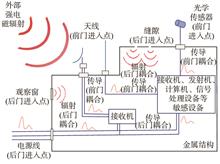
In view of various threats of strong electromagnetic environment to ship information equipment under electromagnetic space countermeasures and the requirement of electromagnetic protection, the mechanism of strong electromagnetic environment effect and basic protection principle of ship electronic equipment are prospected. The principle and development of frequency selective surface, energy selective surface and new electromagnetic shielding materials used to reduce the coupling of radiation field to ship electronic system are described; the principle and development of RF front-end protection technology based on gas discharge tube, semiconductor limiter, RF high power limiter technology based PIN diode and electromagnetic pulse protection technology based on plasma for suppressing the strong electromagnetic pulse transmission on the "circuit" are also introduced. This paper analyzes the applicability and advantages of different protection technologies in the design of ship equipment for strong electromagnetic pulse, and forecasts the future development trends of strong electromagnetic environment protection technology for ship equipment, provides support for the design of strong electromagnetic environment protection for ship equipment.
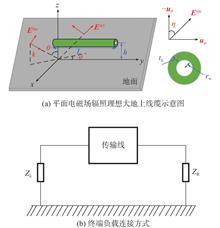
ObjectivesUnder the condition of considering the influence of the sea surface, the relationships between the induced current of a whip antenna on a large ship under the incidence of high-altitude nuclear electromagnetic pulse (HEMP) and the incident angle of the pulse and antenna position are studied.Methods The half-space finite different time domain (FDTD) method is used to consider the influence of the sea surface; the thin wire algorithm is used to solve the problems of huge computational grid and low efficiency caused by the fine structure; the lumped element FDTD method is used to consider the influence of the load behind the antenna on the induced current; and a parallel algorithm based on MPI is used to speed up the calculation.ResultsThe results show that the induced current on the whip antenna of an aircraft carrier model is related to the antenna position and incident angle in the HEMP incident case. The peak value of the induced current at the antenna port is 5.6 A in typical cases.ConclusionsThe analysis shows that the magnitude of the induced current at the antenna port mainly depends on the antenna position and has little relationship with the incident angle of the pulse. The research provides an algorithm basis for the calculation and analysis of induced current in the case of the incident pulse electromagnetic wave of large ships, and the research results provide a theoretical support for the analysis of ship electromagnetic compatibility problems.
ObjectiveThe Baum-Liu-Tesche (BLT) equation is an important calculation method for field-transmission cable coupling which is widely used in the domain of electromagnetic coupling quantitative analysis. The classical BLT equation ignores the distortion effects of the cable's insulation layer on the incident field, leading to large errors in coupling calculation under specific incident and polarization directions. MethodIn response to this issue, a frequency domain modified BLT method is introduced into the time domain to study the calculation method of the load voltage and current response in a single cable excited by a high altitude electromagnetic pulse (HEMP). The correctness of the model is then verified through a comparison with a full wave algorithm (finite integer technique). On this foundation, the characteristics of the cable structure (height, diameter, insulation parameters, etc.) and incident field (incident direction, polarization direction, etc.) applicable to the modified method are analyzed. ResultsUnder HEMP excitation, based on the full wave simulation results, the prediction error of the classical BLT model can be more than doubled, while the accuracy of the BLT model with the insulation layer coefficient is significantly improved. ConclusionThis study verifies the accuracy of the modified BLT model in analyzing the field-transmission cable coupling problem in the time domain, and puts forward the applicability criterion of the modified BLT model which helps to clarify the coupling mechanism between HEMP and actual complex cables.
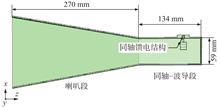
ObjectiveThis paper aims to study the coupling response law of an electromagnetic pulse acting on a pyramid horn antenna under the condition of the random distribution of incident parameters. Methods First, a statistical analysis model of the electromagnetic pulse response of the horn antenna is established on the basis of a computer simulation technology (CST) and Matlab co-simulation. A simulation model of the antenna electromagnetic impulse response is then established by CST, and the rationality of the model is verified by the voltage standing wave ratio (VSWR) and gain curve. The impedance characteristics of the radio frequency port of the communication system under different states such as transmitting and receiving are considered. The coupling response indexes of antenna ports such as open circuit voltage (OCV), short circuit current (SCC) and load current are obtained under high-altitude electromagnetic pulse (HEMP) irradiation with a peak field strength of 50 kV/m. Finally, the azimuth, elevation and polarization angles are set in the spherical coordinate system to obey the uniform distribution, and Matlab is used to fit the main signal indicators such as the peak value and waveform energy of the antenna load response waveform. ResultsThe results show that the probability distribution of the main signal indicators is mostly convex. Taking the waveform peak value as an example, there is a 90% probability that the peak value of the response waveform is less than 0.13A, which is only 16.2% of the maximum peak value of 0.8A; that is, except in the specific electromagnetic pulse incident range, the signal indicators of the pyramid horn antenna response waveform are kept at a low level in most cases.ConclusionThe results of this study lay the foundation for the electromagnetic pulse vulnerability analysis of communication systems.
ObjectivesElectromagnetic pulse can seriously affect and even destroy naval shipborne electronic information systems, weapons, equipment and so on. Due to the complexity of the antenna port load circuit, it is necessary to formulate a numerical method which can easily obtain the antenna load current.MethodsThe induced current of the terminal is obtained on the basis of the finite-difference time-domain (FDTD) and Holland model. According to the Thévenin equivalent circuit, the conductor is equivalent to the voltage source to realize decoupling between the conductor and load end, and the load circuit is solved using Simulink software.ResultsCompared with the traditional terminal model, this method is simple and feasible for high-order circuit processing. The effectiveness of the model is verified using non-linear elements and parallel capacitors and resistors as the load respectively. The results show that the calculation results of this method are consistent with those of the traditional methods. Finally, the antenna of the end-connected protector is calculated. The results show that the lead inductance caused by the installation of the protector is an important factor affecting the protection performance.ConclusionsThe method proposed in this paper can greatly reduce the simulation complexity of the coupling current of an antenna with a complex load, giving it useful reference value for the field of ship electromagnetic pulse protection design.
ObjectiveIn order to improve lightning protection measures for ships, it is vital to evaluate the lightning strike risk and lightning rod protection effect. MethodsThis paper proposes a leader development model that can simulate the natural leader progression, and introduces a ship model to analyze its lightning attachment process. Analyses are made of the electric field distribution on the surface of the ship when the downward leader is approaching at different areas, of the probability of the ship being struck by lightning at each location, and of the protection effect of the lightning rod on the ship. Finally, the calculation results are verified by a ship scaled-down model discharge test carried out in the laboratory.ResultsThe lightning strike attachment point is mainly concentrated in the relatively protruding position of the structure on the ship, and the lightning rod has a positive effect on the potential distribution on the surface of the ship. However, the final lightning strike point is determined by the development area of the downward leader.ConclusionsCombining simulation analysis with the test results, the weak points of direct lightning protection on the surface of the ship are obtained. It is found that the location of the final lightning strike attachment point of the ship is closely related to the connection process of the by-directional leaders, and that the proposed leader progression model can provide accurate predictions of lightning strike points.
ObjectiveIn order to set or improve the lightning protection measures of ships, it is necessary to evaluate the strike risk of critical equipment and the protection effect of the lightning rod.MethodsIn this paper, a lightning leader fractal model is constructed and applied to a simulation study on the lightning attachment process of a ship. The configuration method of the simulation boundary of the model and the quantitative evaluation method of lightning strike risk are improved, and a quantitative study on the influence of different factors on the lightning strike risk of the ship is performed.ResultsThe simulation results show that the protection probability of the lightning rod in the middle of the ship is more than 75% under the basic configuration. The bow, stern and antenna far away from the lightning rod have a relatively large risk of circling strike. The lightning strike probability of the shipboard antenna is lower if the lightning initiation position is closer to the lightning rod, the lightning current is greater or the lightning rod is higher.Conclusions The lightning leader fractal model constructed in this paper can be used to investigate the weak links of direct lightning protection on the surface of ships, which can provide useful references for the direct lightning protection design of ships.
[Objective] This paper carries out an experimental study on the coupling response characteristics of the internal cables of a metal mast when struck by lightning. [Method] A lightning induction coupling test platform is built for the cable system inside the mast. The induced voltages of the coaxial cables, two-core single shielded cables and multi-core double shielded cables are measured under four kinds of termination load characteristics (open circuit at both ends of core wire; end of core wire near to the ground connected to the load; end of core wire far from the ground connected to the load; and both ends of core wire connected to the load). From the perspective of time domain and frequency domain, an analysis is made of the influence of load characteristics on the induced voltage and shielding effects. [Results] The induced voltage of the cable reaches its maximum value when the far ground terminal is grounded by the load. When the near ground terminal is grounded by the load, the main frequency band of the induced voltage frequency response exceeds the lightning current, whereas they are similar under other load characteristics. Grounding the inner shielding layer can reduce the peak value of the induced voltage, but does not affect the main frequency band of the frequency response. The voltage peak value is most significantly reduced when both ends of the core wire are open-circuited or when the end of the core wire far from the ground is connected to the load (approximately 59.3% and 77.2% of the value when the inner shielding layer is ungrounded). In addition, the induced voltage peaks of the three types of cables exhibit considerable differences. However, the rise time and half-peak time of the induced voltage for each cable show insignificant differences. [Conclusion] This study reveals the influence of terminal load characteristics on cable coupling induced voltage when lightning strikes the metal mast of a ship, as well as providing basic data support for the subsequent calculation of the coupling effect.
ObjectiveLightning electromagnetic effects and coupling characteristics are an important analysis basis for the lightning protection design of the electronic and electrical equipment of helicopters.MethodsRP5416 standards, in the CST cable studio based on TLM, the influence factors and rules of the electromagnetic environment and cable coupling level of carrier-borne aircraft under typical lightning strike mode are studied.ResultsThe results show that the establishment of a lightning electromagnetic field is a rapidly changing process which presents complex changes in terms of time, space and structure. The aircraft lightning coupling mechanism is the interaction between the resistive coupling of the lightning flow redistribution and the resonance coupling of the airframe gap, and is strongly dependent on the frequency. The cable induction level is affected by the aircraft skin resistance, lightning current waveform parameters, cable shield impedance and other factors.ConclusionsThis study reveals the mechanism of lightning electromagnetic coupling and the related influence law of the lightning electromagnetic induction of the cable, providing a basis and support for aircraft cable laying and lightning electromagnetic environment protection.
ObjectivesThe equivalent construction of test environment signals according to the standards or test specifications is the premise of conducting high confidence electromagnetic environment tests. How to quantitatively evaluate the equivalence between the constructed environment signal and the standard environment signal is the key to guiding the equivalent construction of test environment signals.Methods A sequence segmentation method integrating important points is proposed to quantitatively evaluate the equivalence of strong electromagnetic environmental effect test signals by integrating two indicators: signal amplitude difference and signal similarity. The stability and feasibility of this evaluation method are verified by a typical strong electromagnetic pulse environment signal construction example.ResultsThe results indicate that the proposed method preserves the local variation characteristics of the signal to be evaluated and improves the accuracy of the evaluation results. We also comprehensively consider the two-dimensional similarity evaluation of signal distance and direction, which compensates for potential defects caused by a single evaluation indicator and ensures the comprehensiveness of the evaluation results.ConclusionsThe proposed evaluation method has the characteristics of simple calculation, strong practicality and intuitive quantification of evaluation results, giving it guiding significance for the realistic construction of experimental environments.
Objective To solve the difficulty of obtaining a radar cross section (RCS) using traditional simulation and measurement methods under high frequency, this study proposes a hybrid method which combines bootstrap aggregation (Bagging) and spectral mixture covariance function-based Gaussian process regression (GPR) model to predict the RCS of ships in the high frequency band efficiently and accurately according to the data in the low frequency band.MethodsFirst, according to the monostatic RCS data of ships in the low frequency band, the training subset is obtained by resampling. The spectral mixture covariance function-based GPR model is then used to extrapolate the RCS data of each subset in the frequency domain. Finally, the extrapolation results of each subset are mixed by the Bagging method to further improve the extrapolation accuracy and robustness of GPR. The proposed method is then tested on the simulation data and measured data respectively. ResultsThe predicted value of the Bagging-GPR hybrid method is basically consistent with the simulated value and measured value, and the root mean square error is very small.ConclusionsThe Bagging-GPR hybrid method has high RCS extrapolation accuracy and good robustness in the frequency domain, providing a new technical means for quickly obtaining the high-frequency RCS characteristics of targets.
Objective When calculating the electromagnetic scattering characteristics of curved targets using the shooting and bouncing ray (SBR) method, there is a large error in the calculation of the wavefront of the ray tube and ray tracing if the surface is discretized using a planar mesh, resulting in the low confidence level of the simulation results. As such, a modified algorithm is required. Methods In the modified method, the surface fitting technique is used to reshape the curvature information of the triangular meshed model, then the wavefront curvature of the ray tube is calculated on the basis of differential geometry, and the divergence factor (DF) is introduced to correct the amplitude of the ray tube. In addition, a new ray-tracing method is designed for the divergent ray tubes to realize oversampling on the target surface. ResultsThe numerical results show that the algorithm in this paper effectively improves the sampling accuracy of the ray tube and the accuracy of the simulation of the curved surface target. ConclusionThe DF correction is important for improving the accuracy of the SBR method in calculating the scattering characteristics of curved targets.
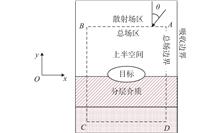
Objectives With the gradual development of marine resources, the number of vehicles operating under the sea surface has rapidly increased, and the problem of the electromagnetic detection of underwater complex targets such as underwater vehicles needs to be solved urgently.MethodsBased on the total-field scattered-field source finite-difference time-domain method (TSS-FDTD) and the method of field value conversion on the sea surface, the spatial distribution of scattering fields generated by the underwater antenna array irradiation of target underwater vehicles is analyzed. The field distributions in the regions near the underwater antenna array and complex target, in the seawater and above the sea surface are obtained by calculation, and the spatial scattering fields of the three groups with different relative positions of target and source are compared and analyzed.ResultsThrough comparison and analysis, the scattering fields of the three groups in the seawater environment are clearly different, and the existence of the underwater target can be determined by observing the scattering fields. While the scattering fields of the three groups above the sea surface show little difference, the existence of the underwater target can be still determined by observing the value and energy distribution of the scattering fields.ConclusionsThe results of this analysis can provide numerical references for detection radar with similar working frequency bands, and provide technical support for the fields of underwater vehicle detection, underwater rescue and sunken ship salvage.
ObjectiveThis study focuses on the turning ship Kelvin wake and its electromagnetic scattering characteristics in order to provide a theoretical foundation for the detection and recognition of nonlinear ship wakes. MethodsBased on the existing Kelvin wake geometric modeling and coordinate transformation methods, a turning ship Kelvin wake is obtained by the continuous changing of a ship's heading. The semi-deterministic facet scattering model (SDFSM) is then used to simulate the electromagnetic scattering characteristics of the arc-shaped Kelvin wake, and calculations and comparisons are performed of the distribution of the facet scattering coefficients of a straight Kelvin wake and arc-shaped Kelvin wake under different navigation speeds and headings. ResultsThe various kinds of wave components of a turning ship Kelvin wake are different from those of a straight Kelvin wake. At the same time, the vertical reception-vertical transmission (VV) scattering characteristics of a composite straight Kelvin wake and the counterparts of a composite turning ship Kelvin wake, which are shown in the figures of scattering coefficient distribution, exhibit significantly different features. ConclusionsThe brightness of the distribution of the Kelvin wake scattering coefficient and the wave vector directions of the different components of the wake are closely related to the relative relationship of radar direction. The results of this study can provide a theoretical basis for applications such as ship information perception, detection, recognition and stealth.
ObjectiveThe induced electromagnetic properties brought forth by disturbed seawater cutting the geomagnetic field can provide important information for non-acoustic detection technologies. In view of the complex and highly nonlinear interaction between the flow field and electromagnetic field of a high-speed submarine, it is necessary to deeply analyze the influence of the turbulence structure caused by natural cavitation on the induced electromagnetic field.MethodsFirst, a multi-physical field mathematical model of fluid-electromagnetic coupling is established on the basis of hydrodynamics and electromagnetics. Next, the intensity and range of near-field electromagnetic signatures in the cavitation evolution, and the time-frequency characteristics of the induced electric field under different cavitation numbers, are obtained through numerical simulation using Fluent software.ResultsThe simulation results demonstrate that the electromagnetic field shows obvious quasi-periodic unsteady fluctuation features due to the evolution of the cavitation morphology. The magnitudes of the induced electric field and magnetic field are 10-1 mV/m and 10-2 nT respectively, which are within the detection range of the most sophisticated sensors. Additionally, the cavitation number is highly correlated with the time-frequency characteristics of the induced electric field. When the cavitation number decreases from 0.4 to 0.2, the fluctuation intensity of the induced electric field is significantly enhanced, its main frequency decreases from 49.94 Hz to 34.19 Hz, and the low-frequency fluctuation component increases accordingly.ConclusionThe induced electromagnetic characteristics of submarines can be employed to guide the non-acoustic detection of underwater moving bodies, and the main frequency range of the induced electric field can provide references for the electromagnetic communication frequency selection of high-speed submarines.
ObjectiveIn order to accurately analyze the time-domain shielding effectiveness (TDSE) of metallic enclosures, a discontinuous Galerkin time domain (DGTD) method based on the local time-stepping (LTS) technique and parallel technique is proposed. MethodsThe full wave electromagnetic simulation of metallic enclosures is carried out by the DGTD method, and the TDSE is then calculated. LTS technology is used to increase the time step size, combined with parallel technology to greatly shorten the computing time. The influence of design parameters such as aperture size, enclosure thickness and array hole spacing on TDSE is then analyzed. ResultsThe numerical results show that the proposed method is correct and effective. ConclusionThe proposed method provides an effective tool for the simulation of electromagnetic shielding problems, and has certain guiding significance for the design of metallic enclosures.
In recent years, the route optimization of intelligent ships has attracted increasing attention in academic and industrial circles. Aiming at the problem of intelligent ship route optimization, this paper expounds upon the characteristics of various route design methods and route optimization algorithms. Combined with the latest research results over the past five years, the development status of intelligent ship route optimization technology at home and abroad is analyzed, and route optimization design methods are summarized into three kinds, namely those based on meteorological data, fuel consumption models and route/waypoint databases, and the technical connotations and applications are analyzed. The characteristics and shortcomings of the improved isochrony method, dynamic programming method, graph search algorithm, intelligent algorithm and artificial intelligence/machine learning algorithm are analyzed in depth, and the main problems existing in the application of various algorithms to intelligent ship route optimization are summarized. Finally, the development trend of intelligent ship route optimization is briefly predicted to provide ideas for future research in this field.
In recent years, the problem of low-frequency line spectrum noise generated by the flow-induced cavity oscillation of underwater vehicles has become increasingly prominent as it seriously threatens stealth performance. Focusing on practical engineering problems such as the flow-induced noise of underwater vehicles, this study analyzes the generation mechanism and characteristics of incompressible cavity flow-induced noise, and summarizes its flow characteristics and the development trend of noise control technology. First, the basic mechanisms and characteristics of cavity self-sustained oscillation are summarized, as well as research progress on the self-sustained oscillation feedback mechanism and three-dimensional instability characteristics. The generation mechanisms and basic characteristics of flow-induced cavity resonance are then introduced, including rectangular/cylindrical cavity acoustic modal resonance and flow-induced Helmholtz resonance. Second, the research progress of active and passive control methods is compared and analyzed. Finally, the future research direction of incompressible cavity flow is predicted. It is recommended to carry out research on the cavity self-sustaining oscillation feedback mechanism and three-dimensional instability, cavity flow-induced resonance mechanism and acoustic radiation characteristics, and incompressible cavity flow-induced noise control methods.
ObjectiveAs tip vortex cavitation (TVC) causes noise radiation and vibration, it is necessary to understand how to predict and control its development, and understand its mechanism in order to suppress it, especially in the field of ship propellers and other rotating machinery. MethodFocusing on an elliptical hydrofoil with an NACA 0012 cross-section, this study uses the Improved Delayed Detached Eddy Simulation (IDDES) turbulence modeling method and Schnerr-Sauer cavitation model to simulate TVC on the hydrofoil and analyze its behavioral characteristics under wet flow and cavitation flow conditions. After that, two active water injection methods, side injection and top injection, are introduced into the simulation to reduce and suppress cavitation inception respectively. ResultsTaking the cavity volume of the tip vortex as the criterion for cavitation suppression, compared with the condition without water injection, top injection can inhibit cavitation by 8.09%. Moreover, under the condition of side injection, the effect of the injecting flow on the cavitation is more obvious, reaching 10.47%. The results show that both top and side injection can effectively suppress TVC. ConclusionTop injection can change the flow direction and speed of the tip vortex incident flow, and increase the dissipation term of the turbulent kinetic energy; while in side injection, the energy it carries acts directly on the vortex structure of the hydrofoil, destroying the vortex and greatly suppressing the generation of cavitation.
ObjectivesThe paper aims to solves the limitations of the Goldstein body force method in a hydrodynamic simulation of a ducted propeller. MethodsAn analysis of the reason for the distortion of the duct hydrodynamic simulation is carried out based on the wing theory, and a correction method based on the mass flow and body force distribution model is proposed. The RANS method is then used to study the simulation accuracy of two kinds of improved body force method. ResultsThe results show that the average relative error of the total thrust coefficient of the two improved body force methods under open water conditions is about 5%. The average relative error of the resultant forward force of the two improved volume force methods behind the underwater vehicle are 1.8% and 11.6% respectively. ConclusionsThe simulation accuracy of a ducted propeller based on the improved body force method in open water and behind an underwater vehicle is greatly improved compared with the traditional method. The proposed method can accurately simulate the hydrodynamic performance of a ducted propeller, laying the foundation for the efficient dynamic maneuverability simulation of underwater vehicles.
ObjectivesIn order to improve ship propulsion performance and efficiency, and overcome such obstacles as numerous propeller parameters, complicated modeling, slow convergence of hydrodynamic numerical calculations and turbulent wake field effects, this paper proposes an efficient propeller optimization method.MethodsA parameterized propeller constructed with non-uniform rational B-spline based free form deformation (NFFD) technology is used as the output. The CFD numerical simulation is applied to predict its performance characteristics and the Gaussian approximate prediction model of the propeller performance is established based on the simulation data. The optimization model aims to improve efficiency and reduce the torque coefficient by using the second-generation non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm (NSGA-II) method to obtain the optimal solution.ResultsThe results show that under the uniform flow field and wake field behind the ship, the optimization results of the propeller have similar laws; that is, the blade width and thickness of the propeller show a decreasing trend, while the inclination angle shows an increasing trend. The flow velocity decreases in the wake field behind the ship, so the reduction in width and thickness and increase in inclination angle of the propeller blade are smaller than those in the uniform flow field. ConclusionThe method proposed in this paper can be used to achieve the more efficient optimization design of propellers under uniform flow fields and wake fields behind ships.
ObjectiveIn order to solve the problem of an underactuated ship responding slowly to heading changes during rudder roll stabilization (RRS) caused by fixed weight values in model predictive control (MPC), a RRS control method based on the finite time extended states observer (FTESO), fuzzy rules and robust predictive control is proposed. MethodsA fixed speed linear underactuated ship model is established for controller design. The FTESO is used to estimate the ship's motion states and external disturbances. By analyzing the conditions of the ship's course-keeping and heading change, the objective function weights under the two conditions and the fuzzy rules between the states and weights are designed respectively. Robust predictive control is used to solve the multi-objective cooperative control problem with constraints. The closed-loop stability of the proposed control method is then proven theoretically. ResultsAccording to a numerical simulation of a multi-purpose naval vessel, the proposed control method is compared with a disturbance compensation MPC and disturbance observer enhanced MPC, and is shown to have a higher roll stabilization rate by 5.74% and 0.898 3%, respectively. The response time of the proposed method for a 30° heading change is also reduced by 1.8 s and 7.3 s respectively. ConclusionThe effectiveness of the proposed method in underactuated ship rolling reduction is proven.
ObjectivesEvacuation analysis is essential for the design and safety assessment of cruise ships. In this study, a fine-grid-based evacuation model is developed to accurately simulate personnel behaviors and evacuation rules during the cruise ship evacuation process.MethodsFirst, some key algorithms of the model are given: the deck spaces are defined as two kinds of areas, the target area and the functional area, divided into 0.1 m × 0.1 m grids to accurately describe the internal spatial layout and arrangement. Next, personnel movement rules are developed by introducing the parameters of the expected movement direction and movement tendency of passengers, and two rules of path planning are established, namely, the free option of the shortest path and the specified shortest path. Finally, a cruise evacuation case is simulated and the results are compared with datasets from a semi-unannounced trial of the EU Safeguard Project. ResultsThe results show that the evacuation model developed herein meets the requirements of the four validation metrics ERD, EPC, SC, TAT%. The times of the overall assembly process and each assembly station are well compliant with the experimental data, and the relative error of the overall assembly time is about 4.9%. Compared with the simulation results of commercial software EXODUS, the calculation results of the model developed herein are more in line with the experimental data. ConclusionsThe proposed fine-grid model for cruise evacuation simulation can improve the design of escape routes and optimization of evacuation plans.
ObjectivesThe afterburning effect need to be considered when TNT explodes inside a confined space. In order to accurately analyze the internal blast load, it is necessary to explore the relationship between the afterburning energy value and the charge volume ratio. MethodsThe explosion experiments of 5 different masses of TNT were performed in the confined spaces filled with air and helium. Based on three different methods of chemical reaction analysis, energy conservation law and hypothetical isentropic process, the corresponding afterburning energy of five different charge volume ratios is calculated. The numerical simulation of explosion in confined space considering afterburning effect was realized by ANSYS/AUTODYN program.ResultsThe comparison between quasi-static pressure simulation results and experimental results shows that the theoretical value of afterburning energy calculated by chemical reaction analysis method can only be used as the upper limit value, the accuracy of energy conservation method depends on the adiabatic index of mixed gas, and the error of assumed isentropic process method is stable between 4% ~ 7%. Different afterburning energy release processes do not change the final quasi-static pressure, but only the reflected shock wave pressure. ConclusionsThe research results can provide more accurate input load for the design and damage assessment of anti-explosion structures.
ObjectivesIn order to reduce the influence of ship service life extension uncertainty and fatigue risk during future service life extension, a dynamic maintenance sequence decision based on the real option analysis method is adopted. MethodsThe local fatigue of a high-speed ship is taken as an example. This strategy strengthens the maintenance in the early stages of the ship's service and determines the adaptive maintenance decision according to the requirements of service life extension in the later stages, thereby adapting to the various possibilities of service life extension in the future. ResultsCompared with the traditional maintenance strategy, the flexible decision under real option analysis can reduce the influence of service life extension uncertainty and effectively reduce failure risk during service life extension. ConclusionsThe sequential decision made via the real option analysis method has strong adaptability to the uncertainty of service life extension in the future and provides a new idea for maintenance decisions.
ObjectiveThis paper analyses the fatigue life of weld cracks in a large opening coaming with a conical shell under uniform pressure load. MethodsFirst, a finite element model of an underwater pressure-hull structure is built. Next, the peril point and its fatigue life are calculated using the structural strain method. Finally, the accuracy of the structural strain method used in the fatigue life evaluation of the underwater pressure-hull structure is verified through a comparison with the calculated results of the experimental data model.ResultsThe results show that the maximum structural stress is located at the weld of the coaming near the large end, which is the same as the appearance location of fatigue cracks in the experiment. The fatigue life calculated using the structural strain method shows good agreement with the experimental results, and the data of the model fatigue experiment is located in a narrow band of the master e-N curve. The normal structural stress is far greater than the shear structural stress at the peril point of the coaming weld. ConclusionsThe structural strain method can effectively solve problems with the fatigue life of weld cracks in a large opening coaming with a conical shell. Under the load conditions of this paper, the initial crack at the peril point should be type one.
ObjectivesThis paper aims to discuss the relationship between the ultimate bearing capacity of a pressure hull and pressure tank under the same strength margin, and obtain a matching design with the equivalent ultimate bearing capacity and strength margins accordingly. MethodsTo this end, a typical external pressure tank is taken as the research object. On the basis of evaluating the stability and ultimate bearing capacity of the initial structural scheme, the influences of the thicknesses of the pressure tank shell, solid floor and transverse bulkhead on the ultimate bearing capacity are studied. The initial scheme is then adjusted to obtain a scheme with the equivalent strength margins of the pressure hull and pressure tank. In this context, the relationship between the ultimate bearing capacity of the pressure hull and pressure tank is discussed. By strengthening the pressure hull to match the ultimate bearing capacities of the pressure tank and pressure hull, the corresponding strength margins are obtained. ResultsThe results show that thinning the pressure tank shell by 30%, solid floor shell by 33.3% and transverse bulkhead shell by 30% reduces the ultimate bearing capacity of the tank by 16.5%, 36.4% and 0.17% respectively. ConclusionsAs further analyses show, under the condition of the same strength margin, the ultimate bearing capacity of the pressure hull is much lower than that of the pressure tank. When the strength margin of the pressure tank is about 25% and that of the pressure hull is about 40%, the ultimate bearing capacities of the pressure hull and pressure tank are roughly the same.
ObjectiveA large opening on the swimming pool structure of a large cruise ship reduces the carrying capacity of the deck structure. The opening reinforcement is an effective approach to improve the structural strength. However, various forms of reinforcements pose a challenge to the optimal design of opening structures. MethodsA variable density topology optimization method is used to optimize the opening reinforcement of a swimming pool, and a new form of opening reinforcement is obtained. Next, a size optimization method is used to obtain a more reasonable distribution of plate thicknesses, thereby achieving better weight reduction.ResultsAs the results show, compared with the prototype structure, the optimized structure has an increased ultimate bearing capacity of 1.1%, maximum stress reduction of 3.3% and weight reduction of 7.0%.ConclusionThe proposed optimization design method can provide a reinforcement approach for designing the deck opening structures of cruise ships.
[Objective] Orthogonally stiffened plates with different plate-to-beam bending stiffness ratios are taken as the research objects to uncover the dynamic coupling characteristics of the beam and plate components of orthogonally stiffened plates, and reveal the mechanism and influence of dynamic coupling between the construction members on their intrinsic dynamic characteristics. [Method] The natural frequencies and mode shapes of numerical models under free boundary conditions and clamped boundary conditions are calculated using the finite element method. Through an analysis of variations in the natural frequencies and mode shapes of an orthogonally stiffened plate against the plate-to-beam bending stiffness ratio, the intrinsic dynamic characteristics of an orthogonally stiffened plate with different bending stiffness ratios are discussed, and the dynamic coupling characteristics between the beam and plate are analyzed. [Results] The numerical results show that with the variation of the plate-to-beam bending stiffness ratios, the dynamic behaviour of the orthogonally stiffened plate transforms between two kinds of characteristics: one dominated by the plate and the other one coupled by the beam and plate. The critical plate-to-beam bending stiffness ratios and the criterion for determining them are presented in this paper. [Conclusion] The dynamic coupling between the beam and plate changes the variation rate of the natural frequencies with the plate-to-beam bending stiffness ratio, leading to the dislocation and distortion of the mode shapes of orthogonally stiffened plates.
ObjectiveThis paper aims to study the overall acoustic radiation properties of a submarine hull-propeller system with a seven-blade highly skewed propeller working under different operating conditions.MethodsTaking the SUBOFF submarine model and a highly skewed propeller as the research object, the large eddy simulation (LES) and acoustic finite element method are adopted, and Fluent fluid calculation software and LMS Virtual.Lab acoustic simulation software are used to carry out joint simulation calculation.ResultsThe results show that the velocity and pressure distributions in the bow, conning tower, stern rudder and propeller area change the most when the submarine has advance speed. The noise propagation direction of the whole system has the highest sound pressure level (SPL) in a certain direction of the hull's circumference, followed by the aft direction. When the submarine has no advance speed, the noise of the coupling system is related to the rotating action of the propeller, and there is a peak at the 440 Hz frequency, which exceeds the SPL under other operating conditions. ConclusionsThe three regions of the bow, conning tower and stern rudder are the key regions that generated pressure pulsation, which is closely related to the advance speed of the submarine. In the low frequency band, the propeller noise is mainly generated by the bow, conning tower and stern rudder. In the middle and high-frequency bands, the overall submarine hull-propeller noise also begins to have an effect, and the total SPL increases gradually with the increase in frequency.