View fulltext
View fulltext
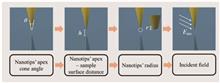
Terahertz (THz) scattering-type scanning near-field optical microscopy (s-SNOM) is an important means of studying and revealing material properties at the nanoscale. The nanotip is one of the core components of THz s-SNOM, which has a decisive impact on the resolution of the system. In this paper, we focus on the theory and design of the nanotip and conduct comprehensive research on it through simulation. The theoretical model is based on full-wave numerical simulation and dipole moment analysis, which can describe the overall nanotip electromagnetic response under the incident field. A comprehensive design model of nanotip geometry, sample materials, and incident field is established to significantly improve the near-field coupling efficiency and spatial resolution to achieve optimal performance.
In this study, we proposed and experimentally demonstrated an electro-optic modulator with a small footprint and high modulation efficiency, achieved through the utilization of a mode-folded phase shifter with lumped electrodes. The three-mode phase shifter recycles the light three times with different waveguide modes while leading to a pronounced tightening of the optical field confinement. We experimentally obtained a 3.7-times improvement in the modulation efficiency. A low VπL for thin-film lithium niobate (TFLN) Mach–Zehnder modulators of 1 V·cm is realized with a device footprint of 2.7 mm × 0.6 mm (0.5 mm for the phase shifter). Even greater improvements in modulation efficiency can be expected through the incorporation of additional modes.
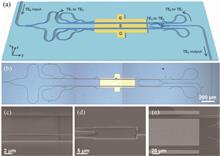
Microwave photonics (MWP) studies the interaction between microwaves and light waves, including the generation, transmission, and processing of microwave signals. Integrated MWP using photonic integrated circuits (PICs) can achieve compact, reliable, and green implementation. However, most PICs have recently been developed that only contain one or a few devices. Here, we propose a multi-channel PIC that covers almost all devices in MWP. Our PIC integrates lasers, modulators, amplifiers, and detectors in the module, successfully manufacturing an eight-channel array transceiver module. We conducted performance tests on the encapsulated transceiver module and found that the cascaded bandwidth of the eight-channel transceiver module was greater than 40 GHz, and the spurious-free dynamic range (SFDR) of the broadband array receiver module was greater than 94 dBm · Hz2/3. The noise figure (NF) is less than -35 dB and the link gain is greater than -26 dB. The success of multi-channel PIC marks a crucial step forward in the implementation of large-scale MWP.
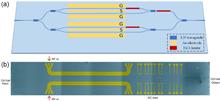
In recent years, thin-film lithium niobate (TFLN) electro-optic (EO) modulators have developed rapidly and are the core solution for the next generation of microwave photonics (MWP) problems. We designed and fabricated a dual-parallel Mach–Zehnder modulator (DPMZM) based on TFLN, achieving a 3 dB electro–electro (EE) bandwidth of 29 GHz and a low drive voltage (Vπ = 6 V). The device we manufactured is metal-encapsulated. It is noteworthy that we proposed a single-channel Doppler frequency shift (DFS) measurement system based on this device and conducted verification experiments. We coupled light from an external laser into the chip and passed it through each of the two sub-MZMs of the DPMZM. These lights were modulated by echo signals and reference signals. By measuring the frequency of the output signal, we can obtain a DFS value without directional ambiguity. The success of this experiment marks a key step in the practical application of TFLN modulators in MWP.
We have developed a remote sea salt aerosol fluorescence spectroscopy system integrating a high-power industrial-grade femtosecond laser to enhance detection sensitivity and precision in complex environments. This system successfully detects sea salt aerosol particles, achieving a detection limit of 0.015 ng/m3 for neutral Na element (Na I) at 589 nm, with a detection range of 30 m. Our findings demonstrate significant improvements in remote aerosol monitoring, addressing previous challenges in long-range and high-precision sensing with a detection accuracy previously unattainable below 10 ng/m3.
In this Letter, we propose a scheme to generate helical optical fields with multi-freedom controllable features. High-quality helical lobes with adjustable radii, chirality, and lobe numbers can be generated by tuning the phase term of two paired high-order Bessel beams. Furthermore, the pitch of the helical beam can be controlled by combining another rotational phase term. The validity of our scheme is demonstrated in both simulations and experiments. Our scheme is promising to facilitate the rapid fabrication of helical structures with diverse parameters, which are critical in various applications, such as optical metamaterials, biology, and particle transport.
In this Letter, waveguide beam splitters (1 × 3) with type I modifications are fabricated in a LiNbO3 crystal by femtosecond laser direct writing. The influence of the relative positions of three sub-waveguides on power splitting ratios are investigated in detail and the corresponding output intensities as functions of the relative positions in the numerical simulation are plotted, which are in good accordance with the experimental results. In addition, the waveguide beam splitter with a 1:1:1 splitting ratio is fabricated by changing the relative widths of the three branch-waveguides. Guiding performances at 532 nm are measured and analyzed by a typical end-face coupling system. The simulation and experimental results demonstrate that the beam splitting ratio of the waveguide splitter can be precisely regulated by the positions and widths of the sub-waveguides.
We proposed an approach for the generation of interference-pattern helico-conical beams (HCBs) both theoretically and experimentally. The HCBs exhibiting intricate fringe structures are obtained by exploiting amplitude modulation and interference techniques. To precisely control the optical field distributions, we manipulate the azimuthal term within the helico-conical phase expression, presenting several illustrative cases that highlight the versatility of our approach. Through further combinations, more sophisticated comprehensive HCB patterns are investigated. This study deepens our knowledge about spiral-like optical patterns and paves a new avenue for potential applications, especially in the fields of particle manipulation, nanostructure fabrication, and optical metrology.
Due to the promising applications of femtosecond laser filamentation in remote sensing, great demands exist for diagnosing the spatiotemporal dynamics of filamentation. However, until now, the rapid and accurate diagnosis of a femtosecond laser filament remains a severe challenge. Here, a novel filament diagnosing method is proposed, which can measure the longitudinal spatial distribution of the filament by a single laser shot-induced acoustic pulse. The dependences of the point-like plasma acoustic emission on the detection distance and angle are obtained experimentally. The results indicate that the temporal profile of the acoustic wave is independent of the detection distance and detection angle. Using the measured relation among the acoustic emission and the detection distance and angle, a single measurement of the acoustic emission generated by a single laser pulse can diagnose the spatial distribution of the laser filament through the Wiener filter deconvolution (WFD) algorithm. The results obtained by this method are in good agreement with those of traditional point-by-point acoustic diagnosis methods. These findings provide a new solution and idea for the rapid diagnosis of filament, thereby laying a firm foundation for femtosecond laser filament-based promising applications.
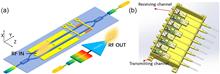
Light detection and ranging (lidar) has attracted significant interest as a sensing technology for its ability to achieve high-resolution imaging and wide-angle perception. However, conventional lidar systems, built with separate components, are often bulky, expensive, complex, and prone to instability. In contrast, solid-state lidar, based on silicon photonics technology, offers a solution with its compact size, less expense, low energy consumption, and improved reliability. However, achieving precise beam steering remains a critical challenge for integrated lidar systems. Various methods have been demonstrated for beam steering, which is one of the simplest and most efficient approaches that utilize wavelength tuning with a grating coupler antenna. In this review, we introduce the fundamental principle of optical phased array for beam steering and provide an overview of the recent advancements in integrated solid-state lidars utilizing orthogonal polarizations and counterpropagation to enhance beam-steering range and angular resolution.
In this paper, we present a remote time-base-free technique for a coherent optical frequency transfer system via fiber. At the remote site, the thermal noise of the optical components is corrected along with the link phase noise caused by environmental effects. In this system, a 1 × 2 acousto-optic modulator (AOM) is applied at the remote site, with the first light being used to eliminate the noise of the remote time base and interface with remote users while the zeroth light is used to establish an active noise canceling loop. With this technique, a 10 MHz commercial oscillator, used as a time base at the remote site, does not contribute to the noise of the transferred signal. An experimental system is constructed using a 150 km fiber spool to validate the proposed technique. After compensation, the overlapping Allan deviation of the transfer link is 7.42 × 10-15 at 1 s integration time and scales down to 1.07 × 10-18 at 10,000 s integration time. The uncertainty of the transmitted optical frequency is on the order of a few 10-19. This significantly reduces the time-base requirements and costs for multi-user applications without compromising transfer accuracy. Meanwhile, these results show great potential for transferring ultra-stable optical frequency signals to remote sites, especially for point-to-multi-users.
In this paper, we present a method to expedite multi-wavelength photoelasticity for efficient stress analysis. By modulating two slightly different-wavelength illumination beams and simultaneously capturing dark-field and bright-field images, our approach acquires four essential polarized images. Spatial filtering of Fourier transforms streamlines inner stress computation, enabling multi-wavelength photoelasticity with a single detector exposure. Theoretical foundations are outlined, and proof-of-principle experiments validate the feasibility with a measurement error below 6.4%. The high measurement speed, determined by the detector’s frame rate, facilitates dynamic sample measurements at video frequency, offering promising advancements in material stress analysis.
This study proposes a method for real-time monitoring of lithium-ion battery (LiB) internal temperatures through the temperature response of an embedded fiber Bragg grating (FBG) sensor. This approach overcomes the limitations of most methods that can only detect the external temperature at limited places by providing the advantages of sensing both the internal temperature and external temperature at multiple points simultaneously for precise condition monitoring. In addition, a numerical LiB cell model was developed to investigate the heat generation and temperature gradient using the finite element analysis method. The outcomes show that this model can be used to predict the temperature with less than 5% discrepancy (1.5°C) compared with experimental results. Thereby, this proposed method can be effectively used to monitor the safety and state of health of LiBs and other types of rechargeable batteries in real-time.
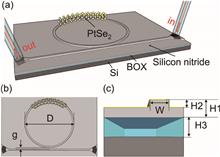
Optical bistability can be used to explore key components of all-optical information processing systems, such as optical switches and optical random memories. The hybrid integration of emerged two-dimensional layered PtSe2 with waveguides is promising for the applications. We demonstrated the optical bistability in the PtSe2-on-silicon nitride microring resonator induced by a thermo-optic effect. The fabricated device has a resonance-increasing rate of 6.8 pm/mW with increasing optical power. We also established a theoretical model to explain the observation and analyze the device’s performance. The study is expected to provide a new scheme for realizing all-optical logic devices in next-generation information processing systems.
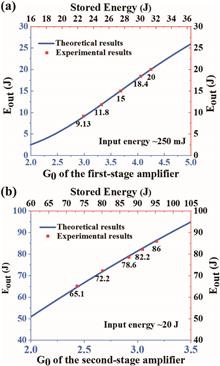
Ultra-short pulse, ultra-intense (USUI) lasers have become indispensable tools for scientific research. High-energy pump lasers are crucial for ensuring adequate energy and beam quality of these USUI lasers. Pump lasers with rod amplifiers are a cost-effective and reliable option for meeting high-energy pump requirements. However, there is a notable dearth of comprehensive reports on the design of high-energy rod amplifiers. This study provides a detailed analysis of rod amplifiers, focusing primarily on the pump unit utilized at SULF-10 PW and SEL-100 PW prototypes. The analysis covers aspects such as gain management, thermal effects, and spatiotemporal evolution.
Mode-locked lasing operations at 1064 and 910 nm wavelengths are demonstrated, respectively, in two all-fiber laser oscillators using our homemade Nd3+-doped silica fiber (NDF) as the gain medium. The Al3+/Nd3+ co-doped silica core glass was fabricated by the modified sol–gel method with 18,300 × 10-6 Nd3+ doping concentration. The NDF drawn by the rod-in-tube method has a core of 4 µm in diameter and a numerical aperture (NA) of 0.14. At 1064 nm, we measure an average laser output power of 18 mW with a pulse duration of 5.75 ps, a pulse energy of 1.14 nJ, and a slope efficiency of 7.2%. Using the same NDF gain fiber of a different length, a maximum average laser output power is 3.1 mW at 910 nm with a pulse duration of 877 ns, a pulse energy of 2.7 nJ, and a slope efficiency of 1.44%.
The miniaturization of spectrometers has received much attention in recent years. The rapid development of metasurfaces has provided a new avenue for creating more compact and lightweight spectrometers. However, most metasurface-based spectrometers operate in the visible light region, with much less research on near-infrared wavelengths. This is possibly caused by the lack of effective metasurface filters for the near-infrared light. We design and fabricate a polarization-insensitive amorphous silicon metasurface that exhibits unique transmission spectra in parts of the visible and near-infrared wavelengths. By passing the light to be measured through a metasurface filter array and measuring the transmitted power, we achieve the precise reconstruction of unknown spectra in the visible and near-infrared range (450–950 nm) using an algorithm matched to the filter model. Our approach is a step towards miniaturized spectrometers within the visible-to-near-infrared range based on metasurface filter arrays.
The optical properties of hybrid core–shell nanostructures composed of a metallic core and an organic shell of molecular J-aggregates are determined by the electromagnetic coupling between plasmons localized at the surface of the metallic core and Frenkel excitons in the shell. In cases of strong and ultra-strong plasmon–exciton coupling, the use of the traditional isotropic classical oscillator model to describe the J-aggregate permittivity may lead to drastic discrepancies between theoretical predictions and the available experimental spectra of hybrid nanoparticles. We show that these discrepancies are not caused by limitations of the classical oscillator model itself, but by considering the organic shell as an optically isotropic material. By assuming a tangential orientation of the classical oscillators of the molecular J-aggregates in a shell, we obtain excellent agreement with the experimental extinction spectra of TDBC-coated gold nanorods, which cannot be treated with the conventional isotropic shell model. Our results extend the understanding of the physical effects in the optics of metal–organic nanoparticles and suggest an approach for the theoretical description of such hybrid systems.
Broadband, low-drive voltage electro-optic modulators are crucial optoelectronic components in the new-generation microwave photonic links and broadband optical interconnect network applications. In this paper, we fabricate a low-loss thin-film lithium niobate complementary dual-output electro-optic modulator chip with a 3 dB electro-optic bandwidth of 59 GHz and a half-wave voltage (Vπ) of 2.5 V. The insert-loss of the packaged modulator is 4.2 dB after coupling with polarization-maintaining fiber. The complementary dual-output modulator also shows a common-mode rejection ratio of 18 dB and a signal enhancement of 6.2 dB when adapted in microwave photonic links, comparable to commercial bulk lithium niobate devices.
Optical modulation is significant and ubiquitous to telecommunication technologies, smart windows, and military devices. However, due to the limited tunability of traditional doping, achieving broadband optical property change is a tough problem. Here, we demonstrate a remarkable transformation of optical transmittance in few-layer graphene (FLG) covering the electromagnetic spectra from the visible to the terahertz wave after lithium (Li) intercalation. It results in the transmittance being higher than 90% from the wavelengths of 480 to 1040 nm, and it increases most from 86.4% to 94.1% at 600 nm, reduces from ∼80% to ∼68% in the wavelength range from 2.5 to 11 µm, has ∼20% reduction over a wavelength range from 0.4 to 1.2 THz, and reduces from 97.2% to 68.2% at the wavelength of 1.2 THz. The optical modification of lithiated FLG is attributed to the increase of Fermi energy (Ef) due to the charge transfer from Li to graphene layers. Our results may provide a new strategy for the design of broadband optical modulation devices.
In this Letter, a kind of optoelectronic chip based on III-nitride is developed as a versatile platform for both fiber-optic sensing and optical communication. The optoelectronic chip consists of a light-emitting diode (LED) and a photodiode (PD), which are fabricated with the same multi-quantum well (MQW) structure and monolithically integrated on a sapphire substrate. By integrating the chip with a polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) encapsulated silica fiber-optic sensor, it can effectively detect the bending-induced light intensity change and generate the photocurrent to point out the angle changes. Besides, such an optoelectronic chip can also be treated as a transceiver, enabling duplex communication for real-time audio and video transmission. The proposed optoelectronic chip has the advantages of miniaturization, versatility, and ease of massive manufacturing, making it promising in integrated optical sensing and communication (IOSAC) systems.
Facing escalating demands for high-speed, large-bandwidth, and low-latency wireless data links, laser communication technology has emerged as a promising technology. While free-space optical communication conventionally utilizes near-infrared light sources, there has been growing interest in exploring new spectral resources, including visible lasers. Recently, laser-based white light has been demonstrated in visible light communication (VLC), with a unique capability to seamlessly integrate with illumination and display systems. This review summarizes the key devices and system technologies in semiconductor-laser-based white light for VLC-related applications. The recent advances and many emerging applications in the evolution of lighting, display, and communication are discussed.