View fulltext
View fulltext
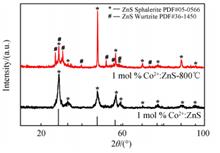
Co2+:ZnS sulfide nanocrystals are prepared by a simplified hydrothermal method without organic materials. These nanocrystals have a cubic sphalerite structure with an average grain size of around 8.3 nm. Mid-infrared fluorescence emissions at 3 400 nm and 4 700 nm were detected under 808 nm laser pumping. By heat treatment at 800℃ in a reducing atmosphere, the prepared nanocrystals transfered to cubic sphalerite and wurtzite mixed crystal forms, and the average grain size increaes to 22.5 nm. After the heat treatment, the nanocrystals possess lower hydroxyl content on surface, therefore exhibit stronger mid-infrared fluorescence. This method is facile and aviods the introduction of organic mid-infrared fluorescence quenching centers during the preparation of Co2+:ZnS nanocrystals. The surface defects and hydroxy content of Co2+:ZnS nanocrystals were reduced and more stronger mid-infrared fluorescence was obtained after heat treatment.
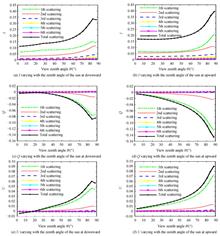
By solving the vector radiation transmission equation with the successive order of scattering method, the polarization characteristics of the light scattered by the atmosphere aerosols under different earth surface reflection models are studied. Two surface reflection models, single surface reflection and coupled surface reflection, are used in the numerical simulations. The reflectivity of earth surface is obtained according the corresponding model. The Stokes vector of the scattered light is derived by solving the vector radiation transmission equation with successive order of scattering method. Furthermore, the polarization degree of the scattered light is calculated. The simulation results show that the scattering radiation intensities of the first scattering order are equal for the two earth surface models. It is the same case for polarization degree of the first scattering order light. On the other hand, the total scattering radiation intensity of the coupled surface reflection model is larger than that of the single surface reflection model; The contribution of the first scattering light of the coupled model is smaller than that of the single reflection model. The results are of significance to the inversion of aerosol optical properties.
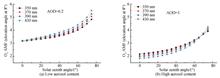
Sensitivity of retrieving aerosol optical parameters from O4 absorption measured by ground-based differential optical absorption spectroscopy was studied. The influence of different wavelength and aerosol optical parameters (aerosol optical density, boundary layer height, single scattering albedo and asymmetric factor) on the absorption of O4 was analyzed by the atmospheric radiation transfer model (McArtim).The results show that the air mass factor is not sensitive to the wavelength change, and the aerosol optical density and boundary layer height have an important influence on O4 absorption (air mass factor). When the aerosol optical density increases from 0.1 to 1, the air mass factor measured at 3° decreases by 28%. And when the boundary layer height increases from 0.1 km to 1 km, the air mass factor measured at 3° increases by 9.2%. The O4 absorption has a good sensitivity to single scattering albedo and asymmetric factor under the flat-latitude observation mode, which provides a new method to retrieve aerosol optical parameters based on the observation of O4 absorption by ground-based MAX-DOAS.
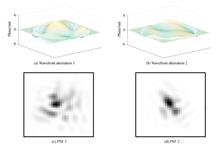
In order to restore turbulence-degraded imaging of astronomical or space targets in real time, this paper proposes the multi-channel blind recognition method, which can be applied to the dynamic changes of atmospheric turbulence. Target imaging at different time after adaptive optical correction are regarded as multiple channels to establish the point spread function of system. The super-Laplace algorithm is used to solve the target after obtaining estimations of point spread function. Results show that there exists a mutual relationship between point spread functions at different moments, which satisfies the theory of multi-channel blind recognition. The Mean Square Error(MSE) between the solved point spread function and the original point spread function is in the order of 10-30~10-27 and the MSE between the recovered target image and the original target is in the order of 10-5~10-4. Research results provide a theoretical basis for real-time restoration of turbulence-degraded images.
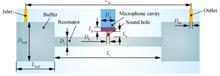
Taking the typical cylindrical photoacoustic cell as the research object, the accurate finite element model of photoacoustic cell acoustic simulation is established. On this basis, the structure parameters of resonant cavity, buffer cavity, intake and outlet holes, as well as temperature and humidity in the photoacoustic cell are studied. The influence of factors on its acoustic eigenfrequency is discussed. The results show that the inlet and outlet holes of a cylindrical photoacoustic cell are insensitive to its acoustic eigenfrequency, and can be neglected in design calculation. The length of the resonator is the most sensitive, followed by the diameter of the resonator. The simulation results also show that the length and diameter of the buffer chamber have a certain influence on it, so it needs to be taken into account when calculating accurately. The influence of temperature and humidity on the acoustic eigenfrequency of photoacoustic cells shows a positive linear growth law. The sensitivity of temperature effect decreases with the increase of resonator length, and the sensitivity of humidity effect decreases with the increase of temperature. When calculating the acoustic eigenfrequencies of photoacoustic units, the effect of humidity can be neglected under room temperature and low humidity.
For further understanding the physical mechanism of space constraints, we used the two-dimensional compressible fluid model, established dynamic simulation of laser-produced plasma under plate constraint, and calculated the evolution of the plasma process under the plate constraint. A series of time-resolved temperature distribution results obtained are basically identical with the experimental results. The mechanism of plasma temperature increase caused by the compression effect of reflected shock wave under the constraint of flat plate is revealed. The effects of different laser energies and different spacing of restraint plates on the peak temperature and the peak time of plasma temperature were also studied. The distance between the two plates increases, the peak time is obviously delayed and the enhancement effect on plasma temperature is weakened.
A narrow-band Metal-Insulator-Metal (MIM) waveguide filter based on a rectangular cavity is proposed and investigated in theory. The influences of the coupling characteristics between the microcavity and the waveguide on the filtering characteristics, which have not been clearly demonstrated before, are studied by establishing a transfer matrix theoretical model for the transmission of electric fields in the filter. The effects of coupling length, rectangular cavity length, and propagation loss on the filtering bandwidth are also analyzed. It is found that for different resonance cavity lengths, there is an optimal coupling coefficient at which the filtering bandwidth is the narrowest. In addition, the greater the resonance cavity length and the lower the cavity loss, the narrower the filter bandwidth. These would provide some reference for the research and development of surface plasmon polariton filters.
In order to improve the anti-interference ability, sensitivity and stability of the electric field sensor, a high Q thin-walled liquid-core capillary microcavity combined with the electrophoretic effect is proposed and experimentally demonstrated for the first time. In this paper, whispery gallery mode resonance of liquid-core microcapillary with different diameter and the wall thickness is theoretically simulated and analyzed based on the finite-difference time domain method and that sensitivity increases with decreasing wall thickness is concluded. Microcapillary resonator with diameter of 86 μm, wall thickness of 2 μm and a Q factor of 2.8×106 is fabricated. Using the principle of electrophoresis and the charge of protein molecules, we built an electric field test system. Liquid core microcapillary with different protein solutions achieves the maximum electric field sensitivity of about 10.6 pm/(kV/m).
A design method of diffractive element that can effectively suppress speckle noise is proposed. Based on the traditional Gerchberg-Saxton algorithm, the uniformity of the light spot is effectively improved without reducing the diffraction efficiency by selecting a special initial phase. Taking the Gaussian beam shaped into an annular flat-top beam as an example, numerical simulation and optical experiments are carried out. The results show that the speckle contrasts of the annular flat-top beams obtained by using the proposed method and the traditional Gerchberg-Saxton algorithm are 11% and 34%, respectively, which verifies the proposed method can obtain a annular flat-top beam with low speckle noise.
Aiming at the problem of high power consumption of electrowetting display during playing video, a low-power video display driving system based on human visual characteristics was designed. Adopting histogram correction and histogram matching, the system seta threshold value in combination with human visual characteristics to reduce the number of high-brightness pixels in the image, thereby reducing system power consumption. At the same time, a low-power multi-grayscales driving waveform was proposed, which combines the photoelectric characteristics of the electrowetting display to further reduce the power consumption of the system while achieving accurate gray-scale modulation. The experimental results show that the system improves the problems of oil-splitting and oil reflow, drives the 1 024×768 resolution electrowetting display successfully and the display effect is good. Besides, the highest gray level of the pixel reaches 16.When measuring the same video, the average power is reduced to 1.75 W and the power consumption is reduced by about 20%.
A polymer-based microring refractive index sensor based on slot waveguide was studied at very-near-infrared region (around 890 nm). The relationships between the sensitivity and the waveguide height, width and gap width were analyzed to find optimum design criteria for refractive index sensing. A silicon master mold was fabricated using electron-beam lithography. A unique class of fluorinated polymer, perfluoropolyether, was used to fabricate the flexible soft mold, which was replicated from the silicon mold successfully. The slot waveguide was fabricated on the polymer platform by using UV-based soft nanoimprint technique. The width and the height of the waveguide, and the width of the slot in the slot waveguide, are approximately 510 nm, 830 nm, and 234 nm, respectively. The thickness of the residual layer of polymeric slot waveguide is approximately 350 nm. The fabricated slot walls with a high aspect ratio are shown compatible with low cost mass production processes.
The effects of the slot waveguide structure and cladding material on the nonlinearity and the power confinement were systematically investigated by using the full vectorial model of the nonlinear effect and the finite element mode solver of the slot waveguide. The results show that the nonlinearity and the power confinement can be significantly affected by the silicon-arms width, the slot width, the thickness of the silicon layer and the cladding material. For the air-cladding slot waveguides with different structural parameters, the corresponding nonlinear coefficients are all above 20 W-1·m-1 for the maximal power confinement factors, and the minimal nonlinear coefficients of 6.5 W-1·m-1 are all obtained near the cut-off mode where the slot waveguides suffer from the leakages to the substrate. The low nonlinearity and the high power confinement can not be realized at the same time for the air-cladding slot waveguide. But the low nonlinearity and the high power confinement can be obtained simultaneously if the silica is coated on the slot waveguide, where the nonlinear coefficient can be as low as 4.12 W-1·m-1 and the power confinement factor can be as high as 42%.
A novel method of estimating perceptive distance based on human factor for binocular image is proposed. Firstly, the stereo depth of binocular images are deduced. Then, subjective experiments are carried out to obtain the distance of human visual perception, and the difference between the perceptive distance and stereo depth is analyzed. Finally, the correlation between perceptual distance, stereo depth, and visual comfort is established using stereo comfort as a physiological factor, and the computational model for perceptive distance is built. Experiments are performed on a public dataset IVY. The results show that when the value of visual comfort is high, the mean absolute error and the root mean square error of the model prediction value are reduced by 0.004 9 and 0.007 3 respectively compared with the subjective evaluation value; and when the value of visual comfort is low, the mean absolute error and the root mean square error are reduced by 0.072 1, 0.059 4 respectively. It is shown that the results of the proposed model are closer to the human subjective perceived depth.
In order to measure the coaxiality error of GNSS antenna connector, a mathematical model of segment rotation of connector is constructed, and a non-contact measurement method combining horizontal turntable and machine vision is proposed. Then the measuring device is built and the measuring experiment is carried out. Based on the analysis of the motion mode of the connector and the measurement method of coaxiality error, the deviation relationship between the axes is determined, and the mathematical model and measurement model of coaxiality error are established. In the measuring device, the camera is mounted above the horizontal turntable with the optical axis parallel to the horizontal turntable axis. Rotate the horizontal turntable, use the camera to capture the center position of the end face of the transfer screw and fit the orbit, and complete the self calibration of the coaxiality error of the measuring device. Place the connector on the horizontal turntable, rotate the horizontal turntable, and measure the deviation of the thread axis at the top of the connector from the axis of the horizontal turntable. Rotate the carrier of the connector, and measure the deviation of the thread axis at the top of the connector from the axis of the carrier. Finally, the maximum coaxiality error of the connector is obtained by synthesizing the deviation relations of the axes. The standard deviation of measurement device for coaxiality error of GNSS antenna connector is 9 μm, and the expanded uncertainty of single measurement result is U=30 μm (k=2), which meets the measurement demand of coaxiality error of GNSS antenna connector in the level of 0.1mm to 1mm. Using connector coaxiality error to correct GNSS ultra short baseline measurement results can significantly improve the baseline measurement accuracy.
A coupled-cavity system with a center is introduced. It is composed of N+1 single-mode cavities, each containing an identical two-level atom. One of them is at the center of the structure and is connected with other N cavities by optical fibers. The situation is considered that atom resonantly interacts with cavity field via a one-photon hopping, and the total excitation number of the system equals one. The evolution of the state vector of the system is derived. The geometrical quantum discords between atoms and that between cavities are investigated. The influences of atom-cavity coupling coefficient and the number of couple cavities on the geometrical quantum discords between two subsystems are studied. The results obtained by the numerical method show:the geometrical quantum discords between atoms and that between cavities are weakened with the increase of the number of coupled cavities; the atom-atom geometrical quantum discords is weakened, and the cavity-cavity geometrical quantum discords is strengthened with the increase of atom-cavity coupling constant.
In order to reduce the power and realize ultrafast response time, a plasmonic waveguide system based on two stub cavities side-coupled is designed, and a plasmon induced transparency effect is investigated. The plasmonic waveguide based on graphene-Ag composite material structures is tuned by the optical Kerr effect. An ultrafast response time of the order of 1 ps is reached. With dynamically tuning the propagation phase of the plasmonic waveguide, π-phase shift of the transmission spectrum in the plasmon induced transparency system is achieved under excitation of a pump light with an intensity as low as 5.83 MW/cm2. The pump light intensity is reduced by adopting graphene-Ag composite material structures. The reason is that the optical Kerr effect is enhanced by the local electromagnetic field of surface plasmon polaritons, the slow light of the plasmon induced transparency effect and the plasmonic waveguide based on graphene-Ag composite material structures with giant effective Kerr nonlinear coefficient. The tunable bandwidth of about 40 nm is obtained. The group delay is controlled between 0.15 ps and 0.85 ps. Moreover, for the indirect coupling between two stub cavities or the phase coupling scheme, the phase shift multiplication effect of the plasmon induced transparency effect is found. The theoretical results are in good agreement with finite difference time domain simulations. Research results are of reference significance in design and fabrication of nanoscale integration plasmonic photonic devices with low power consumption and ultrafast nonlinear responses.
Aiming at the unsatisfactory restoration of the detail information such as boundary artifacts for the conventional blind image inversion algorithm does not consider the characteristics of the spatial target image itself, a joint sparse prior constraint blind inversion algorithm based on sparse representation is proposed. Firstly, according to the sparse feature of space object image gradient, the L0 norm of image gradient is used to extract the salient edge information of image which is beneficial to blur kernel estimation. Secondly, the Lp norm and L0 norm are used to constrain the gradient distribution and space domain of image, so as to ensure the significant contrast between the pixels of the inverted image and the inclusion of edges and textures in the image. Finally, Laplacian distribution priori is used to constrain the blur kernels in order to ensure the sparseness of the blur kernels. An alternative iteration strategy is adopted to optimize the proposed model, and then the estimated values of the blur core and the space target image are obtained. The experimental results show that, compared with several representative blind inversion algorithms, the proposed method can estimate more accurate blur kernels, and has better restoring ability to image edge and texture details, and achieves better inversion results under both subjective and objective evaluation.
Aiming at the problem of illumination image estimation in low-light image enhancement algorithm of the Retinex model, a low-light image enhancement method based on YCbCr color space is proposed. The original low-light image is transformed from RGB (Red Green Blue) color space to YCbCr color space. The Y component in YCbCr color space is extracted and the initial illumination map L1(x, y) is constructed. The enhanced illumination image L2(x, y) is obtained by the gamma transformation of L1(x, y), the enhanced image R(x, y) is obtained according to the Retinex model, and we use a multi-scale approach to boost the details of the image R(x, y) and obtain the final enhanced image Re(x, y).The experimental results show that, the method can not only effectively improve the brightness of the low-light images, enhance the details of the image, obtain a better visual effect with fewer color and lightness distortions, but also has a faster running speed.
A blind watermarking method based on binarization computational ghost imaging was proposed. In this method, a watermark image is firstly encoded by the encryption system based on computational ghost imaging, and then the ciphertext is binarized and embedded in the discrete cosine transform domain of a host image to realize watermark embedding. The process of watermark extraction and reconstruction is the inverse process of embedding and encryption. The watermark is obtained by extraction key and decryption key. Simulation results show that this watermarking technique has good imperceptibility. When α=10, the watermark is also imperceptible and the peak signal-to-niose ratio of the host image containing watermark is above 38 dB. In addition, this method also has some fault tolerance ability. When the error rate of the extracted encrypted data reaches 20%, the reconstructed watermark information can still be distinguished and recognized. Compared with the traditional computational ghost imaging, binarization for the ciphertext data brings convenience for watermark embedding, but does not bring serious deterioration to reconstructed image, and the difference of correlation coefficient is less than 0.1. In the process of watermark extraction, it is unnecessary for the original host image, so it belongs to a blind extraction method.
Institute of Seismology, China Earthquake Administration has developed a new generation of large-aperture mobile satellite laser ranging system TROS1000, which uses a convenient transport structure, a picosecond kHz semiconductor laser, a self-developed picosecond event timer and a nanosecond range gate generator, in order to solve the unbalanced distribution of satellite laser ranging stations in the East and West of China. TROS1000 is the kilohertz satellite laser ranging system, it can be transport conveniently and setup quickly. In september 2019, TROS1000 arrived at Nanshan station of Xinjiang Astronomical Observatory, Chinese Academy of Sciences. TROS1000 acquire kHz satellite laser ranging observation data in Western China for the first time. After data preprocessing, the single accuracy of low earth orbit and medium earth orbit satellites are better than 14 mm, that of high earth orbit satellites are better than 19 mm. Compared with the previous mobile satellite laser ranging system, TROS1000 has higher single accuracy, more valid echo signals and stronger target detection capability.
In order to effectively correct smears in the sun glint produced by spaceborne polarization camera imaging, this paper takes the GF-5 satellite directional polarization camera as an example and combines with imaging characteristics of directional polarization camera on orbit to theoretically analyze the generating mechanism of smears in the process of image acquisition. It sets up a matrix method calibration model and a dark line method calibration model both of which can effectively correct the light leakage smear under the circumstances of without any saturated pixel in the flare region. And it sets up a legacy smear calibration model based on a combination of the matrix method and dark line method under the circumstances of full pixel saturation in the flare region to estimate saturated pixel intensity in the flare region. This algorithm fully considers the leakage smear and legacy smear produced in the sun glint under the circumstances of intense light saturation. The feasibility of this smear correction method is verified by using spots of integrating sphere light source imaging in the laboratory to simulate solar flares in remote sensing images of directional polarization camera when it works on orbit. The experimental results show that this method can not only effectively remove smear noise in images and improve image quality but also effectively estimate spot saturation pixel intensity. In the end, this paper analyzes the influence of the flare region smear in directional polarization camera on-orbit images on radiance measurement accuracy of directional polarization camera. Analysis results show that gray variance can be decreased from 202.69×106 to 2.32×106, and average gradient can be decreased from 5.08×10-1 to 2.26×10-1 after the smear correction.
An object detection algorithm of spatial-transformer regional convolutional neural network with deblurring was proposed. Firstly, based on the principle of active millimeter-wave cylindrical scanning imaging, the human body is three-dimensionally imaged (frequency range from 24 GHz to 30 GHz), and a millimeter wave image data set is established. Then the blur kernel of the millimeter-wave image is estimated. The image prior knowledge is obtained by the convolutional denoiser network and is integrated into an optimization method of half quadratic splitting to achieve non-blind deblurring. Finally, the spatial transform network, composed of a localization net, a grid generator, and a sampling network, is inserted into the feature extraction network to achieve object detection after deblurring. With the proposed non-blind deblurring algorithm, peak signal to noise ratio of the image can reach 27.49 dB. Mean average precision of object detection algorithm can reach 80.9%. The experimental results show that the image quality and detection accuracy can effectively be improved through the proposed method compared with some state-of-the-art methods. New technical support is provided for object detection of hidden dangerous goods in millimeter-wave images.