Editor(s): Ting-Chung Poon, Changhe Zhou, Partha Banerjee, Hoonjong Kang, and Pascal Picart
Year: 2016
Status: Published
This feature issue is the second Joint Applied Optics (AO) and Chinese Optics Letters (COL) Feature Issue on digital holography and three-dimensional (3D) imaging. The first installment of such a joint feature issue was in 2011. In the present feature issue, there are a total of 24 papers in AO and 9 papers in COL. This feature issue contains a representative selection of topics that were presented at the OSA Topical Meeting on Digital Holography and 3D Imaging (DH), held in Shanghai, China, May 2015. The DH Topical Meeting is the world’s premier forum for science, technology, and applications of the digital holograph, and three-dimensional imaging and display methods. The topic areas include interferometry, phase microscopy, novel holographic processes, 3D and novel displays, integral imaging, computer-generated holograms, compressive holography, full-field tomography, and holography with various light sources, including coherent to incoherent and x-ray to terahertz waves. This is a highly interdisciplinary forum with applications in biomedicine, biophotonics, nanomaterials, nanophotonics, and scientific and industrial metrologies. All submitted papers, including invited papers, have undergone peer review. We hope these articles will present state-of-the-art technological developments that are currently under way and stimulate further novel applications of digital holography and 3D imaging. The next DH meeting is scheduled to be held on July 25–28, 2016, at Heidelberg, Germany. DH 2017 will take place in Korea.
One of the most fascinating principles in quantum mechanics must be Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle, which can be briefly stated as follows: every physical observation cannot be precisely determined without some degree of error or uncertainty. And it is by no means can one use the principle within the limit of certainty region, as will be shown in this Letter. Two of the most important pillars in modern physics must be Einstein’s relativity theory and Schr dinger’s contribution to quantum mechanics. Yet, there is a profound connection between these discoveries by means of the uncertainty relationship, in which we shown that the observation of a high-speed object is conceivable if the speed of the observer keeps up with object’s speed.
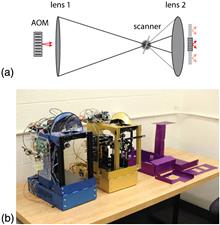
This paper presents progress on the characterization of guided-wave light modulators for use in a low-cost holographic video monitor based on the MIT scanned-aperture architecture. A custom-built characterization apparatus was used to study device bandwidth, RGB operation, and linearity in an effort to identify optimal parameters for high bandwidth, GPU-driven, full-color holographic display.
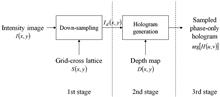
Past research has demonstrated that a phase-only hologram can be obtained by down-sampling the intensity image of the object scene prior to the generation of the hologram. In this Letter, we extend the method to the generation of binary phase-only holograms. A hologram derived with our proposed method is referred to as a binary-sampled phase-only hologram (BSPOH). Being different from the parent scheme, we have adopted an off-axis configuration in the generation of the BSPOH to avoid the quantization noise, the zeroth-order light, and the conjugate lights. An experimental evaluation reveals that the reconstructed image of the BSPOH is of good quality, and only contains slight amount of noise.
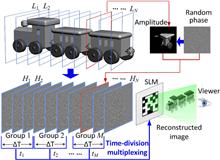
A time-division multiplexing method for computer-generated holograms (CGHs) is proposed to solve the problem of the limited space-bandwidth product. A three-dimensional (3-D) scene is divided into multiple layers at different depths. The CGH corresponding to each layer is calculated by an angular-spectrum algorithm that is effective at a wide range of propagation distances. All of the CGHs are combined into several group-CGHs. These group-CGHs are sequentially uploaded onto one spatial light modulator at a high frame rate. The space-bandwidth product can be benefited by the time-division processing of the CGHs. The proposed method provides a new approach to achieve high quality 3-D display with a fast and accurate CGH computation.
Anisotropic edge enhancement is simulated using a spiral phase plate (SPP) in optical scanning holography (OSH). We propose to use a delta function and an SPP as the pupil functions to realize anisotropic edge enhancement. The interference of these two pupils is used to two-dimensionally scan an object to record its edge-only information. This is done in three ways: first, by shifting the SPP, second, by using two offset SPPs of same charge, and finally, by using two oppositely charged SPPs. Our computer simulations show the capability of selectively enhancing the edges of a given object.
A novel method for a full-parallax three-dimensional (3D) holographic display by means of a lens array and a holographic functional screen is proposed. The process of acquisition, coding, restoration, and display is described in detail. It provides an efficient way to transfer the two-dimensional redundant information for human vision to the identifiable 3D display for human eyes. A holo-video system based on a commercial 4 K flat-panel displayer is demonstrated as the result.
We present a polarization-multiplexing off-axis Mach–Zehnder configuration for dual-wavelength digital holography to achieve phase imaging in one shot. In this configuration, two orthogonal linear-polarized waves with respect to different wavelengths are employed to record respective holograms synchronously, where two recording waves transmit independently through the same optical paths of the interferometer, and by installing two analyzer polarizers each to filter off either of two wavelengths, and filtering through the other, the holograms are acquired, respectively, by a pair of CCDs at the same time. The unwrapped phase image of a grating with groove depth 7.1 μm is retrieved via spatial frequency filtering.
A polarization holographic grating, which integrates the functions of a grating and a wave plate and is called a diffractive wave plate, is recorded by two beams (left and right circularly polarized) of a 532 nm laser in an azo polymer with a liquid-crystal structure. The polarization conversion characteristics of the diffractive wave plates are investigated with a detecting light of 650 nm by metering the polarization state of first-order diffracted light. It is confirmed that the diffractive wave plates convert the incident linear polarization into circular polarization for a linearly polarized probe laser and reverse the sense of rotation of the circular polarization when the detecting light is circularly polarized light.
Because the bottom of the cavity has the shadow and occlusion, the angle between the projection system and imaging system is limited. So the traditional fringe projection technique based on the principle of optical triangulation is inapplicable. This Letter presents a 3D shape measurement method of using the light tube for the cavity. The method can measure an object from two opposite views at the same time, which means it will obtain two different groups of 3D data for the same object in a single measurement. The experimental results show the feasibility and validity of the 3D shape measurement method.