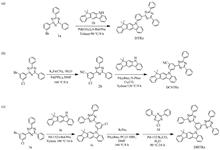
In order to obtain organic electroluminescent diodes (OLEDs) with low driving voltage,long lifetime and high light efficiency,a series of novel n-type host materials DTRz,DBTRz and DCNTRz based on 1,3,5-triazine and 7,7-dimethyl-5,7-dihydroindolinazol [2,1-b] carbazole are introduced in this paper. First,their electrochemical properties,photophysical properties and thermal stability were studied,and DFT calculations were performed. The experimental and computational analysis results show that DTRz,DBTRz and DCNTRz have higher triplet energy levels (2.83,2.71,2.72 eV),higher decomposition temperatures (411,499,419 oC). Then,the photoluminescence spectrum was studied after mixing with P-type host NBPBC (1∶1),and based on this,the device was fabricated with Pt(BBP) as the guest dopant. The analysis of the device results shows that the DCNTRz∶NBPBC-based device has a turn-on voltage of 2.1 V,a maximum external quantum efficiency of 14.3%,a maximum brightness of 221 589 cd·m-2,a current efficiency of 46.5 cd·A-1 at 1 000 cd·m-2,and a maximum power efficiency of 45.7 lm·W-1.In particular,the device lifetime (LT95) reaches 282 h at 4 000 cd·m-2. 54% higher lifetime than DTRz∶NBPBC-based devices. A green OLED with excellent performance such as low turn-on voltage,high lifetime and high luminous efficiency is realized.
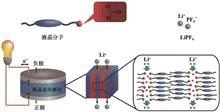
Liquid crystal has the advantages of both solid and liquid. As a battery electrolyte material, it has attracted more and more attention and research for safety, ion transfer rate, processability, electrochemical stability and interface compatibility. Thermotropic liquid crystal materials can construct complete one-dimensional, two-dimensional or three-dimensional ion transport channels through self-assembly, which is a field of widespread concern in electrolyte research. In particular, the stable two-dimensional ion transport channels constructed by smectic liquid crystalline electrolytes have received extensive attention. Compared with other liquid crystalline electrolytes such as columnar phase, bicontinuous cubic phase or ionic liquid crystals, smectic phase has obvious advantages in ion transfer rate. In this paper, the origin, development and structural characteristics of thermotropic liquid crystal materials as ion battery electrolytes are reviewed, and the research progress and application status at home and abroad in recent years are introduced in details.
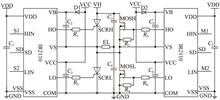
A composite switching circuit for flexible electroluminescent (EL) device driver was designed. The EL devices behave as capacitive loads, resulting in the transistors’ breaking down by the high peak current of the transistors at the instant as they are turned on and thus low reliability of the drivers. The thyristors (SCRs) with higher transient current capacity were employed as the main switching devices for the driver, in parallel connection to the MOSFETs. The MOSFETs play the roles of current shunt and short-circuiting, thereby turn off the thyristors after being turned on. The MOSFETs can stay off the peak current and the two kinds of transistor, both the thyristors and MOSFETs, could have the same or nearly the same temperature rise by properly adjusting the delay time of the MOSFETs, further improve the reliability of this composite thyristor-MOSFET switching circuit.
Flexible display has attracted much attention from consumer for its light weight, ultra slim, durable and foldable properties. In the last few years, flexible display has evolved from edge curved display to foldable display. Now foldable AMOLED display is widely accepted as a standard configuration of high-tech mobile phone. Advances in polyimide material technology have played an important role in the innovation from rigid display to foldable display. In this article, the basic performance of flexible substrate is introduced, including thermal stability, low thermal expansion, surface performance and small separating force in debonding process. Flexible cover performance is also introduced, including transparency, shock resistance, creep resistance and foldability. Flexible substrate and flexible cover are important application of polyimide in foldable AMOLED. Based on BOE foldable AMOLED development process, this progress report reviews the commercial application development of polyimide material in flexible substrate and cover. Finally, the development tendency of polyimide in display is prospected.
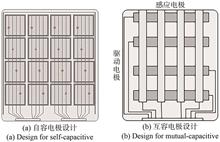
The flexible AMOLED display has lots of advantages, such as thin structure and flexibility. It can provides better user experience than rigid displays, and attracts more attention from end users. As a key component of flexible display module, flexible touch sensor has also been widely studied on its various forms and touch functions. The capacitive touch sensor technology which is suitable for flexible AMOLED display was introduced. The development status of flexible touch sensor was listed, the flexible touch sensors include Out-cell Touch Sensors (ITO touch sensor, metal mesh touch sensor, SNW touch sensor) and On-cell Touch Sensor which is integrated with flexible AMOLED display. The development of On-cell Touch Sensor accelerates the commercialization of foldable displays, because it has better performance in flexibility. The advantages and challenges of On-cell Touch Sensor were introduced, and the development of touch solution for different size of flexible AMOLED displays was discussed.
Research on the relationship of SiNx film to off-angle color shift on white screen is carried out. The research in this paper fills in the lack of research of correlation between TFT film and off-angle color shift of TFT-LCD, and provides a useful reference for the improvement of similar optical chromaticity defects in other products. Through experimental measurement and software simulation, the influence of the thickness of the silicon nitride film on the color shift coordinates is explored. Experimental results show that the silicon nitride film layer is a key factor affecting the color shift, GI and PVX1 have a greater impact on color shift, while PVX2 has a little impact on color shift,and the thickness of the SiNx is nonlinearly related to off-angle color shift on white screen. Taking a HADS product for example, the SiNx film layer includes gate insulating layer (320 nm), 1st passivation insulator layer (100 nm), 2nd passivation insulator layer (200 nm). Based on single-factor experimental and simulation results, comprehensively considering the electrical characteristics and production capacity, the reddish on white screen from the viewing angle is improved effectively when PVX1 140 nm is used as the condition. That means there is no reddish by macroscopic observation and the measured data meets product specifications.
In order to improve the maximum critical force value and anti-pressed capacity of the liquid crystal panel, by the mechanism analysis of LCD’s light leakage due to the pressing, and combining with the actual production, the main factors are screened using the method of design of experiments (DOE). The DOE results show that the main factors of pressed leakage are the size of the photo spacer (PS), width of black matrix (BM), PS locations, and planarization-layer (PLN) thickness. Improved design experiments are carried out in the actual production process and the results show that the panel anti-pressing capacity can be effectively enhanced by 32.69% by increasing the size of the PS, and its elastic recovery rate can be increased by 4.4%, which can effectively reduce the occurrence of light leakage. Also, by increasing BM width by 3 μm, changing the PS locations’ design from upper right to center and reducing the thickness of PLN by 0.6 μm, the average critical value of the panels’ pressing leakage can be increased by 30.61%, 33.33% and 27.08%, respectively.
In multispectral image mosaic, due to the imaging requirements and the information differences of different band images, it is impossible to complete the fast mosaic of full band spectral images under the condition of low overlap rate. To solve this problem, an adaptive low overlap multispectral image fast mosaic algorithm based on phase correlation enhancement is proposed in this paper. Taking the maximum information entropy channel of spectral image as the reference channel, an image correlation enhancement segmentation method is designed to cut off the specific step of two adjacent lens spectral images under the reference channel to improve the overlap rate of spectral images to be matched. The least square method is introduced to dynamically adjust the number of divisions and the division step length to realize the optimization of the relative offset while improving the realization and rationality of the algorithm. Using the principle of consistent offset of two adjacent sub lens images under different channels, through the positioning mapping of the displacement of the reference channel, the problem that individual channels cannot be spliced due to insufficient information is solved, and the splicing efficiency of multispectral images is improved. Experiments show that this method can realize the fast mosaic of 16 channel spectral images with an overlap rate of no less than 5%, which is superior to Harris, SURF and ORB algorithms in overall mosaic quality and time cost.
In order to address the problem that the foreground occlusions in the light path affect the acquisition of information of interest, this paper explores the de-occlusion algorithm based on the application of the camera array through experiments. The array light field camera is used to collect 4D light field data, after which the digital refocusing technology is employed to perform refocusing at different depths so as to highlight the detailed features of target objects. The experimental results support the feasibility of applying the array light field camera to remove occlusions, as well as its ability to enhance the quality of images, reproduce the image of occluded areas, improve the readability of images, and mitigate the effects of noise. According to the no-reference image quality assessment, in terms of the quality of reconstructed images, the algorithm in this paper can improve the signal to noise ratio (SNR) and peak signal to noise ratio (PSNR) by 17.3% and 77.6%, respectively.
In order to enhance the image taken by the camera in night environment, an adaptive night scene enhancement system combined with analog circuit is designed. Firstly, the analog camera captures the video. Next, the AD603 chip amplifies the captured analog video signal decoded by the TVP5150 chip that outputs the data in the ITU-R BT.656 format. Then, the FPGA performs effective data extraction, resolution modification and preprocessing such as video pin. Finally, the adaptive algorithm and D/A conversion circuit control the AD603 chip to adjust the magnification to achieve the system’s adaptive adjustment to the surrounding environment, so that the average gray value of each frame of image is stabilized near the set threshold. The paper uses hardware circuits instead of complex software algorithms to achieve results, while it greatly reduces FPGA resource consumption and implements the design on the ALINX AX545 FPGA platform. The experimental results show that at the resolution of 640×480 and 60 frame/s, it can perform adaptive real-time enhancement of night images, and finally stabilize the average gray value of the image near the set threshold. The system can be applied in the fields of target detection and video surveillance.
Imaging equipment in a dark environment has problems such as low contrast, loss of image detail information, and color distortion, which can cause huge interference in application scenarios such as video surveillance, intelligent transportation, and face recognition. In order to solve this situation, this paper proposes a composite residual network that incorporates the attention mechanism to enhance low-illuminance images. The algorithm firstly puts the brightness component V into the constructed neural network through color space conversion (RGB-HSV). The neural network extracts the shallow features of the image through a multi-branch structure that incorporates the attention mechanism, passes through the composite residual network extracts deep features, and then reconstructs the image to obtain the enhanced V component. Finally, the low-illuminance image enhancement is achieved through component fusion. The experimental results show that compared with the current mainstream low illumination image enhancement algorithms at home and abroad, the proposed algorithm significantly improves the image brightness and contrast in subjective vision. Compared with the traditional algorithm, the PSNR and SSIM are improved about 20% and 15%, respectively. And compared with the deep learning algorithm, the PSNR and SSIM are improved about 9% and 3%, respectively. It performs well in artificially synthesized low-light images or real and natural low-light images, basically meet the requirements of natural color, contrast and robustness for image enhancement.
The purpose of instance segmentation is to use pixel-level instance mask to classify and locate a single object, which is a challenging task in computer vision. At present, there are some problems such as slow segmentation speed, low segmentation accuracy for small objects, and uneven segmentation edge. Aiming at the above problems, a instance segmentation method based on target contour is proposed. On the one hand, the feature extraction is carried out for the nodes on the object contour, which is not affected by the detection box and avoids processing the internal pixels of the object, so as to accelerate the segmentation speed. On the other hand, the gradual segmentation of the image is adopted to extract the features on the contour of the object multi-level, and the multi-scale fusion feature processing method is used to better extract the context semantic information and reduce the feature loss. The average segmentation accuracy of Cityscapes and KINS is 32.4%AP and 32.0%AP, respectively, which is better than the segmentation accuracy of many excellent works. The smoothness and the degree of fit of the object segmentation edge have better processing effect. The instance segmentation network based on target contour has better segmentation ability in instance segmentation task.
Aiming at the problem of low recognition speed and recognition rate of convolution neural network and graph convolution network in campus violence recognition, this paper proposes a lightweight graph convolution network combined with multi-information flow data fusion and spatio-temporal attention mechanism. The human skeleton is taken as the research object. Firstly, the multi-information flow data related to joint points and skeleton are fused to improve the operation speed by reducing the number of network parameters. Secondly, the spatio-temporal attention module based on nonlocal operation is constructed to focus on the most action discriminant nodes, and the recognition accuracy is improved by reducing redundant information. Then, the spatio-temporal feature extraction module is constructed to obtain the spatio-temporal correlation information of the concerned nodes. Finally, action recognition is realized by Softmax layer. The experimental results show that the recognition accuracy of boxing, kicking, falling, pushing, earlighting and kneeling in campus security scene is 94.5%, 97.0%, 98.5%, 95.0%, 94.5% and 95.5%, respectively, and the maximum recognition speed is 20.6 fps. Compared with the two benchmark networks on UCF101 dataset, the recognition speed and accuracy are improved, which verifies the universality of the method for other actions. Therefore, it can meet the real-time and reliability requirements of typical campus violence identification.
With the video captured in driving, the surroundings can be sensed economically and conveniently by using object detection techniques, but the accuracy and speed of detection requires a lot in such kind of real-time scenes. In this work, a deep learning-based one-stage object detection algorithm called YOLOv3 is studied. Self-attention mechanism is introduced into this method, by embedding Gaussian mask self-attention modules in the high layers of YOLOv3 network. These modules can merge more global information into feature map to improve the accuracy of model. According to the results of experiments, trained on the MS COCO 2017 dataset, the mAP@0.5 and precision of this improved model can reach to 56.88% and 65.31%. Compared with YOLOv3, its mAP@0.5 and precision increase by 2.56% and 3.53%. Although there is a little loss in detection speed, detection accuracy is significantly improved when the method is applied to assisted driving system.