In this paper, we report research results of 1 280×1 024 dual-color mid-wavelength infrared InAs/GaSb superlattice focal plane arrays. The detector structure is PN-NP epitaxial multilayer and the signal is read out by sequential mode. The superlattice structure was grown on GaSb substrate using molecular beam epitaxy (MBE) technology. The respective structures of each absorption region are Mid-Wavelength 1(MW1): 6 ML (InAs) /7 ML (GaSb) and Mid-Wavelength 2 (MW2): 9 ML (InAs) /7 ML (GaSb). The pixel center distance of the detector is 12 μm. At 80 K measurements, the detector has spectral response wavelength of 3-4 μm and 3.8-5.2 μm respectively. The MW1 detector has a peak detectivity of 6.32×1011 cm·Hz1/2W-1. The MW2 detector has a peak detectivity of 2.84×1011 cm·Hz1/2W-1. Infrared images of both wavebands have been taken using infrared imaging test by adjusting the device voltage bias. It’s the first time that a 1 280 × 1 024 InAs/GaSb Type II superlattice mid-wave length two-color infrared focal plane detector has been reported in China.
The optical frequency comb (OFC) generation of 2 μm silicon nitride microcavity is investigated. Dispersion modulation of silicon nitride waveguides is carried out by geometrical design. Appropriate bus waveguide dimensions are selected, and the thermal refraction noise of silicon nitride microcavities at different modulation frequencies is discussed by the thermal absorption theory. The nonlinear Schr?dinger equation is used as the basic model to study the evolution of the cavity under different dispersion effects. The numerical results show that silicon nitride is able to observe the hysteretic state transition of the system, i.e., the relaxation oscillation phenomenon during the transition of the system to the stable domain, more clearly in the 2 μm band. At the same time, the cavity is able to transition to the steady state soliton faster under the action of higher-order dispersion, which provides a scheme to study the respiratory soliton.
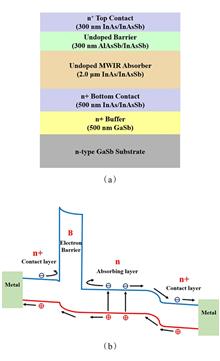
InAs/InAsSb type-II superlattice (T2SL) materials hold great promise for the development of mid-wavelength infrared photodetectors operating at high temperatures, as they avoid the defects caused by Ga atoms in InAs/GaSb T2SL and exhibit long minority carrier lifetime. To reduce the dark current, minority carrier unipolar barrier structures, such as nBn detectors, are commonly employed. In mid-wavelength infrared InAs/InAsSb T2SL nBn photodetectors, the multielement alloy such as AlAsSb is typically utilized as the barrier layer to block the transport of majority carriers. However, the small valence band offset (VBO) between the barrier and absorption layers leads to the saturation of photocurrent at high bias voltage, resulting in increased dark current. In this work, an AlAsSb/InAsSb T2SL barrier was designed to eliminate the VBO and reduce the bias dependency of quantum efficiency. The results show that the fabricated nBn photodetector exhibits a 50% cutoff wavelength of 4.5 μm at 150 K. The optical response of the photodetector saturates under a small bias of -50 mV, achieving a peak responsivity of 1.82 A/W at 3.82 μm and a quantum efficiency of 58.8%. At 150 K and -50 mV applied bias, the photodetector exhibits a dark current density of 2.01×10-5 A/cm2 and a specific detectivity of 6.47×1011 cm·Hz1/2/W.
In the realm of near-infrared spectroscopy, the detection of molecules has been achieved using on-chip waveguides and resonators. In the mid-infrared band, the integration and sensitivity of chemical sensing chips are often constrained by the reliance on off-chip light sources and detectors. In this study, we demonstrate an InAs/GaAsSb superlattice mid-infrared waveguide integrated detector. The GaAsSb waveguide layer and the InAs/GaAsSb superlattice absorbing layer are connected through evanescent coupling, facilitating efficient and high-quality detection of mid-infrared light with minimal loss. We conducted a simulation to analyze the photoelectric characteristics of the device. Additionally, we investigated the factors that affect the integration of the InAs/GaAsSb superlattice photodetector and the GaAsSb waveguide. Optimal thicknesses and lengths for the absorption layer are determined. When the absorption layer has a thickness of 0.3 μm and a length of 50 μm, the noise equivalent power reaches its minimum value, and the quantum efficiency can achieve a value of 68.9%. The utilization of waveguide detectors constructed with III-V materials offers a more convenient means of integrating mid-infrared light sources and achieving photoelectric detection chips.
Based on the current application requirements for wideband response photodetectors, we designed a novel silicon avalanche photodetector (Si APD) with high response in a broad spectral range of 250 -1 100 nm and it could achieve efficient detection of ultraviolet, visible and near-infrared light without splicing. The enhancement of silicon on ultraviolet and infrared bands was separately analyzed. This was followed by simulation on the device structure designs using different methods such as back incidence, to improve short wavelength absorption while maintaining a high infrared absorption. The Si APD shows a peak wavelength at around 940 nm and a high photoresponse at 250 nm and 1 100 nm which exceeds 15% of the peak responsivity. This type of device is suitable for multispectral applications and future high-precision detection.
The lattice-matched XBn structures of InAsSb, grown on GaSb substrates, exhibit high crystal quality, and can achieve extremely low dark currents at high operating temperatures (HOT). Its superior performance is attributed to the unipolar barrier, which blocks the majority carriers while allowing unhindered hole transport. To further explore the energy band and carrier transport mechanisms of the XBn unipolar barrier structure, this paper systematically investigates the influence of doping on the dark current, photocurrent, and tunneling characteristics of InAsSb photodetectors in the PBn structure. Three high-quality InAsSb samples with unintentionally doped absorption layers (AL) were prepared, with varying p-type doping concentrations in the GaSb contact layer (CL) and the AlAsSb barrier layer (BL). As the p-type doping concentration in the CL increased, the device’s turn-on bias voltage also increased, and p-type doping in the BL led to tunneling occurring at lower bias voltages. For the sample with UID BL, which exhibited an extremely low dark current of 5×10-6 A/cm2. The photocurrent characteristics were well-fitted using the back-to-back diode model, revealing the presence of two opposing space charge regions on either side of the BL.
A medium wave (MW) 640×512 (25 μm) Mercury Cadmium Telluride (HgCdTe) polarimetric focal plane array (FPA) was demonstrated. The micro-polarizer array (MPA) has been carefully designed in terms of line grating structure optimization and crosstalk suppression. A monolithic fabrication process with low damage was explored, which was verified to be compatible well with HgCdTe devices. After monolithic integration of MPA, NETD < 9.5 mK was still maintained. Furthermore, to figure out the underlying mechanism that dominated the extinction ratio (ER), specialized MPA layouts were designed, and the crosstalk was experimentally validated as the major source that impacted ER. By expanding opaque regions at pixel edges to 4 μm, crosstalk rates from adjacent pixels could be effectively reduced to approximately 2%, and promising ERs ranging from 17.32 to 27.41 were implemented.
A method for selecting parameters in HgCdTe crystals has been proposed, utilizing Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and clustering methods, with the establishment of a data model for screening the parameters of HgCdTe crystals. Within the model, the initial crystal data undergoes a cleaning and analysis process. PCA is employed for dimensionality reduction, and the Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise (DBSCAN) algorithm is used to identify the densest regions within the crystal data. Furthermore, the high-performance chip data, obtained after post-processing, is utilized to fit boundary ellipses for high-quality HgCdTe crystal parameters. These ellipses act as criteria for identifying high-quality crystals. The model is capable of generating crystal ratings based on input electrical and optical parameters with a coverage rate exceeding 90%.
We report on the performance improvement of long-wave infrared quantum cascade lasers (LWIR QCLs) by studying and optimizing the anti-reflection (AR) optical facet coating. Compared to the Al2O3 AR coating, the Y2O3 AR coating exhibits higher catastrophic optical mirror damage (COMD) level, and the optical facet coatings of both material systems have no beam steering effect. A 3-mm-long, 9.5-μm-wide buried-heterostructure (BH) LWIR QCL of λ ~ 8.5 μm with Y2O3 metallic high-reflection (HR) and AR of ~ 0.2% reflectivity coating demonstrates a maximum pulsed peak power of 2.19 W at 298 K, which is 149% higher than that of the uncoated device. For continuous-wave (CW) operation, by optimizing the reflectivity of the Y2O3 AR coating, the maximum output power reaches 0.73 W, which is 91% higher than that of the uncoated device.
In general, all known applications of high-power microwaves directly use energy to interact with matter. In recent years, with the development of powerful millimeter-wave radiation sources, microwave technology has gradually shifted towards the millimeter-wave frequency band. Due to the wavelength of radiation, millimeter waves have several unique characteristics, which allow for both the active development of existing technologies and the creation of new ones that require high power or radiation energy. This article provides an overview of research on the application of millimeter waves to solve problems in physics, material science, biomedicine, and others, including heating and diagnostics of thermonuclear plasma, processing and analysis of materials, biological effects, etc. The main difficulties arising in the implementation of the described tasks are presented, and the future development is also prospected.
With the analysis of experiment and theory on GaN HEMT devices under DC sweep, an improved model for kink effect based on advanced SPICE model for high electron mobility transistors (ASM-HEMT) is proposed, considering the relationship between the drain/gate-source voltage and kink effect. The improved model can not only accurately describe the trend of the drain-source current with the current collapse and kink effect, but also precisely fit different values of drain-source voltages at which the kink effect occurs under different gate-source voltages. Furthermore, it well characterizes the DC characteristics of GaN devices in the full operating range, with the fitting error less than 3%. To further verify the accuracy and convergence of the improved model, a load-pull system is built in ADS. The simulated result shows that although both the original ASM-HEMT and the improved model predict the output power for the maximum power matching of GaN devices well, the improved model predicts the power-added efficiency for the maximum efficiency matching more accurately, with 4% improved.
For the high-electron-mobility transistor (HEMT) terahertz detector with a side-gate structure, a physical model for DC transport and terahertz detection of the device was constructed. Using a self-alignment process, well-shaped and reliable contacts for the side-gate structure were successfully fabricated, effectively solving contact issues between the dual gates and the mesa. Ultimately, terahertz detectors with different gate widths (200 nm, 800 nm, and 1400 nm) of side-gate GaN/AlGaN HEMTs were obtained. DC tests revealed a clear linear relationship between the gate widths of different devices and their threshold voltages, confirming the DC transport model of the side-gate HEMT terahertz detector. These results provide experimental verification and guidance for the theoretical model of the complete side-gate HEMT terahertz detector, offering significant support for the development of side-gate HEMT terahertz detectors.
The performance of ABS/Ag-coated terahertz hollow waveguide (HWG) was improved through plasma treatment of the ABS structural tube. The adhesion of the silver (Ag) film to the ABS tube was enhanced from level 5 to level 2 after plasma treatment. The 4.2 mm bore waveguide sample treated with plasma has a more uniform and denser silver film than the untreated sample, which contributes to the reduction of transmission losses from 0.72 dB/m to 0.70 dB/m at 0.3 THz and 1.47 dB/m to 1.44 dB/m at 0.1 THz, respectively. After 200 hours of hydrothermal aging and 16 cycles of high and low temperature cycling testing, the straight loss of the HWG sample treated with plasma increased by less than 0.1 dB/m, while the untreated sample underwent an increase of more than 1.0 dB/m. The results indicate that the ABS/Ag-coated HWG fabricated by plasma treatment has lower loss, higher reliability and better anti-aging performance compared with the untreated sample. It can be potentially used for establishment of next-generation communication, sensing, and THz imaging systems.
The performance of radiation sources and detectors currently limits terahertz imaging technology, which still requires further improvement in terms of detail resolution, imaging speed, and noise suppression. This paper proposes a terahertz image super-resolution algorithm based on spatial curve filling. The ViT (Vision Transformer) structure backbone network is utilized to extract terahertz image features through an attention mechanism. A Hilbert spatial curve is constructed to reconstruct the image according to the feature map using the curve filling method. Lightweight one-dimensional convolution processing is used for reconstructing image features, while inverse transformation of reconstructed maps restores the image's spatial structure. Finally, pixel reorganization enables up sampling to obtain an output image with enhanced object contour and details. Experimental results show that compared with conventional ViT structures, this proposed method improves Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR) by 0.81 dB and Structural Similarity Index (SSIM) by 0.007 4, which effectively inhibits the noise influence on texture and significantly improves the resolution and image quality.
The photoconductive antenna is a kind of widely used broadband terahertz (THz) radiation source in THz time-domain spectroscopy systems, and the substrate material of the antenna is crucial for the characteristics of generated THz wave. The widely used photoconductive antenna material is the second-generation semiconductor of GaAs, while the third-generation semiconductor has a larger band gap, which is more advantageous for improving the power of THz wave from photoconductive antenna. In this work, the current surge model of large-aperture photoconductive antennas was used to simulate the characteristics of THz waves radiated by the photoconductive antenna made from commonly used SI-GaAs and LT-GaAs, and the third-generation semiconductors (ZnSe, GaN, SiC) that are expected to be used in the future for photoconductive antennas. The results show that under the same bias electric field and their respective highest pump laser flux, LT-GaAs antenna generates THz waves with the highest amplitude and widest frequency. The photoconductive antenna made by the third-generation semiconductor materials can withstand higher bias electric fields, and the intensity of radiated THz waves is much greater than that from GaAs antennas under their respective maximum bias electrical fields. This work provides theoretical guidance for the development of new third-generation semiconductor photoconductive antennas.
In long-cavity edge-emitting diode lasers, longitudinal spatial hole burning (LSHB), two-photon absorption (TPA) and free carrier absorption (FCA) are among the key factors that affect the linear increase in output power at high injection currents. In this paper, a simplified numerical analysis model is proposed for 1.06 μm long-cavity diode lasers by combining TPA and FCA losses with one-dimensional (1D) rate equations. The effects of LSHB, TPA and FCA on the output characteristics are systematically analyzed, and it is proposed that adjusting the front facet reflectivity and the position of the quantum well (QW) in the waveguide layer can improve the front facet output power.
To address the spatial constraints in unmanned aerial vehicle target detection systems, a scheme for a multi-beam scanning passive Q-switched microchip array solid-state laser is proposed. This system utilizes a six-core semiconductor laser array to compactly pump a strip-shaped Nd:YAG/Cr4+:YAG bonded crystal. At a pumping power of 1.6 W per path, it generates six output laser beams with a wavelength of 1 064.4 nm, pulse width of 2.4 ns, beam quality of 1.39, peak power of 3.75 kW, and a repetition frequency up to 22 kHz. The entire system's volume is only 2 cm×2 cm ×1.5 cm, and achieves simultaneous output of six laser paths. The study investigated the impact mechanism of the initial transmittance of the Q-switching crystal and the reflectivity of the output mirror on the laser pulse repetition frequency and peak power, with a particular focus on the uniformity of the laser output from the pump source cores. The feasibility of using a single laser-bonded crystal to produce multiple narrow pulse laser beams in the nanosecond range was experimentally verified. The research results demonstrate the miniaturized structure's ability to achieve multi-beam emission from a passive Q-switched solid-state laser, providing insights for the miniaturization and integration of laser sources in detection systems.
A modified multiple-component scattering power decomposition for analyzing polarimetric synthetic aperture radar (PolSAR) data is proposed. The modified decomposition involves two distinct steps. Firstly, eigenvectors of the coherency matrix are used to modify the scattering models. Secondly, the entropy and anisotropy of targets are used to improve the volume scattering power. With the guarantee of high double-bounce scattering power in the urban areas, the proposed algorithm effectively improves the volume scattering power of vegetation areas. The efficacy of the modified multiple-component scattering power decomposition is validated using actual AIRSAR PolSAR data. The scattering power obtained through decomposing the original coherency matrix and the coherency matrix after orientation angle compensation is compared with three algorithms. Results from the experiment demonstrate that the proposed decomposition yields more effective scattering power for different PolSAR data sets.
Infrared small target detection is a common task in infrared image processing. Under limited computational resources. Traditional methods for infrared small target detection face a trade-off between the detection rate and the accuracy. A fast infrared small target detection method tailored for resource-constrained conditions is proposed for the YOLOv5s model. This method introduces an additional small target detection head and replaces the original Intersection over Union (IoU) metric with Normalized Wasserstein Distance (NWD), while considering both the detection accuracy and the detection speed of infrared small targets. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm achieves a maximum effective detection speed of 95 FPS on a 15 W TPU, while reaching a maximum effective detection accuracy of 91.9 AP@0.5, effectively improving the efficiency of infrared small target detection under resource-constrained conditions.