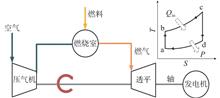
ObjectiveIn order to overcome the influence of the nonlinear time-varying characteristics of gas turbines on dynamic control and performance monitoring, this paper combines the time series memory and nonlinear relation expression ability of a long short-term memory neural network (LSTM) with the interval probability estimation ability of Gaussian process regression (GPR) to propose an online parameter identification algorithm for the key dynamic parameters of gas turbines based on an LSTM and GPR-based hybrid deep learning model (LSTM-GPR). MethodsFirst, the dynamic mechanism model of a gas turbine is established, and a large amount of training data is generated by taking fuel calorific value, compressor efficiency and load power moment as the parameters to be identified. Next, the parameter identification network model of LSTM-GPR is constructed, and the training data is input for network training and weight coefficient learning. Finally, the trained LSTM-GPR hybrid deep learning model is used to identify the dynamic operating parameters of the gas turbine model online, and the identification results are analyzed to verify the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm.ResultsThe simulation results show that the online identification results of the proposed LSTM-GPR hybrid model algorithm are accurate, with a recognition error of less than 1% and good real-time performance. Compared with the LSTM single model, the proposed algorithm can obtain a better mean estimation effect and provide a reliable confidence interval range. ConclusionsThe LSTM-GPR hybrid algorithm can be effectively applied to the online parameter identification of a gas turbine model, laying a foundation for its further application to the dynamic operation parameter identification of practical units.
ObjectivesThis paper uses the probabilistic safety analysis method to review the safety of marine nuclear power plants (MNPPs).MethodsThe relevant data of nuclear power plant systems and equipment is referenced to establish a Level 1 probabilistic safety analysis (PSA) model of the internal event power conditions of MNPPs. For the 17 groups of initial events that may cause reactor core damage, 17 event trees are established, along with 42 fault trees for the eight front/support systems, and then conduct a Level 1 PSA analysis.ResultsThe core damage frequency (CDF) is calculated as 4.38×10–6/(reactor year), and the contribution of each initial event group to the CDF is determined. According to importance analysis, human error events and power system faults are the two factors that contribute the most to the CDF of MNPPs. Sensitivity analysis finds that connecting a third diesel generator can considerably reduce the CDF.ConclusionsThe results of this study can provide references for the safety design of MNPPs.
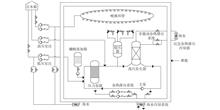
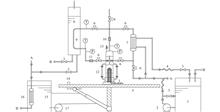
ObjectivesThe heat transfer characteristics of steam condensation in a passive residual heat removal system heat exchanger (PRHR HX) are among the most important factors affecting the operational capability of marine nuclear power platform PRHR systems. This study aims to analyze the heat transfer characteristics of steam condensation in a PRHR HX and obtain the accurate heat transfer coefficient relationship.MethodsThe heat transfer characteristics of steam condensation in a PRHR HX are analyzed by building an experimental device with a power ratio of 1∶50. ResultsThe experimental results show that the heat transfer coefficient increases with the increase in steam pressure. The internal flow pattern of the PRHR HX is a stratified flow or wave flow-annular flow-wave flow. The maximum flow rate of HX vapor is 6.72 m/s when the system pressure is 0.52 MPa, and when the pressure exceeds 0.52 MPa, the steam velocity decreases with the increase in heating power. The proposed new correlation shows good agreement, with an error of ±8% between the calculated and experimental results.ConclusionsThis study can provide useful references for the design of reactor safety systems for marine nuclear power platforms.
ObjectivesTo realize the online identification of hydrogen evolution characteristics and the quantitative design of the hydrogen control system for the lead-acid battery rooms of ships, a hydrogen concentration identification method based on the lumped model is proposed which comprehensively considers key parameters such as the hydrogen evolution rate of the battery and the ventilation & purification air volume and leakage air volume of the battery room.MethodsAccording to the environmental characteristics of the battery room, a mathematical model of the hydrogen concentration characteristics and hydrogen evolution rate prediction of the battery is established, and a corresponding calculation program is developed to analyze the hydrogen concentration variation characteristics of the battery room under different hydrogen evolution rates and ventilation & purification air volumes.ResultsThe various characteristics of the hydrogen concentration in the battery room are affected by the hydrogen evolution rate of the battery and the ventilation & purification air volume and leakage air volume of the battery room. When the hydrogen evolution rate is low (such as with a new battery), the leakage air volume will significantly affect the concentration rise rate. The daily operation frequency of the hydrogen purification system can reflect the actual hydrogen evolution rate of the battery and guide battery life evaluation.ConclusionsThe hydrogen evolution rate of the battery is correlated with several parameters. The proposed prediction model can accurately predict the hydrogen evolution rate of the battery and guide system design and operation strategy optimization. The related ideas and methods can also be extended to other cabin components similar to the hydrogen control system.
ObjectivesFor a marine 690 Vac bidirectional converter based on a three-level flying capacitor, in order to make it start stably and transition to its normal working state, the flying capacitor must be pre-charged. This paper proposes a pre-charging strategy based on single-tube control which is suitable for three-level flying capacitors.MethodsThe on-off of the three-level outer tube is controlled on the basis of the flying capacitor, and efficient and fast pre-charging control is performed.ResultsWhen this strategy is applied to a 690 Vac bidirectional converter, the pre-charging of the flying capacitor is completed within 1 second in Buck mode and less than 5 seconds in Boost mode. After pre-charging, the voltage of the flying capacitor remains at the value of half of the voltage of the high voltage side, and the voltage of the input side capacitor remains at the value of the input side voltage.ConclusionsAfter experimental verification, the proposed pre-charging strategy based on controlling the outer tube of the three-level flying capacitor can be applied to a 690 Vac bidirectional converter device without the need for additional pre-charging power devices, which not only simplifies the topology but also ensures the reliable and fast pre-charging of flying capacitors.
ObjectivesThis study explores the use of a nonlinear adaptive inertia weight particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm to realize the optimal design of the path and arrangement of pipelines in the nuclear power primary loop systems of ships. MethodsAccording to the pipeline layout design characteristics, the constraints, evaluation functions and spatial model of the primary loop system are established. Based on the number of pipeline nodes, a new fixed-length coding method for the PSO algorithm is proposed, along with a direction guidance mechanism. As the standard PSO algorithm has such shortcomings as a slow convergence speed and susceptibility to falling into the local optimal solution, an improved nonlinear adaptive inertia weight PSO algorithm supplemented by a linearly changing learning factor is proposed. The improved PSO algorithm is combined with a co-evolutionary algorithm to form a co-evolutionary PSO algorithm for solving branch pipeline problems. The improved algorithm is then applied to the pipeline layout optimization problem of the nuclear power primary loop systems of ships. ResultsThe simulation results show that the convergence speed of the proposed algorithm is increased by 40% –50% compared with that of the standard algorithm. The improved algorithm can not only obtain higher quality pipeline layouts, but also solve the problem in which the standard PSO algorithm can easily fall into the local optimal solution. Conclusions The results of this study can provide useful references for the pipeline layout optimization of the nuclear power primary loop systems of ships.
ObjectivesThe key to uncertainty design optimization (UDO) is uncertainty quantification (UQ), but the traditionally used Monte Carlo (MC) method can be time-consuming and computationally expensive. Therefore, a ship UDO method based on polynomial chaos expansions (PCE) and the maximum entropy method (MEM) is proposed.MethodsPCE with less computational cost is selected to quantify the stochastic properties of the output under the influence of multiple uncertain parameters. According to the properties of the orthogonal polynomials, an improved probabilistic collocation method (IPCM) based on the linear independence principle is used to solve the polynomial coefficient of PCE. In addition, the first four moments of the constraint obtained by PCE are combined with MEM to solve the probability density function (PDF) of the constraint, and the failure probability of the constraint is obtained by integrating PDF on the failure domain.ResultsThe improved probability collocation method based on the principle of linear independence provides the optimal number of probability collocation points and greatly reduces the number of sample points. When solving the failure probability of the constraint based on PCE and MEM, compared with the results of MC, the accuracy of the proposed method can meet the requirements with no additional calculations. The UDO results of bulk carriers verify that PCE has obvious advantages in accuracy and efficiency in engineering applications compared with MC.ConclusionsThe method proposed herein can efficiently and accurately ensure the robustness and reliability of ship design schemes.
ObjectivesTo ensure the icebreaking navigation capability of polar bidirectional icebreaker ships, it is necessary to focus on the design of their stern line characteristics. MethodsThis paper surveys many polar ships in active service, summarizes the current standards, discusses the ice load modes of the pod propulsion units and ice breakage processes of ships, and analyzes the key design characteristic parameters and adaptability of the stern lines of pod-propelled polar ships.ResultsIt was found that the dip angle of the stern transom plate affects the horizontal and vertical forces on the sea ice by ships directly during the ice-breaking processes. This dip angle should be amplified properly to guide the bending fracture of sea ice effectively. The W type of stern plate transverse profile can resolve the contradiction between the optimization of wake field and the outflow efficiency of broken ice. The pod installation base could play a certain ice-breaking function, but it would affect the flow field of the pod. The tail fin would also affect the stern flow field and the outflow of broken ice obviously. Conclusions The reference for the adaptive optimization design of pod-propelled polar ship stern profile can be provided by the research results.
ObjectivesIn order to improve the efficiency of structural strength verification in finite element calculation, and reduce workloads for size optimization in iterative process, this paper is intended to propose a method for plate seam arrangement and size optimization of double bottom longitudinal girders of bulk carriers.MethodsFirst, based on the theoretical formula, the reliability of the sub-model technology is demonstrated and a multi-condition screening method for the optimization design of double bottom longitudinal girders is proposed. Then, a double bottom longitudinal girder of a real bulk carrier is taken as an example and divided into plate panels. The plate thickness is set as a variable and the permissible stress of the Harmonized Common Structural Rules (HCSR) is used as the optimization constraint in size optimization. The plate seam arrangement with the minimum weight is chosen as the optimized arrangement after using the exhaustive method to list all the seam arrangements and merge the plate thicknesses. Finally, considering the HCSR regulatory requirements about yield strength finite element calculation of hold section, the plate seam arrangement of the longitudinal girder strengthening area of interest is optimized, on this basis, the satisfactory structural sizes that meet the regulatory requirements are obtained using the proposed size optimization method.ResultsThe results show that this method for plate seam optimization and structural strengthening based on size optimization can reduce the weight of the optimized area by 4.9%.ConclusionsThe method proposed herein can effectively reduce the randomness of finite element-based manual calculation of structural strengthening, optimize finite element design scheme and reduce the weight of strengthening.
ObjectivesThe navigation control system is the brain and center of an intelligent ship, and the safety and economy of the ship's navigation are directly determined by its control performance. Therefore, it is necessary to validate the ship intelligent navigation control system. This paper proposes a general verification platform, the variable stabilized ship, to simulate the sailing state of the target ship at different scales and with different hydrodynamic characteristics. MethodsFirst, the structure of the variable stability ship is proposed on the basis of the model-following principle, and an analysis is made of the three degrees of freedom movement characteristics. The steady error between the variable stability ship and the target ship is determined by their position errors, and the variable stability controller is built on the basis of sliding mode control. Finally, Matlab simulations are carried which verify that the proposed method can maneuver the variable stability ship to follow the states of the target ship. ResultsSimulation results show that the proposed method maneuver the variable stability ship to follow the states of the target ship. ConclusionsThe results of this study can provide references for the validation and verification of navigational control systems for intelligent ships.
ObjectiveThis study explores the limited thrust/torque of a remotely operated vehicle (ROV) by addressing the difficulty of achieving precise control in prescribed-performance 3D trajectory tracking. Considering unknown factors such as system uncertainty and underwater environmental disturbances, an accurate tracking control scheme is proposed on the basis of a finite-time extended state observer and prescribed-performance transformation to ensure the rapid stabilization of trajectory tracking errors. MethodFirst, a compensation system is designed to eliminate the thruster input saturation constraint. Second, a finite-time extended state observer is designed to perform lumped observation and compensation for external disturbances and unknown system dynamics. Furthermore, based on the prescribed-performance function and error conversion function, the tracking error limited by the prescribed-performance is transformed into an unrestricted tracking error; an integral sliding mode is constructed; and the fast power reaching law and boundary layer are utilized to reduce the buffeting of the actuator. Finally, the Lyapunov theory is used to prove the overall stability of the proposed algorithm. ResultsThe simulation results verify the effectiveness and superiority of the designed control method. ConclusionThis study can provide a new solution for the accurate prescribed-performance control of the trajectory tracking of an ROV with constrained thrust under lumped disturbance.
ObjectiveThis study addresses the engineering problem of underwater tracked dredging robots sliding due to insufficient adhesion when dredging caissons in bridge construction. Therefore, a trajectory tracking controller based on the barrier Lyapunov function (BLF) is designed. MethodThe algorithm considers the non-coincidence of the centroid and geometric center, influence of unknown bounded disturbances and system dynamic uncertainty to establish kinematic and dynamic motion models. A terminal sliding mode observer (TSMO) is used to approximate external disturbances and system dynamic uncertainty in finite time. The stability of the control system is verified by time-varying symmetric finite time BLF stability analysis, and control failure is prevented by limiting the velocity state of the system. ResultsThe simulation results show that the robot reaches the desired trajectory smoothly and quickly under the control of the designed controller. ConclusionThe proposed algorithm can limit the velocity state of the robot system to an interval that conforms to the actual engineering practice.
ObjectivesThe maritime navigation environment is random, complex and changeable, and intelligent autonomous navigation is an important trend in the development of large ocean-going transport ships, for which a new adaptive control method is proposed. MethodsFirst, the linear quadratic regulator (LQR) control method is integrated with the first-order dynamic integral sliding mode control method based on the grasshopper optimization algorithm (GOA). A nonlinear passive estimator with real-time monitoring of wave disturbance forces is then combined to separate the high and low-frequency motion signals of the ship. Finally, the simulation results of the proposed method are compared with those of the LQR control method and first-order dynamic integral sliding mode control method. ResultsThe results show that the new control method has better transient and steady-state tracking performance, and is able to overcome the effects of random waves under different sea conditions with strong robustness. ConclusionsThe new control method has such abilities as self-adjustment in complex environments, fast control response, high precision and less redundant steering, enabling it to greatly improve the navigation efficiency, safety and stability of large transport ships.
ObjectivesIn order to create a simulation test platform to effectively test the key technologies of intelligent ships such as guidance, navigation and control technology, this study uses system identification technology to identify the parameters of the Nomoto motion model of an intelligent ship with high precision.MethodsA hybrid parameter identification method is proposed by fully combining the advantages of the extended state observer (ESO) and the robust weighted least square support vector regression algorithm (RW-LSSVR), our previously well-evaluated identification method. The ESO-based state estimator is applied to calculate immeasurable states using measurable states and the second-order linear Nomoto model. To evaluate the proposed approach, models of two vessels with predefined parameter values are employed for simulation tests.ResultsThe proposed approach not only estimates immeasurable states with high accuracy, but also ensures good performance in steering model parameter identification, with values very close to the nominal values.ConclusionsThe proposed ESO-based identification method shows good generalizability and can effectively provide satisfactory estimates of immeasurable states, making it highly applicable to parameter identification.
ObjectivesIn this study, an adaptive non-singular fast terminal sliding mode rudder roll stabilization controller based on a multiple-layer recurrent neural network ( MLRNN) is proposed for the rudder roll stabilization control of an underactuated surface ship with unknown nonlinear system functions and random external disturbances. MethodsFirst, in view of the singularity and convergence problems in traditional sliding mode control, a non-singular fast terminal sliding surface is introduced, and the sliding mode control law is designed under the assumption that the ship model is known. The traditional radial basis function neural network (RBFNN) is then improved and used to approximate unknown nonlinear system functions in order to solve the problem of ship models being difficult to establish when the ship is sailing while also improving the control accuracy. The stability and finite time convergence of the system are proven by the Lyapunov theory, and the adaptive laws of the neural network parameters are derived. Finally, a numerical simulation analysis of a multi-purpose naval ship is carried out. ResultsThe results show that when the ship is under the course keeping condition, the roll reduction rate of the proposed controller is 50.41%, which is 19.2% larger than that of the non-singular fast terminal sliding mode controller (NFTSMC). When the ship is under the course changing condition, the roll reduction rate of the proposed controller is 23.46%, which is 12.59% larger than that of the NFTSMC. ConclusionsThis method can provide valuable references for the design of underactuated ship rudder roll stabilization controllers.
ObjectiveTo ensure accurate comprehensive evaluation of naval ship's maneuvering performance as far as possible, this study proposes an improved evidential reasoning approach.MethodThe basic concept of the approach is introduced and its evaluation principle and basic process are summarized and analyzed. The approach is then improved in three aspects: first, in order to effectively reflect the matching degree of ship maneuverability and navy demand, the performance matching degree is defined; second, as existing evidential reasoning approaches cannot integrate multi-temporal evaluation data, the concept of credibility is proposed; and third, to address the problem of the large number of qualitative indicators in the evaluation index system, which makes it difficult to guarantee the reliability of single evidence, the reliability of evidence is introduced to weaken the impact of poor data on the evaluation results. On this basis, an example of comprehensive evaluation is calculated and analyzed based on the maneuvering performance data of a certain type of ship. The comprehensive evaluation results are then compared with the evaluation results at each time, and comparisons are made of the evidential reasoning approach with and without considering evidence reliability.ResultThe comprehensive evaluation results calculated using credibility are the same as the evaluation results two thirds of the time, and credibility follows the principle of minority to majority; and by using evidence reliability correction weighting, the weight of unreliable evidence can be reduced from 20.00% to 13.49%, effectively reducing its impact on the comprehensive evaluation results.ConclusionThe results of this study have good reference value for the application of the evidential reasoning approach, and provide a new idea for the comprehensive evaluation of the maneuvering performance of naval vessels.
ObjectivesIn order to further improve the accuracy of torpedoes in the acoustic homing identification of complex surface targets, a simulation study on the acoustic scattering characteristics of surface ship motion attitudes in random waves is carried out. MethodsTo effectively solve this problem based on Kirchhoff approximation theorem and six-degrees-of-freedom (DOFs) motion decomposition and synthesis method, a simplified prediction model for the multi-path acoustic scattering of surface targets is established. In this model, the effects of sea waves on the amplitude and period of a ship's six-DOFs motion are described by empirical statistics, and the rotation matrix and translation matrix are used to realize the coordinate transformation of each vertex of the surface target in a continuous motion state. On this basis, the model is used to analyze the contribution and influence of six-DOFs motion attitudes on the acoustic scattering characteristics of a surface ship from different horizontal detection angles.ResultsThe results show that the rolling and yawing motions have a great influence on the acoustic scattering of the target in the abeam detection, while the pitching motion has a great effect on the acoustic scattering in the bow and stern directions. Thus, the relationship between the surface ship's motion attitudes and acoustic scattering echoes is grasped.ConclusionsThis study can provide technical support for sonar equipment in the location and identification of surface targets.
ObjectiveThe appendages of a submarine affect the wake field at the propeller disk, which in turn affects the exciting force characteristics of the propeller. Grasping the influence law of the wake field on the exciting force is helpful for the low-excitation force design of submarines and propellers. MethodBased on the Suboff Model and INSEAN E1619 propeller, the RANS method is used to numerically simulate the propeller exciting force under wake fields affected by different appendages, and the harmonic analysis method is used to quantitatively characterize the wake fields at the propeller disk. The mechanism of the linear spectrum exciting force is revealed by combining the distribution characteristics of the transient flow field of the propeller. ResultsThe results show that the distribution of each order of the harmonic components of the wake field is consistent with the distribution of a single-blade linear spectrum exciting force, and the relative amplitude of the single-blade exciting force in its main frequency is basically equal to that of a seven-blade propeller. The harmonic components of circumferential symmetrical rudders to the wake field are mainly concentrated on the fourth and eighth orders, and have little effect on the exciting force of a seven-blade propeller; however, fairwaters influence the harmonic components of the wake field and have a major effect on the exciting force of a seven-blade propeller. ConclusionThe influence of rudders on propeller exciting force is less than that of fairwaters. In order to improve the exciting force characteristics of propellers, the optimization of submarine fairwaters should be emphasized.
ObjectivesThis study aims to investigate the effects of the development of tip leakage vortex (TLV) cavitations on the core characteristics of vortices. MethodsThe numerical simulation associated with the SST k-ω turbulence model and Zwart-Gerber-Belamri (ZGB) cavitation model is used to solve the cavitating flow of the TLV of a ducted propeller under different cavitation conditions. Based on the reliable numerical simulation, the development of the TLV cavitation and the evolution of its core characteristics are studied according to the vapor volume fraction iso-surface and Q criterion. ResultsThe results show that the area of the tip leakage cavitation expands with the development of the TLV cavitation. The TLV cavitation twists near the trailing edge of the tip leakage cavitation under specific conditions. The performance of the ducted propeller is greatly affected by the continuous decrease in the cavitation number. The development of the cavitation makes the TLV gradually flow away from the blade suction surface, increasing the complexity of the velocity distribution at the TLV core center. When the cavitation number σ is 1.488, the continuous development of the cavitation significantly reduces the intensity of the TLV. With the development of the TLV, its ability to absorb the circumferential vorticity from the inner wall weakens, and the turbulent kinetic energy from the tip gap is gradually transported to the vortex center. ConclusionsThe proposed method and results of this study can provide valuable references for the performance prediction of hydraulic rotating machinery and control methods for TLV cavitations.
ObjectivesThis study seeks to correct the distortion of results caused by the inviscid-flow assumption when potential flow theory is used to calculate a two-ship floating system with a small gap, and analyze the motion response characteristics of the gap water.MethodsA CFD numerical model of a ship-to-ship transfer system is established and the water response characteristics and mechanism in the gap are analyzed. The CFD calculation results are then compared with those of potential flow theory in order to obtain the accurate damping coefficient of the two-ship gap and correct the results of potential flow theory.ResultsThe results show that the trend of wave elevation is different when waves of different frequencies pass through the gap. For low frequency waves, the incident wave cannot pass through the gap between the two ships, so the gap wave elevation is smaller than the wave amplitude of the incident wave. For high frequency waves, the incident wave can pass through the gap, so the gap wave elevation is greater than the wave amplitude of the incident wave. There is a high-speed area in the gap between the two ships which decreases the hydrodynamic pressure on the inner sides of the two vessels, resulting in greater suction which may adversely affect transfer operations. ConclusionsThe correction method proposed herein can obtain the damping coefficient of gap water more accurately, providing guidance for the high-precision and rapid hydrodynamic and motion calculation of ship-to-ship transfer systems.
This paper starts with the importance and basic physical phenomena of underwater explosion, explaining the background and significance of ship damage and protection research under underwater explosion loads, research progress and status, as well as key challenges. To address these challenges, the paper elaborates on popular underwater explosion theories, models and methods. In terms of theoretical and computational research, a unified theory of bubble dynamics is presented, as well as a transient strong non-linear gas-liquid-solid fully coupled model and numerical method for underwater explosion, which have been used to develop a fundamental industrial software FSLAB capable of solving practical problems in fluid-structure interaction. In terms of experimental research, underwater explosion surrogate experimental methods and model testing methods are elaborated. Based on this, theoretical analysis, computational and experimental results in the field of ship damage and protection under underwater explosion loads are presented and discussed, aiming to provide references for underwater explosion-related research.
ObjectiveThis paper aims to analyze the explosion loading characteristics in a confined ship cabin with a pressure relief hole, and the impact of the pressure relief hole in propagating shock loads from the explosion affected cabin to the adjacent cabin.MethodFirst, a numerical simulation of the explosion venting effect on a double cabin is conducted, and the pressure drop of the explosion affected cabin is analyzed with the Baker empirical formula. On the basis of the pressure distribution characteristics in the adjacent cabin, the empirical formula for the initial peak pressure in the adjacent cabin is deduced using the least squares principle.ResultsThe results indicate that the increase in the size of the pressure relief hole will change the initial state of the pressure field in the explosion affected cabin and adjacent cabin during the explosion venting process, weakening the pressure convergence and superposition in the explosion affected cabin, and strengthening the pressure propagation in the adjacent cabins. Without considering the influence of structural deformation, the shock wave presents a peach-shaped and jellyfish-shaped pressure distribution after passing through the pressure relief hole, and the phenomenon of pressure stratification and attenuation with angle occurs.ConclusionThe results of this paper can provide references for the study of explosion load characteristics in cabins.
ObjectivesThis paper aims to evaluate the impact resistance of Ti80 alloy under low-velocity impact loads using a numerical study of the dynamic response.MethodsFirst, the finite element software Abaqus/Explicit is used to establish a finite element model of a Ti80 alloy plate under low-velocity impact load. Second, the rationality of the material parameters and reliability of the finite element model are verified through a comparison with the experimental results. Finally, the effects of the impactor shape, yield strength and fracture energy on the dynamic response of the Ti80 alloy plate under low-velocity impact load are discussed on the basis of the finite element model.ResultsThe numerical results agree well with the experimental results in their dynamic response and deformation/failure modes. Under low-velocity impact load, damage initializes on the backside of the Ti80 alloy plate due to excessive tensile deformation. The hole expansion effect of the conical impactor causes serious plugging damage to the Ti80 alloy plate. The peak impact force, peak displacement of the impactor and energy absorbtion exhibit an approximately linear relationship to the yield strength. The fracture energy has a significant effect on the deformation/failure mode of the Ti80 alloy plate. Compared to the yield strength, the energy absorbtion is less sensitive to the fracture energy.ConclusionsThe results can provide references for the impact resistance design of Ti80 alloy structures.
ObjectivesThis study aims to explore nonlinear similarity criteria for box girders under pure bending load, improve the prediction accuracy of the model on the response of prototype structures and provide a theoretical basis for establishing a distortional similarity model design method for actual ship structures.MethodsFirst, based on the stability and nonlinear criteria of axially compressed reinforced slabs, a nonlinear similarity criterion for box girders under pure bending load is established using the theoretical analysis method. Second, the ultimate load-carrying capacity and buckling response of scaled-down prototype box girder models are then analyzed using the numerical calculation method to verify the validity of the similarity criterion.ResultsThe numerical calculation results show that different scale designs based on the proposed method have high similarities in their flexural failure modes, and the ultimate strength of the scaled-down prototype models can be accurately predicted. Under a specific flexural mode, an increase in the initial deformation reduces the ultimate load-carrying capacity of the box girder. In contrast, the initial deformation factor has less influence on the prediction accuracy of the scaled-down model.ConclusionsThis paper provides an effective nonlinear similarity model design method for the ultimate strength testing of hull beams under pure bending load, which has value for the study of the structural safety of ships.
Objectives This study seeks to grasp the effects of the initial deflection shape on the plastic accumulation characteristics of hull plates with circular holes under cyclic loading.MethodsFinite element software ABAQUS is used to carry out the nonlinear elastic-plastic large deflection numerical simulation of hull plates with circular holes of different slenderness ratios and perforation sizes under axial cyclic loading. The plastic accumulation and fracture characteristics of the plates under axial cyclic loading are studied with the initial deflection shape made by the first-order buckling mode and commonly used initial deflection formula respectively.ResultsThe plastic accumulation of plates with the initial deflection shape made by the initial deflection formula is relatively moderate. When the axial cyclic loading amplitude is relatively low, the number of fracturing cycles of plates with the initial deflection shape made by the first-order buckling mode is relatively small, but the difference decreases as the amplitude increases.ConclusionsThe influence of different initial deflection shapes on the plastic accumulation and fracture characteristics of plates with circular holes depends on the slenderness coefficient, perforation size and axial cyclic loading amplitude.
ObjectivesThe wetting gradient surface has potential application value in such fields as ship anti-fouling and submarine drag reduction, requiring further research on low-cost and low-complexity wetting gradient surface preparation technology.MethodsThe preparation and static wetting characteristics of a silica-based wetting gradient surface are analyzed using vapor deposition, alkali corrosion and a combination of both.ResultsThe contact angle using vapor deposition reaches 104.9°, with a largest range of about 23°; that using alkali corrosion reaches 80.2°, with a largest range of about 60°; and that using both methods reaches 102.1°, with a largest range of about 40°.ConclusionsThe results of this study can provide references for the preparation of functional surfaces for marine equipment.
ObjectivesThis paper aims to propose a type of structural verification software for inland ships with embedded specifications, addressing the problem of low calculation efficiency and difficult model reuse in performing manual checking and calculation.MethodsThe software is constructted based on the model-view-controller (MVC) framework, with the hull model as the center and the development of core functional modules such as the structural database, section visualization and specification calculation. A hierarchical model of the structure is designed for parameter management and sharing; the model is abstracted to express special structures and decouple from the specifications; and derivation technology is integrated to facilitate software update and model reuse. ResultsThe calculation example shows that this verification software based on the abstraction of structural parameters can ensure the integrity and accuracy of specification calculation, and realize the complete compatibility and combination verification of various inland ship types and specifications, with an error rate of just 0.1% against the manual calculation results.ConclusionsThe proposed software breaks through the limitations of different ship types and specifications, realizes intelligent and dynamic structural verification, and reduces the dependence of users on complicated rules and regulations. As such, it can significantly improve the quality and efficiency of design and planning approval work. Compared with other standard structural checking software, this software has the advantages of accurate calculation and rapid modeling.
ObjectivesIn order to evaluate the operational effectiveness of surface warships more reasonably, this article proposes improving the existing evaluation methods to better suit complex battlefield environments. Methods First, according to operational test items and test scenarios planning, the content of the warship platform test items are analyzed, and classification standards for complex battlefield environments' operational intensity and electromagnetic environment are designed. An improved method for evaluating combat effectiveness based on the influence factors of complex battlefield environments is then proposed, and the operational effectiveness of a certain type of surface warship in an anti-air warfare environment is evaluated. ResultsThe results show that the proposed method is effective. Conclusions The proposed method fully considers the influence of complex battlefield environments on the combat capability of different operational units, and solves the problem of existing operational effectiveness evaluation methods failing to fit the actual situation of complex battlefield environments. As such, this study can provide valuable references for the operational testing of naval vessels.
ObjectivesThe field of combat resource planning has gradually become the core point of intelligent decision guidance for future combat, and ensuring a better combat resource planning scheme is crucial to the guidance and implementation of actual combat. To this end, a resource planning method for the joint air defense of warship formations based on an improved genetic algorithm is proposed. MethodsFirst, the resources are serviced to improve their versatility; next, the articulation of multi-population genetic algorithms is used to represent multi-stage combat planning, and multi-dimensional quality of service (QoS) combat performance indicators are designed on the basis of multi-population genetic algorithms, thereby establishing a set of strengths and weaknesses for the evaluation of joint warfare planning programs. ResultsAfter the generalization of resources, the proposed method can be effectively combined with multi-population genetic algorithms to obtain a multi-stage optimal combat resource planning scheme. ConclusionThis study has certain reference value for the design and application of combat resource planning.