View fulltext
View fulltext
The geometric shapes of the retro-reflectors are (a) an isosceles triangle, (b) a flat triangle, (c), (d) irregular surfaces, and (e) an array of isosceles triangles.
An automated superpixels identification/mosaicking method is presented for the analysis of cone photoreceptor cells with the use of adaptive optics scanning laser ophthalmoscope (AO-SLO) images. This is an image oversegmentation method used for the identification and mosaicking of cone photoreceptor cells in AO-SLO images. It includes image denoising, estimation of the cone photoreceptor cell number, superpixels segmentation, merging of superpixels, and final identification and mosaicking processing steps. The effectiveness of the presented method was confirmed based on its comparison with a manual method in terms of precision, recall, and F1-score of 77.3%, 95.2%, and 85.3%, respectively.
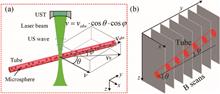
The previous methods to measure flow speed by photoacoustic microscopy solely focused on either the transverse or the axial flow component, which did not reflect absolute flow speed. Here, we present absolute flow speed maps by combining Doppler bandwidth broadening with volumetric photoacoustic microscopy. Photoacoustic Doppler bandwidth broadening and photoacoustic tomographic images were applied to measure the transverse flow component and the Doppler angle, respectively. Phantom experiments quantitatively demonstrated that ranges of 55° to 90° Doppler angle and 0.5 to 10 mm/s flow speed can be measured. This tomography-assisted method provides the foundation for further measurement in vivo.
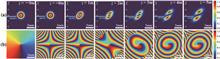
We propose a new kind of optical vortex called the Hermite–Gaussian-like optical vortex (HGOV) inspired by the cross phase (CP). Theoretically, we investigate how the CP is decoupled from the phase of a cylindrical lens. We also investigate the propagation characteristics of an HGOV, which has a Hermite–Gaussian-like intensity distribution but still retains the orbital angular momentum. Furthermore, we derive the Fresnel diffraction integral of an HGOV and study the purity at infinity. Besides, we show a novel function of the self-measurement of the HGOV. Finally, we show that we can change the relative positions of singularities and the direction of an HGOV precisely, which facilitates applications in optical micro-manipulation.
We proposed a hybrid tilted fiber gratings (polarizing grating and tilted fiber Bragg grating)-based surface plasmon resonance (SPR) sensor. The hybrid tilted fiber grating, consisting of a polarizing grating and tilted fiber Bragg grating (TFBG), is fabricated in a single-mode fiber in series by using a UV-inscription technique, in which the TFBG could generate a dense cladding mode resonance to excite SPR and the polarizing grating could filter out the S-polarization cladding mode of the TFBG. Such proposed hybrid tilted fiber gratings could greatly simplify the interrogation system of the TFBG-based SPR sensor. The experiment results showed that the hybrid tilted fiber gratings-based SPR sensor has the refractive index sensitivity of 522.8 nm/RIU. Finally, by using the proposed sensor, we have achieved the hemoglobin concentration detection within a sensing range from 0.1 mg/mL to 1.0 mg/mL and the sensitivity of 8.144 nm/(mg/mL).
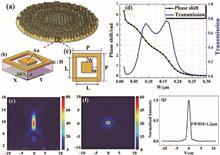
We present a kind of large effective aperture metalens based on an optical sparse aperture (OSA) system. Each subaperture of the system is a metalens, which is comprised of just a thin Au film with patterned subwavelength rectangular annular arrays on a SiO2 substrate and has a numerical aperture of 0.46 with a diameter of 21.6 μm. Ring6 design was selected to enlarge the effective aperture and enhance the spatial resolution. Compared with the absent mid-frequency and high-frequency modulation transfer function of individual metalens, Ring6 can offer a full-frequency band and show a better restored image quality by using Tikhonov regularization.
This Letter describes an approach to encode complex-amplitude light waves with spatiotemporal double-phase holograms (DPHs) for overcoming the limit of the space-bandwidth product (SBP) delivered by existing methods. To construct DPHs, two spatially macro-pixel encoded phase components are employed in the SBP-preserved resampling of complex holograms. Four generated sub-DPHs are displayed sequentially in time for high-quality holographic image reconstruction without reducing the image size or discarding any image terms when the DPHs are interweaved. The reconstructed holographic images contain more details and less speckle noise, with their signal-to-noise ratio and structure similarity index being improved by 14.64% and 78.79%, respectively.
We report on laser diode (LD) pumped passively Q-switched Yb,Gd:SrF2 lasers with high single-pulse energy for the first time, to the best of our knowledge. In addition, a stable Q-switched laser based on a Cr4+:Y3Al5O12 saturable absorber was demonstrated. The maximum output power of the Q-switched laser obtained was 495 mW, with a pulse width and a pulse repetition rate of 233 ns and 1.238 kHz, respectively. The corresponding single-pulse energy and the peak power were as high as 400 μJ and 1.714 kW. The laser was operated under a transverse electromagnetic mode, and the beam quality was near-diffraction-limited.
A 400 nm femtosecond laser was used to ablate the surface of a high-pressure and high-temperature diamond, and subwavelength surface micro structures with a period of 100 nm were achieved. A variety of micro-nano composite surface structures were prepared by changing the polarization direction and laser scanning direction. By dynamically adjusting the laser polarization and the laser scanning tracks, a maskless direct writing fabrication of micro-nano complex structures was realized. The micro-nano patterning on an ultra-hard and super-stabile diamond provides a new idea for the preparation of friction reducing surfaces, nano imprint transfer templates, surface enhanced Raman scattering test substrates, and micro-nano optical structures.
Coherent beam combining of 60 fiber lasers by using the stochastic parallel gradient descent algorithm has been demonstrated. The functions of pinhole(s) on the power distributions in the far-field have been systematically simulated on both in-phase and out-of-phase modes. Only one photoelectric detector was used to detect the combined power in the far-field central lobe of the in-phase mode state. When the phase controller was in a closed loop, the contrast of the far-field intensity pattern was as high as ~97% with residual phase error of ~λ/30, and ~34.7% of the total power was contained in the central lobe.
A novel way to design arbitrarily shaped retro-reflectors by optics surface transformation is proposed. The entire design process consists of filling an optic-null medium between the input and output surfaces of the retro-reflector, on which the points have 180 deg reverse corresponding relations. The retro-reflector can be designed to be very thin (a planar structure) with high efficiency. The effective working angles of our retro-reflector are very large (from -80 deg to +80 deg), which can, in principle, be further extended. Layered metal plates and zero refractive index materials are designed to realize the proposed retro-reflector for a TM polarized beam.
In this Letter, a low-frequency acoustic sensor based on an extrinsic Fabry–Pérot (FP) interferometer with a silicon nitride (Si3N4) membrane is demonstrated. Using micromachining techniques, the 800 nm thick Si3N4 membrane is deposited on an 8 mm × 8 mm × 400 μm silicon (Si) substrate. All the assembly procedures of the sensor are focused on the substrate to avoid any damage to the membrane itself, compared to general membrane transfer methods. The frequency response of the proposed sensor is discussed theoretically and experimentally demonstrated. The sensor exhibits an excellent flat response to the tested acoustic frequency range of 1 Hz to 250 Hz. The phase sensitivity is around ?152 dB re 1 rad/μPa with sensitivity fluctuation less than 0.8 dB. The frequency response characteristic shows a promising potential of the sensor in low-frequency acoustic signal sensing applications.
This Letter presents a new type of optical fiber probe used to detect temperature, whose structure is very simple. The optical fiber probe is filled with cholesteric liquid crystals (CLCs) whose reflected light varies with temperature. The experimental results show that the proposed sensor can achieve a temperature sensitivity of 5.64 nm/°C in the temperature range of 18–40°C. The sensor has the advantages of simple structure, low cost, and easy mass manufacture. Its size is very tiny (the tapered structure, 125 μm in maximum diameter and <300 μm in length) and it is easy to integrate and measure. Meantime, the tapered structure of the probe is also ideal for measuring small samples such as cells and microfluidic channels, which will be a promising candidate for monitoring temperature fluctuations in small spaces.
We propose a novel modified frequency-shifted interferometer, where a Mach–Zehnder interferometer is added in order to obtain wavelength information. We use the Hilbert transform to extract the wavelength information from the phase of the interference pattern and construct the relationship between phase and wavelength. The laser wavelength measurement experiment is used to verify the compound interferometer. Experimental results demonstrated that our method could obtain the wavelength from the phase, which is of great significance for demodulation of the fiber Bragg grating based on a frequency-shifted interferometer.
All-optical magnetization switching with features of low-power consumption and high writing speed is a promising road map to satisfy the demand for volume data storage. To promote denser and faster magnetic recording technologies, herein, all-optical helicity-dependent switching (AO-HDS) in multi-layer magnetic recording is proposed based on the chromatic aberration of an optical lens (Thorlabs’s N-BK7 plano-convex uncoated lens). The power of the incident beams and the thickness of the multi-layer magnetic recording film are designed carefully. Besides, the uniformity of this multi-layer magnetic recording is optimized. At last, a prototype system of information multiplexing based on this multi-layer magnetic recording technology is constructed as well. Flexible and controllable magnetization reversals in different layers are also demonstrated by tuning the wavelength and helicity of working beams. We believe that such a prototype system can pave the way for increasing the storage density in an effective and low-cost mode.
Optical orbital angular momentum (OAM) is a special property of photons and has evoked research onto the light–matter interaction in both classical and quantum regimes. In classical optics, OAM is related to an optical vortex with a helical phase structure. In quantum optics, photons with a twisted or helical phase structure will carry a quantized OAM. To our knowledge, however, so far, no experiment has demonstrated the fundamental property of the OAM at the single-photon level. In this Letter, we have demonstrated the average photon trajectories of twisted photons in a double-slit interference. We have experimentally captured the double-slit interference process of twisted photons by a time-gated intensified charge-coupled device camera, which is trigged by a heralded detection. Our work provides new perspectives for understanding the micro-behaviors of twisted particles and enables new applications in imaging and sensing.
Nonlocal correlations observed from entangled quantum particles imply the existence of intrinsic randomness. Normally, locally projective measurements performed on a two-qubit entangled state can only certify one-bit randomness at most, while non-projective measurement can certify more randomness with the same quantum resources. In this Letter, we carry out an experimental investigation on quantum randomness certification through a symmetric informationally complete positive operator-valued measurement, which in principle can certify the maximum randomness through an entangled qubit. We observe the quantum nonlocal correlations that are close to the theoretical values. In the future, this work can provide a valuable reference for the research on the limit of randomness certification.
Ultrathin Ge films with thickness of about 15 nm at different deposition temperatures were prepared by electron beam evaporation. Spectral measurement results showed that as the deposition temperature increased from 100°C to 300°C, the transmittance of the films in the wavelength range from 350 nm to 2100 nm decreased. After annealing in air at 500°C, the transmittance significantly increased and approached that of uncoated fused quartz. Based on the Tauc plot method and Mott–Davis–Paracrystalline model, the optical band gap of Ge films was calculated and interpreted. The difference in optical band gap reveals that the deposition temperature has an effect on the optical band gap before annealing, while having little effect on the optical band gap after annealing. Furthermore, due to oxidation of Ge films, the optical band gap was significantly increased to ~5.7 eV after annealing.
High-order harmonic generation originated from zigzag graphene nanoribbons (ZGNRs) induced by intense laser pulses is investigated theoretically. During the interaction between the intense mid-infrared laser and the ZGNR, we find that localized edge states mainly contribute to the generation of the low-order harmonics, while cutoff harmonics result from the other confined states. Our result shows that the edge-state effect of ZGNR with narrow width can enhance the conversion efficiency of low-order harmonics, rather than the higher-order harmonics extended to the cutoff region.