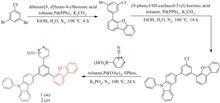
High-performance blue phosphorescent host materials are one of the important factors for realizing high-efficiency electroluminescent devices. A pair of trisubstituted benzene isomers (material 1 and 2) as new bipolar host material with tunable triplet energy levels are well designed and prepared by incorporating carbazole and dibenzo[b,d]furan as the hole transport moieties and cyanophenyl as the electron transport moiety. Material 1 and 2 show intense violet fluorescence in the non-polar or less polar solvents. The introduction of cyano unit into the different position on phenyl moiety could effectively tune the triplet energy level (T1) of the bipolar host materials, especially for material 1 with much higher T1, which is suitable for efficient blue phosphorescent organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs). Moreover, the trisubstitution molecular design strategy also provides the bipolar host materials with the steric hindrance in favor of OLEDs. The peak current efficiency, power efficiency, and external quantum efficiency of the blue phosphorescent OLED using materiat 1 as host reach 31.53 cd/A, 26.93 lm/W, and 16.17%, respectively. The preliminary results suggest that the trisubstitution molecular design strategy has great potential in designing new host materials for high-performance blue electroluminescence in the future.
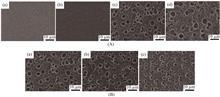
Polymer dispersion liquid crystal (PDLC),as a new type of display material,simple preparation process and high performance,make it occupy an important position in the field of optoelectronic display,and has received wide attention and research. The type and content of liquid crystal molecules and prepolymers are crucial to modulate the microscopic morphology and electro-optical properties of PDLC. The size of liquid crystal droplets dispersed in the polymer network affects the driving voltage of PDLC,while the selection of polymeric monomers directly affects the size of liquid crystal droplets. The effects of (meth)acrylate monomers,thiol/polythiol monomers,and the common additives as polymer components on the PDLC microscopic morphology as well as the driving voltage and contrast are mainly reviewed in this paper according to the different types of prepolymers. And the process of variation of liquid crystal micro-drop morphology caused by polymer networks,which in turn affects electro-optical properties,is explained in detail.
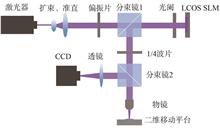
This paper proposed a projection splicing photo-alignment technology based on a liquid crystal on silicon spatial light modulator (LCOS SLM). By combining SLM and two-dimensional translation stage, the fabrication of liquid crystal optical elements with arbitrary size and arbitrary Pancharatnam-Berry phase pattern can be realized. Based on this technology, a variety of liquid crystal optical elements were fabricated by continuous scanning exposure method, such as one-dimensional polarization grating, two-dimensional grating, microlens array and hologram. The experimental results show that: this technology can realize the fabrication of optical elements with continuous phase distribution and enlarge the aperture of optical elements; the diffraction efficiency of a one-dimensional polarization grating with a size of 25.4 mm×25.4 mm reaches 98.32%, and the error in each area does not exceed 1%; the liquid crystal optical elements with two-dimensional periodicity or other complex pattern can be fabricated only by changing the exposure pattern loaded to the SLM. The SLM-based projection splicing photo-alignment technology has the characteristic of high resolution, high efficiency, simple process, and can realize the fabrication of optical elements of any scale, which can further promote the development and practical application of liquid crystal optical elements.
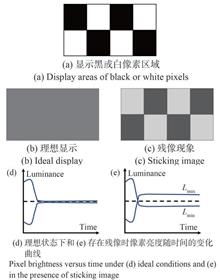
Organic Light-Emitting Diode (OLED) display technology exhibits the advantages of wide color gamut, low energy consumption and flexibility through the self-luminescence of organic materials, and is one of the most promising display technologies. At present, OLED displays still have problems such as short lifetime, low brightness and poor reliability. These problems eventually lead to the occurrence of sticking image. This paper aims to analyze and summarize the research progress and related solutions of OLED sticking image. Firstly, the relationship between OLED sticking image problem and OLED material lifetime as well as thin film transistor (TFT) stability is explained, focusing on the structural difference between flexible and rigid OLED devices, and the principle of OLED sticking image is further generalized. Secondly, for different causes of sticking image, the methods to alleviate and compensate OLED display sticking image are discussed, including schemes to improve the lifetime of organic materials, threshold voltage stability of TFT, and external compensation circuits. Finally, the further solution to the OLED display sticking image is prospected.
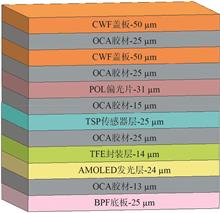
The internal components of flexible OLED module will be damaged due to impact and other factors while used. Modifying the structure of the module and testing the performance through mechanical test are the effective way to improve the impact resistance strength of the module. In this paper, the finite element simulation method is used to establish a finite element model of pencil-impacted test. The model is used to analyze how the single or double cover window, the different thickness and modulus of cover window, the different thickness and modulus of OCA layers and whether add a SUS layer under the bottom will influence the maximum strain of TFE layer which is easily damaged in OLED panel. The simulation results show that using the double cover window structure, increasing the thickness and modulus of the upper cover window and OCA layer, and adding a steel SUS layer under the bottom plate can reduce the maximum strain of the TFE layer, which is beneficial to improving the impact resistance strength of the module, and some results are verified by the test. The simulation results provide guidance for optimizing structural design and improving the impact resistance strength of existing structures.
In order to reduce the harmful blue light component of LEDs and other illumination modalities to human eyes, we propose a reduced harmful blue light attenuator based on the local surface plasmon resonance effect of self-assembled metal nanoparticles. The silver-covered gold nanoparticles (Au@Ag NPs) and silver nanoparticles (Ag NPs) were prepared by synthesis. Nanoparticle monolayers film were prepared on quartz glass using the self-assembly method, and the particle morphology film and distribution were changed by post-treatment through annealing. The scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images were used to analyze the morphology of nanoparticles of different samples as well as the arrangement pattern. The samples were subjected to UV-Vis transmission spectroscopy and the transmission was simulated with the help of time-domain finite difference method to analyze the factors affecting the transmission peaks. The results show that the samples prepared by the self-assembly method have selective attenuation of light transmission at different wavelengths and the attenuation peaks are blue-shifted after annealing. Finally, this paper shows the actual light transmission effects of different samples under white LEDs, in which the annealed Ag NPs sample can reduce the transmission to 24.5% at the 416 nm harmful blue light band, which significantly and effectively attenuates the harmful blue light and has excellent blue light protection effect.
Color gamut represents the capability of the display system to display colors. It is an important indicator of the display system. Color gamut is not only affected by each primary color but also related to the white point coordinates of the display system. Different standards have different reference white points, so it is necessary to study the influence of different white point coordinates on the color gamut of the display system under various conditions. By using the total differential formula, the factors affecting the stereo color gamut of the display system are divided into two parts: the direct part caused by the light source parameters and the indirect part caused by the white point color coordinate. Considering the addition of the two effects, a more accurate stereo color gamut can be obtained. For a light source that meets the Rec.2020 standard, the central wavelengths of the three primary colors are 630, 532, 467 nm, and the spectral width is 1 nm, every 0.01x color coordinate increases the stereo color gamut by 0.80%, and every 0.01y color coordinate reduces the stereo color gamut by -2.15%. When the assumption that the color coordinates of the white point remain unchanged is selected, the green spectral width has the greatest impact on the stereo color gamut, and a narrow spectral width of green light should be maintained to ensure a high color gamut. When the assumption of constant intensity is selected, the three primary colors have similar effects on the stereo color gamut. Considering that the red light has the least influence on the color coordinates of the white point, the spectral width of the red light can be appropriately sacrificed to balance the stereo color gamut and the spectral width.
The hyperspectral SPRi sensor was used to perform microscopic analysis of polystyrene microspheres, and the hyperspectral SPR data collected under different polarization conditions were processed, resulting in effective suppression of the contrast of inherent stains in the SPR hyperspectral images and making the position and outline of the polystyrene microsphere sample clearer. The processed SPR spectra become smooth, reducing the influence of the spectral characteristics of the light source and random noise on the SPR resonance information extraction. By comparing the SPR image of polystyrene microspheres with the reflection bright field microscopic image, it is found that there are obvious differences between the two images. The main reason is the limitation of the penetration depth of the evanescent field. The results show that SPR images can clearly reflect the contact between particles and metal surfaces in the evanescent field, but cannot quantify the true size of objects beyond the penetration depth of the evanescent field compared with reflection bright field microscopy images.
To solve the problems of high dynamic range, low image contrast and blurred edges of original infrared images, an infrared image detail enhancement algorithm based on adaptive guided filtering is proposed. Firstly, the input image is divided into a base layer and a detail layer using the designed parameter-adaptive guided filtering. Then, the plateau histogram equalization is used to compress the dynamic range of the base layer, and mask weighting and gamma transform are used to suppress detail layer noise and enhance the image details. Finally, the processed base and detail layers are linearly weighted and stretched to the display range. The experiment results show that compared with the traditional and advanced infrared image detail enhancement algorithms, the proposed algorithm has stronger scene adaptability, and has obtained better enhancement effects in scenes such as high dynamic range scene, complex outdoor, and sea and sky. Compared with the advanced algorithm, the proposed algorithm has an average improvement of 35.3% in the average gradient and an average of 10.7% in the perception-based image quality evaluator. The proposed algorithm can effectively compresses the dynamic range of infrared images, significantly improves image contrast and sharpness, and the processing results are more helpful for human eyes to observe.
Accurate segmentation of red blood cell (RBC) from blood smear images is an important technique and a difficult problem, mainly because RBCs often overlap and have no distinct boundaries. To solve this problem, a deep learning network called NODE-UNet++ is proposed, which is based on U-Net++ and neural ordinary differential equations (NODE). It is mainly used for pre-segmentation of RBCs, and then the marker watershed algorithm is adopted to segment clustered RBCs from blood smear images. Firstly, an image is clipped and labeled to highlight the region to be segmented. Then, a new semantic segmentation architecture NODE-UNet ++ is applied for pre-segmentation of the preprocessed image to obtain the probability grayscale image. Finally, the marker watershed method is used to separate the clustered RBCs in the grayscale image to obtain final RBC segmentation result. The experimental results show that the Dice similarly coefficient is 96.89%, the mean pixel accuracy is 98.97%, and the mean intersection over union is 96.33%. Segmentation results of different blood smear images show that the proposed method can extract each RBC efficiently and accurately to meet the requirements of subsequent RBC image processing.
To address insufficient contextual information and partial loss of spatial detail information in semantic segmentation of road images, a real-time segmentation method is proposed based on LinkNet. Firstly, a new attention mechanism is constructed in the encoding to capture the location and channel dependence of road images to increase the extraction capability of target features. Then, an atrous spatial pyramid pooling is introduced in the central region to capture richer multi-scale features without affecting image resolution. The experimental results on the general database show that the proposed method achieves 64.78% MIoU on the Cityscapes dataset, which is 5.01% higher in comparison with LinkNet. And it can significantly improve the visual effect of fine target objects and boundary segmentation, and the segmentation accuracy has been greatly improved.
Space remote sensing image is developing towards miniaturization, large width and high resolution. Different from the conventional method of push-broom scanning alone the orbit, this paper puts forward a new rotate-broom scanning method using the reflector, which can obtain thousand-kilometers-level width. In this system, combining with the satellite motion model, we analyze the calculation methods of scanning line frequency, resolution and image width. Based on the design parameters, we simulate and analyze the influence on the imaging system when the height of satellite orbit changes. When the height of orbit becomes higher, the resolution is lower, the image width is larger, the transit time is larger, the line frequency is lower, and the design requirement for the back-end readout system is lower. On the contrary, when the height of orbit becomes lower, the resolution is higher, the image width is smaller, the transit time is larger, the line frequency is lower, and the design requirement for the back-end readout system is lower.
At present, most of the research on forestry pest detection is based on traditional machine learning algorithms, and there are some problems such as low accuracy and poor effect. Therefore, a new forestry pest detection model based on YOLOv4, Pest-YOLOv4, is proposed. K-means++ algorithm is used to cluster anchor boxes to obtain a higher avg-IoU value. Combining ECA(Efficient Channel Attention) and CBAM(Convolutional Block Attention Module) to form ECA-CBAM attention mechanism, the network can pay more attention to the characteristic information. Reorganizing the network neck to SPP-PANet, the feature information can be fused with multiple receptive fields effectively. Using Focal Loss to improve the loss function, the learning of samples that are difficult to distinguish is paid attention, and the proportion of positive samples and negative samples are balanced. The experimental results show that Pest-YOLOv4 mAP reaches 90.4%, 4.2% higher than YOLOv4, while the FPS remains at 33.4 f/s, which meets the detection accuracy and real-time requirement of forestry pest detection tasks.
Aiming at the problems that the YOLOv5s algorithm has weak detailed feature learning ability, excessive redundant information, and insufficient key feature fusion in complex highway environments leads to low accuracy of vehicle target detection, a real-time detection model of highway vehicle is proposed based on YOLOv5s (YOLOv5s-CRCP). Firstly, convolutional attention module is embeded in the residual unit to strengthen the learning of detailed features and suppress the interference of redundant information. Secondly, convolutional attention is integrated into pyramid network to distinguish different important information and strengthen the fusion of key features. Experiments are conducted on the constructed Ningxia highway vehicle data set, and the average detection accuracy reaches to 91.2%, which is 4.1% higher than that of original algorithm. Experimental results show that the proposed method has better detection performance in comparison with YOLOv5s and the mainstream real-time vehicle target detection algorithms.