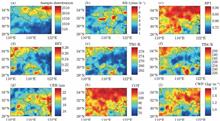
The optical and microphysical features of the cloud top are key information for quantitative precipitation retrieval based on satellite spectra. With the spectral and radar observation data of the Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission satellite collected during the Meiyu periods of the Yangtze-Huaihe Valley from 1998 to 2007, this paper built a random forest algorithm model that used the cloud-top spectral information of precipitating clouds to retrieve precipitation intensity. It also investigated the relationship between cloud-top microphysical characteristics and the intensity variation of Meiyu precipitation. The results show that in the precipitation retrieval testing set of the random forest model, the correlation coefficient R between predicted precipitation intensity and observed precipitation intensity is 0.67, and the root-mean-square error is 4.06 mm/h. This means the random forest model has high precipitation prediction accuracy. In the model, the cloud water path (CWP) ranks high in the importance hierarchy of all input variables. Further analysis shows that when the CWP is leas than 1.0 kg·m -3, precipitation at light rain level is dominant during the Meiyu period of the Yangtze-Huaihe Valley, while when the CWP is more than 1.5 kg·m -3, the probability of precipitation at heavy rain and torrential rain levels increases significantly. On the whole, the probability of precipitation at all levels increases monotonically with the increase of cloud effective radius (CER), which is mainly over 10 μm. It also increases with the increase of cloud optical thickness (COT). When COT is more than 120, it increases significantly, especially the probability of heavy precipitation.
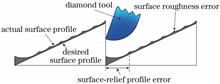
In order to improve the surface quality and diffraction efficiency of CaF2 diffraction optical element (DOE) processed by single point diamond turning, a mathematical model is proposed to reveal the effect of surface roughness error and surface profile error on diffraction efficiency based on Beckman scalar scattering theory and effective area method first. Then, the turning model of CaF2 DOE is optimized combining with the turning characteristics of CaF2 and the structural characteristics of DOE. At the same time, the optimal turning positions and tool radii of half-round tool under different process conditions are given, which realizes the control of the surface roughness of CaF2 DOE. Finally, the high surface quality CaF2 DOE with a surface roughness of 3.4 nm and a shadow region width of 28.7 μm is obtained with the guidance of the optimized model, which verifies the reliability of the proposed optimized turning model. The proposed optimized turning model has great significance for improving the imaging quality of the refraction-diffraction hybrid optical system containing CaF2 DOE.
We reported a single-frequency fiber laser at 915 nm based on the neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet (Nd∶YAG) crystal-derived fiber (NYDF). Using Nd∶YAG crystal with doped atomic number fraction of 2.5% as the core material and a high-purity silica tube as the cladding material, we fabricated the NYDF by the molten-core method. Its transmission loss was 8 dB/m and its gain coefficient at 915 nm was 1.16 dB/cm. A stable single-frequency fiber laser at 915 nm based on the NYDF was developed, with a signal-to-noise ratio of above 50 dB. The experimental results show that the NYDF is a promising candidate material for single-frequency lasers at 890 nm--920 nm waveband.
In this paper, wireless multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) ultraviolet communication is combined with a linear water-filling algorithm. First, a wireless non-line-of-sight (NLOS) MIMO ultraviolet communication model based on the linear water-filling algorithm is established and its channel capacity model is derived. Then, the equal power allocation algorithm and the linear water-filling algorithm are used for power allocation at the signal transmitter. The influences of these two methods on the channel capacity of the wireless NLOS MIMO ultraviolet communication system are studied, and simulation analysis and verification are conducted. The simulation results show that at the same signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), when the transmitting and receiving antennas are asymmetrical, the channel capacity of the communication system adopting the linear water-filling algorithm in wireless NLOS MIMO communication is significantly higher than that of the system employing the equal power allocation algorithm. When the transmitting and receiving antennas are symmetrical and the SNR is small, the water-filling algorithm can significantly improve the channel capacity. When the SNR increases to a certain value, the channel capacity of power allocation obtained via the water-filling algorithm is close to that obtained via the equal power allocation algorithm.
In order to make full use of the spatial-spectral bandwidth of optical correlation recognition system and to enhance the parallel processing efficiency and recognition accuracy of optical correlation recognition technology, a recognition method for multiple channeled joint transform correlation is proposed based on the compression and translation of power spectra, in which the standard deviation of the variation of position of correlation peak is derived to act as a new criterion for correlation recognition. The scene image and N reference images are first uploaded on the different zones of the input spatial light modulator. Then, the optimized phase maps using the iterative algorithm are superimposed onto the images. In the Fourier plane, interference will occur between the Fourier spectrum of the scene image and that of every single reference image within different zones of the Fourier plane. No interference of Fourier spectra among the reference images will appear when the restriction parameter is suitably adjusted in the phase optimization algorithm. As a result, the N channeled parallel processing without crosstalk is achieved. The relationship between the localized peak clutter mean of the Fourier spectrum with the optimized phase and the standard deviation of the variation of position of correlation peak is analyzed and utilized as a criterion for the selective preference on the optimized phase mask. The results indicate that the proposed multiple channeled joint transform correlator can achieve 16-channel correlation recognition without the increase of system complexity compared with the classical optical correlator under specific experimental conditions, which is quite important for the practicality of an optical correlator.
Based on the existing phase-only spatial light modulator (SLM), a computer generated phase-only rainbow holographic near-eye display is proposed and realized. It is pointed out that the calculation of the phase distribution of the object light on the holographic plane under the band-limited condition and the control of longitudinal dispersion by high-frequency blazed grating are the key elements to realize the phase-only rainbow holography. When calculating the phase-only rainbow hologram, the complex amplitude distribution of the object light on the holographic plane is obtained by using the angular spectrum diffraction algorithm under the band-limited condition, and the complex amplitude distribution is encoded as the phase distribution by the bidirectional error diffusion algorithm first. Then, the phase of high-frequency blazed grating corresponding to the reference light is encoded, and the computer generated phase-only rainbow hologram is obtained. Finally,a holographic near-eye color display system including a white light point source, a collimating lens, a spatial light modulator, a 4f filtering system and an eyepiece is designed and the phase rainbow holographic near-eye display effect is obtained by optical reconstruction, which proves the effectiveness of the proposed method.
Data from hyperspectral remote sensing have provided detailed spectral and spatial information regarding ground objects. To solve the problems of low robustness and classification accuracy due to the underutilization of spatial information of hyperspectral data in previous classification methods, this paper proposes a classification method based on improved superpixel segmentation and 3D convolution neural network. First, the hyperspectral remote sensing data are segmented via superpixel segmentation and fuzzy clustering; then, the spatial-spectral joint data formed by the regional segmentation results and hyperspectral data are trained and classified using a 3D convolution neural network. The proposed method improves the role of spatial information in classification by dividing and fusing spatial regions, reduces the impact of the phenomenon of “same objects different spectra” on classification, and introduces a 3D convolution neural network to train and classify the spatial-spectral joint data, improving hyperspectral classification accuracy. In the Pavia University and Salinas datasets, the proposed method has an overall accuracy of 97.53% and 98.48%, respectively. When compared with the control experiments, the proposed method exhibits a better classification effect, which proves its efficacy.
In this paper, an improved DR-Net recognition algorithm based on DR-Net model is proposed to solve the problems of unbalanced diabetic retina image dataset, insufficient feature extraction of tissue morphology, and low classification accuracy of diabetic retinopathy. The Kaggle APTOS 2019 contest dataset is selected, which is expanded with various data enhancement strategies, and the Eye-PACS dataset is introduced for unbiased correction. Moreover, morphological methods such as Gaussian filtering are used to intensify the fundus image characteristics. Then the aggregated residual structure of ResNext50 is pre-trained and the parameters and structure of the baseline model are fine-tuned through transfer learning. In addition, the cavity convolution is introduced to replace the ordinary convolution, and the attention mechanism is also involved to further optimize the model performance. The test results show that the improved DR-Net model greatly improves the accuracy of diabetic retinopathy classification: the positive and negative predictive values reach 97.9% and 98.03%, respectively, with the accuracy being up to 98.04%, which is much higher than those of similar algorithms. In short, the screening of retinopathy with the assistance of deep learning technology is of guiding significance for the research of early automatic screening for retinopathy.
A wide-band high-resolution echelle grating spectrometer is designed on the basis of an off-axis three-mirror reflective optical system and a multi-column linear array detector in this paper. First, the structural parameters of the echelle gratings are optimized with the instrument performance indicators as constraints so that the gratings can fold and overlap the wide working band within a small spectral order while ensuring high dispersion. The multi-column linear array detector is used for signal acquisition. Then, for the aberration correction of the wide free spectral region with high dispersion, the off-axis three-mirror reflective optical system is used as the focusing mirror and the off-axis parabolic mirror is used as the collimating mirror. The working band of the designed echelle grating spectrometer is 400--900 nm, and the F number is 4.5. The spectral resolution is 0.003, 0.004, and 0.005 nm at 402.31, 541.82, and 870.48 nm, respectively, and the system volume is 380 mm×325 mm×230 mm.
In the process of measuring highly reflective objects using binocular structured light 3D shape measurement technology, overexposure occurs at different positions of the corresponding object surface in the left and right images, resulting in invalid phase data in the corresponding area. First, the projection system as the reverse camera, and the multiple visual geometry system is composed of the binocular system and the projection system. Second, the more on every point on the surface of the object system matching. Then, the validity of the phase corresponding to each pixel is judged by modulation, and the two-view collinear equation is obtained by discarding the pixels in the over-exposed image region. Finally, the 3D point cloud reconstruction is realized by global multi-view equation. This method can effectively solve the problems of coordinate system transformation, data redundancy and fusion error of multi-system reconstruction results. The experimental results show that the proposed method can effectively measure the 3D shape of highly reflective objects in the field of view of 500 mm×700 mm.
Given that the precise pose of space non-cooperative targets is difficult to obtain during close rendezvous and docking, an efficient and reliable pose measurement method of space non-cooperative targets based on the time-of-flight (TOF) camera is proposed. Firstly, in view of the characteristic that light intensity can be stored in gray-scale images taken by the TOF camera, a dot calibration board made from retro-reflective materials is adopted to improve the calibration accuracy. Secondly, the ellipse detection method based on the combination of edge arcs is applied for calculating the inner and outer ellipse parameters of the target surface butt ring. Thirdly, the connected components of the depth image are analyzed via the region growing method based on local thresholds and the target surface connector is extracted under constraints such as area and aspect ratio. Finally, a target coordinate system is established through the docking ring and the connector and the three-axis position and attitude angle of the system in the camera coordinate system are calculated. Besides, a ground verification system is set up to verify the robustness and measurement accuracy of the proposed method. To this end, the proposed method and the ORB (Oriented FAST and Rotated BRIEF) method are compared using the experimental results of 4 groups of 100 frame images, indicating that the TOF camera has broad prospects in the pose measurement of non-cooperative targets.
Transport of intensity equation (TIE) is one of the important methods for non-interferometric phase retrieval. Traditional methods are restricted by the shape of the input image or the convergence speed, which limits the universality and phase recovery efficiency of TIE. Therefore, a TIE phase retrieval method based on fast iterative finite difference method (FIFDM) is proposed. On the basis of the TIE solution method based on the finite difference method (FDM), the correlation of each point in the iterative process is considered and the relaxation factor is introduced in FIFDM to realize the phase retrieval. Simulation and experimental results show that, compared with discrete cosine transform (DCT) method and FDM, the proposed method has faster recovery speed, higher accuracy and stronger anti-noise performance.
Compared with the symmetric Lorentzian line shape, asymmetric resonant Fano line shape can realize dramatical variation of optical transmission intensity in the integrated optical circuits, which can effectively improve the sensitivity of optical switches, modulators, and sensors. A Fano resonator based on grating-assisted microring resonator is proposed. The resonator is made of silicon-on-insulator, and the Fano resonance is realized by adding two groups of waveguide grating structures in the runway microring. Based on the transfer matrix theory, the output spectra of the Fano resonator is deduced, the effects of variation of structural parameters in the resonator on the resonant wavelength, notch depth, and slope of the Fano spectra are analyzed. A Fano spectrum with the slope of -299.67 dB/nm, notch depth of 9 dB, and insertion loss of 6.4 dB is realized. The Fano resonator has advantages of high slope, small size, and simple manufacture, which can be widely used in the fields of optical switching, optical sensing, and optical detection.
With the development of beam combining and the improvement of unit chip power, diode lasers have shown their own advantages in the field of laser processing. Aiming at the requirement of thermal curing of glass fiber reinforcement bars in the field of laser processing, the single tube laser with the power of 18 W is used as the unit module. The laser heating light source with the output power of greater than 2 kW, the wavelength of 915 nm, and the spot size of 700 mm×10 mm is obtained through the combination of spatial multiplexing, polarization multiplexing, and beam shaping technology, which meets the requirement of high power and long spot laser heating in industry.
Aiming at the problems of multi-scale inshore ship detection in surveillance videos, this paper proposes a ship target detection algorithm based on feature re-focusing network, and designs a feature re-focusing strategy, which consists of a multi-scale feature aggregation module (MFAM) and attention feature re-assignment module (AFRM). Specifically, MFAM fuses the semantic information of different levels of features of multi-scale ships by constructing a feature aggregation block based on the input feature pyramid. AFRM is composed of multi-branch dilated convolutions as well as channel and spatial attention mechanisms, which can improve the network's representation of target non-local information and suppressing interference of background, and a feature re-focusing pyramid is established for target detection. The experimental results on the Seaships7000 ship public data set show that compared with other algorithms, the algorithm has a better detection effect on multi-scale inshore ships in surveillance videos.
Visual odometry is commonly used in various applications including intelligent robots and self-driving cars. However, traditional visual odometry algorithms based on the pinhole camera with a limited field of view (FOV) are usually fragile to moving objects in the environment and fast rotation of the camera, resulting in insufficient robustness and accuracy in practical use. This paper proposes panoramic annular semantic visual odometry as a solution to this problem. Using the panoramic annular imaging system with ultra-wide FOV into visual odometry and coupling semantic information provided by the panoramic annular semantic segmentation based on deep learning into each module of the algorithm, the effect of moving objects and fast rotation is reduced; then, the performance of visual odometry in dealing with these challenging scenarios can be improved. Compared with traditional visual odometry systems, experimental results show that the proposed algorithm achieves more accurate and robust pose estimation in realistic scenarios.
By varying the anchoring condition, the helical structure with a long-range order is achieved as a thermodynamically stable state without external supports. Poly [6-(4-methoxy-azobenzene-4'-oxy) hexyl methacrylate] (PMMAZO) is deposited onto the silicon substrate to tune the anchoring. Both orientation and pitch can be controlled by varying the PMMAZO grafting density. As the grafting density increases, the enhanced titled deformation of helical structure suppresses the pitch size. As the cell thickness increases, the pattern transition from a long-range order stripe to a small fingerprint domain is facilitated.
For conventional microscopes, the phase contrast imaging mode requires the configuration of special diaphragms, condenser or the addition of inserts to the objective lens, which increases the difficulty and cost of phase contrast microscopic imaging. Therefore, a method of virtual phase contrast imaging based on deep learning algorithm is proposed. Only an ordinary optical bright field microscope is required to acquire cellular bright field images, and then the bright field images are converted to phase contrast images on a computer using a deep learning method. We compare the virtual phase contrast images with the standard phase contrast images acquired by the microscope. The results demonstrate the effectiveness of this virtual phase contrast imaging method, which provides an example of low-cost phase contrast microscopic imaging.
Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) is a polymer organic silicon compound, which is widely used in microfluidic chip preparation, biology, optics, and composite material matrix. The optical fiber interferometer is constructed through the combination of PDMS and optical fiber structure, the refractive index and linear expansion pressure response characteristics of PDMS are tested by optical fiber sensing technology. Experimental results show that the rate of change for refractive index of PDMS with the pressure is -2.1×10-2 RIU/MPa (RIU is the unit of refractive index), the rate of change for linear expansion of PDMS with the pressure is 17.3 μm/MPa. The refractive index and linear expansion pressure response of PDMS are studied in the form of optical measurement, which has higher accuracy and reliability.
In order to improve the performance of the acousto-optic frequency shifter, the positional mismatch characteristics between the internal acousto-optic crystal (AOC) and piezoelectric ultrasonic transducer (PZT) electrodes are studied, and several geometric assembly mismatches between AOC and PZT electrodes are analyzed. By constructing a three-dimensional finite element model of AOC and electrode mismatch, the ultrasonic sound field in the AOC is simulated and analyzed under different axial assembly dislocation conditions. According to the acoustic field distribution characteristics of ultrasound, it can be found that the geometrical assembly dislocation will lead to the formation of an area without acousto-optic interaction inside the AOC, and the relationship between the length of this area and the amount of dislocation can be revealed. By analyzing the optical interface between the acousto-optic interaction area and the non-acousto-optic interaction area, it is found that the position mismatch will cause the double-beam interference effect in the output light, which will affect the output of the actual optical system. Based on the principle of double-beam interference, an experimental system is built to measure the length of without acoustic interaction occurs region, and the results prove the rationality of the theoretical analysis.
In this paper, an amorphous silicon (a-Si) nanocylinder cluster metasurface is used to realize dual-peak near-perfect absorption in the visible spectral range. The contributions of electric dipole (ED), magnetic dipole (MD), and electric quadrupole to the scattering cross section of the nanocylinder cluster metasurface are studied via discrete dipole approximation. The transmission, reflection, and absorption spectra and electric field distribution of the a-Si nanocylinder cluster metasurface are simulated and analyzed. The Mie resonance of ED, MD, and electric quadrupole is tuned for the overlap and coherent coupling of the spectra, which further results in the local enhancement of the electric field and the dual-peak near-perfect absorption in the visible spectral range that is insensitive to the incident angle. The dual-peak near-perfect absorption of the a-Si nanocylinder cluster metasurface with low loss and angle insensitivity is expected to be applied to nanophotonic fields such as optical separation and energy collection.
Due to the influences of atomic clock and classical radio signal measurement accuracy, Loran C system is difficult to provide high-precision timing for users. In this paper, a microwave-optical entangled timing scheme used in Loran C system is proposed. The entangled microwave-optical signal is firstly prepared by the electro-opto-mechanical converter, then the signal propagation time is obtained by the second-order coherence function of the entangled signal, and finally the local clock time for users is corrected based on the timing sequence relationship and the timing is realized. The influence of electro-opto-mechanical converter parameters on timing accuracy is simulated and analyzed. The proposed scheme theoretically improves the timing accuracy of Loran C system, and has certain advantages in resisting suppression interference and deception interference.
The current remote sensing object detection methods, only identifying the category and location of remote sensing objects, cannot generate text caption related to the contents of remote sensing images. A remote sensing image caption method based on attention and reinforcement learning is proposed in this paper to solve this problem. First, the convolution neural network is used to construct an encoder and thereby extract remote sensing image features. Secondly, a decoder is built through the long short-term memory network to learn the mapping relationships of the image features with text semantic features. Thirdly, the attention mechanism is introduced to enhance the attention of the model on salient features and reduce the interference of irrelevant background features. Finally, the reinforcement learning strategy is adopted to optimize the model directly according to the discrete and non-differentiable evaluation indexes and thus to eliminate the defects of exposure bias and inconsistent optimization directions. Experimental results of public data sets of remote sensing image caption show that the method achieves high detection accuracy and has good caption performance for remote sensing images in complex environments such as dense small targets, fog accumulation, and similar background and object features.
Traditional light detection and ranging (lidar) loop-closure detection algorithms are greatly interfered with by dynamic obstacles, and key-frame search and feature matching take a long time. In response, this paper proposed a less time-consuming SR-Context lidar loop-closure detection algorithm with stronger robustness based on the multiple-features random sample consensus (MF-RANSAC) algorithm and an improved ScanContext algorithm. Firstly, the region growing algorithm was used to cluster the point clouds that had undergone fan-shaped rasterization. Then, an MF-RANSAC algorithm was proposed to eliminate dynamic targets quickly. This algorithm was based on multi-point selection in a dynamic region and query of corresponding points with multiple attributes rather than target recognition and tracking. Finally, the ScanContext algorithm was improved by simplifying the feature matching calculation and deleting the loop-closure historical matching frames. Loop-closure detection of the point clouds of the current frame after elimination of dynamic targets was thus achieved. Tests were carried out on a KITTI dataset and a real vehicle dataset. The experimental results show that the proposed method delivers quick and accurate loop-closure detection in dynamic urban environments and thereby improves lidar mapping accuracy. The average time it takes is only 40% of that of the ScanContext algorithm.
When polarized light propagates in the scattering medium, the polarization information is disturbed and lost due to multiple scattering of scattering particles. In order to ensure efficient and high-fidelity transmission of polarization information in scattering media, a polarization recognition method through scattering media based on deep learning is proposed. A convolutional neural network is constructed to extract the characteristics of the polarization information of incident light wave from the speckle light intensity information to realize the high resolution recognition of the polarization state of incident light wave, and the robustness of the convolutional neural network for polarization state recognition is verified by using polarized light with different initial phases. Experimental results show that the proposed method has the advantages of fast recognition speed and high accuracy, and the neural network can be trained with infinite data in theory. Therefore, the method has great application potential in polarization optical imaging and laser communication.
This paper proposed a solution method of spectral classification modeling for multi-scene optimization. Firstly, a modified power function equation was constructed through a simulation analysis of the Mie scattering of particles, and the direct fitting method was used to achieve accurate turbidity correction of the sample spectra. Then, the absorbance normalization method was employed to obtain the linear feature spectra of different scenes and develop a scene-based feature library. Subsequently, the partial least-squares (PLS) method was applied to build a solution model for each scene and thereby establish a chemical oxygen demand (COD) solution model library. When an unknown water sample went through the COD detection, its normalized spectrum was first matched with the linear feature spectra of the scene-based library through the Jaccard similarity theory for the identification of the scene it belonged to. Then, its COD concentration was calculated with the optimal solution parameters obtained from the solution library. The experimental results show that the proposed method holds application value in that it delivers high scene-matching accuracy and reduces the COD solution error under multi-scene conditions.
A novel reconfigurable visible light filter based on nanofilms with a black layer was proposed in view of the tunable dielectric properties of ferroelectric materials. The reconfigurable performance of its reflection spectrum was compared with that of the one-dimensional photonic crystal filter. The experimental results demonstrate that the reflection color contrast is significantly improved by the black layer that absorbs the incoherent scattered light. When the thickness of the barium titanate (BTO) film changes from 100 nm to 140 nm, the peak wavelength of the reflection spectrum shifts from 383.7 nm to 501.2 nm, and the reflection color turns from purple to turquoise. The test results of the reflection spectra are in good agreement with the finite element simulation outcomes. According to the numerical results, when the BTO film is 170 nm thick, its refractive index decreases from 2.4 to 2.0 under 21.8 V direct-current (DC) driving voltage. Consequently, the peak wavelength of the reflection spectrum shifts from 595.3 nm to 513.9 nm.
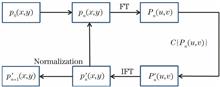
Ptychographic coherent diffraction imaging is a novel lensless imaging method, which removes the resolution limitation by imaging elements in traditional optical lens imaging, so that its theoretical resolution is only limited by the X-ray wavelength and the numerical aperture of detector. However, the experiment background noise limits the further improvement of the imaging quality by this method, and may lead to the failure of image reconstruction. A new phase-retrieval iterative algorithm is proposed in this paper after studying the existing ptychographic iterative algorithms. The new algorithm uses the high redundancy of the ptychographic data set, and uses the gradient descent minimization method to reconstruct the background noise in synchronization with the reconstruction of the object and the detection, and realizes the blind separation of the noise and the signal. This algorithm is compared with the traditional iterative algorithms in simulation and experiment data reconstructions, demonstrating that this new algorithm can achieve a better signal-noise separation and a higher imaging quality.