View fulltext
View fulltext
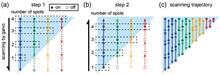
Multi-focus parallel scanning can effectively increase laser fabrication throughput. However, the conventional approach of using a spatial light modulator (SLM) to generate multi-foci and scan this fixed number of foci with galvanometer scanners can only achieve a periodic scanning trajectory due to the low switching speed of the SLM. Here we demonstrate a multi-focus non-periodic scanning method for femtosecond lasers by using, instead, a fast-switching digital micromirror device (DMD) to generate a dynamic number of foci. The number of effective foci is quickly switched by introducing aberration to the undesired focus. In this way, the intensity allocated to each focus will not be affected by the number of foci, and a uniformity of 98% with different numbers of foci is achieved without adjusting the total laser energy. Finally, we validate the effectiveness of this scanning method by demonstrating corneal flap fabrication of porcine cornea in vitro.
Diffraction intensities of the 3D ptychographic iterative engine (3PIE) were written as a set of linear equations of the self-correlations of Fourier components of all sample slices, and an effective computing method was developed to solve these linear equations for the transmission functions of all sample slices analytically. With both theoretical analysis and numerical simulations, this study revealed the underlying physics and mathematics of 3PIE and demonstrated for the first time, to our knowledge, that 3PIE can generate mathematically unique reconstruction even with noisy data.
A multi-functional full-space metasurface based on frequency and polarization multiplexing is proposed. The metasurface unit consists of metallic patterns printed on the two faces of a single-layered dielectric substrate. The unit cell can control electromagnetic wavefronts to achieve a broadband transmission with amplitudes greater than 0.4 from 4.4 to 10.4 GHz. Meanwhile, at 11.7 GHz and 15.4 GHz, four high-efficiency reflection channels with a reflection amplitude greater than 0.8 are also realized. When illuminated by linearly polarized waves, five different functions can be realized at five different frequencies, which are demonstrated by theoretical calculations, full-wave simulations, and experimental measurements.
Recently, Mach–Zehnder modulators based on thin-film lithium niobate have attracted broad interest for their potential for high modulation bandwidth, low insertion loss, high extinction ratio, and high modulation efficiency. The periodic capacitively loaded traveling-wave electrode is optimally adopted for ultimate high-performances in this type of modulator. However, such an electrode structure on a silicon substrate still suffers from the velocity mismatch and substrate leakage loss for microwave signals. Here, we introduce a thin-film lithium niobate modulator structure using this periodic capacitively loaded electrode on a silicon substrate. Backside holes in the silicon substrate are prepared to solve robustly the above difficulties. The fabricated device exhibits an insertion loss of 0.9 dB, a halfwave-voltage–length product of 2.18 V·cm, and an ultra-wide bandwidth well exceeding 67 GHz for a 10-mm-long device. Data transmissions with rates up to 112 Gb/s are demonstrated. The proposed structure and fabrication strategy are compatible for other types of monolithic and heterogeneous integrated thin-film lithium niobate modulators on a silicon substrate.
For joint modulation format identification (MFI) and optical signal-to-noise ratio (OSNR) monitoring, a simple and intelligent optical communication performance monitoring method is proposed, and the feasibility is demonstrated by digital coherent optical communication experiments. The experiment results show that for all modulation formats, including 28 GBaud polarization division multiplexing (PDM) QPSK/8-QAM/16-QAM/64-QAM, 100% MFI accuracies are achieved even at OSNR values lower than the corresponding theoretical 20% forward error correction limit, as well as the high accuracies for OSNR monitoring. Furthermore, the proposed scheme has a reasonable monitoring level when chromatic dispersion and fiber nonlinear effects are varied.
A method of preparing panda-shaped photonic crystal fibers (PCFs) based on secondary drawing technology is proposed in this paper. The secondary drawing can not only reduce fiber diameter but also reduce core size by adding a glass sleeve. Silver-filled and non-silver-filled panda PCFs are prepared. The two ends of silver-filled panda PCF are connected with a broadband light source and a spectrometer, respectively, and the surface plasmon resonance phenomenon is detected. The secondary drawing technology provides a meaningful reference for the preparation of PCF in the future, and the prepared silver-filled panda PCF can be prepared into an optical fiber filter.
We propose a trellis-compressed maximum likelihood sequence estimation (TC-MLSE)-assisted sliding-block decision feedback equalizer (DFE) to suppress the error propagation resulting from the DFE in high-speed systems. We use an out-of-range detector to detect the end of burst errors from the DFE and activate the optional TC-MLSE to correct burst errors. We conduct experiments to transmit a 201-Gbit/s PAM-8 signal. The results show that the proposed method achieves a bit error rate of 3.65 × 10-3, which is close to that of MLSE. The optional MLSE is only activated when needed and processes 11.4% of the total symbols. Moreover, the proposed method compresses the maximum length of burst errors from 19 to 5.
The coexistence of a noise-like pulse (NLP) and a dark pulse was experimentally demonstrated in a net-anomalous dispersion Er/Yb co-doped fiber (EYDF) laser, for the first time, to our knowledge. The cavity was mode-locked by nonlinear polarization rotation (NPR) technique. Meanwhile, a Sagnac loop with a section of polarization-maintaining fiber (PMF) was used as a comb filter to enable multiwavelength pulse operation. When the PMF length was 0.3 m, an asymmetric two-peak spectrum with central wavelengths of 1565.3 and 1594.2 nm was obtained by adjusting polarization controllers (PCs). It is a composite state of NLP and dark pulse due to the cross-phase modulation between the two different wavelength components along orthogonal polarization axes. The two pulses are synchronized with a repetition rate of 7.53 MHz. By adjusting the PC in the Sagnac loop, the spectral ranges of NLPs and dark pulses can be tuned from 1560 to 1577.8 nm and from 1581.8 to 1605.4 nm, respectively. In addition, the pulse characteristics were investigated by incorporating the PMF with different lengths, where the coexistence patterns can be generated when the PMF lengths were 0.2 and 0.3 m. A longer PMF can lead to a narrowband comb filtering, which causes a larger loss and is not favorable for stable operation of the coexistence regime. This fiber laser demonstrates an interesting operation regime and has significant potential for numerous practical applications.
The alkali-atom density measurement method based on light absorption is highly suitable for a spin-exchange relaxation-free (SERF) atomic magnetometer because of its high-precision measurement and complete nonmagnetic interference. In this study, the optical rotation angle detection system based on polarization balance detection is utilized to realize the alkali-atom density real-time measurement without affecting magnetic field measurement. We discovered that there exists an optimal frequency detuning of the probe light, which offers the highest sensitivity in alkali-atom density measurement and the lowest susceptibility to temperature fluctuations in terms of the scale factor. In contrast to conventional light absorption measurements based on pump light, this method demonstrated a threefold improvement in alkali-atom density measurement sensitivity while remaining immune to ambient magnetic fields and incident light intensity fluctuations. Furthermore, we utilized this method to achieve closed-loop temperature control with an accuracy of 0.04°C.
Effective methods are urgently required to optimize Raman spectroscopy technology to ameliorate its low detection sensitivity. Here, we superposed two near-concentric cavities to develop a dual near-concentric cavities group (DNCCG) to assess its effect on gas Raman signal intensity, signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), and limit of detection (LOD). The results showed that DNCCG generally had higher CO2 Raman signal intensity than the sum of two near-concentric cavities. Meanwhile, the noise intensity of DNCCG was not enhanced by the superposition of near-concentric cavities. Accordingly, DNCCG increased the SNR. The LOD for CO2 was 24.6 parts per million. DNCCG could be an effective method to improve the detection capability of trace gases and broaden the dynamic detection range, which might aid the future development of innovative technology for multicomponent gas detection.
The optical frequency comb based on microresonators (microcombs) is an integrated coherent light source and has the potential to promise a high-precision frequency standard; self-reference and a long-term stable microcomb are the keys to this realization. Here, we demonstrated a 0.7-octave spectrum Kerr comb via dispersion engineering in a thin-film lithium niobate microresonator, and the single-soliton state can be accessed passively with long-term stability over 3 h. With such a robust broadband coherent comb source using thin-film lithium niobate, a fully stabilized microcomb can be expected for massive practical applications.
An unstable resonator with seven large aperture ceramic disks and intra-cavity adaptive correction is presented. The composite ceramic disks with absorption rings were adopted to suppress amplified spontaneous emission. An intra-cavity aberration non-conjugate correction based on round-trip wavefront and relaxation iteration was applied in the resonator. After tilt and defocus were corrected in turn, an average output power of 4.5 kW was obtained. The corresponding beam quality factor β was 19.5. After tilt, defocus, and high order aberrations were corrected, the average output power was increased to 5.4 kW, and the beam quality factor β was improved to 6.8.
We experimentally demonstrate tunable dual-comb soliton rains in a polarization multiplexing fiber laser based on a single-walled carbon nanotube. The repetition frequency difference of dual-comb pulses is about 39 Hz, with a maximum extinction ratio of 29 dB. With suitable polarization states, one of the dual-comb pulses switches into soliton rain sequence with chirped isolating soliton trains. The signal-to-noise ratio reaches 61 dB, which is 11 dB higher than that of the normal dual-comb pulses. The intervals between chirped isolating solitons are distributed progressively, and the number of isolating solitons can be flexibly tuned from 2 to 11 by adjusting polarization state or pump power. Our work will provide support for further understanding of interaction dynamics of solitons and give a new route to the application of precision measurement.
In this research, we report the latest progress in the suppression of nanosecond prepulses from regenerative amplifier and multipass amplifiers in the SULF-1PW laser. The prepulse generated from the Pockels cell (PC) in a regenerative amplifier is delay-shifted by enlarging the distance between the PC and the nearby cavity mirror, and then removed by the extra pulse pickers outside the regenerative amplifier. The prepulses arising from multipass amplifiers are also further suppressed by adopting a novel amplifier configuration and properly rotating the Ti:sapphire crystals. After the optimizations, the temporal contrast on a nanosecond time scale is promoted to be better than a contrast level of 10-9. This research can provide beneficial guidance for the suppression of nanosecond prepulses in the high-peak-power femtosecond laser systems.
In this paper, a spectral beam combining (SBC) structure of multi-single emitters laser diode based on a polarization full feedback (PFF) external cavity is proposed and demonstrated. The maximum combining efficiency is 75.6%, which leads to an output power of 38.48 W, a degree of polarization (DOP) of 99.42%, and electro-optical conversion efficiency of 35.63% under continuous wave operation at a current of 8 A. Compared to the conventional SBC, the output power, the combining efficiency, the electro-optical conversion efficiency, and the DOP of the PFF-SBC structure present improvements of 5.73 W, 11.26 percentage points, 5.3 percentage points, and 7.26 percentage points, respectively. The results show that this SBC method can achieve a high efficiency and linearly polarized laser output of SBC, thereby making the subsequent polarization beam-combining efficiency approach the limit.
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first time that a mid-infrared Er3+:CaF2-SrF2 laser has achieved continuous-wave mode-locked operation by a semiconductor saturable absorber mirror. The laser emits a maximum output power of 93 mW at 2.73 µm with a repetition rate of approximately 69 MHz and demonstrates a high signal-to-noise ratio of around 71 dB. In addition, a MgF2 birefringent plate was utilized to enable wavelength tuning of the Er3+:CaF2-SrF2 laser, resulting in operation at approximately 2.73 µm, 2.75 µm, 2.79 µm, and 2.81 µm. These results demonstrate that Er3+:CaF2-SrF2 is a promising alternative for the generation of efficient diode-pumped mode-locked lasers around 2.8 µm.
We propose a method for optimizing the phase stability of microwave signal transmission over long distances. First, the design of the photon link was modified to reduce the radio frequency (RF) signal’s baseline noise and increase power. Second, a low-noise driver circuit was developed for a two-section distributed feedback (DFB) laser designed using reconstruction equivalent chirp (REC) technology to create an ultra-stable laser, and its performance was characterized through linewidth data. Test results indicate that the DFB laser achieved narrower linewidth, improving system phase stability. When an injection current (30 mA) is applied to the reflection section of the two-section DFB laser, the laser linewidth will be narrower (1.38 MHz), further enhancing the system’s phase transmission stability. At a 1 Hz offset frequency, a residual phase noise of -88.65 dBc/Hz is obtained. The short-term stability with an averaging time of 1 s is 1.60 × 10-14, and the long-term stability over a testing time of 60,000 s is 3.41 × 10-18. Even after incorporating temperature variations, the long-term stability reaches 8.37 × 10-18 at 22 h.
The metalens has attracted remarkable attention due to its ultra-thin and ultra-light characteristics, which indicate great potential for compact imaging. However, the limited efficiency at a large angle incidence severely hinders the application of wide-angle focusing and imaging, which is pursued in the fast-developing imaging systems. Therefore, new strategies to improve the lens performance at large incident angles are in demand. In this work, we propose tilted structures for large-angle focusing with improved efficiency. Metalenses based on dynamic phase and geometric phase are designed and systematically characterized by numerical simulations. We show that tilted structures of unit cells significantly improve the lens performance at oblique incidences. In detail, the focusing efficiency of the metalens with tilted structures is increased over 25% at 30° incidence, as well as the modulation transfer function. In addition, we develop a hybrid metalens array achieving highly efficient wide-angle imaging up to 120°. We believe this design provides a feasible route toward wide-field and high-performance imaging applications.
Tunability, ultracompact design, high group index, low loss, and broad bandwidth are desired properties for integrated optical delay lines (ODLs). However, those properties are challenging to achieve simultaneously in the visible region. This paper proposes a tunable hexagonal boron nitride topological optical delay line (ODL) in the visible region based on valley photonic crystals. The topological edge state from the beard-type boundary allows the achievement of an ultralow group velocity close to zero, which results in a large group index of 629 at 645 nm. Moreover, we demonstrate tuning of the slow-light wavelength and optical delay times with electrically tunable liquid crystals by applying external voltage. The device has an ultracompact size of 5 µm × 2.7 µm with an optical delay distance of 25a (a is the lattice constant) and a delay time of 12 ps. Our design can provide a new possibility for designing ODLs working in the visible region for optical communication and quantum computing systems.
We report the generation of quasi-cw vacuum ultraviolet (VUV) light at 160 nm with a repetition rate of 82 MHz by two second-harmonic generations and one sum frequency mixing. The VUV laser light is produced as a fifth-harmonic generation of a mode-locked ps Ti:sapphire laser system by successive stages with nonlinear crystals of LBO and KBBF. A stable generation of laser light at 200 nm for more than 6 h is the most important step for obtaining the generation of light at a wavelength of 160 nm.
A novel backside-illuminated double-cliff-layer uni-traveling-carrier (DCL-UTC) photodiode with both high responsivity and ultra-broad bandwidth is designed and demonstrated. A thick absorption layer is adopted for high responsivity, and a depletion region with double cliff layers is proposed to alleviate the space charge effect and maintain overshoot electron velocity under large photocurrents. In addition, inductive coplanar waveguide electrodes are employed to enhance the frequency response performance. The 6-µm-diameter photodiode exhibits a high responsivity of 0.51 A/W and a large 3-dB bandwidth of 102 GHz. A high RF output power of 2.7 dBm is recorded at 100 GHz.
We report the generation of polarization-entangled photon pairs in the 1550 nm band by pumping an uneven nonlinear interferometer loop with two orthogonally polarized counterpropagating pump pulses. The uneven nonlinear interferometer, providing a more ideal interference pattern due to the elimination of secondary maxima, consists of four pieces of dispersion-shifted fibers sandwiched with three pieces of standard single-mode fibers, and the lengths of the nonlinear fibers follow the binomial distribution. The mode number of the photon pairs deduced from the measured joint spectrum is ∼1.03. The collection efficiency of the photon pairs is found to be ∼94% (after background noise correction). The directly measured visibility of two-photon interference of the polarization-entangled photon pairs is ∼92%, while no interference is observed in the direct detection of either the signal or idler photons.
Smart beams play a vital role in modern intelligent vehicles and have recently attracted significant attention. A spatial light modulator with high optical efficiency, low cost, and compact size is crucial for designing smart beams. Here, we mix cholesteric liquid crystals with dichroic black dye and a monomer. After UV polymerization, the sample exhibits a low driving voltage of 26 V, a high transmittance of over 70%, and an On-off ratio over 280, thanks to the joint contribution of both the absorption and the scattering effect. A smart beam device is demonstrated by electrically addressing the dye-doped and polymer-stabilized cholesteric liquid crystal with pixelated electrodes. Light patterns with arbitrary designs are projected dynamically. The switching time reaches several tens of milliseconds. This strategy brings new designs to intelligent vehicles and may also inspire applications in public information displays, advertising, and even AR/VR displays.