Pterocephalus hookeri Hoeck., a commonly utilized Tibetan medicinal material, exhibits a broad spectrum of pharmacological activities and plays a crucial role in numerous Tibetan medicine compound formulas. Modern research has identified that the primary chemical constituents of P. hookeri possess diverse pharmacological effects, indicating promising prospects for its development. This review aims to summarize the main biological functions and chemical compounds of P. hookeri based on relevant domestic and international literature. The paper highlights key chemical components such as iridoids, flavonoids, triterpenoids, and phenylpropanoid compounds. These compounds demonstrate various pharmacological activities, including anti?inflammatory and analgesic properties, immunomodulation, antiviral effects, anti?aging benefits, cardiovascular protection, anticarcinogenic properties, and regulation of blood sugar and lipid, thereby contributing significantly to the treatment of human diseases.
Chaenomeles speciosa is the fruit of Chaenomeles speciosa (Sweet) Nakai, a perennial deciduous woody plant belonging to the Rosaceae family, serves as a dual-purpose resource for both medicine and food, demonstrating significant value in pharmaceutical, dietary, and nutraceutical applications. This review systematically summarizes recent advances in bioactive constituents of C. speciosa, including terpenoids, organic acids, and flavonoids, along with their phys?iological activities such as anti-inflammatory, anti-rheumatic, and uric acid-lowering effects. Furthermore, health claims and safety profiles are critically evaluated. Through systematic literature review and analysis, we propose evidence-based health claims for C. speciosa: aiding in lowering uric acid levels and regulating immune function, thereby providing scientific references for its medicinal and dietary applications. This paper is expected to facilitate the development and utilization of C. speciosa-derived products in functional foods and therapeutic interventions.
The variety breeding work has a basic supporting role and a promoting effect on the quality and efficiency of the Dendrobium officinale industry. The morphological traits (biological characteristics), quality traits (active ingredient content) and regional adaptability (stress resistance) of 6 high?quality provenances of Dendrobium officinale were systematically studied. The differences among different geographical provenances were compared, and the screening system of excellent varieties was established by analytic hierarchy process. The experimental data showed that the stem components of different germplasms of Dendrobium officinale were different :R1 germplasm presented the highest polysaccharide accumulation (30.41%), R2 germplasm possessed the maximum mannose content (25.47%) while R5 germplasm had significantly higher crude fiber content (8.21%) than other seed sources. Under the conditions of natural low temper?ature in winter, R6 germplasm showed the best stress resistance, with a frost damage index of only 6.19 and a single clump sprouting of 8 new shoots, demonstrating strong ecological adaptability. Through the comprehensive evaluation of analytic hierarchy process (AHP), R1 germplasm obtained the highest score (8.860 2) in the development dimension of fresh food products, while R6 was the best germplasm of potted type and obtained the comprehensive evaluation value of 9.673 8, which became the preferred material for horticultural cultivation. Through comprehensive evaluation, the best target varieties suitable for the production of Dendrobium medicinal materials were screened out, which laid a foundation for the breeding and cultivation of new high?quality resources.
Houttuynia cordata is an important medicinal and edible plant with abundant germplasm resources. How?ever, systematic studies on its genetic diversity have been relatively scarce in the past five years, particularly those utiliz?ing SSR molecular markers, which has hindered progress in variety improvement and resource conservation. To address this issue, this study employed both SSR and ISSR markers to analyze the genetic diversity of 140 H. cordata samples collected from 10 geographic populations across eight provincial-level administrative regions in China. The results revealed a high proportion of polymorphic loci, with SSR and ISSR markers showing rates of 94.20% and 93.20%, respectively, indicating high genetic diversity in H. cordata. Genetic differentiation and gene flow analysis demonstrated that the majority of genetic variation existed among populations, with genetic differentiation coefficients (GST) of 0.9508 (SSR) and 0.8903 (ISSR) and low number of migrants (Nm), suggesting that geographic isolation may be the primary driver of population differentiation. Cluster analysis and principal component analysis (PCA) further revealed close genetic relationships between certain populations (e.g., Mianyang and Chengdu in Sichuan; Maoming in Guangdong and Liuzhi in Guizhou), while the genetic distances of other populations showed no obvious correlation with geographic distribution. These findings provide valuable insights for the conservation and breeding of H. cordata germplasm resourc?es.
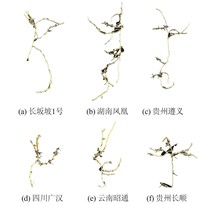
Five wild germplasm resources collected from Yunnan, Guizhou, Sichuan, Hunan and other places, with Changbanpo No.1 variety of Houttuynia cordata in Dangyang City, Hubei Province as the control (CK), were introduced to Liangzihu District of Ezhou, and the main agronomic and yield traits including the plant height, stem thickness, branch number, leaf length and leaf width, petiole length, inflorescence length, peduncle length, bract number, yield, number of nodes and node length of the above- and below-ground parts, as well as the moisture content, vitamin C, free amino acids, soluble sugar, soluble protein, crude fat, chlorogenic acid, and flavonoids were comprehensively evaluated. The results showed that the geographical provenances had a significant impact on the agronomic, yield traits, and functional component accumulation of Houttuynia cordata. Houttuynia cordata from Zunyi, Guizhou, had excellent growth indicators such as yield, plant height, tillering number, stem thickness, leaf morphology, and inflorescence morphology, as well as quality indicators such as water content, free amino acids, and crude fat in the aboveground parts. The yield of the aboveground parts reached 5.24 kg/m2, which was significantly higher than the control, with an increase of 60.7%. The content of free amino acids reached 4.321 mg/g, with an increase of 102.3%. The resources from Zhaotong, Yunnan, showed significantly better performance in all nutritional quality traits than those from other producing areas, with a soluble sugar content of 9.089 mg/g, 2.27 times that of the control. However, the underground stem from Guanghan, Sichuan, had better medicinal quality, with a flavonoid content of 7.744 mg/g, 2.27 times that of the control. The correlation analysis showed that plant height was significantly positively correlated with yield (r=0.82), leaf length was extremely significantly positively correlated with leaf width (r=0.99). The water content of the aboveground part was significantly positively correlated with free amino acids and soluble sugars (r=0.82), and the crude fat of the underground stem was extremely significantly positively correlated with flavonoids (r=0.95). This study clarifies the differences in agronomic, yield, and quality traits of the germplasm resources from six typical planting areas across the country in the Li?angzihu District of Ezhou, which can provide a reference for the introduction and development and utilization of Houttuynia cordata germplasm in the Jianghan Plain.
Ramet propagation is the main made of propagation for Centella asiatica. In order to improve the efficiency of ramer propagation, we studied the factors that affect ramet propagation of C. asiatica. The ramet seedlings were cultivated using substrates with different ratio of vermiculite to nutrient soil. The morphology, physiology, and the content of asiaticosides were investigated. Using paraffin sections and microscopy, the structures of stolon nodes at various developmental stages were examined. The results showed that the aerial part of C. asiatica grew most vigorously and the roots grew well when the substrate with a 1∶2 ratio of vermiculite to nutrient soil was applied. In this substrate ratio group the contents of water, chlorophyll, protein, soluble sugar, and starch, as well as the contents of asiatic acid and madecassic acid were not lower than those of the other ratio groups. The structures of stolon nodes in various developmental stag?es remained unchanged and possessed the capacity to propagate. By screening stolon nodes and appropriate substrate for ramet propagation, the present work would serve as the foundation for high quality cultivation of C. asiatica.
Phenotypic traits and microscopic structures of rhizomes as key indicators for the identification of medicinal rhizome herbs. This study conducted observations on the phenotypic traits and microscopic characteristics of rhizomes of Polygonatum spp. germplasm resources from 29 different origins. The results indicated that there were significant vari?ations in phenotypic traits among Polygonatum spp. from different regions.Among them, the coefficient of variation of fresh weight was the highest (77.95%), and that of chromaticity was the lowest (8.78%). In the genetic diversity analysis, the bud diameter exhibited the highest genetic diversity index (2.0646). Principal component analysis revealed high loading rates for yield-related trait indicators (0.879, 0.727, 0.857, 0.838, and 0.732, respectively). Cluster analysis of rhizome phenotypic traits categorized the Polygonatum spp. germplasm resources into three distinct groups. Additionally, variations were observed in the microscopic structures, particularly in the vascular bundles and mucilage cells of the selected varieties. In conclusion, significant differences exist in both phenotypic traits and microscopic structures of Polygonatum spp. from different regions, providing a theoretical foundation for the screening and evaluation of the germplasm resources, as well as for the variety identification.