E. A. Vishnyakov, A. Sagisaka, K. Ogura, T. Zh. Esirkepov, B. Gonzalez-Izquierdo, C. D. Armstrong, T. A. Pikuz, S. A. Pikuz, W. Yan, T. M. Jeong, S. Singh, P. Hadjisolomou, O. Finke, G. M. Grittani, M. Nevrkla, C. M. Lazzarini, A. Velyhan, T. Hayakawa, Y. Fukuda, J. K. Koga, M. Ishino, K. Kondo, Y. Miyasaka, A. Kon, M. Nishikino, Y. V. Nosach, D. Khikhlukha, I. P. Tsygvintsev, D. Kumar, J. Nejdl, D. Margarone, P. V. Sasorov, S. Weber, M. Kando, H. Kiriyama, Y. Kato, G. Korn, K. Kondo, S. V. Bulanov, T. Kawachi, and A. S. Pirozhkov
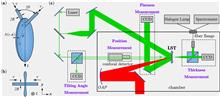
Tight focusing with very small f-numbers is necessary to achieve the highest at-focus irradiances. However, tight focusing imposes strong demands on precise target positioning in-focus to achieve the highest on-target irradiance. We describe several near-infrared, visible, ultraviolet and soft and hard X-ray diagnostics employed in a ∼1022 W/cm2 laser–plasma experiment. We used nearly 10 J total energy femtosecond laser pulses focused into an approximately 1.3-μm focal spot on 5–20 μm thick stainless-steel targets. We discuss the applicability of these diagnostics to determine the best in-focus target position with approximately 5 μm accuracy (i.e., around half of the short Rayleigh length) and show that several diagnostics (in particular, 3$\omega$ reflection and on-axis hard X-rays) can ensure this accuracy. We demonstrated target positioning within several micrometers from the focus, ensuring over 80% of the ideal peak laser intensity on-target. Our approach is relatively fast (it requires 10–20 laser shots) and does not rely on the coincidence of low-power and high-power focal planes.
Jul. 23, 2024
Vol. 12 Issue 3 03000e32 (2024) View fulltext
View fulltext