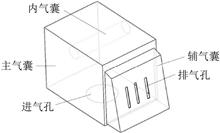
The existing airbag buffer system of airdrop equipment is poor in applicability, and it is difficult to meet the future demand of airdrop buffer of large weight equipment with low impact and anti-rollover. To solve these problems, this paper designs a combined airbag suitable for a new generation of airdrop equipment, adopts the optimal Latin hypercube design test method for sampling, and constructs a polynomial proxy model aiming at maximum overload and maximum rollover angle based on these samples. The multi-objective particle swarm optimization algorithm is applied to optimize the structural parameters of the airbag on the basis of the agent model, and the optimized cushioning system is subjected to finite element analysis: the maximal overload of the optimized airbag cushioning system is reduced by 24.7%, which improves the buffer performance;the maximal rollover angle is reduced by 42.6%, which greatly improves the lateral stability, and greatly reduces the risk of rollover. The research results show that the airbag cushioning system designed and optimised in this paper meets the future demand of large load and rollover resistance, and provides technical support for the airbag cushioning system of future airdrop equipment.
According to the requirement of prediction of dynamic stability and recovery and landing of hypersonic inflatable aerodynamic decelerator, this paper presents a detailed analysis of structural deformation effect on the dynamic stability for the decelerator in the most sensitive velocity range of Ma=0.15 to 4.6. The flow field and aerodynamic coefficients of the aircraft with and without structural deformation are obtained with a Reynolds average Navier-Stokes equation solver. Steady simulation results shows that the static structural deformation results in local flow separation on the winward surface of the aircraft and increases the axial aerodynamic coefficient. Unsteady simulation results of forcing pitching oscillation and rigid moving mesh technique show that the high pressure on winward surface stablizes the aircraft dynamic stability while the vortex in the wake flow weakens the vehicle dynamic stability, the axial symmetric structural deformation enhances the decelerator dynamic stability in total.
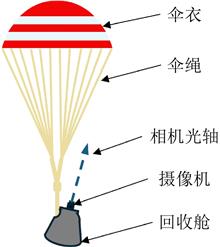
During the development process of parachutes, a large amount of video image data is generated. By analyzing and processing the video data, many useful parachute parameters can be obtained, enriching the evaluation means of parachute performance. Therefore, the analysis of parachute video images is being paid more and more attention by researchers. However, in the parameter identification of parachute video images, the segmentation of canopy area is mainly based on traditional digital image processing algorithms. This method requires frequent adjustment of algorithm parameters to achieve canopy precise segmentation for different types of parachute images, not only leading to low segmentation efficiency, but also insufficient universality. Therefore, this paper introduces YOLOv8 for canopy segmentation, improving its universality and parachute parameter identification efficiency through YOLOv8's automatic and efficient segmentation capabilities. By comparing the canopy tilt angle, canopy projected perimeter, and canopy projected area, obtained by parameter identification based on traditional digital image processing algorithms and the proposed method, the results show that the proposed method effectively improves the efficiency of parachute parameter identification while maintaining the identification accuracy of parachute parameters.
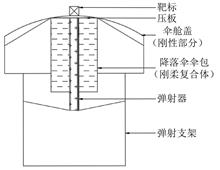
In the parachute ejection process, there is a significant difference between the estimated ejection speed and the actual ejection test results. An energy consumption issue can not be ingored in the ejection process, and it is difficult to accurately describe the ejection consunmption mechanism of the ejection process in current research. Firstly, the counterweight ejection simulation is performed using the catapult. Then, a spring-damping dynamic model of the catapult combination is established. Using the simulation results of the ballistic counterweight and the data from the parachute test as inputs, the key parameters of the spring damping model are solved through data fitting. Finally, completed the dynamics simulation of parachute ejection from the capsule and verified under another test condition. The investigation revealed that the spring damping model can accurately describe the parachute ejection process from the capsule. When the damping coefficient remains constant, the greater the stiffness coefficient of spring, the less energy the parachute pack will ultimately dissipate. When the stiffness coefficient of spring remains constant, the greater damping coefficient, the more energy the parachute pack will ultimately dissipate. The higher the proportion of rigid mass in the ejection assembly, the less energy consumption. The research results can provide some reference for parachute package design and energy dissipation analysis of parachute ejection process from the capsule.
Small satellite constellations have attracted considerable attention due to their cost-efficiency, flexible deployment, and ability to facilitate multi-satellite operations. Aluminum-based optical payloads, benefiting from their high integration, thermal and mechanical stability, design flexibility, and low production cost, are an ideal choice for these systems. This paper reviews the current uses and recent advances of aluminum-based optical payload technology. It examines traditional approaches for designing, manufacturing, and integrating aluminum-based payloads, and discusses how metal additive manufacturing is transforming these processes, highlighting its potential in future space missions.
For the effective design and image quality analysis of spaceborne digital TDI systems, a method for analyzing the factors affecting the entire link image quality of spaceborne digital TDI systems is proposed. The principles and influencing factors of spaceborne digital TDI technology are analyzed, an end-to-end simulation model considering all the stages including scenario, atmosphere, spaceborne system and processing algortithm of the digital TDI imaging system is constructed, and digital TDI imaging simulations and analysis evaluations under the influence of multiple factors are carried out. The results show that at a resolution of 0.9 m, with an exposure time of 0.063 ms, a quantization bit of 12 bit, and a TDI level of 6, good image quality can be obtained. The use of digital TDI technology can relieve the platform stabilty requirement to 0.1 (°)/s. This study can provide some reference for the design and analysis of spaceborne digital TDI system.
With the increasing demands for precise navigation in human activities such as outdoor exploration and emergency response, traditional navigation technologies struggle to provide high-accuracy navigation in complex environments. In recent years, the atmospheric polarization navigation technology, based on polarization characteristics, has become a research hotspot due to its high environmental stability, strong anti-interference capability, and fully autonomous features. However, current atmospheric polarization navigation based on visible light wavelengths is primarily effective in clear weather conditions, showing insufficient performance and poor navigation accuracy in complex weather conditions. To solve this problem, this paper starts from the characteristics of atmospheric radiation transmission and conducts simulation calculations and field test verifications of atmospheric radiation transmission and polarization information under different cloud conditions, based on Mie scattering and the principle of Monte Carlo transmission. The results indicate that under complex cloud conditions, the 350 nm ultraviolet wavelength demonstrates higher forward scattering and transmission capabilities, providing superior detection performance. In shallow cloud, medium cloud, and thick cloud weather conditions, the degree of atmospheric polarization in the ultraviolet wavelength is higher than that in the visible wavelength by 78.57%, 168.37%, and 126.73%, respectively, and the atmospheric polarization angle images in the ultraviolet wavelength exhibit much higher structural stability and image clarity compared to the visible wavelength. The research findings of this paper can provide new insights for the application and development of atmospheric polarization navigation in complex environments.
In order to mitigate the impact of micro-vibration on the performance of the multi-load integrated small satellite, the paper proposes a satellite vibration isolation scheme and establishes an integrated analysis model for multi-load micro-vibration to evaluate the suppression effect. First, a two-stage passive isolation scheme from the vibration source to the load is designed. Second, the relationship between image shifts is established for the linear optical system and the optical element motion, and then the micro-vibration integrated analysis model with different optical loads is established to account for the difference of sensitivities of optical loads to micro-vibration. The comprehensive image shifts before and after the satellite vibration isolation are calculated. Finally, both the micro-vibration measurement test on the ground and the push-scan imaging verification in orbit are carried out. The results show that the maximum integrated image shift calculated by the integrated model is less than 0.25 pixels, the maximum peak-to-peak vibration values for the laser and camera's primary mirror in the ground test are 0.05″ and 0.012″, respectively, and the maximum image shift value in the frequency domain for the in-orbit imaging optical camera is 0.061 pixels. Both the ground and in-orbit micro-vibration measurement data validate the effectiveness of the vibration isolation system design and the integrated analysis model.
Satellite remote sensing is currently a economical and effective method for monitoring atmospheric methane concentration, to understand the subtle differences in XCH4 data across different observation systems. This paper proposes a multidimensional evaluation method of the XCH4 data from GOSAT-2 and Sentinel-5p satellite, conducts uncertainty analysis by spatiotemporal matching of satellite data with ground station data, and quantitatively analyzes the effective coverage of XCH4 observations from the two satellites in different latitude bands and typical research areas. The research results indicate that: 1) The Sentinel-5p satellite data has a higher correlation coefficient (R2) with TCCON data compared to GOSAT-2 satellite data. (GOSAT-2: R2=0.7707, Sentinel-5p: R2=0.8494), 2) the distribution ratio of the two satellites data in the medium to low latitude zones (50° S~50° N) is as high as 70%, and 3) Sentinel-5p satellite data has a better cumulative coverage effect than GOSAT-2 satellite in a typical study area for 15 days (GOSAT-2: 0.81%, Sentinel-5p: 36.85%). This study can provide reference for the spatiotemporal fusion of multi-source carbon satellites and related research.
Aiming at the research problems of large-scale landscape patterns such as provinces, taking Guangdong Province as the research object, using Sentinel-2 remote sensing images with a resolution of 10m and their corresponding land use type data, taking landscape pattern index and remote sensing images as feature sets, and taking image types based on visual features as label sets, Adam optimization algorithm is used to construct a landscape visual feature classification model based on Keras deep learning framework. The feature set and the corresponding label set data are divided into training set and test set according to 8∶2, and cross-validated. The results show that the accuracy of the model on the training set and test set is 99.57% and 98.93%, respectively. The model can effectively correlate landscape pattern index and image visual features, and has strong generalization ability. It is suitable for remote sensing image classification tasks in large-scale regional landscape pattern research and township layout planning.
Limited by the carrying capacity of image spectral information, single-mode target detection methods based on visible light or infrared are usually difficult to effectively deal with complex scenes of remote sensing images. Aiming at this problem, a super-resolution remote sensing image target detection method based on hierarchical fusion mechanism is proposed, which effectively fuses visible light and infrared data information. Firstly, the residual fusion module and the single-branch module are used to construct a hierarchical fusion mechanism. The residual fusion module combines the potential complementary information of visible and infrared images, and the single-branch module enhances the single-modal features and assists in enhancing the dual-modal data fusion feature expression. Secondly, in order to solve the problem of missing target details in low-resolution images, a super-resolution auxiliary branch is introduced to enhance the ability of target detail feature generation and further improve the detection accuracy. The experimental results show that the detection accuracy (mAP50) of the proposed method on the VEDAI and Drone Vehicle datasets is better than that of the existing target detection methods, reaching 79.45% and 81.29%, which effectively improves the accuracy and robustness of remote sensing image target detection in complex environments.
This paper proposes a fractional-order Gabor transform convolution-based algorithm for aircraft target detection in remote sensing images, addressing challenges such as background noise, target size, and rotation angle which interfere with feature extraction. Firstly, in the feature extraction network, a novel and efficient attention feature extraction module is introduced by combining an efficient layer aggregation network with a convolutional block attention module, enhancing both the quality and efficiency of feature extraction. Secondly, a fractional-order Gabor transform convolution module is constructed in the feature fusion network to emphasize fine-grained details such as the edges, textures, and orientations of aircraft targets, thereby improving feature fusion. Finally, a learnable dynamic detection head is applied in the detection layer, where a scale-aware attention module strengthens attention to multi-scale targets, a spatial-aware attention module enhances spatial position discrimination, and a task-aware attention module facilitates more precise distinction of task-specific requirements. Experimental results on the DOTAv1 dataset demonstrate that the proposed method achieves a detection accuracy of 96.2%, which is 2.2% higher than the baseline YOLOv7 model. The method also has a smaller model weight, with a notable improvement in detection accuracy in complex scenarios. This approach provides a more efficient solution for aircraft target detection in remote sensing images.
To overcome the high sensitivity of the traditional Markov random field model to the speckle noise of synthetic aperture radar (SAR) images and the blurring of the oil spill boundary identification in marine oil spill identification, this study proposes an edge-constrained hidden Markov random fields (HMRF) at the super-pixel scale algorithm (SE-HMRF) for oil spill recognition in SAR images. Super-pixel segmentation of SAR images using simple linear iterative clustering (SLIC) to overcome the effect of speckle noise in SAR images. To improve the accuracy, HMRF is constructed to describe the spatial relationship of the image based on super-pixel segmentation, and transform the problem into an energy function minimization problem by theorems. To overcome the over-segmentation or under-segmentation of oil spill edges by SLIC, the oil spill edge information is introduced into the energy function to constrain the oil spill identification results. To verify the accuracy of this study's algorithm for oil spill identification, Sentinel-1 satellite SAR images are selected for comparison experiments, and the Kappa coefficient and probability Rand index of the oil spill identification results of this study's algorithm reach 0.951 and 0.954, respectively, while the global consistency error is only 0.024, and the results of the qualitative and quantitative evaluations are both better than those of the comparison algorithms, indicating that this study's algorithm can maintain the identification efficiency while obtaining accurate oil spill identification results.
Methane (CH4), as a critical anthropogenic greenhouse gas, significantly impacts the Earth’s radiation balance and the concentration of ozone in the troposphere. There is considerable uncertainty in the current bottom-up emission inventories when estimating the total methane emissions and their spatial distribution. Satellite remote sensing technology, with its wide coverage and efficient monitoring capabilities, provides an effective means for monitoring the global atmospheric CH4 concentration. This study reviews the techniques for detecting and inverting atmospheric methane based on satellite remote sensing, categorizing methane remote sensing satellites into two main types: regional flux plotters and point source imagers. It summarizes the performance of CH4 satellite-borne detection satellites and the development of detection technology. Furthermore, it analyzes the application of various sensor CH4 inversion algorithms and their data products in emission monitoring and flux inversion, discussing the strengths and limitations of different inversion algorithms. Finally, in line with the strategic needs of China’s dual-carbon targets, the future development trend of methane remote sensing satellites is predicted, and the future direction of CH4 inversion technology research is prospected, aiming to provide a reference for the construction of China’s atmospheric CH4 satellite remote sensing system.