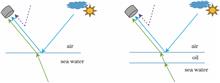
The outdoor experiments at three wavebands (290, 320, and 355 nm) are carried out to study the reflection characteristics of seawater targets and oil spill targets (e.g., crude oil, heavy oil, diesel oil, gasoline, and palm oil). The relationship curves of upwelling radiation intensity and the oil-seawater contrast of the detected target with the solar altitude angle and azimuth angle are obtained. Results show that when the solar altitude angle is 40°--60°, the contrast ratio between crude oil and seawater is 14%--44%, that between dead oil and seawater is 15%--35%, that between gasoline and seawater is 12%--26%, that between palm oil and seawater is 15%--47%, and that between diesel oil and seawater is 3%--12%. These results indicate that the detection and identification of different oils can be realized at different solar altitude angles and azimuth angles by the combination of three wavebands, among which the ultraviolet waveband exhibits an outstanding advantage in the early detection and identification of oil spills on sea surface.
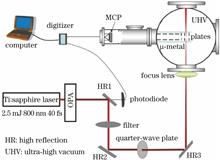
In this study, the ion yields of homonuclear diatomic molecules (O2) were experimentally measured as a function of the laser intensity at two different wavelengths (800 and 1500 nm) in the linearly polarized (LP) and circularly polarized (CP) strong laser fields, exhibiting a peculiar dependence on wavelength and polarization. The O2+ yields were reduced at long wavelengths, and the yield difference between 800 and 1500 nm was larger in the CP field when compared with that in the LP field. The experimental results were qualitatively reproduced using the S-matrix model. Furthermore, the calculated electron-momentum distributions confirm the effect of the molecular orbitals on the strong-field single ionization of O2.
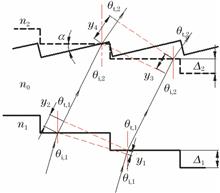
The tilt error introduced in the system assembling process affects the diffraction efficiency of diffractive optical elements (DOEs). An increase in the incident angle also affects the diffraction efficiency of DOEs. Based on the phase delay expression of multilayer DOEs (MLDOEs), this paper proposes a theoretical model of the relationship between the diffraction efficiency/bandwidth integrated average diffraction efficiency (BIADE) and the tilt error. The effect of the tilt error on the diffraction efficiency/BIADE at oblique incidence is analyzed. The relationship between the comprehensive BIADE working within a certain incidence angle and the tilt error is established. When the range of incident angle for the MLDOEs, operating within the 8--12-μm infrared waveband, is 0°--20°, if the comprehensive BIADE is required to be higher than 98%, the tilt error should be less than 0.25°. When there are other errors, such as the decenter error and the microstructure height error, the tilt error is further analyzed to reach the required comprehensive BIADE. The method and conclusions can be used to assist in designing and assembling the MLDOEs in hybrid optical systems.
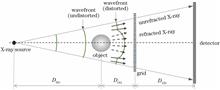
Compared with traditional phase-contrast imaging methods, the X-ray single grating phase-contrast imaging based on Fourier transform has the advantages of low radiation dose and fast imaging speed, and has a broad application prospect in the fields of materials and medical treatment. The extraction of object spectral information is a key step to recover the phase using this technique, but the extraction process is easily affected by Moiré artifacts, which leads to the degradation of the imaging quality and in turn limits the development and application of this method. In view of the above problems, based on the theoretical analysis of Moiré artifacts and the structural characteristics of the imaging system, two schemes by rotating grating and adjusting the projection frequency of grating are proposed to eliminate the artifacts, and their feasibilities are verified successfully in experiments, providing a reference for the promotion and application of X-ray single grating phase-contrast imaging.
The off-axis reflective optical system with large field-of-view can obtain more abundant information resources, which is the development trend of the future space optical systems. The application of freeform surfaces in off-axis reflective optical systems can increase the field-of-view, but freeform off-axis reflective optical systems with large field-of-view are difficult to design due to fewer initial configurations and complicated optimization processes. In this paper, a design method for the freeform off-axis reflective optical system with large field-of-view is proposed. First, the unobscured freeform initial system with good imaging quality is directly obtained based on the vector aberration theory and the Fermat principle. Then, the final freeform optical system is obtained after simple optimization. This method can reduce the design difficulty of a freeform off-axis reflective optical system with large field-of-view. A freeform off-axis three-mirror optical system with a field-of-view of 30°×3° and an F number of 2 is designed, which verifies the effectiveness of the proposed method.
The signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of a star map is an important factor affecting the accuracy of star point identification. For the threshold denoising methods, the noise residual caused by the threshold selection problem in the ground all-day star map affects the accuracy of the star point centroid extraction. This study proposes a near-earth all-time star map wavelet denoising method based on the local outliers factor. The proposed method applies the local outliers factor algorithm to the wavelet denoising of the star map to perform the denoising of the ground all-time star map without threshold. Herein, the real star map is considered as the original data, and the peak SNR (PSNR) and local peak value relative error (LPVRE) are used to compare and analyze the denoising effect of the star map processed using different denoising methods. Results show that compared with the traditional mean filter and wavelet threshold denoising, this method improves the PSNR and reduces the local peak relative error, and it can more efficiently remove the background noise and retain the target information.
Because of the continuously increasing detection ability in astronomy, polarization aberrations are playing increasingly important roles in the performance of astronomical telescopes. In this paper, the polarization aberrations of an unobscured off-axis astronomical telescope used to detect weak gravitational lensing effect are analyzed using polarization ray tracing. The diattenuation map and retardance map of each mirror for the telescope are obtained, and both its Jones pupil and amplitude response matrix are determined. It is found that the polarization aberrations of the telescope have an impact on both the imaging contrast and the spatial distribution of the point spread function (PSF). The optics ellipticity of the telescope is analyzed. The variations of optics ellipticity, which are dependent on the field of view (FOV), are induced by polarization aberrations. The maximum and mean variations of the optics ellipticity in all FOVs are 7.5×10 -3 and 2.7×10 -3, respectively. At the FOV [-0.0487°, 0.155°], the maximum ellipticity interpolation error increases from 1.2×10 -4 to 1.1×10 -3. Our analyses reveal that polarization aberrations should not be ignored and should be optimized in telescopes that require ultrahigh imaging performance, such as those used for detecting weak gravitational lensing effect.
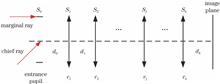
The stray radiation generated by an uncooled infrared detector will form a non-uniform image on the focal plane. The key to suppress stray radiation is to use a stop near the detector window and optimize its aperture shape. The model for calculating the illuminance distribution of stray irradiance on the focal plane by Zone method and the models of variables and objective functions are established. The interval exhaustion method is adopted as the extremum seeking method, and the program for optimization is completed. Aiming at an uncooled infrared detector with stray radiation, the proposed mathematical method is applied to optimize its stop aperture shape, which greatly reduces the “pot cover effect” caused by stray radiation, and thus the correctness and practicability of this optimization design method is confirmed.
Synthetic aperture imaging technology can be used to effectively detect local occluded targets by means of virtual large-size apertures, but the quality of refocused images is greatly reduced when there exist strong backscattering factors in the scene. Aiming at the above problems, a synthetic aperture imaging method based on confocal illumination is proposed, which modulates the illumination source according to the depth information of the scene target distribution, effectively realizes the illuminance difference between the focus surface target and the non-focus surface target, and combines the synthetic aperture imaging refocusing method to achieve high quality reconstruction of locally occluded confocal illumination surface targets. The confocal illumination synthetic aperture imaging system is built by an anti-mirror array, and the confocal illumination refocusing imaging is performed on the specified depth target. The results show that the proposed method can effectively distinguish the intensity of the reflected light from the focal plane and the non-focus surface target in the scene, and can obtain high quality image information of the confocal illumination surface target, and the effect is far superior to those of the existing synthetic aperture imaging methods.
Particle diameter analysis method based on traditional particle tracking velocimetry (PTV) technology can be used to detect particle diameter only by geometric imaging, and it is impossible to analyze particle images when diffraction imaging size is much larger than geometric imaging size. Based on the principles of diffraction imaging, a quantitative relationship model for determining image gray value and particle diameter of a micro-nano-scale tracer particle is proposed through the quantitative analysis of the whole physical process related to laser, particle scattered light, CCD signal, and image gray value and thus the shortcomings of PTV technology in particle diameter detection are addressed. Based on the PTV experimental system, the digital camera and software of Micro Vec V3 are used to complete the shooting of SiO2 particle images, and the proposed model is used to analyze particle diameter from the captured images. The experimental results show that the proposed method has a high accuracy.
To resolve the problem that the available data on the ground-to-air infrared aircraft identification task is considerably scarce, the small samples infrared aircraft identification classification method is proposed on the basis of an improved relation network. This method combines the relation network model and the multi-scale feature fused method with the meta learning training strategy. First, a multi-scale feature extraction module is constructed to extract the feature tensors of input images. Then, the feature tensors of support samples and test samples are inputted into the relation module, and the category labels corresponding to test samples are predicted based on the relation value. The results of the proposed model on the mini-ImageNet dataset show that the classification accuracy of the proposed model is significantly higher than those of other conventional learning models using small samples. The experimental results based on the Infra-aircraft dataset verify that the proposed model can realize the ground-to-air infrared image classification task of various aircraft types even when the number of samples is limited.
The vertical cavity surface emitting laser (VCSEL) offers higher beam quality and reliability compared with the traditional edge emitting laser. It has significant application prospects in light imaging detection and ranging (LiDAR). The luminescence characteristics of a VCSEL with TO (transistor outline) package and a VCSEL with bare chip are examined under the narrow pulse and large current conditions. Using Pspice parameter scanning analysis, the experimental results combined with the theoretical calculation are used to compare the sizes of stray parameters and to analyze their effects on the luminescence characteristics of these two encapsulated lasers. Moreover, the formula about power conversion efficiency of a VCSEL under the pulse condition is derived and the influence of stray parameters on the power conversion efficiency of a VCSEL is analyzed.
Based on the characteristic that the conductivity of photosensitive semiconductor material can be controlled by external pump light, a dynamic optical-controlled single-/dual-band switchable metamaterial absorber is designed by embedding the semiconductor material of gallium arsenide into the nested square ring-like cell structure. On this basis, according to the different excitation characteristics of different semiconductor materials pumped by light with different wavelengths, the first structure is expanded by introducing the second semiconductor material of germanium, and an optical-controlled multi-band metamaterial absorber is proposed. The proposed absorber possesses the absorption characteristic of arbitrary switch among the single-/dual-/triple-band absorption states by using pump light with different wavelengths to tune the conductivities of the semiconductors. The simulation results show that the proposed absorber has the characteristics of insensitive polarization and wide-angle incidence, which is expected to be applied in modulators, frequency selectors, detectors, and so on.
Testing the full-aperture of convex aspheric surface with large aperture and large relative aperture is challenging. To solve this problem, we propose a convex aspheric surface testing method using an autocollimation lens in this study. In the proposed method, a self-aligning lens is formed by plating a semi-inverted semi-permeable film onto the convex surface of a single lens to correct the spherical aberration of the aspheric surface, enabling the full-aperture testing of the large-aperture convex aspheric surface. We derive initial structure parameters using the third-order aberration theory, and then introduce the design method in detail. We design and simulate an optical system to test a convex oblate spheroid with an aperture of 240.62 mm and relative aperture of 0.48, and then perform a tolerance analysis of the system. The peak valley (PV) value of the residual aberration of the optimized system is 0.00025λ and the root-mean-square (RMS) error is 0.0001λ. The proposed method is also applied in testing a practical convex hyperboloid with an aperture of 287 mm and relative aperture of 0.74. We obtain an RMS of 0.021λ, which verifies the feasibility of the proposed method. Finally, the applicability of this method and the aberration correction ability are analyzed. In summary, the proposed method can be used to test the full-aperture of any eccentricity convex aspheric surface, and it has great advantages in testing full-aperture of convex aspheric surface with large aperture and large relative aperture.
In this study, we propose a design method of advanced Offner-type convex grating spectral radiation calibration light source optical system to solve the problem of low energy output in case of digital tunable light sources. Further, we theoretically deduce the relation between slit and astigmatism of the Offner-type spectral imaging structure based on the theory of ray tracing. The residual astigmatism in the large slit of the Offner-type spectral imaging system is compensated using a double cylindrical lens. Using the proposed method, a traditional Offner-type spectral imaging system with a slit length of 0.4 mm and an advanced Offner-type spectral imaging system with a slit length of 8 mm are designed having the same spectral range from 500 to 800 nm. The results indicate that the advanced Offner-type spectral imaging system exhibits good image quality and that the root mean square (RMS) radius of full field of view spot diagram is less than 8.1 μm; the RMS radius along the Y direction is less than 6.7 μm, which is within the size of a single pixel. The smile is 6.2% of the size of a single pixel, whereas color distortion is 5.8% of the size of a single pixel; thus, spectral overlapping and spectral offset are diminished. Therefore, the proposed method has some research significance and engineering value to ensure the improved precision of spectral radiometric calibration in case of remote sensing instruments.
In this paper, a spectral optimization method for a mixed white light-emitting diode (LED) cluster comprising a red/green/blue/cyan/yellow/warm white (R/G/B/C/Y/WW) LED based on pulse width modulation (PWM) is proposed. Following the principle of the spectral combination of multicolor LEDs, the proposed method adopts the 1931 CIE-XYZ tristimulus value to determine the relationship between the color coordinates and the contribution ratio ρG+WW(r1),ρB+C(r2),ρR+Y(r3) for each component, i.e., G+WW,B+C,and R+Y, respectively. Using an optimized traversal range under different flux contribution ratios, i.e., r1,r2,and r3, a maximum color rendering index (Ra) of 96.4, 97.0, 97.3, and 97.4 is attainable when the correlation color temperatures (Tc) of the synthesized white LED cluster are 2700, 4000, 5500, and 7000 K, respectively. Furthermore, experimental verification was conducted with R/G/B/C/Y/WW LEDs. Results show that an R/G/B/C/Y/WW LED module can realize tunable white light in a wide range of Tc (2700--7000 K). When the luminance flux is set to 500 lm, the maximum relative errors of Tc and Ra are 1.96% and 1.24%, respectively, and the luminous efficiency varies in the range 146.81--152.40 lm·W -1.
The absorption and photoluminescence spectra of green and red CdSe/ZnS quantum dot/silicon composite films are measured. The results show that the composite films have stable photoluminescence spectra at different excitation wavelengths and the peaks are located at 527 nm and 628 nm wavelengths, respectively. Two white light emitting diodes (WLED) with different structures are prepared by the combination of the quantum dot/silicon composite films with YAG∶Ce 3+ yellow phosphors, and their optical properties and surface temperatures are measured under different driving currents. For 350 mA driving current, the surface temperature of WLED II is 26.5 ℃ lower than that of WLED I. The aging test is conducted at 55 ℃ temperature and 55% relative humidity, and the results show that the optical performances of these two WLEDs typically remain the same under different driving currents, indicating an excellent stability.
Traditional fixed abrasive pads (FAPs) present difficulty in guaranteeing the workpiece machining quality in the lapping of hard and brittle materials owing to the single form of grooves fabricated on the pad surface. To address this problem, in this study, a new type of FAP design called DPP, which has a non-uniform coupling and spiral concentric structured pattern, was proposed and tested. To reduce debris blockage on the DPP surface, spiral grooves were used as chip disposal grooves to ensure that the machined workpiece surface had a lower roughness and thus prolonged DPP life. Moreover, concentric circular grooves were used to adjust the distribution of abrasives on the DPP surface, which can improve the material removal uniformity and surface flatness of the machined workpiece. Based on the proposed design principle, the DPP for sapphire lapping was fabricated and compared with a traditional grid grooved pad (GGP). Experimental results show that the number of pits and scratches on the machined workpiece surface is much fewer when using DPP, which is ~35% of that of GGP, and the degree of blockage of the DPP after lapping is lower, which is ~30% of that of GGP. In lapping with DPP, the material removal rate is ~14% lower than that of GGP, but the nonuniformity of material removal thickness is ~0.0494, which is 32% lower than that of GGP. The surface roughness is ~129.4 μm, which is ~16.2% lower than that of GGP. Therefore, when DPP is used for sapphire lapping, the distribution of material removal is more uniform and the surface quality of the workpiece is much better. The test results prove that DPP can not only facilitate better workpiece surface quality but also prolong the pad service life, which meets the efficient and precision machining requirements for high-quality surfaces and large-scale production of brittle and hard materials such as sapphire.
In this paper, we propose a novel microwave photonic phase shifter based on a polarization division multiplexing dual-parallel Mach-Zehnder modulator (PDM-DPMZM). In this scheme, by adjusting the direct current (DC) bias voltages, the PDM-DPMZM is employed to generate a frequency-doubled or frequency up-converted and down-converted signals with their phases tuned across a full range. The phase shift is changed just by tuning the angle α between the polarizer’s polarization direction and one of the principal axes of the modulator. Supported by the optical frequency comb, the system is easy to be extended to multichannel system with independent phase tuning capability. The simulation results show that a radio frequency (RF) signal with a frequency of 5 GHz can be converted into a 10-GHz frequency-doubled signal, a 1-GHz frequency up-converted signal, and a 13-GHz frequency down-converted signal. Their phases can obtain a full-range phase shift from -180°to 180°, and the power response of the generated signal with different phase changes is relatively flat.
The potassium tantalate niobate (KTN) crystal has a high quadratic electro-optic coefficient and a fast response speed; therefore, it can be used to develop a high-speed electro-optic switch, which can quickly achieve a large beam deflection angle at a low voltage. However, the dispersion problem of the KTN crystal limits its application as an electro-optic switch in a wide spectral range. We investigate the effects of control voltage, temperature, and wavelength on the deflection characteristics of the KTN crystal, and find that simultaneous adjustment of voltage and temperature can balance the beam deflection angle and dispersion. This study provides guidance to the application of KTN crystals in wide-waveband beam deflection.
Only calibrating the response non-uniformity among three polarization channels of 0°, 60°, and 120° in the same waveband of a GF-5 satellite directional polarization camera (DPC) can make the accuracy requirement of polarization detection met. The wide field-of-view with DPC range of -50°--50° is divided into 15×15 sectional field-of-view and a high-accuracy two-dimensional turntable is used to adjust the position of each sectional field-of-view for aiming the integrating sphere reference light for imaging. The mosaic algorithm of the sectional field-of-view image data based on time stability is designed to obtain the mosaic images of the entire field-of-view. Furthermore, the logarithm enhancement method is used to detect the location and number of bad pixels in the mosaic images. The mosaic images are used to calculate the relative transmittance, low frequency relative transmittance, and high frequency relative transmittance of three polarization channels in the same waveband of DPC, and a calibration factor is provided for the calibration of DPC polarization channel response non-uniformity. The results show that the measurement uncertainty of DPC polarization channel response non-uniformity is superior to 0.67%. The proposed method provides a high-precision tool for calibrating the response non-uniformity among DPC polarization channels and for improving the analytical accuracy of polarization information.
The spectral diagnostic bands and their ranges of styrene in different soils are extracted under indoor conditions and used as the basis for the identification and content prediction of styrene in soil. The soil spectral reflectance is processed by the differential processing method and the spectral data conversion method to increase the difference in spectral change among samples. The stepwise multiple linear regression (SMLR), partial least squares regression (PLSR), and support vector machine regression (SVMR) methods are used to model and predict the styrene content in different soils. The results show that the spectral characteristics of different soils contaminated by styrene are located near 1800, 2200, and 2400 nm, respectively. Under the influence of its physical and chemical properties and styrene content, the decrease rate of the soil spectral reflectance increases first and then decreases until the styrene is saturated in soils, and the change in reflectivity tends to be stable. The PLSR model has the best prediction effect on the styrene content in soils, followed by the SMLR model, and the SVMR model has the worst effect. The determination coefficient of the PLSR model is 0.982--0.998, indicating that the model is stable, and the difference between the corrected and predicted standard deviations is 0.004--0.016, indicating that the model has high prediction accuracy.
In this paper, the directional emissivity of Ti-6Al-4V alloy at 0°--84° was measured using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy at a temperature range of 573--953 K and a wavelength range of 3--20 μm. The influence of direction on the spectral emissivity was systematically studied. Results show that the emissivity of Ti-6Al-4V alloy is similar to that of an insulator in the angle range of 0°--84° when the measurement wavelength is less than 10.3 μm, and therefore, it is more similar to that of metal when the wavelength exceeds 10.3 μm. The emissivity increases with temperature that ranges between 573--773 K, and it is observed that the change trend of emissivity with wavelength is opposite for the angle range of 0°--70° and 80°--84°. When the Ti-6Al-4V alloy is oxidized, its emissivity is maximum at 60°, and the non-metallic properties of emissivity at long-wavelength are evident with the increasing oxidation time. Therefore, this study enriches the directional spectral emissivity database of Ti-6Al-4V alloys and provides data support for radiation temperature measurement technology.
In this work, after analyzing the noise characteristics of interferograms from a spaceborne Fourier transform infrared spectrometer, a method for suppressing impulse noise is proposed. After calculating the symmetrical points and the sampling points on both sides of the interferogram obtained by the sampling points and the relative zero optical path difference, the reference values for the interpolation points obtained are established. The impulse noise position is then determined by comparing a threshold with this reference value. Experimental results show that the relative spectral deviation of the proposed method can be suppressed from 0.24% to 0.17%; furthermore, the noise equivalent radiance difference is suppressed from 0.069 to 0.056 mW·m -2·sr -1·cm. The proposed method can suppress the impulse noise while retaining the effective spectral information, thereby improving the detection sensitivity of the spaceborne Fourier transform infrared spectrometer.
According to the characteristics of a thin film narrowband filter at oblique incidence, an angle-tunable narrowband filter with stable transmission peak and bandwidth can be designed by improving the structure of spacer film system to adjust its equivalent refractive index. According to the eight standards related to the dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM) system such as channel frequency, insertion loss, bandwidth, isolation degree, polarization dependent loss (PDL) and so on, in combination with the theory of thin film matrix and the newly constructed evaluation function, a tunable filter membrane system is constructed, and the optimal membrane systems satisfying different requirements are obtained by changing the weighting factor of each parameter. Using the built system, the angle-tunable narrowband filters with high isolation and low polarization-dependent loss for 100 GHz DWDM system on O-band and C-band are designed. The maximum tuning angle of the film system on C-band is 11°, and the isolation degree of adjacent channels is up to -30.3 dB. Finally, the transmission characteristics and the factors influencing the tuning angle limit are analyzed.