View fulltext
View fulltext
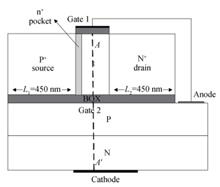
A novel Tunneling Field Effect Transistor (TFET) photodetector based on silicon on insulator is proposed, which combines a photodiode with TFET to realize photodetection and amplication. The anode pole of the photodiode is tied with the gate of TFET. After illumination, the photogenerated potential of the photodiode controls the channel state and drain current of the TFET photodetector, and converts the light into current. The subthreshold region is used to amplifies the drain current, and the responsivity of the detector is improved obviously. Two dimensional numerical simulations were performed in SILVACO. The P region of the photodiode forms the bottom gate of the TFET through the thinner BOX, which enhances the control of the channel and increases the drain current. The results show that the detector has higher responsivity in weak light. When the light intensity is less than 10 mW/cm2, the responsivity of TFET photodetector can exceed 104 A/W. In addition, adjusting the photodiode bias and inserting n+ pockets between the source and the channel can also improve the drain current and responsivity of photodetector.
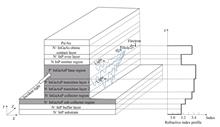
To improve the responsivity and working speed of an InP-based optical detector, an uni-traveling carrier heterojunction phototransistor with gradual coupled ridge waveguide is designed. The optical transmission mode of the gradual coupled ridge waveguide is analyzed through effective index method and beam propagation method, and the waveguide width and length are optimized as 2.6 μm and 250 μm respectively to achieve single mode transmission and high absorption efficiency. Because the direction of optical transmission is perpendicular to the direction of carrier motion, the absorption efficiency and speed of the phototransistor are optimized, and the output photocurrent and characteristic frequency of the device are improved. The responsivity is 33.83 A/W, the saturation output photocurrent reaches 90 mA and the highest characteristic frequency is 87 GHz. Compared to the vertical-illuminated uni-traveling carrier heterojunction phototransistor, the saturated output current and characteristic frequency of the uni-traveling carrier heterojunction phototransistor with gradual coupled ridge waveguide are increased by 20% and 24% respectively. However, the uni-traveling carrier heterojunction phototransistor with gradual coupled ridge waveguide has a bigger absorption volume, and then the input light power at which it gets the saturation current is larger too, therefore its responsivity is slightly smaller than that of the vertical-illuminated uni-traveling carrier heterojunction phototransistor.
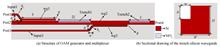
Based on an integrated silicon platform, a device for generating and multiplexing optical orbital angular momentum modes is proposed, which is consisted of asymmetric directional coupler and trench waveguides. According to the principle of phase matching, the fundamental mode TE00 is coupled to the first-order mode via an asymmetric directional coupler. Single-trench waveguide can support two orthogonal linear polarization-like modes whose optical axes are rotated by around 45° with respect to the horizontal and vertical directions. Adjusting the phase difference of two orthogonal eigenmodes to make them degenerate, TE00 can be converted into orbital angular momentum modes with various topological charges, and multiplexed in the second trench. The simulation is carried out with finite difference domain method. The results show that the device can realize the generation and multiplex of orbital angular momentum modes with topological charges of +1, 0, -1. The proposed device is very compact with a footprint of μm×5.3 μm and an insertion loss of 0.24 dB, and is fit for a wavelength range from 1.47 μm to 1.58 μm. The structure is simple and easy to integrate, having a good application in orbital angular momentum multiplexing system.
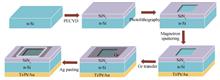
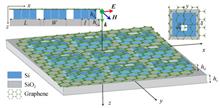
A photodetector based on Graphene/n-type Si Schottky junction is designed and fabricated. I-V and C-V characteristics are analyzed from the band energy perspective. The results show that Graphene/SiNx/Si(metal/insulation layer/semiconductor) capacitor has effects on device characteristics. Under the illumination of near-infrared light(808 nm), the photodetector exhibits that the reverse photocurrent is approximately the same value as the forward one owing to photo-generated holes, which diffuse from Si/SiNx interface to Graphene/Si junction and the responsivity is 0.26 A/W. The Schottky barrier height and ideality factor extracting from I-V dark current curve are 0.859 eV and 2.3 respectively based on thermionic emission model. The Schottky barrier height extracting from C-2-V curves on account of the equation of depletion layer capacitance increases and tends to be stable around 0.82 eV with increasing frequency. The value of depletion layer width of Gr/Si Schottky junction increases with increasing frequency, while doping concentration of Si donor atoms and capacitance of device decrease, which are attributed to surface states.
It has proposed an all-dielectric metasurface consisting of subwavelength particles, which supports "trapped" mode after the introduction of properly symmetry-breaking in the silicon meta-atoms. Combining the monolayer graphene with all-dielectric metasurface that enables to detect nucleic acids such as DNA and RNA. it has been found that the proposed metasurface is ultra-sensitive to the surrounding environment, its sensitivity in sensing detection can be up to 173 nm/RIU, with the corresponding quality factor of 14 416 RIU-1, which exhibits excellent biosensing performance by comparing the resonant state in the transmission spectrum. It indicates all-dielectric metasurfaces could be a promising way and platform to realize ultra-sensitive bio-sensors.
An experimental facility designed for the detection efficiency mesaurement of silicon single-photon avalanche detector traceable using standard detector is described. The photon rate is determined from the standard detector and a large dynamic range attenuation technique. Furthermore, the afterpulsing probability and dead time are considered and meaured. The component uncertainties associated with the measurement of detection efficiency are analyzed. The obtained expanded measurement uncertainty is 0.6% (k=2). Combining the monochromatic source consisted of supercontinuum laser and monochromator, the detection efficiency of silicon single-photon avalanche photodiodes could be automatic measured in a broad wavelength range using the standard detector in the setup.
A tungsten oxide thin film (WOx) with 30% oxygen content was sputtered on indium tin oxide (ITO) glass by DC reactive magnetron sputtering. On this basis, tantalum oxide thin films (TaOx) with different oxygen content were sputtered. The phase structure and the relative change of elements of tantalum oxide film were analyzed by X-ray diffraction and energy dispersive spectrometer. The surface morphology of tantalum oxide film was analyzed by scanning electron microscopy. The transmission of tantalum oxide film was measured by ultraviolet spectrophotometer and electrochemical workstation. The electrochromic property of tantalum oxide film was studied. The results show that the sputtering tantalum oxide films are all amorphous structure. With the increase of the oxygen content, the oxygen content of the films is close to 71.4%, and the protection performance of the films to tungsten oxide shows a downward trend. When the oxygen content is 70.08%, the optimal protection performance to tungsten oxide is obtained. At this time, the coloring response time of the electrochromic films is 21 s. The addition of tantalum oxide film reduces the switching peak current and leakage current of the electrochromic film, and keeps the charge capacity stable and improves the cycle stability of the device.
Optotype test method in the field of ophthalmic diagnosis was simulated. The contrast sensitivity of visual images through Fresnel microprisms was investigated. An imaging system for stroke test objects through Fresnel microprisms was set up. Experimental data on contract were obtained using new electronic method for registering the resolution of test stroke images. The experimental data obtained by the imaging system is consistent with the visual acuity data obtained by the traditional optotype test method. It was stated that applying microprisms noticeably reduce the contrast of test stroke optotypes which is diminishing proportionally to the prism strength and to the initial contrast value of the optotypes. The main reason for the reducing of the contrast and for the worsening of the resolution of optical images when using prisms is the white light chromatism and the diffraction of light beams at the microrelief of microprisms with different prismatic strength. The practical ways for the diminishing effect of reducing the contrast of the test optotypes are proposed by adopting the neutral glass filters with a sprayed layer of chromium.
In order to diagnose the physical process of laser inertial confinement fusion, a X-ray microscope was established. The imaging characteristics of the toroidal mirrors used in the system, optical design and parameter optimization, aberrations and tolerance analysis of the system and alignment were studied. Firstly, based on the requirements of plasma diagnosis, some optical system parameters were determined, and the the microscope for imaging the X-ray through the basic structure of two tandem toroidal mirrors in u-shaped arrangement and one planar mirror for spectrum selection was designed. The structural parameters of the three mirrors were preliminarily determined according to the anastigmatic focusing. Then the optical design software was used for modeling and optimization. The spherical aberration, coma aberration, field obliquity and astigmatism of X-ray microscope were also analyzed. By analyzing the influence of system parameters change on the image quality and the accuracy requirement of the system, reasonable tolerance was established. Finally, An auxiliary aiming system was designed to solve the off-axis problem of grazing incidence mounting of the toroid mirrors when adjusted offline, also a bidirectional binocular intersection online aiming system was designed to solve the problem of assembling and aiming accuracy of the system. Experiment results show that the resolution of the microscope is less than 5 μm at 500 μm field of view, which basically meets the requirements of large field of view and high resolution in laser plasma hard X-ray imaging.
In order to break through the selection limitation of substrate materials and achieve high imaging quality in the imaging wave band, the imaging diffractive optical elements is introduced to the ultrathin annular aperture imaging system. A hybrid refractive-diffractive ultrathin annular aperture imaging system is designed with four reflection structure, and the results of image quality evaluation and tolerance analysis are given. The substrate material of the hybrid refractive-diffractive ultrathin annular aperture imaging system is polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), focal length is 35 mm, and effective aperture is 29 mm. The results show that the lateral color aberration is less than 2.2 μm and the Modulation Transfer Function (MTF) is more than 0.4 at the spatial frequency of 166 lp/mm, thus high imaging quality is achieved. The tolerance analysis and thermal analysis of the annular aperture imaging system are given. The MTFs of tangential and sagittal direction are greater than 0.2 for each field of view when the spatial frequency is 166 lp/mm. The MTFs of tangential and sagittal direction are greater than 0.28 for each field of view at 0℃ ~40℃ when the spatial frequency is 166 lp/mm.
In order to improve the sensitivity and limit of detection of 81° tilted fiber grating, bovine serum albumin immunosensor based on graphene oxide modified cladding-etched 81° tilted fiber grating was proposed, the principle and sensing properties of the sensor were analyzed. Refractive index sensitivity of 81° tilted fiber grating was improved by etching with hydrofluoric acid. Then the etched 81° tilted fiber grating was coated with graphene oxide, and bovine serum albumin monoclonal antibody were modified on the surface of 81° tilted fiber grating for the specific detection of bovine serum albumin. Experimental results show that the detection range of the immunosensor is 0.15~15 nmol/L, limit of detection ~0.165 nmol/L, and the sensitivity in its linear response region is ~182 pm/(nmol·L-1). Although the detection range decrease, the sensitivity is ~5.3 times of that of the un-etched graphene oxide coated 81° tilted fiber grating, and the limit of detection is also improved.
According to real-time and precision requirements of online compensation, a support vector regression method improved by particle swarm optimization was proposed to establish the fiber optic gyroscope temperature error compensation model. A real-time acquisition method of temperature change rate based on multi-data window was adopted to meet the requirements of online compensation and model input. The fiber optic gyroscope was placed in a thermostat for temperature change test range from -15 to 50℃ to obtain the measured data. The temperature and temperature change rate were taken as inputs, and the least squares, radial basis function neural network and particle swarm optimization support vector regression algorithm were modeling respectively. The results show that the proposed model achieve the best compensation effect. The real-time compensation comparative experiment verified that the proposed model has good real-time compensation performance and generalization ability for non-training data.
Aiming at the problem of a poor signal-to-noise ratio in the laser Doppler acceleration measurement system, the digital correlation phase-detection algorithm was proposed for acceleration demodulation. The phase difference between the two interference signals in the laser Doppler acceleration measurement system was calculated by the digital correlation phase discrimination algorithm, and the acceleration of target was calculated from the rate of change of the phase difference, thereby the continuous acceleration measurement of the moving object was realized. The simulation results show that the error of the acceleration measurement is 0.135 m/s2 and the resolution is 7.3×10-3 m/s2, when the signal-to-noise ratio is 20 dB. The laser Doppler acceleration measurement system was built to measure the acceleration of the piezoelectric ceramic oscillator, the error of the acceleration measurement is 0.13 m/s2. The measurement results show that the algorithm can reduce the interference of random noise and improve the accuracy of acceleration measurement.
The source electrode and drain electrode are prepared with inkjet printed active layer on the spin-coated transparent source electrode, obtaining a vertical phototransistor with high photoresponsivity of ~1 500 A/W and high detectivity of ~1.6×1014 Jones. By doping electron capture materials PCBM into the active layer, the recombination of photo-generated holes in the active layer decreases and the photo-generated current increases. Thus the photodetector performance is improved further. It is found that when the electron capture material doping is 5wt%, the performance of phototransistor is better. The photoresponsivity is boosted to about 6 000 A/W and the detectivity is up to 1.4×1015 Jones.
A metal film with higher work function is deposited at the output electrode of the microchannel plate to cover the original nickel-chromium electrode, which further reduces the kinetic energy of the output electrons of the microchannel plate and the dispersion of output electrons on the phosphor screen, thus improving the resolution of the microchannel plate. The experiment results show that the resolution of the image intensifier increases by 6.6% from 60 lp/mm to 64 lp/mm when a 20 nm thick silver layer with work function of 4.3 eV is deposited on the output electrode of the microchannel plate, while the resolution of the image intensifier increases by 13% from 60 lp/mm to 68 lp/mm when a 20 nm thick platinum layer with work function of 6.4 eV is deposited on the output electrode of the microchannel plate. At the same time, the gain of microchannel plate decreases. For silver plated microchannel plate and platinum plated microchannel plate, the gain decreases to 74% and 33% of the original value respectively. The higher the work function of metal film, the higher the percentage of resolution improvement, and the higher the percentage of gain decreases. Therefore, when the proposed method is used to improve the resolution of microchannel plate, it is necessary to use the microchannel plate with higher gain, so as to make up the influence caused by the decrease of microchannel plate gain.
Aiming at the difficulty in the preparation process of the optical inverted cone narrow tip, through a special design mask, the photoresist was subjected to two consecutive patterning processes by one stepping using a stepper. Breaking through the resolution limit of the UV lithography machine, an inverted cone structure pattern with a tip close to 50 nm was prepared.The photoresist was reflowed to solve the problem of layering, which ensures the smoothness of the sidewall of the structure and the integrity of the tip. In the deep silicon etching process, by adjusting the gas components in the etching, the surface morphology of the tapered structure is improved, and the uniformity and integrity of the structure are improved. Finally, an optical inverted cone with a tip close to 50 nm suitable for interlayer coupling is obtained.
Facing the flexible support problem of the ultra-light mirror for micro-remote sensing payloads, a flexible support structure with folded-arm beam was proposed. According to the structural characteristics of the mirror, a parametric model of the flexible support structure is established. The second-generation non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm is used to establish a multi-constrained and multi-objective parameter optimization model. The key parameters of the flexible structure are optimized. The minimum size is only 1.30 mm. The strength of the bonded area is checked and the safety margin is 3.6. Finally, the engineering analysis and mechanical test of the mirror assembly are carried out. The flexible structure designed can ensure that the surface accuracy of the ultra-light mirror is better than 3 nm, when it is under the gravity and temperature is changed by 4℃. The relative error of simulation analysis and mechanical test is less than 10%. Finally, the mirror surface accuracy of the mirror assembly was detected. Before and after the mechanical vibration test, the surface error RMS of the mirror is 0.020λ, indicating that the mirror assembly has good stability. The feasibility of the design method and reliability of the flexible support structure with folded-arm beam proposed in this paper are verified.
Taking a 30×continuous zoom lens as an example, the method of changing the pressure angle of the curve is researched. The pressure angle is taken as the objective function, and the cam curve rotation angle is constructed as a piecewise function to re-divide the angle, the position where the pressure angle is too large is distributed large rotation angle, and the rotation angle of position where the pressure angle is small is compressed, so as to reduce the overall pressure of the curve, and also to restrain the large inflection point effectively in the curve. The optimization results of various angular allocation values are compared with the simulation using Matlab and the optimal cam curve is obtained. The optimal result reduces the maximum pressure angle of the curve from the original 76.9° to 41.9°. The experimental results show that the zoom lens optimized by this method has good imaging quality, the line-of-sight liner is not more than 3 pixels, and the stability of the line-of-sight is not more than 1 pixel.
Tunable Diode Laser Absorption Spectroscopy (TDLAS) technology and Computed Tomography (CT) technology were combined to reconstruct two-dimensional temperature distribution of bunsen burner flame through getting the most fitting spectrum. Zeromean Normalization Cross Correlation (ZNCC) value and Sum of Squared Difference (SSD) value were used as target to analyze accuracy of 32-path reconstruct temperature distribution. And ZNCC value comes to 0.994, SSD value comes to 0.000 86. 32-path CT-TDLAS system was designed and applied to measure the two-dimensional temperature distribution of Bunsen burner flame, and compared with the results of thermocouple. The results show that the temperature distribution trends between thermocouple and TDLAS are same while CT-TDLAS has higher precision and resolution. The feasibility and accuracy of reconstruction using tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy technology and computed tomography technology is demonstrated.
A compact electro-optical Q-switched 1 064 nm Nd:YAG laser end-pumped by high temperature Laser Diode Arrays (LDAs) was demonstrated. In order to achieve the compactness, high-temperature LDAs were used as the pumping source because it can effectively reduce the heat dissipation need within the system. The temperature field of the high temperature LDAs was simulated using Ansys. Lens duct made out of K9 glass was used as the coupling lens to couple the pumped light into the Nd:YAG crystal. The light field distribution before and after the coupling lens was simulated by Traceproc software. The gain medium was a 5 mm×5 mm×40 mm Nd:YAG with a doping concentration of 1.0 at.%. The internal temperature field distribution of the crystal under 200 μs and 250 μs pump pulse width was simulated by Ansys, and the focal length of the thermal lens during laser operation was calculated. The experiment results show that this compact laser can achieve stable pulsed laser output. With a repetition frequency of 20 Hz and the pump source voltage pulse widths of 250 μs and 300 μs, output pulsed energy of 44.1 mJ and 50.2 mJ were achieved corresponding to the pulse durations of 18.3 ns and 21.3 ns. The slope efficiency were 12.35% and 12.24%, respectively.
A scheme for generating broadband optical frequency comb was proposed and numerically simulated. For this scheme, a 1 550 nm vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser under a large signal current modulation with a modulation frequency of fm=f0/n (f0 is the frequency interval of two orthogonal polarization components of a 1 550 nm vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser, n is an integer) can output an optical frequency comb in the dominant Y polarization component direction while the X polarization component is suppressed. By further introducing a linearly polarized optical injection, both the two polarization components (spectral main-peak ratio less than 15 dB) can output optical frequency combs. Finally, via a polarizer the two optical frequency combs with orthogonal polarization components can be decomposed by spectral splicing to obtain a broadband optical frequency comb. Based on the spin-flip model, the optical frequency comb performances of generated by this scheme is numerically investigated. The numerical results demonstrate that, when the bias current of a 1 550 nm vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser with a threshold current of 2.6 mA is set at 11.5 mA, the Y polarization component dominates while the X polarization component was suppressed, and the ratio of the main spectral peaks of the two polarization components is more than 30 dB. Under a current modulation with a large modulation index, only the Y polarization component of the laser can realize an optical frequency comb output. By further introducing a linearly polarized optical injection, both two polarization components can output optical frequency combs by adjusting the polarization direction of the linearly polarized light. Finally, a polarizer is used to guide the two polarization components to the transparent direction of the polarizer to achieve the spectral splicing, and then an optical frequency comb with a bandwidth more than 80 GHz can be obtained.
In order to study the scintillation characteristics of vortex beam and Gaussian beam in underwater turbulence, an experimental system consisting of water turbulence have been set up. In the water tank, the intensity of turbulence is controlled by using a circulating pump, and the scintillation index of the beam is measured by using a scintilloscope. Using this experimental system, the scintillation index of vortex beams and Gaussian beams propagating in underwater turbulence are investigated in detail. It is found that the scintillation indices of vortex beams and Gaussian beams are getting bigger with the increasing of the transmission distance, as well as with the increase of the intensity of underwater turbulence. Within the propagation distance 12.6 meters, the scintillation index of vortex beam with topological charge m=2 is much bigger than that of Gaussian beam. At 5.4 meters, the radial scintillation index of vortex beam with m=6 decreases firstly and then increases in underwater turbulence. In addition, the scintillation index of a topological vortex beam with topological charge m=6 is lower than that of a topological vortex beam with topological charge m=4 after a certain distance of propagation. The research results obtained by our experiments have important value in exploring the application of vortex beam in oceanic turbulence.
Aiming at the complex atmosphere environment on Mars, using the T-matrix theory, the scattering characteristics of three kinds of Mars dust particles with non-spherical shape were studied. Then the scattering characteristics of non-spherical Mars dust particles with lognormal distribution were calculated, and under the conditions of sandstorm and no sandstorm, the variation trend of attenuation coefficient and transmittance of non-spherical Mars dust particles with particle number concentration, wavelength and height was analyzed, and compared with spherical particles.The results show that the extinction efficiency factor and scattering efficiency factor of non-spherical and spherical particles are quite different, and the difference between them is as large as 1.786 8 and 1.761 9. The scattering characteristic of chebyshev particles is the closest to that of spherical particles. When the incident wavelength is 0.55 μm, the overall scattering of dust particle swarm on Mars is mainly concentrated within 40° forward direction, and the scattering intensity of non-spherical and spherical particles are basically equal within 60° forward direction. When the scattering intensity is larger than 60°, the non-spherical particles have higher scattering intensity than spherical particles. The attenuation coefficient and transmission of non-spherical Mars dust particles (with wavelength, particle concentration, and height) are basically consistent with the spherical particles, and when the size ratio is closer to 1, its attenuation coefficient and transmission coefficient are closer to the value of spherical particles.
To investigate the two important characteristic parameters of threshold value and gain coefficient of Stimulated Brillouin Scattering (SBS) in water, the effects of temperature and salinity on SBS gain are analyzed theoretically, and meanwhile coupling wave equation combined with average attenuation coefficient are employed for analyzing the dependence of SBS threshold value on the temperature and attenuation coefficient of water. The results show that, SBS is positively correlated with temperature and salinity of water; the threshold value decreases with the increase of temperature and increases with the increase of attenuation coefficient. The results provide theoretical basis for understanding the SBS process in water.
In order to realize the laser one-dimensional range profile detection with long distance and high resolution and the echo feature analysis of space targets, on the basis of establishing one-dimensional heterodyne detection model of point target laser range image, furthermore the laser one-dimensional range profile of 3-D target is obtained by means of 3-D modeling. The differences and relations among the one-dimensional range profile acquired by optical heterodyne detection of a specific target, its range-resolved laser radar cross section and pulsed laser one-dimensional range profile are compared. The effects of target size, attitude, frequency modulation bandwidth and surface material on the target laser one-dimensional range profile are analyzed. The experiment result shows that the target one-dimensional range profile can reflect the shape features. The conclusions can provide references for analysis of target characteristics and target recognition.
The internal solitary waves are studied by analysis of optical remote sensing images in the whole sea area of the Northern South China Sea. This paper mainly collects MODIS optical remote-sensing images from Jan.2015 to Dec.2018, and the amplitude inversion model of internal solitary waves applicable to deep sea and shallow sea in the Northern South China Sea are established by using neural network. The calculation results of the model are compared with the situ data in the Northern South China Sea, and the accuracy is higher than 15% for both shallow sea and deep sea. Using the inversion model, the amplitude distribution of internal solitary waves in the Northern South China Sea is obtained. It is found that the amplitude distribution is positively correlated with water depth, with a correlation coefficient of 0.81. The amplitude distribution of internal solitary waves in Wenchang sea area, Dongsha atoll area and deep sea basin was calculated. It is found that the amplitude of single internal solitary waves is different. The amplitude of internal solitary waves in Wenchang sea area, Dongsha atoll area and deep sea basin is positively correlated with the water depth, with correlation coefficients of 0.79, 0.91 and 0.81 respectively. This study provides a new method for inversion of internal solitary waves amplitude in both deep and shallow areas of Northern South China Sea.
Aiming at the fact that the traditional fixture positioning can not meet requirements of complex curved blade damage in the process of aero-engine blade repair, an adaptive positioning method for blade repair on complex curved surface based on speckle measurement was proposed. Firstly, a visual measurement system was constructed. The three-dimensional configuration of the blade was achieved by matching the speckles on the blade surface and calculating the spatial coordinates of the reference measuring points and the data of the blade solid point cloud. Then, an adaptive positioning model was established, and the pose matrix of each positioning coordinate system was calculated to realize the adaptive positioning of curved surface blades under under-positioning clamping in machine tool coordinate system. Finally, an adaptive positioning experiment based on demage five-axis NC machining center was carried out to verify the effectiveness and practicability of the positioning method. The experimental results show that the deviation of translation vectors is less than 0.25 mm and the deviation of Euler angle of rotation matrix is less than 0.2°. The shape and position information of blades are extracted by one-time clamping and fixing using visual measurement to reduce the locating process, which can provide an experimental basis for the subsequent adaptive positioning and repair of complex surface blades.
In order to solve the problems of surface reconstruction and high-light weak texture objects, such as holes and noise, and information loss, a reconstruction method of illumination compensation combined with depth image was proposed. Combined with the parameter estimation of illumination direction and illumination intensity, the highlight area was determined and uniform illumination was applied. Then the drift region of the mean shift algorithm was corrected by the change track of the laser point, and an improved mean shift center descriptor was established, and the noise and holes of the depth image were determined and repaired. Finally, the surface reconstruction of the object was achieved. The results show that the proposed method can maintain the complete reconstruction of different kinds of objects, avoid the lack of information and reduce the negative impact of the external environment and the characteristics of the object itself. The robustness and effectiveness of the proposed method are verified by the high-light weak texture standard picture and real-time object reconstruction experiments, and the performance indexes such as root mean square error, peak signal-to-noise ratio and structural similarity.
A modified Kalman real-time adaptive filter method was proposed for micro-electro-mechanical system gyro which is easy to be susceptible to environmental influences and stability, and lead to the problems that the established random drift model parameter and the noise statistical property change. The order of random drift ARMA model was determined by analyzing the measured data. On this basis, the recursive least square method was used to update the model parameters in real time. According to the characteristics of gyro noise parameters, a real-time filtering method of Allan variance analysis based on fading memory factor and Sage-Husa adaptive filter algorithm was proposed to estimate the parameters of Q and R at the same time. The coupling and restriction of system state estimation and measurement noise parameter estimation were avoided. The experimental results show that, compared with the standard Kalman filter compensation method, the proposed method in this paper can compensate the random drift error of MEMS gyro more effectively in real time, and has better adaptability and stability.
Profile measurement plays an important role in aspherical mirror testing. However, the coordinate deflection and shift will lead to errors in result. In this paper, the analytical mathematic formula for misalignment error is presented. The measurement results are optimized by numerical differentiation method and nonlinear optimization algorithm based on least square method and the influence of these errors is eliminated. This method can effectively reconstruct the off-axis aspherical surface with systematic error. After four times polishing of the 570 mm off-axis aspherical mirror, the surface PV and RMS are decreased from 34.80 μm to 13.83 μm, and from 3.28 μm to 1.89 μm, respectively. For further comparison, the 220 mm×96 mm off-axis rectangle-shaped mirror is measured and proved that this method has strong applicability and generality for special shape mirror.
Experiments on measuring the photometric characteristics of space targets were conducted based on Jilin-1 video satellites, the method of using video satellite to image space targets and perform luminosity inversion were demonstrated. The inversion and estimation on luminosity characteristics of targets was based on grey scale value of output images from camera sensor. An analysis on the effect from the error of radiation calibration coefficient and image noise on the inversion precision was also conducted based on the principle of error transfer. By using star targets as the standard radiation source, the inversion precision was verified. Results show the error of luminosity inversion is less than 0.15 magnitude. A statistics analysis on targets filmed by Jilin-1 satellites was performed and examples were listed, giving estimation on the maximum sensing distance, probability of target capture and the observation performance. Results show that the agile imaging mode of video satellite which is designed for ground remote sensing performs well in space target observation as well.