View fulltext
View fulltext
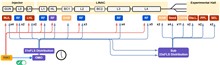
This paper presents a detailed technical overview of the femtosecond precision timing and synchronization systems implemented at the Shanghai high repetition rate XFEL and extreme light facility (SHINE). These systems are designed to deliver stabilized optical references to multiple receiver clients, ensuring high-precision synchronization between the optical master oscillator (OMO) and optical/RF subsystems. The core components include an OMO, fiber length stabilizers and laser-to-laser synchronization modules that achieve femtosecond-level accuracy. Our discussion extends to the various subsystems that comprise the synchronization infrastructure, including the OMO, fiber length stabilizer and advanced phase detection techniques. Finally, we highlight ongoing research and development efforts aimed at enhancing the functionality and efficiency of these systems, thereby contributing to the advancement of X-ray free-electron laser technology and its applications in scientific research.
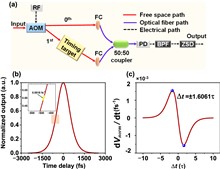
We presented an attosecond-precision timing detector based on linear optics. The minimum measurement floor is 1×10–10 fs2/Hz with only 1 mW input optical power. With this novel technique, the residual dispersion of a 5.2 km fiber link is characterized and precisely compensated. Finally, a comprehensive feedback model has been developed to analyze the noise coupling in a long-distance link stabilization system. The simulation results demonstrate an out-of-loop jitter of merely 359 as, integrated at [1 Hz, 1 MHz], at 1 mW input power per photodetector of our timing detector. Remarkably, the system is capable of maintaining sub-femtosecond precision even at optical power levels as low as 240 nW (for a 5.2 km link length), or link lengths as long as 20 km (with 1 μW optical power), respectively.
Nonlinear optical gain modulation (NOGM) is an effective approach for generating highly coherent femtosecond Raman pulses. In a typical NOGM system, the pump pulse energy boosting unit and nonlinear frequency conversion unit are separated, which poses a difficulty in generating Raman solitons with pulse energy over the μJ level. Here, we demonstrate an integrated ultrafast ytterbium-Raman fiber amplifier, which accomplishes pump pulse amplification and Raman pulse conversion simultaneously in ytterbium-doped fiber (YDF). The integrated ytterbium-Raman fiber amplifier could generate approximately 1 μJ 1121 nm Raman pulses with a pulse duration of 589 fs under a conversion efficiency of 69.9%. The result represents the highest pulse energy experimentally recorded in NOGM systems. Simulation further reveals that YDF gain could promote Raman conversion efficiency and reduce nonlinear chirp accumulation, which leads to improved performance of generated Raman pulses. Meanwhile, the feasibility of generating 10 μJ level Raman pulses using such a hybrid gain setup was also confirmed numerically.
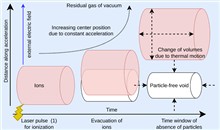
Ultra-intense lasers can generate the strongest electromagnetic fields in laboratory conditions, and are expected to perform tests of quantum electrodynamics (QED) in yet unexplored parameter ranges. Such experiments require knowledge of the field strengths and all possible interaction pathways. The latter can be simplified if a perfect, particle-free vacuum is present, thereby excluding competing interactions. We propose a method to evacuate all residual gas particles prior to QED interactions, based on tunnel ionization by a preceding auxiliary laser pulse and a static electric field. We present modelling and experimental results of testing this method on a $0.5\;\mathrm{TW}$ chirped pulse amplification laser system. Experimental results match well the simulations for the given conditions and thereby provide valuable understanding to extrapolate this method for QED experiments with PW-class laser systems where it can likewise be employed for in situ peak field strength characterization.
We report the characterization of the pump absorption and emission dynamic properties of a $\mathrm{Tm}:{\mathrm{Lu}}_2{\mathrm{O}}_3$ ceramic lasing medium using a three-mirror folded laser cavity. We measured a slope efficiency of 73%, which allowed us to retrieve the cross-relaxation coefficient. The behavior of our system was modeled via a set of macroscopic rate equations in both the quasi continuous wave and the pulsed pumping regime. Numerical solutions were obtained, showing a good agreement with the experimental findings. The numerical solution also yielded a cross-relaxation coefficient in very good agreement with the measured one, showing that the cross-relaxation phenomenon approaches the maximum theoretical efficiency.
Measurements of the bunch arrival times at the European X-ray free-electron laser show noise contributions in the spectral range between 0.05 and 0.5 Hz with peak-to-peak jitter of up to 25 fs. Correlation with distributed acoustic sensing measurements confirms the seismic origin. The seismic noise in this frequency band is known to be ocean-generated microseism. Both primary and secondary ocean-generated microseisms were identified using seismometers and a numerical ocean wave model. Whereas secondary microseism has a strong impact on the bunch arrival time, primary microseism has no notable effect. Rayleigh waves cause the effect, while Love waves have minimal impact. In the presented cases, the noise originates from the North Atlantic and/or the North Sea. The amplitude of the noise depends on the local weather conditions and is much stronger in winter. Ocean-generated microseism is a significant bottleneck that must be addressed to achieve femtosecond bunch arrival time stability in the sub-Hz regime.
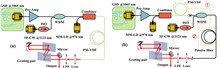
We propose a B-integral management strategy for manipulating the nonlinear effects by employing a discrete single-crystal fiber (SCF) configuration, enabling direct amplification of 2-μm femtosecond pulses at high repetition rates without additional pulse picking, stretching and compression. The system delivers an average power of more than 56 W at 75.45 MHz with extremely high extraction efficiency (>55%) and near-diffraction-limited beam quality (M2 < 1.2). The dynamic evolution of the optical spectra and temporal properties in the power amplifier reveals that detrimental nonlinear effects are largely suppressed due to the low accumulated nonlinear phase shift in the discrete SCF layout. This straightforward, compact and relatively simple approach is expected to open a new route to the amplification of 2-μm ultrashort pulses at MHz and kHz repetition rates to achieve high average/peak powers, thereby offering exciting prospects for applications in modern nonlinear photonics.
High gain greater than 106 is crucial for the preamplifiers of joule-class high-energy lasers. In this work, we present a specially designed compact amplifier using 0.5%Nd,5%Gd:SrF2 and 0.5%Nd,5%Y:SrF2 crystals. The irregular crystal shape enhances the gain length of the laser beam and helps suppress parasitic oscillations. The amplified spontaneous emission (ASE) induced by the high gain is analyzed through ray tracing. The balance between gain and ASE is estimated via numerical simulation. The gain spectral characteristics of the two-stage two-pass amplifier are examined, demonstrating the advantages of using different crystals, with bandwidths up to 8 nm and gains over 106. In addition, the temperature and stress distributions in the Nd,Gd:SrF2 crystal are simulated. This work is expected to contribute to the development of high-peak-power ( $\ge$ terawatt-class) high-energy (joule-class) laser devices.
A dual-beam platform is developed for all-optical Thomson/Compton scattering, with versatile parameter tuning capabilities including electron energy, radiation energy, radiation polarization, etc. By integrating this platform with a 200 TW Ti:sapphire laser system, we demonstrate the generation of inverse Compton scattering X-/gamma-rays with tunable energies ranging from tens of keV to MeV. The polarization of X-/gamma-rays is manipulated by adjusting the polarization of the scattering laser. In the near future, by combining this platform with multi-PW laser facilities, our goal is to explore the transition from nonlinear Thomson scattering to nonlinear Compton scattering, ultimately verifying theories related to strong-field quantum electrodynamics effects induced by extreme scattering.
The generation of intense radio-frequency and microwave electromagnetic pulses (EMPs) by the interaction of a high-power laser with a target is an interesting phenomenon, the exact mechanisms of which remain inadequately explained. In this paper we present a detailed characterization of the EMP emission at a sub-nanosecond kilojoule laser facility, the Prague Asterix Laser System. The EMPs were detected using a comprehensive set of broadband diagnostics including B-dot and D-dot probes, various antennas, target current and voltage probes and oscilloscopes with 100 and 128 GS/s sampling. Measurements show that the EMP spectrum was strongly dependent on the laser energy: the maximum frequency of the spectrum and the frequency of the spectrum centroid increased with increasing laser beam energy in the signals from all detectors used. The highest observed frequencies exceeded 9 GHz. The amplitude and energy of the detected EMP signals were scaled as a function of laser energy, power and number of emitted electrons.
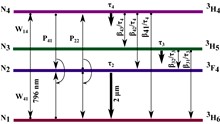
An all-silica-fiber thulium-doped fiber laser emitting at 0.82 μm on the transition from 3H4 to the ground state 3H6 outputs 105 W continuous-wave power and 555 W quasi-continuous-wave instantaneous power with 0.96% duty cycle in 240 μs rectangular pulses. The system comprises a double-clad thulium-doped fiber designed and fabricated in-house, incorporated into an all-fiber cavity and cladding-pumped by diode lasers at 0.79 μm. Co-lasing at 1.9 μm counteracts population trapping in 3F4. The slope efficiency reaches 64% and 77.5% under quasi-continuous-wave and continuous-wave operations, respectively. Under quasi-continuous-wave conditions, the beam quality M2 becomes 2.2 (beam parameter product: 0.57 mm mrad) and 2.45 (0.64 mm mrad) in orthogonal directions at approximately 250 W of instantaneous output power. In addition, a modified quasi-continuous-wave setup is continuously wavelength-tunable from 812 to 835 nm. We believe this is the first reported demonstration of high-power laser operation of the 3H4 → 3H6 transition in a thulium-doped fiber.
A reduced dispersion relation for multibeam laser–plasma instability is derived. The dispersion relation includes the combined effects of self-coupling and interaction with other beams by sharing a common scattered light (SL modes) and by sharing a common plasma wave (SP modes). The latter two have the most prominent collective effects of all. We have solved the dispersion relation numerically for stimulated Raman scattering, and set different beam configurations and polarizations to discuss the spatial distributions of the temporal growth rate. The instability in the beam overlapping region is complicated, but there are still a few simple rules that govern the system, such as the dominancy of SL modes and subdominancy of backscattering and SP modes. The maximum growth rate always occurs at these special modes, or a new mode formed by combining two or three of the special modes. The reduced model provides us with the ability to understand the underlying physics of multibeam instabilities under general laser and plasma conditions.
We present a fully three-dimensional kinetic framework for modeling intense short pulse lasers interacting with dielectric materials. Our work modifies the open-source particle-in-cell code EPOCH to include new models for photoionization and dielectric optical response. We use this framework to model the laser-induced damage of dielectric materials by few-cycle laser pulses. The framework is benchmarked against experimental results for bulk silica targets and then applied to model multi-layer dielectric mirrors with a sequence of simulations with varying laser fluence. This allows us to better understand the laser damage process by providing new insight into energy absorption, excited particle dynamics and nonthermal excited particle distributions. We compare common damage threshold metrics based on the energy density and excited electron density.
High-power 808 nm vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser (VCSEL) chips have unique characteristics for neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet (Nd:YAG) laser pumping compared with conventional edge-emitting laser bars, including a chip surface with high reflectivity, near flat top distribution in the near field, larger emitting width and smaller divergence. A novel symmetrical pump cavity with an inter-reflective chamber was invented by introducing even-numbered pumping geometry and removing the conventional internal reflector. Several optical tuning measures were taken to improve the uniformity of the pumping distribution, including power and spectrum balancing in the cross-section and the long axis of the laser rod, a diffuse mechanism in the pump chamber by a frosted flow tube and optional eccentric pumping geometry. A series of VCSEL pumping experiments were conducted and optical tuning measures were evaluated through distribution profiles and efficiencies. A new design philosophy for the VCSEL side-pumped Nd:YAG laser cavity was finally developed.
Coherent beam combining (CBC) of laser arrays is increasingly attracting attention for generating free-space structured light, unlocking greater potential in aspects such as power scaling, editing flexibility and high-quality light field creation. However, achieving stable phase locking in a CBC system with massive laser channels still remains a great challenge, especially in the presence of heavy phase noise. Here, we propose an efficient phase-locking method for a laser array with more than 1000 channels by leveraging a deep convolutional neural network for the first time. The key insight is that, by elegantly designing the generation strategy of training samples, the learning burden can be dramatically relieved from the structured data, which enables accurate prediction of the phase distribution. We demonstrate our method in a simulated tiled aperture CBC system with dynamic phase noise and extend it to simultaneously generate orbital angular momentum (OAM) beams with a substantial number of OAM modes.
Fiber-coupled laser pumps with low size, weight and power consumption (SWaP) have become more and more compelling for applications in both industrial and defense applications. This study presents an innovative approach employing the spectral beam combining technique and double-junction laser diode chips to create efficient, high-power, high-brightness fiber-coupled packages. We successfully demonstrated a wavelength-stabilized pump module capable of delivering over 560 W of ex-fiber power with an electro-optical conversion efficiency of 55% from a 135 μm diameter, 0.22 numerical aperture fiber. The specific mass and volume metrics achieved are 0.34 $\mathrm{kg}/\mathrm{kW}$ and 0.23 ${\mathrm{cm}}^3/\mathrm{W}$ , respectively. The module exhibits a stabilized spectrum with a 3.6 nm consistent interval of two spectral peaks and a 4.2 nm full width at half maximum across a wide range of operating currents.
A broadband, antireflective metasurface optic on a silica substrate is subjected to laser-induced damage-threshold measurements to quantify its performance under exposure to high-intensity/fluence laser pulses in the near-infrared at four pulse durations, ranging from 20 fs to 1.4 ns. The performance of the metasurface is benchmarked against that obtained from an equivalent bare fused-silica substrate that did not receive reactive-ion-etching metasurface treatment. Results showed that the damage threshold of the antireflective metasurface was always lower than the input-surface damage threshold of the untreated substrate. The damage initiations with nanosecond and picosecond pulses resulted in localized modification and removal of the nanostructures, whereas the onset of laser-induced modification with 20-fs pulses in a vacuum environment manifested as changes in the optical and electronic properties without significant material removal. The broader goal of this work is to develop a preliminary understanding of the laser-induced failure mechanisms of silica-based metasurface optics.
A technique developed to accurately simulate the amplification of back-reflected light through a multi-petawatt laser system is presented. Using the Frantz–Nodvik equation, we developed an iterative algorithm to simulate the amplification of the main beam as it propagates through solid-state multipass amplifiers, while also accounting for back-reflections from experimental targets and the residual gain within the crystals. Our technique builds on the theoretical model by estimating the energy levels after multiple passes through all amplifiers and refining the simulated data using a brute-force optimization algorithm. We also demonstrate an application of this tool aimed at evaluating machine safety: optimizing the laser system to minimize crystal gain in the post-pulse regime and, consequently, the amplification of back-reflections, while taking advantage of the B-integral.
 EditorialErratumLetterPerspectiveregular articlesreviewReviewsLettersResearch ArticlesCommentaryCorrigendum
Special Issues
EditorialErratumLetterPerspectiveregular articlesreviewReviewsLettersResearch ArticlesCommentaryCorrigendum
Special Issues