View fulltext
View fulltext
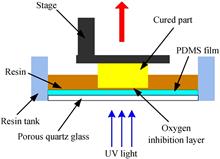
To find out the influence rule of micro-pore geometric characteristics in the confined forming chamber on the propagation properties of the curing light source, and then analyze and predict the manufacturing accuracy in stereolithography process, numerical study was done using FDTD software to obtain the light transmittance of the substrate machined micro-pore array and the characteristics of light energy distribution in the curing zone. The simulation results were verified by experiments. The research results show that the shape, size and period of the micro-pore formed in the constrained substrate affect the light transmittance and the light intensity distribution in the forming area. Compared with the shape of the micro-pore on the substrate, the size and period of the micro-pore show a more significant effect, in which, reducing the size and period of the micro-pore facilitate the light transmittance and the light intensity uniformity improvement. If the diameter of micro-pore is less than half wavelength and the ratio of micro-pore edge spacing to micro-pore diameter is less than 1:1, the negative effect of micro-pore can be reduced significantly. When the diameter of micro-pore is much larger than half wavelength, an undesirable additional feature on the surface of the fabricated part will be formed due to the micro-pore in constrained substrate and thus affecting the manufacturing accuracy. The results can provide direction and theoretical basis for the improvement of substrate preparation process.
To discuss the preparation and reflective spectral properties of two-dimensional aluminum-doped zinc oxide (ZnO:Al) gratings on back contact mental Al, a thickness of 80 nm ZnO:Al thin film was deposited on 300 nm Al substrate, then a layer of AZ5206 photo-resist was spin coated on ZnO:Al thin film. Mask pattern was acquired with 325 nm laser holographic lithography. Using lift off technology, two-dimensional ZnO:Al gratings with 624~1 250 nm periods and 100~300 nm heights on Al substrate were acquired. Grating periods and heights could be regulated independently. Surface morphologies were observed by atomic force microscopy and scanning electron microscopy, reflection spectrum was tested using spectrophotometer with integrating sphere, bidirectional reflectance distribution function was measured by scattering instrument. Results showed that total reflectivity, diffuse reflectivity and haze of those gratings with 228 nm heights all increased obviously as periods increasing from 624 nm to 986 nm. As periods increasing from 986 nm to 1 250 nm, the increment of total, diffuse reflectivity and haze were only small. The tested results of bidirectional reflectance distribution functions further confirmed the above conclusions, namely more large periods, more large diffuse reflectivity peak value, and more peak position numbers. It was concluded that back contact ZnO:Al grating with 986 nm period and 228 nm height had excellent scattering effects, such as the percentage of diffuse reflectivity to total reflectivity was up to 45%.
Considering the possible existence of three types of compounds, namely K3Sb, K2CsSb and Cs3Sb in the growth of K2CsSb photocathode, a first-principles study based on density functional theory was employed to establish the cubic bulk models and the (111) surface models for the three types of antimonide cathode materials. Through theoretical calculations, electronic structures and optical properties were obtained, wherein band structures, densities of states and optical properties were acquired for bulk models, and work function, optical properties and surface energy were calculated for (111) surface models. The results demonstrate that, as for the three types of antimonide cathodes, in the radiation energy range of 2.4~3.2 eV produced by interaction between neutrinos and scintillators, the absorption and relectivity of K2CsSb bulk material are close to those of Cs3Sb and K3Sb ones, whereas the values of K2CsSb (111) surface material are lower than those of Cs3Sb and K3Sb ones. In addition, K3Sb has the narrowest bandgap, maximum work function and maximum surface energy, while Cs3Sb has the minimum surface energy and its work function is close to that of K2CsSb, but its band gap is smaller than that of K2CsSb. By contrast, K2CsSb with the widest bandgap has the smaller work function and surface energy. Therefore, K2CsSb photocathode is suitable to serve as a stable and high-efficient photoemitter in the blue-violet spectral region.
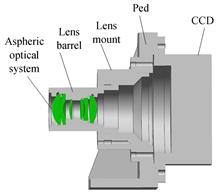
During the ascent of the airborne camera, due to the temperature drop and the thermal conductivity of the material of each part of the lens, the lens portion can have a temperature gradient, which causes the aspherical optical system to produce a gradient index. Using the finite element analysis software to perform transient thermal analysis on the lens part to simulate the temperature change during the ascent of the airborne camera, the finite element analysis of the temperature distribution results of different time nodes was introduced into the prepared refractive index gradient coefficient fitting program, and the solution was solved. The gradient index coefficient established the optical system model in the optical software through the mirror type interface, and use the speckle radius of the dot-column diagram to evaluate the influence of the image quality on the gradient index of the different time nodes. The results show that the temperature gradient of the airborne camera is the highest when it is lifted into the working height, and the influence on the imaging quality is also the most serious. The gradient refractive index coefficient decreases with the decrease of the temperature gradient coefficient, and the imaging quality is improved, which has guiding significance for the optical system design.
A kind of diffractive projection method and projector without holographic computation and coherent illumination was proposed. Instead of holographic iterative calculation, a incoherent collimated light-emitting diode and compact Fourier transform lens were used to generate the frequency spectrum of the projected images in real time. The Rayleigh-Sommerfeld diffraction of the spatial frequency spectrum of the images in free space was used to project the images with short throw ratio and infinite depth of focus. The imaging principles of the projection method were deduced analytically in detail. The intensity impulse response function of the projector was given. A non-holographic diffractive projector was demonstrated experimentally. The aberration and inhomogeneous intensity of the projection images were corrected. High quality diffractive images free from coherent artifact noises are realized. A diffractive projector with 0.87 throw ratio and infinite depth of focus is achieved. The projector can project clear images in different depth planes simultaneously which are separated at a distance more than 800 mm. The projection method and system have potential application in sphere projection, arbitrary surface projeciton, and augmented reality projection.
Gauss fitting function is used to determine the Gauss-like radiation pattern of LED with small divergence angle, and the line-of-sight channel model of LED is established according to the optical radiation characteristics and radiation pattern. The relationship between the received optical power and the channel parameters of various multi-band LEDs obeying the Lambertian and Gauss-like modes is actually measured. The experimental results show that the average relative error between the measured value of received optical power and the theoretical value of channel DC gain calculation is less than ±6%, which verifies the versatility and correctness of the line-of-sight channel model proposed in this paper.
An immunosensor based on graphene oxide modified cladding etched long-period fiber grating sensor for detection of avian influenza virus is presented in this paper. Graphene oxide is coated on the surface of long-period fiber grating by hydrogen bonding using sodium hydroxide and the avian influenza virus monoclonal antibodies are combined with graphene oxide surface by a covalent bond. The resonant wavelength change of long-period fiber grating caused by the specific binding of avian influenza virus monoclonal antibody aolsorbed on graphene oxide to avian influenza virus antigen was used for detection. The experimental results show that the limit of detection of the graphene oxide modified cladding etched long-period fiber grating immunesensor can reach 40 ng/mL, the dissociation constant ~1.6×10-7 M and the detection range 40 ng/mL~200μg/mL. The detection results of avian influenza virus in avian influenza virus blank allantoic fluid, Avian influenza virus allantoic fluid and Newcastle disease virus allantoic fluid show that the immunosensor has good specificity and clinical characteristics. Therefore, the immunosensor could be potentially applied in the fast detection and early diagnosis of avian influenza virus.
The Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence Organic Light-Emitting Diodes (TADF-OLEDs) was fabricated, using bipolarmaterial 4, 4'-bis (carbazol-9-yl) biphenyl (CBP) as host, green fluorescent material (4 s, 6 s)-2, 4, 5, 6-tetra (9H-carbazol-9-yl) isophthalonitrile (4CzIPN) as dopant. The device structure was optimized by adjusting concentration of 4CzIPN doped into CBP, then the photoelectric properties and lifetimes of device were studied. The performance of 12% 4CzIPN-doped device is the best. To study the influence of driving mode on device lifetime of the TADF-OLEDs, the AC driving circuit of positive constant current reverse constant voltage was designed, and the parameters of the AC driving circuit were optimized and adjusted. Research shows that the TADF-OLED achieved a longer device lifetime under AC driven of frequency of 50 Hz, reverse bias of 0 mV and duty cycle of 50%. By comparing the lifetime curves of the same device driven by DC and AC, it is found that the TADF-OLED lifetime under the AC driving scheme is about 1.5 times longer than that of under the DC driving scheme.
CsPbBrI2 Quantum Dots (QDs) with good air stability were prepared by hot injection method. The photoluminescence performance of QDs was studied using 375 nm pulsed laser as excitation source. Photodetectors (PD) based on air-stable CsPbBrI2 QDs were designed and fabricated using a facial spin-coating method. The optoelectronic properties and stability of the devices were also studied in detail.The results show that the quantum dots have strong fluorescence effect near 635 nm, the spectral luminescence peak is relatively narrow, and the half-peak width is about 35 nm. The band gap of CsPbBrI2 quantum dots is 1.90 eV. As a result, the PDs are capable of broad bandwidth photodetection from deep UV 260 nm to visible 650 nm region with good photoresponsivity of 0.26 A/W, high on/off ratio up to 104 and very short rise/decay time of 3.5 ms/3.5 ms. Furthermore, the device performance shows very little degradation at 25%~35% humidity and 25℃ over the course of 60 days of storages in ambient condition. The combination of high performance broad bandwidth photodetection, remarkable stability and easy fabrication categorizes the CsPbBrI2 QDs as a kind of very promising semiconducting materials for optoelectronic applications.
Charge generation unit consisting of B3PyMPM:Cs/Al/HAT-CN was employed to fabricate a highly-efficient tandem green phosphorescent organic light-emitting device. The maximum current efficiency and the maximum luminous efficiency of tandem organic light-emitting device are as high as 172.2 cd/A and 111.0 lm/W, respectively. At the given current density of 5 mA/cm2, the voltage and luminance of the tandem device are 2.04 times and 2.84 times those of single-unit device. In order to explore the reason why the performance of tandem device is better than the single device, the charge generation and injection processes in charge generation unit, and the effect of ultrathin Al layer on electron injection capability and the stability of charge generation unit systemically were studied. Experimental results show that the charges can be efficiently generated in the charge generation unit and smoothly injected into the electron transport layer. The insertion of the thin layer of aluminum between B3PyMPM:Cs and HAT-CN can increase both the electron injection and the device stability.
To solve serious efficiency roll-off of phosphorescent organic light-emitting devices (OLEDs) that still hinders further development of OLEDs, ultrasonic spray coating poly(3, 4-ethylenedioxythiophene) polystyrene sulfonate (PEDOT:PSS) films were proposed as transparent electrode for fabricating red, green and blue OLEDs. The water-soluble PSS molecular chain, which is insulating, was retained in the PEDOT:PSS transparent electrode by utilizing the high utilization rate of ultrasonic spraying materials, resulting in hole buffer effect of such PEDOT:PSS transparent electrode. Dual functions of this type of PEDOT:PSS transparent electrode is used to improve carrier balance under high current density, reduce the polaron density in the red, green and blue emitting layers, and finally improve the efficiency roll-off of these OLEDs. From the luminance of maximum current efficiency to the luminance of 10 000 cd/m2, efficiency roll-off of red, green and blue devices is only 14.9%, 12.4% and 16.0%, respectively. The results show that the introduction of dual functional electrode significantly improves carrier balance in organic luminescent devices, and is universal to reduce efficiency roll-off of three primary color devices, which is of great significance to achieve high brightness efficienct OLEDs.
In order to explore the mode of corner cube resonator, taking the cone plane mirror cavity as an example, the corner cube prism is equivalent to a diffraction grating. Considering the influence of the diffraction effect of the corner pyramid width in the resonator and the additional phase distribution caused by the dihedral angle error on the laser mode of the resonator, a theoretical analysis model for solving the intrinsic mode is established based on the theory of the optical resonant cavity. The fast Fourier transform method is adopted to simulate the distribution of the laser oscillation modes of the passive corner cube cavity in different cavity length, apex widths and dihedral angle error. When the cavity length is 30 cm, the width of the corner cube is less than 75 μm, and the angle error of the two sides is between -10'and 5', the complete circular distribution output mode of the light spot can be realized, and the beam quality is good. When the width of the edge is not less than 0.4 mm and the dihedral angle error is between -40'and 10', the spot is a transverse mode of TEM03 and the light field is a six-lobe distribution. When the width of the corner cone mirror is 0.4 mm, the error of the dihedral angle is 3' and the cavity length increases in the range of 30~90 cm, the laser mode of the resonator is converted from TEM03 to TEM10.
The position coordinates of the observers' eyes were derived in real time based on the depth camera and human eye detection model. Reasonable display area was calculated based on coordinate transformation model. The ambient color temperature and brightness were estimated based on the color component data of the color sensor. Finally, the display state was adjusted to make it nearest to the color performance of ambient light based on the pre-calibrated display parameter mapping table. A scene fusion experimental system was built, which can be divided into five parts:position monitoring camera, image capture camera, color sensor, display device and processor. Fusion experiments were carried out in indoor scenes with color temperature of 6 354 K and illumination of 160 lx, and outdoor scenes with color temperature of 6 197 K and illumination of 848 lx. The experimental results show that this scene fusion scheme can adjust display area for the observers in different locations, and change display parameters according to ambient light information, then achieve excellent fusion effects. The single execution only takes 283 ms.
For the application of conventional infrared image non-uniformity correction method, when the integration time is adjusted, the image gray level may change accordingly, an infrared image nonuniformity correction method adapted to adjustment of integration time was proposed. In this method, the black-body calibration images with different integration time and temperature, and the corresponding theoretical infrared radiation were integrated into a whole database, with the loss function of neural network and error reverse transfer mechanism, the correction coefficients in the model were learned during the training. The trained network correct non-uniformity can ensure the stable output of images during the real-time adjustment of infrared camera integration time, it is significant for post infrared image processing. And it is proved that the training of this network does not need enormous calibration datum. In order to deal with the problem of infrared detector response drift, an online learning correction coefficient method is proposed.
Traditional infrared small target detection methods based on the human visual system can easily cause false alarm detection in complex backgrounds. Therefore, to address this issue, an accurate and robust infrared small target detection method called Double-layer Local Contrast Measure (DLCM) was proposed. First, a double-layer-diagonal gray difference contrast was proposed to enhance the visual saliency of the target and alleviate the impact on background clutter and noise. After that, an adaptive threshold segmentation was used to obtain the real target. The experimental results show that, compared with the mainstream detection methods based on human vision system, the background suppression factor of the proposed method is increased by an average of 9.3 times and the signal to clutter ratio gain is increased by an average of 7.8 times, which have better detection performance in different complex scenarios.
In order to enhance the accuracy and the stability of attitude data, the basic attitude determination principle of star camera and gyroscope sensor was analyzed, and the attitude determination algorithm of star camera and gyroscope based on Unscented Kalman Filter (UKF) was derived with the error quaternion as the state variables. Because of the high-precision characteristics of star camera and gyroscope sensor, the UKF attitude determination experiments were carried out with the simulative star camera and gyroscope data of various precision, and were compared with the Extended Kalman Filter (EKF) attitude determination experiments. The results show that the UKF algorithm is effective and reliable, the attitude determination accuracy of star camera is effectively improved and the tri-axis accuracy is increased by about 10% to 20%.
In order to improve the detection accuracy of multi-scale remote sensing ship targets in complex scenes, a feature enhancement single shot multi-scale detector is proposed. Firstly, the shallow feature enhancement module is designed to improve the feature extraction ability of the shallow network in the pyramid structure of Single Shot MultiBox Detector(SSD). Then the deep feature fusion module is designed to replace the deep network in the pyramid structure of SSD to improve the feature extraction ability of deep network. Finally, the image features are matched with candidate frames of different aspect ratios to adapt to remote sensing image targets of different scales. The experiments tested on the optical remote sensing image dataset demonstrate that the proposed method can adapt to target detection under different background and effectively improve the detection performance of multi-scale remote sensing targets in complex scenes. On the extended experiment, the proposed method performance over SSD in blurry target detection.
In order to improve the theoretical prediction accuracy of the image motion which is affected by coupling characteristics of the flywheel and the satellite, a numerical compensation algorithm for the stiffness and damping parameters of the on-board flywheel installation is proposed. Firstly, the mathematical model of the compensation algorithm is established. Based on the radial swaying mode of the flywheel and the linear whole-wave micro-vibration transfer function model, and by combining the measured data of disturbances of flywheel on the dedicated measuring platform with jitter-affected image motion data of flywheel installed on the satellite to construct an optimization function to compensate for the installation stiffness and damping parameters of the flywheel on the satellite. Secondly, the algorithm is used to compensate and estimate the stiffness and damping of the flywheel installation in a certain type of satellite. Finally, the theoretical prediction and comparison of the jitter-affected image motion before and after the parameter compensation are carried out. The comparison results show that the estimated image motion data after parameter compensation is closer to the measured image motion data than estimated image motion data after parameter compensation and the radial rocking mode natural frequency curve is more obvious, which proves that this parameter compensation algorithm is feasible. This study significantly reduces the analysis error caused by the inconsistent installation stiffness of the flywheel on the satellite and the installation stiffness of the test platform during the whole-wave micro-vibration analysis, and provides a new idea for solving the equivalent parameters of the coupling characteristics of the flywheel and the satellite.
The direct measurement of the smooth and high-reflected surface was realized using images acquired by a single camera. Firstly, the image of the reference plane in the standard plane mirror was captured by the camera. Then, the depth distance of the mirror to be measured was obtained, by using the dense reflection correspondence between the points on the reference plane and the image points on the normalized imaging plane. Finally, the measurement of high-reflected surface was achieved. The high-reflected surface was measured by finding the "intersection point" between the camera ray beam and the corresponding incident ray beam. The ray tracing was used to transform the measurement process into an intersection problem between the two corresponding ray bundles in the solution space. The normal fields of the surface were obtained and the corresponding reflected light beam was solved based on the surface profile gradient which is obtained by taking the phase information as the carrier. The standard plane mirror is tested and the measured flatness is 0.19 mm. The rearview mirror is detected by the traditional method and the method proposed in this paper, and the average distance between the corresponding points in the test result is 0.15 mm, which verifies the effectiveness of the method for detecting the mirror surface shape.
In order to improve the efficiency of digital zenith camera, the orientation method was studied on the basis of precision position. Coordinate transformation model for identified star points was constructed. Then the coordinate transformation model was analyzed. The effects of instrument tilt and optical axis tilt on star points were analyzed respectively. Influence of focal length and astronomical coordinates of optical axis on the theoretical image coordinates of star points were also studied. Then the orientation model was established based on coordinate transformation. Analysis of experimental data shows that the orientation accuracy of single group star images is within 5″. The orientation accuracy is high, which can meet the requirements of orientation accuracy under actual conditions.
In view of the lack of space objects' attitude estimation based on space-based optical observation, this paper applied the Unscented Kalman Filter (UKF) to the Geosynchronous Orbit objects' attitude estimation based on space-based optical observation. Taken the Optical Cross Section (OCS) instead of magnitude as observed variable, linearizing and simplifying the observation equation. In addition, an OCS observation model based on the improved Phong model was established, which improves the description ability of the observation equation. And the angle was used as the input of the model, which greatly simplifies the calculation and enhances the real-time capability. Finally, compare the attitude estimation of the Kapton cuboid and the Lambert cuboid, the effectiveness of this method is verified, and the attitude estimation of the regular hexagonal prism and eight prism is also carried.
An on-orbit low spatial frequency error compensation method has been proposed to restrain low spatial frequency error brought by the difference between on ground calibration and on-orbit environment. Firstly, principle points, initial value of focal length and distortion coefficients are calculated during on-ground calibration. Then, focal length is updated by extended Kalman filter based on angle distance error minimization criterion using selected star pairs during on-orbit calibration. Faster convergence rate and better robustness has been validated by simulation. Sky tests data and on-board data proved that the mean value of angle distance error can be decreased by more than 90% and the low spatial frequency error decreased by more than 40%.