View fulltext
View fulltext
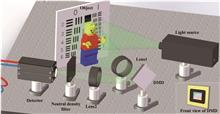
Hadamard single-pixel imaging is an appealing imaging technique due to its features of low hardware complexity and industrial cost. To improve imaging efficiency, many studies have focused on sorting Hadamard patterns to obtain reliable reconstructed images with very few samples. In this study, we propose an efficient Hadamard basis sampling strategy that employs an exponential probability function to sample Hadamard patterns in a direction with high energy concentration of the Hadamard spectrum. We used the compressed-sensing algorithm for image reconstruction. The simulation and experimental results show that this sampling strategy can reconstruct object reliably and preserves the edge and details of images.
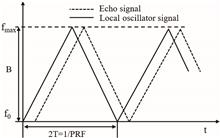
Aiming at coherence degradation during target detection, a suppressing method based on frequency-modulated continuous wave coherent lidar is proposed. Combined with a random iteration algorithm, a long-pulse echo signal with coherent degradation is matched with random phase noise of a certain frequency and achieves coherence restoration. Simulation and field experiment results show that this proposed method can recover the intrapulse coherence in long-pulse echo signals. In addition, for the real target echo signal at 4.2 and 19.8 km, the peak signal-to-noise ratio processed by this method is increased by 0.35 times and 4 times after pulse compression, respectively.
Modulation of a vector light field has played an important role in the research of nanophotonics. However, it is still a great challenge to accurately measure the three-dimensional vector distribution at nanoscale. Here, based on the interaction between the light field and atomic-sized nitrogen-vacancy (NV) color center in diamonds, we demonstrate an efficient method for vectorial mapping of the light-field distribution at nanoscale. Single NV centers with different but well-defined symmetry axes are selected and then interact with the same tightly focused light field. The excitation of a single NV center is related to the angle between the NV center axis and the polarization of the light field. Then the fluorescence patterns of different NV centers provide the information on the vectorial light field distribution. Subsequently analyzing the fluorescence patterns with the help of a deep neural network, the intensity and phase of the light-field vectorial components are fully reconstructed with nanometer resolution. The experimental results are in agreement with theoretical calculations. It demonstrates that our method can help to study light–matter interaction at nanoscale and extend the application of vector light fields in research on nanophotonics.
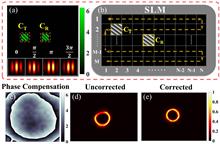
In the femtosecond two-photon polymerization (2PP) experimental system, optical aberrations degrade the fabrication quality. To solve this issue, a multichannel interferometric wavefront sensing technique is adopted in the adaptive laser processing system with a single phase-only spatial light modulator. 2PP fabrications using corrected high-order Bessel beams with the above solution have been conducted, and high-quality microstructure arrays of microtubes with 20 µm diameter have been rapidly manufactured. The effectiveness of the proposed scheme is demonstrated by comparing the beam intensity distributions and 2PP results before and after aberration corrections.
Overlay (OVL) for patterns placed at two different layers during microchip production is a key parameter that controls the manufacturing process. The tolerance of OVL metrology for the latest microchip needs to be at nanometer scale. This paper discusses the influence on the accuracy and sensitivity of diffraction-based overlay (DBO) after developing inspection and after etching inspection by the asymmetrical deformation of the OVL mark induced by chemical mechanical polishing or etching. We show that the accuracy and sensitivity of DBO metrology can be significantly improved by matching the measuring light wavelength to the thickness between layers and by collecting high-order diffraction signals, promising a solution for future OVL metrology equipment.
We have successfully generated a 1.3/1.4 µm random fiber laser (RFL) using bismuth (Bi)-doped phosphosilicate fiber. The Bi-doped RFL has shown excellent long-term operational stability with a standard deviation of approximately 0.34% over 1 h at a maximum output power of 549.30 mW, with a slope efficiency of approximately 29.21%. The Bi-doped phosphosilicate fiber offers an emission spectrum ranging from 1.28 to 1.57 µm, indicating that it can be tuned within this band. Here, we demonstrated a wavelength-tuning fiber laser with a wavelength of 1.3/1.4 µm, achieved through the using of a fiber Bragg grating or a tunable filter. Compared to traditional laser sources, the RFL reduces the speckle contrast of images by 11.16%. Due to its high stability, compact size, and high efficiency, this RFL is highly promising for use in biomedical imaging, communication, and sensor applications.
We demonstrate spectral-furcated vector solitons in normal-dispersion fiber lasers comprising a section of polarization-maintaining fiber. The spectrum of each orthogonal-polarized component is confined by the birefringence-related phase-matching principle, and the bicorn spectral structure corresponds to the zero-order sidebands of two vector modes. Due to the Hopf bifurcation effect, the vector soliton evolves into a breathing state at the higher pump level, accompanied by an extra set of sub-sidebands that continuously exchange energy with the zero-order sidebands. Simulation results fully reproduce experimental observations of the spectral furcation and soliton breathing, offering comprehensive insights into the pulse-shaping mechanism of the birefringence-managed soliton.
The terahertz photonics technique has bright application prospects in future sixth-generation (6G) broadband communication. In this study, we have experimentally demonstrated a photonics-assisted record-breaking net bit rate of 417 Gbit/s per wavelength signals delivery in a fiber-wireless converged communication system supported by advanced digital-signal-processing (DSP) algorithms and a polarization multiplexing-based multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) scheme. In the experiment, up to 60 GBaud (480 Gbit/s) polarization-division-multiplexing 16-ary quadrature-amplitude-modulation (PDM-16QAM) signals are transmitted over 20 km fibers and 3 m wireless 2×2 MIMO links at 318 GHz with the bit error rate (BER) under 1.56×10-2. It is the first demonstration to our knowledge of signals delivery exceeding 400 Gbit/s per wavelength in a photonics-assisted fiber-wireless converged 2×2 MIMO communication system.
All-dielectric metasurfaces are usually limited because of their static functionality and small scale. In this paper, we use an easy nanofabrication technique to fabricate all-dielectric metasurfaces with the advantages of having dynamic tunability and a large area. Using an anodized aluminum oxide (AAO) template as an evaporation mask, a large-area metasurface embedded in polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) (>2 cm2) is fabricated. The metasurface exhibits remarkable electric dipole (ED) and magnetic dipole (MD) resonances. Based on the solvent-swelling effect of PDMS in 20% toluene, the ED/MD resonance peak shifts dynamically ∼40 nm to red. So far, to the best of our knowledge, a large-area metasurface embedded in PDMS and achieved by using the AAO template method has not appeared.
The self-focusing phenomenon of partially coherent beams (PCBs) was simulated using the complex screen method combined with the split-step Fourier method to solve the nonlinear Schrödinger equation. Considering the propagation of Gaussian Schell-model beams in a nonlinear medium as an example, the suppression effects of intensity, propagation distance, and spatial coherence on small-scale self-focusing were demonstrated. Simulations of overall and small-scale self-focusing using this method were compared with the existing literature to demonstrate the validity of the method. This method can numerically analyze the degree of self-focusing in PCBs and advance the study of their nonlinearity.
Scintillators are the vital component in X-ray perspective image technology that is applied in medical imaging, industrial nondestructive testing, and safety testing. But the high cost and small size of single-crystal commercialized scintillators limit their practical application. Here, a series of Tb3+-doped borosilicate glass (BSG) scintillators with big production size, low cost, and high spatial resolution are designed and fabricated. The structural, photoluminescent, and scintillant properties are systematically investigated. Benefiting from excellent transmittance (87% at 600 nm), high interquantum efficiency (60.7%), and high X-ray excited luminescence (217% of Bi4Ge3O12), the optimal sample shows superhigh spatial resolution (exceeding 20 lp/mm). This research suggests that Tb3+-doped BSG scintillators have potential applications in the static X-ray imaging field.
We numerically demonstrate that the tight focusing of Bessel beams can generate focal fields with an ultra-long depth of focus (DOF). The ultra-long focal field can be controlled by appropriately regulating the order of the Bessel function and the polarization. An optical needle and an optical dark channel with nearly 100λ DOF are generated. The optical needle has a DOF of ∼104.9λ and a super-diffraction-limited focal spot with the size of 0.19λ2. The dark channel has a full-width at half-maximum of ∼0.346λ and a DOF of ∼103.8λ. Furthermore, the oscillating focal field with an ultra-long DOF can be also generated by merely changing the order of the input Bessel beam. Our results are expected to contribute to potential applications in optical tweezers, atom guidance and capture, and laser processing.
Multimode photonic quantum memory could enhance the information processing speed in a quantum repeater-based quantum network. A large obstacle that impedes the storage of the spatial multimode in a hot atomic ensemble is atomic diffusion, which severely disturbs the structure of the retrieved light field. In this paper, we demonstrate that the elegant Ince-Gaussian (eIG) mode possesses the ability to resist such diffusion. Our experimental results show that the overall structure of the eIG modes under different parameters maintains well after microseconds of storage. In contrast, the standard IG modes under the same circumstance are disrupted and become unrecognizable. Our findings could promote the construction of quantum networks based on room-temperature atoms.
A cylindrical Öffner stretcher based on ternary reflector (COSTER) is proposed and analyzed. Compared with the traditional Öffner stretcher, the COSTER has no off-axis aberration in the multipass configuration, and the output laser of COSTER has lower spectral phase noise and higher temporal contrast in the far field. The COSTER is quite suitable to be used in multi-petawatt laser facilities, and it might be the preferred stretcher configuration for ultrafast and ultra-intense lasers.