View fulltext
View fulltext
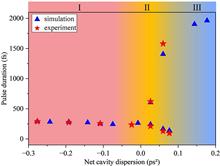
We demonstrate the sub-100 fs pulse generation from a dispersion-managed mode-locked Er:ZBLAN fiber laser at 2.8 μm. Both numerical simulation and experiment demonstrate that stretched-pulse and dissipative soliton mode lockings coexist in the near-zero-dispersion region of a fluoride fiber laser. With fine dispersion management, the shortest pulse of 95 fs was obtained from the stretched-pulse mode-locked Er:ZBLAN fiber laser, with an average power of 280 mW and repetition rate of 52 MHz. To the best of our knowledge, this is the shortest pulse to date directly generated from a mid-infrared mode-locked fluoride fiber laser.
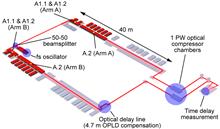
Simultaneous ultra-intense pulses at petawatt laser facilities enable a broad range of experiments in nuclear photonics and strong field quantum electrodynamics. These experiments often require very precise control of the time delays between pulses. We report measurements of the time delay between the two 1 PW outputs of the Extreme Light Infrastructure - Nuclear Physics (ELI-NP) facility in Romania. The short-term standard deviation of the time delay was approximately half of the pulse duration of 23 fs, and the average delay drifted with up to 100 fs/h. The drift and sporadic delay jumps were corrected using a feedback loop, which reduced the long-term standard deviation of the delay close to its short-term value. These results imply that in ELI-NP experiments using two simultaneous pulses, a temporal overlap of better than half of the pulse duration can be achieved for more than two thirds of the shots, which would enable high data rate experiments using simultaneous petawatt pulses.
Suppressing mode degradation is the key issue for high-power laser delivery; however, diagnosing mode degradation in its entirety, ranging from the contents and origins to locations, has always been a major obstacle. Here, a versatile approach for tracing the origins of mode coupling is demonstrated through addressing the differential intermodal dispersions of fiber modes. Full recognition for modal contents and the origins of mode degradation are experimentally completed in a two-mode fiber laser delivery system, which assists a significant improvement of beam quality M2 from 1.35 to 1.15 at the highest power of over 300 W. This method yields a quantitative characterization for manipulating the individual mode of dual-mode coupling origins or their combinations. This work points toward a promising strategy for the online tracing of mode coupling in cascade fiber links, thus enabling further pursuit of seeking extreme beam quality in high-power fiber laser systems.
Thin-film beam combining technology is an effective approach to improve output power while maintaining beam quality. However, the lack of comprehensive research into the key factors affecting the beam quality in systems makes it challenging to achieve a practical combined beam source with high brightness. This paper clearly established that the temperature rise of dichroic mirrors (DMs) and sub-beam overlapping precision are the main factors affecting the beam quality of the system, with quantified effects. Based on this understanding, a combined light source of four channels of 3 kW fiber lasers was achieved, and an output power of 11.4 kW with a beam quality of M2x = 1.601 and M2y = 1.558, using three high-steepness low-absorption DMs and the active control technique. To the best of our knowledge, this is the best beam quality for a 10 kW light source. This study offers a solution for practical high-power laser sources in the tens of kilowatts range.
We report on an improved ytterbium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet thin-disk multi-pass amplifier for kilowatt-level ultrafast lasers, showcasing excellent beam quality. At a repetition rate of 800 kHz, the 6.8 ps, 276 W seed laser is amplified up to an average power of 1075 W, corresponding to a pulse energy of 1.34 mJ. The 36-pass amplifier is designed as a compact mirror array in which the beam alternately propagates between the mirrors and the disk by a quasi-collimated state. We adopted a quasi-collimated propagation to confine stray and diffracted light by the slight curvature of the disk, which enables us to achieve an outstanding extraction efficiency of up to 57% with excellent beam quality in stable laser operation at high power. The beam quality at 1075 W was measured to be M2 < 1.51. Furthermore, stability testing was demonstrated with a root-mean-square power fluctuation of less than 1.67% for 10 min.
Real-time evaluation of laser-driven byproducts is crucial for state-of-the-art facilities operating at high repetition rates. This work presents real-time measurements of hard X-rays (bremsstrahlung radiation) generated from the interaction of high-intensity laser pulses with solid targets in the target normal sheath acceleration regime using a scintillator stack detector. The detector offers insights into the effectiveness of laser–plasma interaction through measured fluctuations in bremsstrahlung radiation temperature and scintillation light yield on a shot-to-shot basis. Moreover, a strong correlation of the bremsstrahlung measurements (i.e., temperature and yield) with the cutoff energy of laser-driven protons was observed. The scintillator stack detector serves not only as a diagnostic for online monitoring of the laser–plasma interaction but also as a promising tool for estimating proton energy fluctuations in a non-disruptive manner, which is particularly important when direct proton source characterization is impractical, for example, during experiments aimed at irradiating user samples with the accelerated proton beam.
Blast waves have been produced in solid target by irradiation with short-pulse high-intensity lasers. The mechanism of production relies on energy deposition from the hot electrons produced by laser–matter interaction, producing a steep temperature gradient inside the target. Hot electrons also produce preheating of the material ahead of the blast wave and expansion of the target rear side, which results in a complex blast wave propagation dynamic. Several diagnostics have been used to characterize the hot electron source, the induced preheating and the velocity of the blast wave. Results are compared to numerical simulations. These show how blast wave pressure is initially very large (more than 100 Mbar), but it decreases very rapidly during propagation.
X-ray frequency combs (XFCs) are of great interest in many scientific research areas. In this study, we investigate the generation of high-power tunable XFCs at the Shanghai soft X-ray Free-Electron Laser facility (SXFEL). To achieve this, a chirped frequency-beating laser is employed as the seed laser for echo-enabled harmonic generation of free-electron lasers. This approach enables the formation of an initial bunching of combs and ultimately facilitates the generation of XFCs under optimized conditions. We provide an optical design for the chirped frequency-beating seed laser system and outline a method to optimize and set the key parameters that meets the critical requirements for generating continuously tunable XFCs. Three-dimensional simulations using realistic parameters of the SXFEL demonstrate that it is possible to produce XFCs with peak power reaching 1.5 GW, central photon energy at the carbon K edge (~284 eV) and tunable repetition frequencies ranging from 7 to 12 THz. Our proposal opens up new possibilities for resonant inelastic X-ray scattering experiments at X-ray free-electron laser facilities.
We present the generation of high-repetition-rate strong-field terahertz (THz) pulses from a thin 4-N,N-dimethylamino-4’-N’-methyl-stilbazolium 2,4,6-trimethylbenzenesulfonate (DSTMS) organic crystal pumped by an ytterbium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet laser. The generated THz pulse energy reaches 932.8 nJ at 1 kHz repetition rate, with a conversion efficiency of 0.19% and a peak electric field of 819 kV/cm. At a repetition rate of 10 kHz, it is able to maintain a peak electric field of 236 kV/cm and an average THz power of 0.77 mW. The high-repetition-rate, strong-field THz source provides a convenient tool for the study of THz matter manipulation and THz spectroscopy.
The delay-shift of the pre-pulse may mislead the determination of its origination and cause problems for the temporal contrast improvement of high-peak-power lasers, especially when the corresponding post-pulse is beyond the time window of the measurement device. In this work, an empirical formula is proposed to predict the delay-shift of pre-pulses for the first time. The empirical formula shows that the delay-shift is proportional to the square of the post-pulse’s initial delay, and also the ratio of the third-order dispersion to the group delay dispersion’s square, which intuitively reveals the main cause for the delay-shift and may provide a convenient routing for identifying the real sources of pre-pulses in both chirped-pulse amplification (CPA) and optical parametric chirped-pulse amplification (OPCPA) systems. The empirical formula agrees well with the experimental results both in the CPA and the OPCPA systems. Besides, a numerical simulation is also carried out to further verify the empirical formula.
We reported on an efficient high-power continuous-wave laser operation on the 3H4 → 3H5 transition of Tm3+ ions in a diffusion-bonded composite YVO4/Tm:GdVO4 crystal. Pumped by a laser diode at 794 nm, a maximum output power of 7.5 W was obtained from a YVO4/Tm:GdVO4 laser at 2.29 μm, corresponding to a slope efficiency of 40.3% and exceeding the Stokes limit. To the best of our knowledge, this result represents the maximum power ever achieved from a Tm laser at 2.3 μm.
Er:CaF2 crystals are crucial gain media for producing 3 μm mid-infrared (MIR) lasers pumped by 976 nm continuous-wave (CW) lasers owing to their low phonon energy and high conversion efficiency. This study investigated the damage characteristics and mechanism of Er:CaF2 crystals irradiated with a 976 nm CW laser. The laser-induced damage threshold of Er:CaF2 crystals with different Er3+ doping levels was tested; the damage morphology consists of a series of regular 70° cracks related to the angle of the crystal slip system on the surface. A finite-element model was used to calculate the temperature and stress fields of the crystals. The results indicated that the damage can be attributed to surface tensile stresses caused by the temperature gradient, and crystals with higher doping concentrations were more susceptible to damage owing to stronger light absorption. These findings provide valuable insights into the development of high-power MIR lasers.
Femtosecond oscillators with gigahertz (GHz) repetition rate are appealing sources for spectroscopic applications benefiting from the individually accessible and high-power comb line. The mode mismatch between the potent pump laser diode (LD) and the incredibly small laser cavity, however, limits the average output power of existing GHz Kerr-lens mode-locked (KLM) oscillators to tens of milliwatts. Here, we present a novel method that solves the difficulty and permits high average power LD-pumped KLM oscillators at GHz repetition rate. We propose a numerical simulation method to guide the realization of Kerr-lens mode-locking and comprehend the dynamics of the Kerr-lens mode-locking process. As a proof-of-principle demonstration, an LD-pumped Yb:KGW oscillator with up to 6.17-W average power and 184-fs pulse duration at 1.6-GHz repetition rate is conducted. The simulation had a good agreement with the experimental results. The cost-effective, compact and powerful laser source opens up new possibilities for research and industrial applications.
The high-power narrow-linewidth fiber laser has become the most widely used high-power laser source nowadays. Further breakthroughs of the output power depend on comprehensive optimization of stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS), stimulated Raman scattering (SRS) and transverse mode instability (TMI). In this work, we aim to further surpass the power record of all-fiberized and narrow-linewidth fiber amplifiers with near-diffraction-limited (NDL) beam quality. SBS is suppressed by white-noise-signal modulation of a single-frequency seed. In particular, the refractive index of the large-mode-area active fiber in the main amplifier is controlled and fabricated, which could simultaneously increase the effective mode field area of the fundamental mode and the loss coefficient of higher-order modes for balancing SRS and TMI. Subsequent experimental measurements demonstrate a 7.03 kW narrow-linewidth fiber laser with a signal-to-noise ratio of 31.4 dB and beam quality factors of Mx2 = 1.26, My2 = 1.25. To the best of our knowledge, this is the highest reported power with NDL beam quality based on a directly laser-diode-pumped and all-fiberized format, especially with narrow-linewidth spectral emission.
A high-energy picosecond 355 nm ultraviolet (UV) laser operating at 100 Hz was demonstrated. A 352 mJ, 69 ps, 1064 nm laser at 100 Hz was realized firstly by cascaded regenerative, laser diode end-pumped single-pass and side-pumped main amplifiers. The stimulated Raman scattering-based beam shaping technique, thermally induced birefringence compensation and 4f spatial filter-image relaying systems were used to maintain a relatively homogeneous beam intensity distribution during the amplification process. By using lithium triborate crystals for second- and third-harmonic generation (THG), a 172 mJ, approximately 56 ps, 355 nm UV laser was achieved with a THG conversion efficiency of 49%. To the best of our knowledge, it is the highest pulse energy of a picosecond 355 nm UV laser so far. The beam quality factor ${M}^2$ and pulse energy stability were ${M}_x^2$ =3.92, ${M}_y^2$ =3.71 and root mean square of 1.48%@3 hours. This laser system could play significant roles in applications including photoconductive switch excitation, laser drilling and laser micro-fabrication.