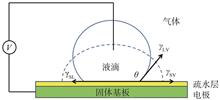
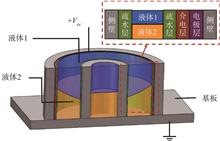
New display is one of the important footstones for electronic information industry, and one of the few industries with one trillion Yuan. Reflective display which is also called electronic paper display without backlight, using ambient light to read and having a similar “traditional paper” viewing experience, may become one of the mainstream display technologies. As a new reflective display technology, electrowetting display technology has the advantages of low energy consumption, visual health and flexibility, similar to the commercial electrophoretic electronic paper display products. At the same time, it breaks through two bottlenecks of “color” and “video playback” in the application field of electronic paper display technology and has been developed rapidly in recent decades. This review paper will systematically introduce the latest progress of electrowetting display technology, including key materials, device preparation, filling and packaging process, colorization.
Traditional Fresnel lenses cannot be used for active axial focusing without mechanical movement. In order to better apply the Fresnel lens to imaging, display, target tracking, photovoltaic system, and other fields, we proposed a ring chamber liquid Fresnel lens based on the typical structure of Fresnel lens and electrowetting effect. The proposed lens can be controlled by voltage to change the angle of inclination of the liquid surface within the ring chamber. So the axial focal length can be adjusted by controlling the deflection direction of the beam. The experimental results show that the proposed liquid Fresnel lens has the function of axial focusing. Its driving voltage is about 20 V, saturation voltage is about 220 V, and focal length varies from -52 mm to -73 mm.
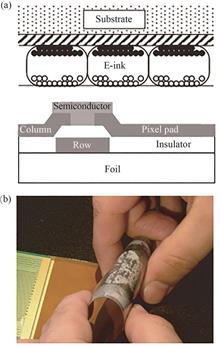
Thin film transistors (TFTs) are used as switching components in pixels, and together with the storage capacitors, form the driving circuit for electronic paper (E-paper) displays. In this paper, we classify the flexible TFTs according to their active layer: organic thin film transistor (OTFT), amorphous silicon (a-Si) TFT, metal oxide thin film transistor (MOTFT). Their research progress in flexible E-paper displays is presented, focusing on the flexibility, electrical properties and stability of the devices. Finally, the comparative analysis suggests that MOTFT is expected to be the best candidate to drive the next generation of flexible E-paper displays by virtue of the excellent electrical properties, high optical transparency and relatively low process temperature.
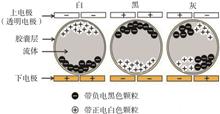
Reflective display which is also called electronic paper display without backlight, using ambient light to read and having a similar “traditional paper” viewing experience, may become one of the mainstream display technologies. Electrophoretic display (EPD), as a new reflective display technology, has attracted much attention because of its low cost, low weight, low power consumption and high reliability. EPD is based on the movement of charged particles through oppositely charged electrodes in dielectric fluid. Some parameters of electrophoretic particles, such as particle size, particle size distribution and surface charge etc., have an important impact on image quality, image control and image response time. Therefore, the researchers have done a lot of work on the preparation, surface morphology modification of electrophoretic particles and preparation of microcapsules. This paper will review the progress in these fields of EPD.
With the development of liquid crystal display technology, blue phase liquid crystal has entered the researcher’s field of vision due to its advantages and has attracted continuous attention. However, there are many difficulties in its research and practical application. For example, the blue phase only exists in a very narrow temperature range, so the rapid identification of the blue phase liquid crystal and the rapid calculation of blue phase temperature range are extremely important. In this paper, a model trained by a machine learning algorithm combined with Labview software can realize the rapid recognition of the liquid crystal phase state and the rapid reading and calculation of the blue phase temperature range. During the experiment, the overall recognition accuracy of 159 840 sample point phase images was above 93%. The research results of this paper can help to effectively identify the blue phase, quickly obtain the blue phase temperature range, and quickly screen the applicable blue phase liquid crystal formula, so as to improve the research efficiency of blue phase materials and to promote their application in display devices.
New display technologies such as organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) have become a key industry of information technology. Although great breakthrough has occured in OLED technologies such as materials and stack design processes, currently the research and development still mainly rely on trial-and-error approaches, and the understanding of the physical mechanism of the device remains mostly qualitative and empirical. In this article, the physical theories of OLEDs are systematically introduced and reviewed, especially focusing on how to physically describe the amorphous disordered nature of molecular systems, how to describe charge transport and excitonic processes, how to calculate the optoelectronic properties of devices, and how to apply these theories to experimental OLED research and development.
The reflection band gap of cholesteric liquid crystal (CLC) is usually between 50 and 100 nm. To enhance the usefulness of CLC, the external stimulation can be applied to broaden the reflection bad gap. The polymer network can be moved by the action of direct current voltage in polymer-stabilized cholesteric liquid crystal (PSCLC) with negative dielectric anisotropy, results in broadening the reflection band gap, which is usually driven by a large voltage. In this paper, the influence of polymer monomer’s concentration, cell thickness of liquid crystal, and ultraviolet absorption dye on the reflection band was studied. The reflection band of PSCLC is broadened by 3 times, and the required driving voltage is lowered to 7.5 V. After the driving voltage is removed, PSCLC system quickly returns to the original optical performance, shows the good reversible change.
The influence of white level and color saturation of LCD smartphone on visual comfort and visual fatigue is researched in this paper. The measurement is performed by the combination of subjective evaluation and objective evaluation, and the principal component analysis is adopted to reduce the dimension of parameters. The results show that the optimal white level of LCD smartphone in the dark environment is about 50 cd/m2 with generally higher visual comfort. As to color saturation, the statistically significant discomfort is induced when saturation adjusting coefficient is below 0.7, which brings a degree of visual and physiological discomfort. In addition, LCD cellphone causes the feeling of tiredness both from eye and body after white level experiment while only visual fatigue is found after saturation experiment.
Electrostatic discharge is harmful to electronic products because of its high voltage, strong electric field, instantaneous large current and broadband electromagnetic radiation, especially air electrostatic discharge is more common and harmful. In this paper, the Rompe-Weizel SPICE model describing nonlinear arc air-discharge, the 3D full-wave model and the IBIS model describing chip operation are combined to establish the field-circuit co-simulation model of the intelligent display terminal under air discharge. The discharge current, electromagnetic field distribution and signal transmission under air electrostatic discharge event are monitored through the discharge process. The simulation results show that the longer discharge arc length leads to the smaller current peak and the longer rise time. Under the influence of air discharge, the interference is different at different terminals of the signal transmission line, and the influence is mainly concentrated in the first 2 ns. And it is not that the stronger the electromagnetic field radiation is, the greater the interference is. Field-circuit co-simulation provides a more realistic simulation method for air discharge research in complex electronic products, and provides theoretical guidance for reducing electrostatic interference in the design and manufacture of electronic products.
Liquid crystals (LCs) have been one of the hot topics in physics, chemistry and material science for decades. Nematic liquid crystals (NLCs) are composed of molecules tending to align in a preferred direction and thus have orientational order. Hence, NLCs possess electromagnetic and optical properties similar to crystals, and play an important role in applications ranging from display to light field regulation, etc. LCs usually contain defects and therein exhibit special optical textures. In order to study these defects, a prevailing method is to build proper theoretical models for the LCs. In this review article, several static models of LCs and their applicable conditions are reviewed. The variation of free energy caused by anchoring energy under the interface effect is also analyzed in detail. Moreover, this article introduces the recent advances of the most widely used Landau-de Gennes Q-tensor model in case of elastic constant L→0 and low temperature limit. Finally, the progress of these theoretical models in practical applications is also discussed.
Liquid crystals, with external filed induced tunability of optical properties, has great application advantages in switchable glass. Compared with traditional single liquid crystal materials, liquid crystal-polymer composites can achieve dynamic regulation of incident light by adjusting the interaction between liquid crystals and polymer networks. Therefore, the photoelectric properties of liquid crystal-polymer composites are more excellent. The electrical response switchable glass based on polymer liquid crystal material has the characteristics of easy control, stable effect, fast response, etc., which can meet people’s immediate needs and has been widely concerned by researchers. In this paper, the research progress of electric controlled switchable glass based on polymer dispersed liquid crystals (PDLCs), polymer stabilized liquid crystals (PSLCs) and polymer stabilized cholesterol phase liquid crystals (PSCLCs) in recent years is reviewed and discussed, and the future development trend of these switchable glasses is forecasted.
Liquid crystals are a typical functional soft matter, possessing both the fluidity of liquids and the ordering of crystals. Liquid crystals show rich self-assembled microstructures and unique physical and chemical properties. Besides, liquid crystal display, applications of liquid crystals in areas such as optics and functional materials have achieved a large progress. Liquid crystal droplets, which could serve as basic functional elements, own the characteristics of rich features, easy orientation and processing integration, have received extensive attention. The functions and properties of cholesteric liquid crystal droplets could be tuned by their microstructures and compositions, which show a great potential for applications. This review systematically summarizes the molecular arrangements, physicochemical properties and frontier applications of spherical, oblate and complex cholesteric droplets. The application prospects of liquid crystal droplets as functional elements in smart functional materials, photonic devices and soft robotics are also discussed.
A novel low-voltage driven liquid crystal diaphragm driven by four-channel voltage is designed and prepared to realize the elliptical ratio, scale and center variable diaphragm with better applicability. The characteristics of the circular effective diaphragm region of the liquid crystal device are tested by experiment and numerical simulation software. Firstly, through numerical calculation and simulation of the distribution characteristics of the device, the simulation results of the voltage conditions of the device in different working states and the method of moving the center of the diaphragm are obtained. Then, the diaphragm characteristics of the device are tested through the optical path to achieve the distribution effect of the circular diaphragm and the elliptical diaphragm. Finally, the change of the optical axis of the device after moving the electric field is compared with the simulation results. The test results show that the working state of the liquid crystal diaphragm can be controlled by changing the amplitude and phase of the voltage. Under the conditions of different frequency of upper and lower substrate electrodes and different initial phase difference, the elliptical aperture transmission function is basically realized. In the effective region, the average error between the actual value of center translation measurement and the simulation result is 3.33%. The device basically meets the requirements of different aperture pass and moving aperture center in the scene.
A method is proposed to prepare a liquid crystal lenticular lens array (LCLA) with switchable positive and negative focal length. The LCLA exhibits a “sandwich” structure which consists of top electrode substrate, LC layer, polymeric lenticular lens array, and bottom electrode substrate. In order to integrate the convergence and divergence functions in a single LC cell, the refractive index of the polymer should be between the ordinary refractive index (no) and exordinary refractive index (ne) of LC material. The hydrophobic-hydrophilic strips array modified on the surface of the bottom substrate enables the formation of lenticular lens array self-assembly. There are two methods to switch the focal length of LCLA from negative to positive values: by changing the polarization direction of the incident light for 90°; or by applying an external electric field to adjust the effective refractive index of the LC layer. The experimental results show that when the applied voltage adjusted from 0 Vrms to 0.7 Vrms, the focal length of the LCLA changed from -4 mm to ∞. When the applied voltage changed from 1 Vrms to 7 Vrms, the focal length of the LCLA varied from 6.0 mm to 4.5 mm. The as-obtained LCLA has the advantages of simple fabrication, compact structure, low driving voltage and large range of focal length, which has potential applications in the fields of imaging, display, and optical communication.
The photoelectric response characteristics of polymer-stabilized liquid crystal (PSLC) devices have not yet fully met the practical needs of smart windows. The characteristics of the liquid crystal material itself are fundamental to determine the photoelectric properties of the liquid crystal device. Therefore, in this paper, the influences of dielectric anisotropy and birefringence of negative liquid crystal materials on the photoelectric response characteristics of PSLC devices are studied, and the corresponding optimal parameters are given. This work adopts the research method of combining experiment and simulation. Firstly, the negative liquid crystal materials with different parameters are selected to prepare PSLC devices, and the effect of dielectric anisotropy on photoelectric properties of the devices are studied and analyzed. Then, the effect of birefringence of negative liquid crystal material on photoelectric effect of PSLC is studied by simulation. Finally, the optimal negative liquid crystal parameters are obtained through comprehensive analysis of experimental and simulation results. The results show that the photoelectric performance of PSLC device is better when the dielectric anisotropy is larger, this is because the liquid crystal molecules can be driven more easily by the electric field. In the case of fixed polymer stabilized network birefringence, when the birefringence of the negative liquid crystal is ne=1.49, no =1.593, the optimal haze is obtained. These results can provide theoretical guidance for the performance optimization and industrialization of PSLC devices.
Protein analysis is an important method in disease diagnosis and medical research. In this paper, a single substrate liquid crystal biophotoelectric sensor is proposed for rapid detection of protein concentration. The sensor is composed of a single substrate ITO glass and a vertically oriented liquid crystal layer. Bovine serum albumin (BSA) can interfere with the orientation of the liquid crystal. The concentration of BSA can be calibrated by the brightness of polarizing microscope images under different applied electric fields to realize the sensor function. It was found that the linearity of concentration detection and the upper limit of detection were improved by setting the applied electric field, and the detection range of BSA was 10-3~10-7 g/mL. Furthermore, the liquid crystal cell array was prepared by photolithography on a single ITO glass substrate, and the function of multi-channel, high-throughput protein concentration detection based on a single substrate liquid crystal sensor was realized. In this paper, the single substrate liquid crystal photoelectric biosensor method has the characteristics of electric control and high efficiency, which provides a new technical scheme for the study of liquid crystal device applications.