool to evaluate α-particle generation in laser-driven proton–boron fusion experiments. We also show the production of 11C radioisotopes, $\approx 6 \times 10^{6}$ , and of 44Sc radioisotopes, $\approx 5 \times 10^{4}$ per laser shot. This result can open the way to develop laser-driven radiation sources of radioisotopes for medical applications.