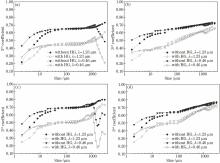
Based on a new multi-shape ice cloud radiative parameterization scheme and the Beijing Climate Center radiative transfer mode (BCC_RAD), the effects of the Henyey-Greenstein (HG) approximation on the shortwave ice-cloud radiation are analyzed in details, in which the HG approximation is widely used in radiative calculations. To the optical properties of the single ice crystal, the HG approximation causes large errors on 3rd and 4th coefficients of the Legendre expansion of the phase function, and the maximum values of the errors are -0.28 and -0.33, respectively, while the maximum values of the relative errors are -55.7% and -73.8%, respectively. The errors of 4th coefficients are higher than those of 3rd coefficients, and the errors in near-infrared waves are higher than those in visible waves. To the bulk optical properties of the ice clouds, the HG approximation causes large errors on 3rd and 4th coefficients, and the maximum values of the errors are -0.18 and -0.22, respectively, while the maximum values of the relative errors are -27.9% and -37.1%, respectively. The errors of 4th coefficients are higher and so as in visible waves, which are same to the single ice crystal. The HG approximation also causes large errors on the radiative calculations. The maximum value of the errors on the shortwave downward fluxes is -2.78 W·m-2, and on the shortwave upward fluxes is -1.06 W·m-2, while on the shortwave heating rates is 0.27 K·d-1. The HG approximation underestimates the shortwave downward fluxes and overestimates the shortwave heating rates. Therefore, phase function accurately describing on ice clouds radiation transfer is necessary.
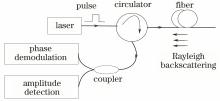
Phase-sensitive optical time domain reflectometry (φ-OTDR) uses narrow line-width laser with high coherence. In the sensing fiber, scattered lights from optical pulse interfere, and the interference light is highly sensitive to external disturbance. But the traditional amplitude-detection φ-OTDR is not quantitative detection, so that phase demodulation is necessary. Phase demodulation system based on 3×3 Michelson interferometer is cost-effective, but is of lower spatial resolution than the traditional amplitude-detection φ-OTDR. We propose a four-channel detection method to preserve the same spatial resolution as amplitude-detection φ-OTDR by adding only one detection channel. But the interference of scattered lights may have critical influence to phase demodulation. A four-channel detection system of phase demodulation φ-OTDR is analyzed based on 3×3 Michelson interferometer, from the aspect of Rayleigh backscattering light. The experiment shows that the disturbance around the fiber is detected quantitatively, with a linearity of 0.9956, phase sensing range of 31.85 rad, and the spatial resolution is same as that of amplitude-demodulation φ-OTDR.
The ultraviolet interference field behind the phase mask for fabricating fiber Bragg grating (FBG) and the interference contrast are studied. The relationship between the interference contrast of light field and the refractive index modulation of FBG is taken into account in this paper. The experimental results show that increasing the distance between the optical fiber and the phase mask makes the interference contrast decrease. The reduction of interference contrast leads to an increase of loss in FBG. The numerical investigations also demonstrate that the increase of non ±1 order diffraction energy, the deterioration of the time and the spatial coherence of ultraviolet (UV) laser and the increase of oblique incident angle of UV light beam could reduce the interference field contrast. In order to fabricate low-loss fiber gratings, these unfavorable factors must be overcome. The results provide the technical basis for the selection of ultraviolet laser source, phase mask and optical path alignment in the FBG fabrication used in high power fiber lasers.
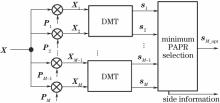
Peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR) reduction is a challenge for intensity modulation/direct detection (IM/DD) optical orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) systems. Selective mapping (SLM) is a classical algorithm that can effectively reduce PAPR with high complexity. We propose an improved SLM scheme which employs discrete multitone modulation (DMT) to obtain several candidate signals through an inverse fast Fourier transform (IFFT) and cyclic shift addition operation, thereby reducing the computational complexity significantly. Both simulation results and experiments show that the proposed scheme achieves better PAPR reduction performance with low computational complexity and improves the receiver sensitivity.
A human action recognition algorithm is proposed based on the decision-making level fusion with spatial and temporal features. Shape context feature of human body is extracted to match the contours of template images and test images in the spatial domain, while the motion feature is described by a changing spatial feature sequence in the time domain. Then, the motion feature is combined with the robust spatial feature for effective human action recognition. At the recognition stage, the dynamic time warping is applied to calculate the posterior probabilities of two kinds of features for each class. The weighted-average method is used to fuse the two posterior probabilities at the decision-making level, and the corresponding class with the maximum probability is recorded as the final classification result. Aiming at the dynamic time warping algorithm, we propose an improved searching strategy based on the elliptic boundary constraint, which can effectively reduce the space for searching for the optimal path, while eliminate the noise interference in the video sequence. The constraint performance of elliptical boundary is analyzed from two aspects of computational complexity and recognition accuracy. Experimental results show that the performance of elliptical boundary constraint is better than that of the parallelogram and diamond boundary constraints, and the optimal boundary size range is given. Experimental results on Weizmann, KTH and UCF101 datasets demonstrate that the average recognition rate of the proposed method is higher than 93.2%, 92.7% and 81.2%, respectively, indicating that the proposed method can effectively obtain the efficiency and stability of indoor intelligent monitoring system.
In the early studies, when the double-pass system with the same diameter is used for the measurement of the human eyes aberration, the odd aberrations (such as coma) are cancelled because the odd aberrations of the two channels cancel each other out. A new model eye is proposed to verify whether the human eye′s odd aberrations are cancelled in double-pass system. Entrance pupil size (1-8 mm) is changed and exit pupil is fixed to 6 mm. The results shows that human eye′s odd aberration could be measured by a typical double-pass system, that is Hartmann wave-front sensor system. Human eye′s odd aberration is not related to the size of entrance pupil and exit pupil. Finally, the conclusion that the double-pass system does not cancel human eye′s odd aberration is obtained.
Disparity is one of the main factors which affect the visual comfort of stereo content. Combined with the visual attention mechanism, the influence of disparity factor on visual comfort of three-dimensional (3D) image is studied through a large number of subjective experiments and a quantitative range is obtained. First, the salient stereo image is obtained through a stereo salient region extraction algorithm, and an eye tracker is used to verify its rationality. Then, the pixel shifting method is used for disparity conversion on the salient stereo image. A large number of subjective experiments are carried out with the converted images. Finally, the comfort disparity range is obtained after process of the experimental data. The experimental results show that the human visual system responds very differently to horizontal disparity and vertical disparity, and the comfortable range of horizontal disparity is (-0.379°,0.644°), while the comfortable range of vertical disparity is (-0.10°,0.11°). The correct rate of verification experiment is over 90%, which indicates the obtained comfortable disparity ranges reflect the comfort of stereo image well, and can provide a quantitative standard for the making of 3D contents.
Spectral computed tomography can distinguish the different photon energy in the data acquisition process, and get the projections of multiple energy channels simultaneously. As a single energy channel, it only contains a small part of the total number of photons, and most of the photon counting detectors can only carry a limited count rate, multi-channel projections often contain large amounts of noise. In order to rebuild the high-quality energy spectrum images from noise projections, and to reconstruct the images with different energy channels, we propose a weighted non-local total variation (NLTV) reconstruction algorithm based on the structural prior information. We design a simple model and a complex one, and both of them are simulated by TV algorithm, NLTV algorithm, weighted NLTV algorithm and weighted NLTV algorithm based on the structural prior information, then compare their reconstruction effects. Results show that this algorithm has obvious advantages for the reconstruction of complex model and high noise model.
Speckle noise is one of the main limiting factors for the image quality of Fourier domain polarization-sensitive optical coherence tomography (FD-PS-OCT). It reduces image contrast and makes tissue boundaries blurred. In order to improve the image quality, a split-spectrum method for speckle noise reduction is proposed. The method splits FD-PS-OCT interference spectrum into several narrower spectrum. Then a filtering window function is performed on every individual narrower spectrum. After the traditional FD-PS-OCT data processing, the several individual spectrums can be averaged to suppress speckle noise. Simulations and experiments show that the proposed method can reduce speckle noise effectively and improve the image quality.
In order to solve the problem of online calibration of angle measuring system, we propose a self-calibration method based on multi-head layout. Through the measurement data of multiple sets of sensors, the relationship between the measured value and the error is established with the properties of circle closure and Fourier series. Based on the principle of multi-reading head, the self-calibration reading head layout is optimized to suppress the error and achieve a single reading head self-calibration sensor. To carry out a test verification, we design a one axis turntable. The experimental results show that the angular error of the sensor is 6.10″ with the proposed self-calibration method. In the same measurement environment, the calibration accuracy is close to the traditional harmonic calibration method with external reference. It is proved that self-calibration method can effectively suppress the angle error and improve the measurement accuracy.
To improve the anti-noise ability of the digital image correlation method, we analyze the influence of gray gradient calculation error on the measurement accuracy of the digital image correlation method. An improved algorithm is proposed to calculate the gray gradient of the image by the Tikhonov regularization method and the sub-pixel displacement of the image by the inverse compositional Gauss-Newton (IC-GN) method. On the basis of the numerical simulation of the speckle pattern, the relative calculation error of the gray gradient is studied, and the measurement accuracy of the digital image correlation method is analyzed after calculating the gray gradient of the image by the Tikhonov regularization method. The proposed method is verified by experiments in the noise environment. The results show that the gray gradient has great influence on the measurement accuracy of the digital image correlation method. Meanwhile, the measurement accuracy and the anti-noise ability of the digital image correlation method can be effectively improved by the Tikhonov regularization method.
In order to verify the polarization and radiation calibration precision of the directional polarization camera (DPC) under natural targets, a verification experiment of measurement precision is designed. The data of the degree of polarization and radiation luminance for sky are obtained by imaging the sky in a clear weather and these data are compared with the simultaneous observation data by the CE318 sun-sky radiometer. The results show that, the average difference of the degree of polarization for the three polarization bands is smaller than 0.02, which meets the requirements of the polarization measurement precision of DPC, but the radiation luminance difference is big. After the correction of system deviation, the effect of the spectral non-matching between the calibration light source and target, and the effect of the inconsistency of the observation waveband and the observation visual field of two instruments, the average difference of radiation luminance for 490 nm and 670 nm channels of two instruments is less than 1%, and for the 865 nm channel is less than 2%, which verifies the validity of calibration data of DPC and the measurement precision of instruments.
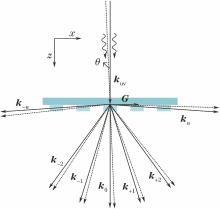
A beam smoothing scheme for multi-color laser quad based on combination of hybrid gratings is proposed, which can achieve a combination of transverse and rotary moving of the speckles on target plane. The physical model of the transverse moving speed of the speckles on target plane is built up, and the analytical expression for the transverse moving speed of the speckles on target plane is also derived. Furthermore, the variation of the transverse moving speed of the speckles on target plane is discussed. On the basis, the influences of different combinations of hybrid gratings on irradiation uniformity on target plane are analyzed, and the parameters of hybrid gratings are optimized. Results indicate that, compared with the traditional scheme of smoothing by spectral dispersion based on linear gratings, the moving speed and direction of the speckles on target plane are more complicated based on hybrid gratings, resulting in the further improvement of the smoothing effect. Compared to the typical schemes of beam smoothing, the optimized scheme of beam smoothing for multi-color laser quad based on the combination of hybrid gratings can effectively improve the irradiation uniformity and reduce the ratio of hot spots. Additionally, the power spectral density is proposed and used to preliminarily analyze the longitudinal intensity distribution characteristics of laser quad, and it is found that the beam smoothing for multi-color laser quad based on the combination of hybrid gratings can effectively decrease longitudinal peak intensity of laser quad.
In a precision pointing system for space laser communication, the hysteresis nonlinearity of the steering mirror driven by the piezoelectric actuator (PEA) can not only reduce its pointing accuracy greatly, but also affect the acquisition of beacon light and link stability. To address this issue, an improved Prandtl-Ishlinskii (P-I) model based on the PLAY hysteresis operator and a parameter identification method are presented, and on this basis, a feedforward linearized inverse compensation method for the steering mirror is proposed. In order to further improve the tracking accuracy of the system, on the basis of linearization, a static output feedback controller is designed to form a composite control method, and a laser communication terminal precision sighting system experiment is designed to verify the effectiveness of the composite method, in which sine signals with different frequencies and amplitudes are input. Experiment results show that the maximum fitting error of the improved P-I model is less than 1%. Inverse compensation of the feedforward model can reduce the linearity error of the PEA from 5% to less than 1%. Tracking errors of the system based on the compound method are reduced by 80%.
As the development of computer and machine vision technology, the rapid, accurate and intelligent characteristics of computer vision technology are widely used in the field of industrial detection. The three main applications of machine vision are measurement, guidance and inspection. The visual measurement technology can ensure the qualified products of the factory by measuring the key dimensions, surface quality and assembly effect of the product. The visual guidance technology can significantly improve manufacturing efficiency and body assembly quality by guiding the machine to complete automatic handling, optimum matching assembly and precise drilling. The visual inspection technology can monitor the stability of the body manufacturing process, and can also be used to ensure the integrity and traceability of the product to reduce the cost of manufacturing. Predictably, with the performance improvement of the core hardware such as cameras, lenses, computer and the development of software technology such as image processing and deep learning, machine vision technology will play a more important role in all areas in the future and there will be a wider space for development.
The authors comprehensively review technique of automated optical (visual) inspection(AOI) technique from aspects of the basic principle, optical imaging method, key techniques of system integration, image processing and defect classification at the application background of automated online surface defect inspection in intelligent manufacturing industry. The key technologies of system integration in automated optical inspection, such as visual lighting, high speed imaging in a large field of view, distributed high-speed image processing, precision transmission and positioning for the inspected objects, and networked control, are briefly summarized. The basic optical principles, functions and applications of the optical imaging methods commonly used in automated optical defect inspection are comprehensively reviewed. The image processing, defect geometric feature definition, feature recognition and classification algorithm for surface defect inspection are systematically summarized. Particularly, the methods of texture background removal in the images with periodic textures, and the detect detection, recognition and classification methods for complex and random texture surface based on depth learning are reviewed.
The development status of mirror binocular vision measurement technology is reviewed. The measurement models of the binocular vision structure based on mirrors, including structures using plane mirrors and curved mirrors, are analyzed in the aspects of measurement principle and sensor, measurement model and calibration, measurement accuracy and evaluation, etc. The advantages and disadvantages of the existing mirror binocular measurement system are summarized with respect to the structure model, image acquisition and corresponding matching. In addition, the development trend of precision measurement technology based on mirror binocular vision is described.
In order to solve the problem that images shot under industrial environment is considerably influenced by noise and distortion, precision of traditional algorithms for calibrating matching parameters cannot meet field measurement demand, a new method for calibrating large field of view image matching parameters based on non-metric correction is proposed. A layout plan of colinear feature points is designed, and based on non-metric correction, image coordinates of colinear feature points can be undistorted, which can be recognized and matched automatically with the aid of layout plan. Modified random sampling consensus algorithm based on regional division is proposed, and matching parameters can be calibrated. Experimental results show that matching precision is increased by 51% at least, which meets precision requirements under industrial environment.
The composite fringe projection techniques have been widely studied and applied in many fields because multiple fringe patterns can be extracted from single color image. Crosstalk between color channels exists in projecting and imaging systems in order to cover all the range of spectrum. Therefore, the obtained fringe patterns are deformed and the measurement accuracy of three-dimensional (3D) shape data is affected. The compensation method of crosstalk between color channels in color composite fringe projection 3D measuring profilometry is reviewed. The crosstalk between color channels is analyzed with respect to the camera and projector in color fringe projection system. The corresponding crosstalk elimination methods are classified and summarized. The effects of these elimination methods are also compared. The reviewed methods have important application value in choosing the appropriate crosstalk elimination methods and improving the accuracy of color composite fringe pattern projection profilometry.
Two-dimensional phase unwrapping is the key step of the later data processing in the existing advanced metrology technologies such as optical interferometry, optical three-dimensional sensing measurement, satellite radar interferometry (SAR), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). In this paper, the anti-noise performance of three common spatial phase unwrapping algorithms, branch-cut phase unwrapping algorithm, minimum discontinuity algorithm, and fast phase unwrapping algorithm, are compared by simulating the situation of noise interference. The result shows that the minimum discontinuity algorithm has the best performance in anti-noise, but its time consuming is far greater than the other two algorithms. Two hybrid algorithms, combining the minimum discontinuity algorithm with the branch-cut phase unwrapping algorithm and the fast phase unwrapping algorithm respectively, are proposed considering the advantages and disadvantages of the three algorithms mentioned above. In these two proposed algorithms, the advantages of fast speed of branch-cut phase unwrapping algorithm and fast phase unwrapping algorithm are fully taken into account, and the advantage of the strong anti-noise of the minimum discontinuity algorithm is also exploited. These two combined algorithms guarantee both the speed and accuracy of the phase unwrapping. The effectiveness of two combined algorithms is verified by the results of simulation and actual experiment.
The anomaly in the crowd is a great potential threat, and the automatic detection of abnormal behavior for surveillance has become a hot topic in recent years. However, because the anomaly is unknown and complex, the previous detection methods still suffer from a low detection rate and poor location accuracy. To this end, a method is proposed for anomaly detection and location in the crowded surveillance videos. First, the motion regions are extracted according to the distributions of the gray-scale value and the optical flow field. Second, the effective motion blocks are obtained by segmenting the motion regions. Two features, namely the local H histogram of gradient G and the local H histograms of flow F, are extracted from the motion blocks, representing the appearance and dynamics. Third, the motion blocks are clustered with the k-means method, and each cluster is modeled using a one-class classifiers. Finally, the motion continuity constraint is added to suppress the noisy noises. Experimental results on two complex abnormal behavior datasets show that the proposed method is obviously better than previous detection methods. It could meet the practical engineering needs such as high accuracy and strong anti-interference ability.
An adaptive fringe projection method is proposed to avoid measurement errors, which is caused by non-uniform surface reflectivity of colored objects, and to enhance accuracy of a 3D measurement system. RGB images are captured by a camera, and optimal color and intensities at each pixel are calculated according to reflectivity characteristics. A set of horizontal and vertical fringe patterns are captured and the corresponding absolute phase are calculated. Optimal color and intensities at each pixel in the camera pixel coordinate system are transformed into the projector coordinate system by using calculated absolute phase. The adapted fringe patterns are projected by projector for measuring object's 3D shape. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method can effectively measure the 3D shape of colored objects and has high measurement accuracy.
To solve the problem of complicated initialization in existing parametric calibration models of the Scheimpflug camera, a new method based on general non-parametric imaging model is presented, which avoids the complicated initialization process and models the Scheimpflug camera as a set of image pixels and their associated projection rays in space. Thus, the calibration underlying general non-parametric imaging model simply refers to computation of the mapping between the pixels and the corresponding three-dimensional projection rays. Based on the assumption that multiple control points in respective local coordinate systems corresponding to same the pixel from different views should be collinear in a certain common coordinate system, a two-step calibration method using checkerboards is presented. A rough calibration is performed by using images of checkerboards with a sufficient overlap, and the rest image with largest overlap is iteratively added to calibration process to the complete the initial calibration. Then, a refinement of calibration is carried out through bundle adjustment. The real data experiments including calibration, reconstruction and pose estimation are performed, and the results demonstrate that the presented method is flexible, effective and accurate.
The phase shifting shadow moiré is an efficient technique for three-dimensional (3D)object surface measurement, of which the performance can be improved further. This paper focuses on improving its measurement accuracy without adding the complication of the experimental set-up. An effective method, based on the idea of random phase shifting, is proposed. In the method, the parameters of shadow moiré system are calibrated by stereo vision technique and the phase of the fringe pattern is extracted by three-frame random phase shifting algorithm. We assume that the introduced phase shifting is unequal and unknown, so the stringent requirements for the shifter are relaxed. The proposed method can lower the application requirement of shadow moiré. Besides, the proposed method is not affected by the background light in the phase demodulation process, and is insensitive to the non-sinusoidal light intensity distribution of the fringe pattern, and has the advantages of high accuracy and easy application. Experiments show that the proposed method has high accuracy and high speed and is superior to the existing typical algorithms.
Feature point extraction is the key technology for visual detection and location of weld seam, especially for micro gap in commercial production. Most of the current methods have considerable errors and cannot guarantee the highly-required extracting precision, even fail to recognize the position of micro gaps. Based on autonomous threshold value, the improved median filtering algorithm and feature points extraction algorithm are proposed to deal with the scanning image. Firstly, on the basis of traditional median filtering, the range of threshold value is set by calculating regional mean value and variance, this method is good at protecting the image detail of narrow gap as well as removing noise points. Then, a new method named magnifying details by threshold value is proposed. This method enlarges the gap between feature points of micro gap and nearby data, which enhances seam image details and makes the process of extraction easier. Finally, the error is reduced to 1/5 of that before utilizing time-domain analysis. Experimental results show that this method meets the requirement of high precision, which can greatly recognize the weld seam varying from 0.1 mm to 0.5 mm with an error less than 0.08 mm. It also has the advantages of good adaptability, strong anti-interference ability along with great practical significance in the field of automatic welding of narrow gap.
In order to acquire high precision robot pose measurement when robot moves in large range, we propose a large field of view vision method based on zoom lens. Homography matrix between image matching points is used to dynamically calculate internal parameters while zooming. Camera coordinate system transformation is united according to target pose before and after zooming. In addition, by taking distortion into consideration, we introduce PnP algorithm which is related to zoom parameters and implement parameters optimization. We also propose a two-step zooming control strategy based on zoom and focus for dynamic pose measurement, as well as a target plate position measurement algorithm based on image template, which can detect and distinguish the mark points in any visible effective position of the target. Large number of measurement experiments including signal point error experiment and large scene tracking experiment are carried out to verify the effectiveness of the system. The experiment data show good performance in both pose measurement error and measurement range. Under different zoom parameters, the precision of single point measurement is high, as the average position precision is up to 21.8 μm. In the range of 400-1600 mm, position error is 0.09 mm which cannot be realized with ordinary fixed focus camera. Multiple experiments show that zoom camera can be used to measure during the range of 178.7461 to 9022.31 mm. The proposed method has an extensible measurement space and an advantage of position and orientation measurement in the case of variable measurement range with limited camera motion.
The slight sudden changes in the surface of metal object can be highlighted by the distortion of reflection stripes. Therefore, the reflection stripe technique can be applied in the surface inspection of reflective objects. We propose a machine vision detection method for the surface indentation of cold stamping valves based on reflection stripe image. Along the way, stripe image information of cold stamping valves is extracted, and defect features are recognized automatically. A series of preprocessing methods, such as noise filtration and multi-scale Retinex algorithms, are adopted to improve the image quality. Characteristic parameters, such as fringe-centerlines, sum of pixels, and projection vectors in child windows, are selected to reduce the computation complexity and improve the robustness of the computing system. The experimental results show that this detection method for the surface indentation of cold stamping valves based on reflection stripe image has high accuracy and high efficiency. This method can achieve effective identification of subtle indentation on the surface of cold stamping valves to an accuracy of 0.1 mm, and detection time efficiency (one valve takes 2 seconds) meets the online detection demand for the cold stamping valve production line.
To improve the automation level and measurement accuracy of the visual measurement system, a novel method based on template matching and peaks of gradient histogram is proposed to extract the corners of diagonal markers automatically. The rotation-invariant template matching method is used to get the coefficient correlation matrix of the original image and the standard template, and the candidate positions of markers are obtained by two thresholding selection. The false candidates are eliminated and the initial coordinates of markers are found depending on the properties, which are two lines intersecting at the center of the marker and their gray gradient of the marker with multiple peaks. The subpixel is located by generating ideal templates of diagonal markers and applying the correlation coefficient fitting extreme value method. The experimental results show that the proposed method can automatically extract the corners of diagonal markers or checkboard images in a complex environment.This method has the merits of few adjustable parameters, strong robustness, precision and universality. It can be used in measuring situations where the environment light source greatly in engineering practice.
Owing to its ability of focus change not relying on any mechanical movements, liquid crystal lens is expected to be used in many fields such as robot vision, automatic pilot, and depth measurement. In the liquid crystal lens vision imaging system, in order to obtain high-contrast images without a polarizer, an optimization algorithm for polarizer-free imaging of liquid crystal lens is proposed. Image edge reflects the main contour information, and it decides the contrast of the image, so in the algorithm image edge is extracted first, then image processing is carried out with out-of-focus image and in-focus image in the edge parts, but not in the smooth area. Low frequency components caused by non-modulated ordinary wave are removed to improve image edge contrast and suppress noise in the smooth area. Experiments show that the optimized algorithm enhances the contrast of image edges, and the image noise is reduced by 50% compared with the algorithm before optimization.
Aiming at the drawbacks that for probabilistic Hough transform it consumes a lot of memory and the line endpoints searching is vulnerable to interference from reticular aggregation points, a probability-based local Hough transform optimization algorithm is proposed. The edge is classified into two categories: sortable and non-sortable. For the former, sampling points are randomly picked and combined with their adjacent points for straight line searching. For the latter, the local probabilistic Hough transformation is carried out in the region of interest which is established around the random edge point, the endpoints are searched after the line is detected and the slope is fixed in real time. The error lines resulting from mesh aggregation points are excluded by the interval counting and the total interval length limit method. Experiments were carried out by 500 images. The proposed algorithm consumes less than 1/3 of the time of the probabilistic Hough transform, and it is highly resistant to line mis-detection of meshed aggregation edge points. Line detection is more accurate and memory consumption is reduced by more than 90%, compared with the probabilistic Hough transform.
For the stereo matching method of deep learning based on patches, the network structure is vital for the calculation of the matching cost, and the time-consuming of convolutional neural network (CNN) in the image processing field also needs to be solved. We propose a stereo matching method of CNN based on a “shrink network”. The CNN method is utilized to train the similarity of the left and right image patches, and the matching cost of the stereo matching is obtained by the similarity. At the feature extraction stage, by adding batch normalization layers to each layer, the gradient dispersion in the backward propagation can be improved effectively. Besides, the full-connection layer adopts a "layer-by-layer reduction" form with other network optimizations to increase the speed while ensuring the accuracy. We utilize the KITTI datasets to test the algorithm. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method increases the accuracy and speed fairly compared to some other methods.
The image background of the crack on the sagger bottom is complicated, the distribution of cracks is dense and intermittent, and characteristics of cracks are not obvious, so crack extraction of the sagger bottom is difficult. To solve the problems, a method for detecting sagger cracks based on sector neighborhood difference histogram is proposed. A multi-scale, multi-direction sector filter is constructed according to the spatial clustering characteristic and directional characteristic of the crack pixels. By calculating the convolution of the filters with the image, a sector neighborhood difference histogram that can reflect the crack distribution probability feature is obtained. Crack extraction is realized depending on the difference in crack distribution probability characteristics between the crack pixels and non-crack pixels. Finally, the global and local length and distribution area characteristics of the cracks are integrated to evaluate the degree of cracking. The experimental results show that the proposed algorithm can achieve good extraction results for all types of cracks on the sagger bottom. The precision and recall of the algorithm can reach higher than 90%, which is better than some of the existing good methods for crack extraction. The assessment results of the method for assessing the severity of cracks are also basically the same as those of a person's subjective assessment.
Aiming at the laser stripe images with the local bending obtained by the laser triangulation measurement system, a method based on the Fourier-polar transformation algorithm to measure the local bending is proposed. Through the computing, the normal direction of laser stripe is obtained. The gray projection of the spatial-domain image along the normal direction is conducted, and the magnitude of the local bending is obtained directly. This method has advantages of a simple computing process and high immunity to random noises and the non-uniform intensity distribution of laser stripe. The theoretical analysis and experimental test verify the effectiveness of this method.
In speckle interferometry, there are a large number of speckle noises in the speckle phase map, which need to be filtered. However, the existing filtering evaluation indexes are not suitable to determine the continuous filtering process of single image, and the automation of the filtering process is difficult to be achieved. Therefore, a filtering evaluation method based on smoothing spline fitting is presented in this paper. Firstly the smoothing spline fitting method is used to process the distribution of the phase map . Secondly, the root-mean-square error is used to evaluate the result of continuous filtering process by the smoothing spline fitting. Finally, the experimental images of speckle interferometry are used to verify the proposed method. The results of the experiment show that the method can realize the quantitative analysis of the filtering effect and the judgment of the completion of the image filtering in continuous filtering process, and the effectiveness and universality of the method are also verified.
The phase measurement profilometry (PMP) based on binary gratings with an unequal duty cycle is proposed. The adopted binary gratings have only two grayscales of 0 and 255, and the effect of the gamma nonlinearity on the grayscale of the sinusoidal grating is eliminated. At the same time, the refresh frequency of the projection system can be increased by an order of magnitude. The measurement accuracy of this proposed method is higher than that of the Roach grating defocus projection Fourier transform profilometry and the repeat accuracy is higher than that of the traditional PMP based on sinusoidal gratings.
We present a three-dimensional (3D) shape measurement technique based on parallel four-color channels (red, green, blue and infrared) fringe projection, which only needs one-time measurement to reconstruct the 3D surface shape of an object. The proposed technique overcomes the shortcomings of slow measurement speed caused by multi-frame fringe images projection in the traditional fringe projection, and possesses high accuracy. Two-step phase shift, Fourier transform with the optimum three-frequency method are combined to calculate the absolute phase point-by-point independently and recover 3D shape measurement of complex objects, such as discontinuities, from the deformed composite color fringe pattern and infrared fringe pattern captured simultaneously. A beam splitter has been used to realize coaxial design and to build the projecting transformation between the visible light projector and the infrared light projectors, so that they build up the accurate pixel-to-pixel correspondence. Several experiments on static and dynamic objects are performed to obtain the 3D shape, and experimental results show that the proposed method is suitable for fast 3D shape measurement.
Knowledge of pulmonary fissure anatomy plays an important role in localization of lesions and evaluation of lung disease. In computed tomography images, pulmonary fissure detection is an intricate task due to factors such as pathological deformation, partial volume effect and noise. To solve the problem, a novel method based on shape features is proposed for pulmonary fissure detection. Firstly, the orientation information and magnitude information of pulmonary fissures are fused to enhance pulmonary fissures and suppress interferences. Then region property analysis algorithm is used to remove interferences like airways and vessels for pulmonary fissure identification. Finally, surface curvature approach is utilized to remove adhering interferences for pulmonary fissure segmentation. The performance of the proposed method is validated in experiments with a publicly available LOLA11 dataset. Compared with manual references, the proposed method acquired a high median F1-score of 0.8451. Experimental results show that the proposed method has a good performance in pulmonary fissure segmentation.
In order to effectively detect crack, a crack segmentation method using multi-scale structured forests and wavelet transform is proposed to improve robust performance of crack detection. The multi-channel feature extraction of crack image, and discrete mapping of the corresponding ground truth is carried out respectively with assistance of multiple crack image and ground truth. Triangle filter and down-sample are adopted to process regularity candidate features and correlation candidate features, which are used to train and validate structured forest classifier. And, structured forest classifier is used to crack segmentation of test images in multi-scale. According to experiment results in 776 structural crack image and 600 steel beam image datasets, the proposed method can obtain highest segmentation accuracy in a short time than single multi-scale structured forest method and other segmentation methods.
An airport detection method is proposed for the navigation of fixed-wing unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) autonomous landing in this paper, which aims at improving the efficiency of detection. A hierarchical architecture is adopted to obtain airport candidate regions which reduces the search space gradually. The pseudo horizon is detected to limit the searching space to the ground area, then candidate approximate airport area is acquired based on the fact that the airport area contains lots of orthogonal line segments. Edge Boxes is adopted to obtain proposals with good localization on the candidate approximate airport areas. Locality-constrained linear coding (LLC) is used for feature extraction with scale-invariant feature transformation (SIFT) as the basic features and linear support vector machine (SVM) is used to finish the task of airport detection. We evaluate the proposed method under different conditions and compare it with other methods. The results show that our method improves the efficiency of airport detection and has a higher average precision.
An editable projection display technology of free-form surfaces based on height information is proposed. The plane calibration technology based on fringes projection is used to establish the phase-height mapping table within the measurement range. The horizontal phase and vertical phase distributions on the free-form surface can be obtained by using the high-precision phase-shifting technique and the three-frequency temporal-phase unwrapping method. The geometry and intensity transfer relations between the projector pixels and the CCD camera pixels are established by the inverse fringe projection technology. By this display technique, the expected encoded image based on its height information can be projected on the free-form surface to realize an editable projection of high information and a 3D display. Some examples, such as the contour and the pseudo-color encoding projection on free-form surfaces the dynamic projection of glacier snowline variation and the add of simulation entities are given.
The region of interest (ROI) is first extracted under the combination lighting mode of high and low angle light sources and then the median filter kernel of scratch morphology is constructed to obtain the accurate background images from ROI. The scratches are extracted after the background difference. An improved region growing algorithm based on directional gradient is adopted to achieve an effective connectivity for the same scratch, which reduces the miss rate of scratch detection. By analyzing the confidence of main scratch detection parameters such as area, length-width ratio and so on, a scratch detection method based on weighted fusion of multi-features is proposed. The results show that, for this method, the accuracy of scratch detection is 95.7%, and the processing time is less than 1.21 s, which meets the accuracy and efficiency requirements for the engineering application.
An unstructured path recognition and robot vision guidance method based on the fuzzy-rough set is proposed. With the image definition automatic control algorithm based on the self-adaptive surface array charge-coupled device, the images with the best amount of information are obtained. The unstructured path recognition model based on a fuzzy-rough set is built, in which the image target, background and uncertainty area are predefined under the help of the rough set theory and the relative fuzzy connectedness competition mechanism is fused to reclassify the pixels in the uncertain region according to the ambiguity and the robot navigation path is delineated. With this model, the automatic recognition of the unknown and unstructured path areas can be realized, and the gray priori features to recognize the specified path areas can be introduced. The results show that the proposed method has a practical significance for improving the autonomous exploration ability of mobile robots in unstructured environments.
A kind of photonic crystal (PC) film, which is compatible stealth in middle and far infrared bands, is designed and prepared based on the transfer matrix method and the evaporation film technology. The practical thicknesses and the middle and far infrared spectral characteristics of this kind of PC thin film are measured, which are in a good agreement with the theoretical design values. The results show that, compared with two kinds of conventional infrared stealthy material as the infrared stealth coatings and the conventional camouflage fabrics, the PC film has the strongest ability to suppress infrared radiation at both middle and far infrared bands. The influences of outdoor environment irradiation on the stealth effects of PC film at the bands of 8-14 μm and 3-5 μm are relatively weak.
The Sn2+-doped SiO2-B2O3-Gd2O3-La2O3 glass is prepared in the reducing atmosphere and its density, absorption spectra, photoluminescence, fluorescence lifetime and radioluminescence excited by X-ray have been tested. The research results show that, in the SiO2-B2O3-La2O3 glass system, with the increase of Sn2+concentration, the ultraviolet absorption cut-off wavelength is redshifted, and the photoluminescence intensity first increases and then decreases due to the concentration quenching effect, which reaches the maximum at Sn2+ concentration of 0.3 %. With the replacement of La2O3 by Gd2O3, the glass density increases and the fluorescence lifetime of Sn2+ gets shorter, but Gd3+ does not show the sensitizing enhancement effect on Sn2+. Under the X-ray excitation, the radioluminescence intensity of Sn2+ increases with the increase of Gd2O3 concentration and does not decreases under the Gd3+ concentration quenching effect, which indicates that maybe there exists the energy transfer between Gd3+ and Sn2+ under the X-ray excitation.
Hyperspectral remote sensing image classification is usually based on the spectral features of objects, but there are plenty of spatial informations in the images. The effective use of spatial information can significantly improve the image classification effect. Because of the special structure of convolution neural network (CNN), CNN has been successfully applied in the field of image classification, and has a good effect on the classification of two-dimensional images. How to improve classification performance through deep learning combined with spatial-spectral information is a key point. Combining the spatial features and spectral information of hyperspectral images, we have developed a three-dimensional convolution neural network model (3D-CNN) for hyperspectral pixel classification, and the multi labels conditional random field is optimized on the basis of the initial classification. Three general open hyperspectral datasets (Indian Pines dataset, Pavia University dataset, Pavia Center dataset) are selected for testing. Experiments show that the accuracy is greatly improved after the classification optimization, the overall accuracy can reach 98%, and the Kappa coefficient reaches 97.2%.
In order to study the enhancement effect of hemispherical cavity on plasma emission, we use hemispherical cavity with different diameters to confine the plasma generated by laser ablation alloy steel. It is found that the optimum enhancement factor of the hemispherical cavity on the plasma emission increases first, then decreases, then increases and finally decreases with the increase of the hemispherical cavity diameter. There is a linear relationship between the delay time corresponding to the best enhancement factor and the hemispherical cavity diameter. The results have shown that the hemispherical cavity has the best enhancement effect on the plasma emission when the diameter is 10 mm and the corresponding delay time is 10 μs. Spatial resolution measurement of the plasma emission spectra with and without hemispherical cavity are measured. It is found that the plasma without confinement evolved into an emission source with larger size and less intensity as a result of expansion. Whereas the plasma has a smaller size but higher intensity with hemispherical cavity confinement. It is demonstrated that the enhancement of the plasma emission is caused by the three-dimensional compression effect of the hemispherical cavity on the plasma, and the enhancement effect is affected by the diameter of the hemispherical cavity.
To overcome the problems of traditional multispectral imaging system, such as sophisticated algorithm and time-consuming for reflectance reconstruction, and high cost etc., we present a multispectral imaging system for measuring colors by using LEDs illumination and monochrome high-speed camera. Multiple monochrome LEDs are used to fit lighting source and to ensure that the spectral power distribution of the source is reciprocal of the spectral sensitivity curve of monochrome high-speed camera, and then the spectral reflectance of the object is reconstructed by using the camera response directly. The experimental results show that compared with a spectrophotometer, the method can achieve an average of 2.3 CIELAB color difference for 24 Macbeth ColorChecker chart. The whole system is simple and feasible, and does not need filters, and the spectral reflectance reconstruction algorithm is simple.