The in-plane photonic integrated circuits (PICs) can integrate a large number of active and passive photonic devices in a monolithic integration manner or a hybrid integration manner on a common substrate. The in-plane PIC exhibits diverse functions like wavelength tuning, filtering, routing, amplifying, modulation, detection, power monitoring, and so on. In PICs, the wavelength tunable laser and the power monitor photodiode (PD) are basic blocks. Compared to the edge-emitting laser used for the in-plane PIC, vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser (VCSEL) has many advantages, such as high modulation speed, low cost, low power, small footprint, two-dimensional array configuration, on-wafer testing, and circular beam. Since the light emits normally to the substrate of the VCSEL, VCSELs are the ideal laser sources for the vertically integrated photonic systems. In the future, the three-dimensional (3D) vertically integrated photonic system based on VCSELs will be promising in artificial intelligence and 3D sensing. VCSELs will be the key devices in future 3D vertically integrated photonic systems.
The wavelength tuning function is an important requirement for future 3D vertically integrated photonic systems. Micro-electro-mechanical system (MEMS) VCSEL is an ideal broadband tunable laser source. Wavelength tuning can be achieved by moving MEMS tunable mirror through the electrostatic or electrothermal forces to change the cavity length. Tunable MEMS-VCSELs have received a lot of attention, and are important laser sources in the fields such as optical coherence tomography (OCT), frequency modulated continuous wave (FMCW) light detection and ranging (LiDAR), gas sensing, and so on.
Integrating the power monitoring function in the tunable MEMS-VCSEL is challenging. A PD can be monolithically integrated into the n-type distributed Bragg reflector (DBR). However, this will deteriorate the tunable performance of MEMS-VCSEL and increase the complexity of the device fabrication. Integrating a monitor PD into the p-type side will also lower the output power and tuning performance of the device.
To address these challenges, Professor Anjin Liu et al. from the Institute of Semiconductors, Chinese Academy of Sciences propose a detector-integrated MEMS-VCSEL with a movable high contrast grating (HCG) mirror. This device can monitor the output power while the wavelength is widely tuned. Relevant research results were recently published in Photonics Research, Volume 12, Issue 7, 2024. [Minglu Wang, Hongling Peng, Chenxi Hao, Xuyan Zhou, Wanhua Zheng, Anjin Liu, "Detector-integrated vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser with a movable high-contrast grating mirror," Photonics Res. 12, 1437 (2024)]
The structure of the detector-integrated VCSEL with a movable HCG mirror is shown in Figure 1. The device has an n-i-p type MEMS structure, including a tunable HCG mirror. The n-i-p type MEMS structure (i.e., PD structure) can realize wavelength tuning by the reverse bias voltage. Meanwhile, the i-type sacrificial layer absorbs the scattered light from the cavity to monitor the output power, without affecting the wavelength tuning of MEMS-VCSEL.
The experimental results show that the tunable MEMS-VCSEL can achieve a total wavelength tuning range of 27 nm at 25 ℃, as shown in Figure 2. Although the bandgap energy of the integrated PD (i.e., n-i-p MEMS structure) is greater than the energy of the lasing photons, the power monitoring can be achieved based on the photo-assisted Shockley-Read-Hall mechanism, as shown in Figure 3.
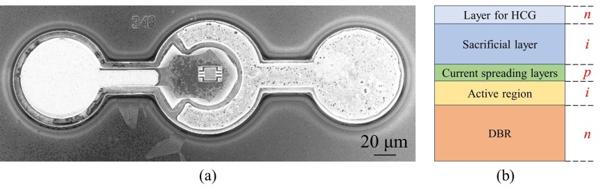
Figure 1 (a) SEM image of the 940-nm detector-integrated VCSEL with a movable HCG. (b) Schematic of the epitaxial structure and doping profile of the device.
.png)
Figure 2 (a) Measured wavelength tuning spectra of the detector-integrated VCSEL with a movable HCG at different tuning voltages under continuous-wave operation at 1.0 mA. (b) The wavelength of the fundamental mode as a function of the tuning voltage.
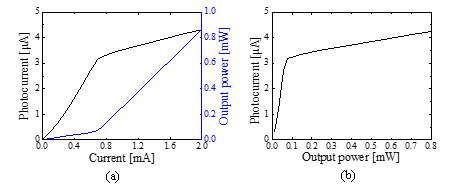
Figure 3 (a) Measured photocurrent and output power curves as a function of injection current of the detector-integrated VCSEL with a movable HCG. (b) Photocurrent-power curve of the detector-integrated VCSEL with a movable HCG.
The device can also serve as a resonant-cavity-enhanced PD to detect the incident light and the response peak wavelength is around 926 nm. This work provides a new approach for detector-integrated tunable MEMS-VCSELs.







