View fulltext
View fulltext
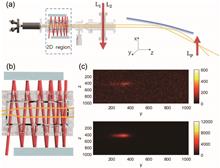
Isotope shifts among different isotopes can be effectively addressed using narrow-linewidth lasers, facilitating laser isotope separation and achieving significant enrichment at a single stage. The separation of potassium isotopes, employing optical pumping and magnetic deflection, has proven to be efficient. To further improve the enrichment of 40K, we introduce 2D transverse cooling to minimize the divergence angle. Through this modification, we demonstrate enrichment of 40K, elevating it from 0.012% to 12%–20%. This represents an enrichment increase by three orders of magnitude, surpassing our previous result by one order. Our method is particularly well-suited for isotope enrichment of elements with extremely low abundance.
The suppression of polarization cross talk in lead zirconate titanate phase modulators as a key error source has been challenging for open-loop fiber optic gyroscopes (FOGs). We developed a polarization-diversity optical frequency domain reflectometry (OFDR) to measure the distributed modulation polarization error in the modulator. The error contributes 8 × 10-6 rad to FOG’s bias instability. Using a UV-fabricated in-fiber λ/4 wave plate and polarization-mode converter with fiber taper technology, the modulation error has been suppressed by 15 dB in assembled FOGs. This approach reduced error with temperature from 25°/h to 0.7°/h, meeting the requirements of control-level gyroscopes with bias errors less than 1°/h.
We propose a transfer-learning multi-input multi-output (TL-MIMO) scheme to significantly reduce the required training complexity for converging the equalizers in mode-division multiplexing (MDM) systems. Based on a built three-mode (LP01, LP11a, and LP11b) multiplexed experimental system, we thoughtfully investigate the TL-MIMO performances on the three-typed data, collecting from different sampling times, launching optical powers, and inputting optical signal-to-noise ratios (OSNRs). A dramatic reduction of approximately 40%–83.33% in the required training complexity is achieved in all three scenarios. Furthermore, the good stability of TL-MIMO in both the launched powers and OSNR test bands has also been proved.
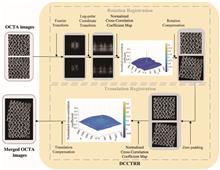
A large field of view is in high demand for disease diagnosis in clinical applications of optical coherence tomography (OCT) and OCT angiography (OCTA) imaging. Due to limits on the optical scanning range, the scanning speed, or the data processing speed, only a relatively small region could be acquired and processed for most of the current clinical OCT systems at one time and could generate a mosaic image of multiple adjacent small-region images with registration algorithms for disease analysis. In this work, we investigated performing cross-correlation (instead of phase-correlation) in the workflow of the Fourier–Mellin transform (FMT) method (called dual-cross-correlation-based translation and rotation registration, DCCTRR) for calculating translation and orientation offsets and compared its performance to the FMT method used on OCTA images alignment. Both phantom and in vivo experiments were implemented for comparisons, and the results quantitatively demonstrate that DCCTRR can align OCTA images with a lower overlap rate, which could improve the scanning efficiency of large-scale imaging in clinical applications.
In this Letter, we employ fused silica and two types of optical glass as examples to investigate the coherent terahertz (THz) wave emission from laser-ionized isotropic transparent dielectrics. Based on the laser energy and incident angle dependences, we ascribe the THz emission to the ponderomotive force-induced dipole oscillation. Additionally, our investigation on the dependence of THz amplitude on the laser pulse duration confirms the dominant role of avalanche ionization in solid dielectrics. The THz emission can be utilized to indirectly monitor the ultrafast dynamics of carrier generation and motion during the laser ionization process of solid dielectrics.
In this work, we propose a method using frequency-modulated continuous-wave (FMCW) self-mixing interferometry (SMI) and all-phase fast Fourier transform (APFFT) for simultaneous measurement of speed and distance. APFFT offers superior accuracy in frequency determination by mitigating issues like the fence effect and spectrum leakage, contributing to the high-accuracy measurement for speed and distance. Both simulations and experiments have demonstrated relative errors at the levels of 10-4 and 10-3 for distance and speed measurements, respectively. Furthermore, factors impacting measurement performance have been discussed. The proposed method provides a high-performance and cost-effective solution for distance and speed measurements, applicable across scientific research and various industrial domains.
Optical phased arrays (OPAs) have broad application prospects due to their advanced capability in beamforming and steering. In this work, we achieve independent dual beams in the far field by dividing the array elements of the OPA, with the maximum scanning range reaching 100°. Based on the working principle of OPAs, theoretical considerations of such multi-beam generation are presented. A phase data allocation approach for OPAs in the presence of fabrication-induced random phase variation is developed. Simulations of large ensembles of OPAs with various levels of random residual phase errors have been conducted to help analyze the results. This approach can help OPAs realize multi-beams for light detection and ranging (LiDAR).
A 2 × 3 kW-level bidirectional output fiber oscillator is realized by combining the specially designed spindle-shaped ytterbium-doped fiber, non-wavelength-stabilized 976-nm LDs, and grating bandwidth optimization to balance transverse mode instability and stimulated Raman scattering. The maximum output powers at both ends are 3265 and 2840 W, respectively, with a total efficiency of 73.2%. The M2 factors of the lasers at both ends are about 1.98 and 2.38, respectively. The beam profile at both ends shows that a bidirectional output annular beam fiber oscillator has been realized, which has great potential in practical applications.
We demonstrate an all-polarization-maintaining (APM) fiber mode-locked laser based on nonlinear polarization evolution (NPE). A well-designed Sagnac fiber loop is employed to establish the nonlinear polarization evolution process in a polarization beam splitter (PBS) figure-8 fiber laser. Nonlinear loss curves are calculated to verify the saturable absorption characteristic of this NPE-based APM oscillator. Then, we simulate the pulse propagation process in the cavity to demonstrate the pulse mode-locked formation. Finally, we also design a realizable compact scheme to further reduce noise disturbances, achieving a 101-fs mode-locked pulse train with a 0.3-mrad integrated phase noise and a 0.006% integrated relative intensity noise (RIN). This figure-8 fiber laser provides a new scheme for compacting low-noise compact APM fiber lasers based on the NPE mode-locked mechanism.
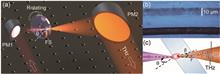
Soliton generation schemes have attracted considerable scholarly attention. This paper introduces a novel backward tuning method for the reversible generation of dissipative Kerr solitons (DKSs). Reversible soliton generation relies on the thermal stabilization of the auxiliary laser, coupled with backward tuning of the pump laser, significantly increasing the range of soliton steps by over 10 times. Moreover, the method alleviates the stringent auxiliary laser detuning requirement. By adjusting the detuning of the auxiliary laser, diverse numbers of solitons can be deterministically generated, enhancing both flexibility and precision.
We propose and experimentally demonstrate a photonic method for wideband multipath self-interference cancellation using a silicon photonic modulator chip. The chip generates phase-inverted reference signals by leveraging the opposite phase between optical sidebands. Effectively managing amplitude and phase imbalances between self-interference and reference signals, the approach rectifies discrepancies through consistent chip manufacturing and packaging processes. Employing photonic multi-dimensional multiplexing, including wavelength and polarization, enables the acquisition of multiple reference signals. Experimental results show multipath cancellation depths of 25.53 dB and 23.81 dB for bandwidths of 500 MHz and 1 GHz, achieved by superimposing 2-path reference signals.
We present a tunable terahertz (THz) spectrum analyzer with hyperspectral resolution formed from electrically tunable metamaterial and plasmonic structures. As few as eight encoders based on four detectors are needed to recover 396 spectral bands. The incident spectra in the range of 1–5 THz can be reconstructed with a localization precision of 0.3 GHz and a minimum average mean squared error (MSE) of 6.9 × 10-5. Our proposed analyzers are faster and more portable than those based on frequency combs and power meters, and more accurate than existing Fourier transform techniques, showing promising applications in pathology, biomedical imaging, and many other areas.
In this work, a simple fabrication method of germanium-based metasurfaces is proposed, where the deposited Al2O3 layer with high selectivity is chosen as the hard mask and retained after the dry etching process. The simulation and experimental characterization results verify the feasibility of the fabrication method. The experimental study on the fabrication methods of germanium-based metasurfaces is very significant as the meta-atoms with a higher refractive index can achieve 0 to 2π transmission phase variation with a smaller period under the same thickness-to-period ratio, which is consistent with the requirement of the period miniaturization in some cases.
A 3D nonlinear photonic crystal containing four parallel segments of periodic χ(2) grating structure is fabricated employing the femtosecond laser poling of ferroelectric Ca0.28Ba0.72Nb2O6 crystal. The second harmonic generation from this four-segment structure is studied with a fundamental Gaussian wave. By tuning the wavelength of the fundamental wave, the second harmonic varies from the Laguerre–Gaussian beam (topological charge lc = 1) to the higher-order Hermite–Gaussian beam and Laguerre–Gaussian again (lc = -1). This effect is caused by the wavelength-dependent phase delays introduced by the four-grating structure. Our study contributes to a deeper understanding of nonlinear wave interactions in 3D nonlinear photonic crystals. It also offers new possibilities for special beam generation at new frequencies and their control.
Stimulated Brillouin scattering in planar integrated circuits promises to realize compact and highly coherent lasers. Here we report efficient Brillouin lasing at telecommunication wavelength from a planar Ge25Sb10S65 chalcogenide (ChG) resonator with a high quality factor above 106. A low lasing threshold of 24.8 mW is achieved with a slope efficiency of 8.3%. An 8-kHz linewidth is measured for 1.56-mW on-chip output power. This work offers a good opportunity to enrich the versatility and functionality of the ChG photonics on account of their intrinsic advantages of low loss, high third-order nonlinearity, and potential capacity for wafer-scale fabrication.
We use a broad Gaussian beam with perturbations to motivate rogue waves (RWs) in a two-dimensional optical-induced lattice. In a linear situation, we fail to observe RWs. Nevertheless, under a nonlinear condition, the probability of RWs in the lattice is less than that in a homogeneous medium. Additionally, we obtain a shorter long-tail distribution of probability density function in an optical lattice.
Electron-trapping materials, due to their exceptional ability of energy storage and controllable photon release under external stimulation, have attracted considerable attention in the field of optical information storage (OIS). In this work, Gd3Al3Ga2O12:Ce3+, Yb3+ fluorescent ceramics, were developed using air and vacuum sintering technology. By co-doping Ce3+ and Yb3+, the trap density was significantly increased by 7.5 times compared to samples containing only Ce3+. Vacuum annealing further enhanced trap density by 1.6 times compared to samples sintered solely in air, while generating deep traps (1.44 eV), making Gd3Al3Ga2O12:Ce3+, Yb3+ an excellent OIS medium. This work is expected to facilitate the development of OIS materials.
The generation of high-power laser pulses using a compact hetero-integrated assembly based on a semiconductor laser with a dual-element composite 2 µm × 100 µm aperture and a compact heterothyristor switch is demonstrated. The achieved peak optical power was 33 W with a pulse duration of 3 ns at a thyristor operating voltage of 55 V. The leading edge of the laser pulse turn-on was 50 ps to a power level of 24.7 W, and the turn-on delay between the elements of the composite aperture was 160 ps.
Frequency-modulated continuous-wave (FMCW) Lidar has the characteristics of high-ranging accuracy, noise immunity, and synchronous speed measurement, which makes it a candidate for the next generation of vehicle Lidar. In this work, an FMCW Lidar working at the single-photon level is demonstrated based on quantum compressed sensing, and the target distance is recovered from the sparse photon detection, in which the detection sensitivity, bandwidth, and compression ratio are improved significantly. Our Lidar system can achieve 3 GHz bandwidth detection at photon count rates of a few thousand, making ultra-long-distance FMCW Lidar possible.
We demonstrate a resolution enhancement scheme of radio-frequency signals by tailoring a phase-squeezed state. The echo radio-frequency signals collected by photonic radar give rise to displacements in the phase quadrature of a probe laser and are estimated by the balanced homodyne detector. In contrast to the conventional coherent state, the noise variances for radio-frequency estimation with a squeezed state are reduced by approximately 6.9 dB. According to the Rayleigh criterion that defines the resolution limit, the minimum resolvable displacement Δa with a squeezed state is reduced to 45% compared to that with a coherent state, demonstrating the quantum advantage. The squeezing-enhanced technique has extensive applications for multitarget recognition and tracking in contemporary photonic radar systems.
A highly sensitive carbon dioxide (CO2) sensor based on light-induced thermoelastic spectroscopy (LITES) utilizing a self-designed low-frequency quartz tuning fork (QTF) and a fiber-coupled multipass cell (MPC) is reported in this paper. The QTF with a low resonant frequency of 8675 Hz and a high Q factor of 11,675.64 was used to improve its energy accumulation time and the sensor’s signal level. The MPC with the fiber-coupled structure and optical length of 40 m was adopted to significantly increase the gas absorbance and reduce the optical alignment difficulty as well as improve the robustness of the sensor system. A distributed feedback (DFB), near-infrared diode laser with an emission wavelength of 1.57 µm was used as an excitation source. The experimental results showed that this CO2-LITES sensor had an excellent linear response to CO2 concentrations. The minimum detection limitation (MDL) of this CO2-LITES sensor was obtained to be 445.91 ppm, and it could be improved to 47.70 ppm (parts per million) when the integration time of the system reached 500 s. Further improvement methods for the detection performance of such sensors were also discussed.
In this work, we introduce a kind of new structured radial grating, which is named the even-type sinusoidal amplitude radial (ETASR) grating. Based on diffraction theory and the principle of stationary phase, a comprehensive theoretical investigation on the diffraction patterns of ETASR gratings is conducted. Theoretical results show that novel carpet beams with beautiful optical structures and distinctive characteristics have been constructed on the basics of the ETASR grating. Their diffraction patterns are independent of propagation distance, that is, the new carpet beams have diffraction-free propagating characteristics. The non-diffracting carpet beams are divided into two types by beam characteristics: non-diffracting integer-order and half-integer-order carpet beams. Subsequently, we experimentally generate these carpet beams using the ETASR grating. Finally, their particularly interesting optical morphology and features are explored through numerical simulations and experiments.