View fulltext
View fulltext
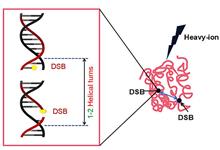
Heavy-ion beam radiation can cause cell DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs), which are factors that lead to genomic instability. Existing studies have demonstrated that homologous end joining, homologous recombination, single-strand annealing, and selective end joining play critical roles in the repair of DNA DSBs. However, the factors that affect the selection of repair pathways for DNA DSBs remain unclear. In this study, recent findings on DNA damage characteristics and repair pathways generated by heavy-ion radiation cells are reviewed, and the selection mechanism of DSB repair pathways in cells is explained in terms of the types and distribution of DNA DSBs, chromatin status, DNA terminal structures, DNA terminal excision, and cell cycles. This review is of great significance for the study of DNA damage repair and provides a reference for investigating the biological effects of heavy-ion radiation technology.
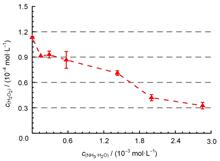
In this study, the γ-radiolysis of boric acid-lithium hydroxide-ammonia coolant was investigated under different conditions, including boric acid concentration, absorbed dose, and absorbed dose rate. The concentrations of H2O2, NO2-, and NO3- were determined using UV-visible spectroscopy and ion chromatography. With an increase in boric acid concentration, the concentrations of H2O2 and NO2- in the coolant system did not change significantly within a pH range commonly used in pressurized water reactor operation. Specifically, the concentration of H2O2 varied from 9.28×10-5 to 1.07×10-4 mol/L, while that of NO2- changed from 0.9×10-5 to 1.5×10-5 mol/L. In contrast, the concentration of NO3- fluctuated significantly, ranging from 4×10-5 to 8×10-5 mol/L. With an increase in the absorbed dose (1-30 kGy), the equilibrium concentration of H2O2 and NO2- in boric acid-lithium hydroxide-ammonia system increased to 1.28×10-4 mol/L and 1.30×10-5 mol/L, respectively. Meanwhile, the concentration of NO3- did not change significantly (4×10-5 to 6×10-5 mol/L). The concentrations of the three radiolytic products were not significantly affected within the given absorbed dose rate range (1.27 to 18.86 Gy/min). Overall, this work provides valuable basic data for optimizing the new boric acid-lithium hydroxide-ammonia coolant system.
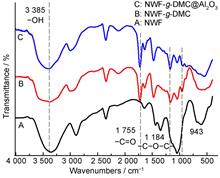
Chlorite and other disinfection byproducts have been listed as carcinogens by the International Center for Research on Cancer. The effective treatment of chlorite is imperative for the drinking water purification process. A series of Non-woven fabric - ethyl methacrylate trimethyl ammonium chloride - nano aluminum oxide (NWF-g-DMC@Al2O3) adsorbent materials were synthesized using the pre-radiation grafting–embedding reaction. In this study, water was used as the solvent to systematically discuss the effects of adsorption dose, monomer concentration, and other factors on the weight gain rate and subsequently evaluate the effects of different weight gain rates, embedding rates, and solution pH on the adsorption rate to obtain a complete static adsorption equilibrium curve. Infrared spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy, thermogravimetric analysis, and X-ray diffraction analysis were used to characterize the structure and adsorption properties of the synthesized samples. The results showed that the weight gain rate was the highest at a monomer concentration of 40 %. The adsorption rate was the highest at an adsorption dose of 100 kGy, embedding embedding amount 4 %, pH of 2, and initial concentration of 10 mg/L. The chlorite removal rate of the NWF-g-DMC@Al2O3 adsorbent was 89%. The new adsorbent is expected to be extensively used in the purification of drinking and industrial water.
Stereotactic body radiotherapy, a hypofractionated radiation therapy method with fewer fractions and a large single radiation dose, is the preferred method for treating patients with early-stage non-small cell lung cancer who are clinically unsuitable for or refuse surgery. Accuracy and repeatability requirements of the target position are, therefore, necessary. In view of this, adjuvant treatments such as image-guided and respiratory motion management technology and immobilization devices are used clinically to reduce the impact of respiratory motion. This paper summarizes the research status of these approaches and proposes future directions based on the problems existing in each technology.
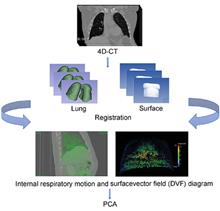
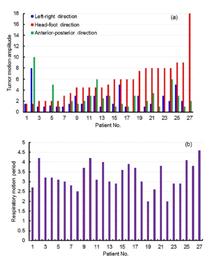
To assess the effect of respiratory movement on dose distribution via intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) in patients with lung cancer based on real respiratory movement parameters. Twenty-seven patients with lung cancer who underwent four-dimensional computed tomography (4DCT) and received IMRT were analyzed retrospectively to determine the three-dimensional tumor motion amplitude and respiratory period. Based on the above movement parameters, the dose distribution of the tumor on the respiratory movement platform in the head-foot and left-right directions was measured. The difference in IMRT dose distribution between the respiratory motion and static states was compared using the two-dimensional gamma analysis method, and the effect of respiratory motion on dose verification was analyzed. The mean respiratory motion period of patients was 3.3 s, and the mean tumor motion amplitude in the head-foot direction (5.6 mm) was greater than that in the left-right direction (2.1 mm) and the anterior-posterior direction (2.3 mm), with the maximum at 18 mm. The γ-passage rate tended to decrease gradually with the increase intumor motion amplitude. When the tumor motion amplitude was greater than 3 mm, the γ passage rate was less than 95% in most beams. The differences of γ-passage rates grouped by the median respiratory period were statistically significant in the left-right directional motion state. IMRT dose validation in lung canceris affected by the amplitude of tumor motion and the respiratory motion cycle. Respiratory motion management techniques are recommended for patients with a large respiratory motion amplitude to improve the accuracy of dose delivery to the target.
This study investigated the effect of poly-ADP ribose polymerase inhibitor (PARPi) on X-ray repair cross complementing 1 gene (XRCC1) expression and radiotherapy sensitivity of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). Tissue samples from patients with ESCC treated with irradiation using a linear accelerator were collected to detect the expression of XRCC1 and PARP-1 with immunohistochemical staining, and the effect of their expression on radiotherapy efficacy was evaluated. A linear accelerator was used to irradiate ECA109 cells after treatment with different concentrations of AZD2281 (a PARP inhibitor) to detect the radiotherapy sensitization ratio (SER) of PARPi. An RT-PCR assay was used to assess the relative expression of XRCC1 mRNA in ECA109 cells treated with irradiation and AZD2281 and to explore the effect of PARPi on the transcription of the XRCC1 gene in ECA109 cells after irradiation. Our data indicated that the objective response rate (ORR) of XRCC1-positive patients was lower than that of XRCC1-negative patients (38.1% vs. 88.9%, p=0.017), while the ORR of PARP-1-positive patients was lower than that of PARP-1-negative patients (36.8% vs. 81.8%, p=0.026). The SER of the cells treated with irradiation and AZD2281 at a concentration of 3 μmol/L was 1.744, implying that AZD2281 can enhance the irradiation damage of ECA109 cells. The relative expression level of XRCC1 mRNA increased significantly at 48 h after irradiation; however, when combined with PARPi, the radiation-induced up-regulation of XRCC1 mRNA was inhibited. The results of this study showed that patients with ESCC with a high expression of XRCC1 and PARP-1 display poor short-term radiotherapy efficacy and that irradiation can induce XRCC1 gene transcription. AZD2281 effectively inhibited the radiation-induced up-regulation of XRCC1 expression and increased the radiosensitivity of ECA109 cells. A possible mechanism is that PARPi inhibited DNA-PKcs and then down-regulated XRCC1 expression. These results suggest that PARPi may increase the radiotherapy sensitivity of patients with ESCC by inhibiting XRCC1 expression and reducing DNA damage repair.
In this paper, a new collimator based on Hygeia GMX-1 cobalt (60Co) radiosurgery system was designed and analyzed using the Monte Carlo simulation program GEANT4. The results of EBT3 film measurements showed that the field penumbra of the improved collimator was reduced by 17.6% and the absorbed dose rate was 2.12 times higher, while the source activity, source axis distance and field size remained unchanged. The collimator has significant advantages in the two key technical parameters of absorbed dose rate and penumbra.
The purpose of this study was to retrospectively investigate the prognostic significance of the lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio (LMR) in patients with middle and advanced thoracic malignant tumors (esophageal and lung cancer) prior to and after radiotherapy. The clinical data of 74 patients with middle-advanced stage lung and esophageal cancer who received radiotherapy in Jiangsu Shengze hospital from January 2017 to December 2021 were screened for this retrospective analysis. Peripheral blood was collected, and LMR was recorded before and within one week following radiotherapy. The receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) was established to obtain the best cut-off value for overall survival (OS). The correlation between LMR and prognosis before and after radiotherapy was examined. The Kaplan-Meier method was used to create the survival curve, and Cox proportional hazard regression model was used for univariate and multivariate analysis. The median follow-up time was 15 months, and the median age was 70 years. According to the ROC curve, the best critical value of LMR prior to radiotherapy was 2.46, AUC=0.719, while the best critical value of LMR after radiotherapy was 1.07, AUC=0.682. The Cox risk ratio model showed that clinical stage, diagnosis, combination therapy, and LMR before and after radiotherapy were all related to prognosis. Multivariate analysis revealed that clinical stage, combination therapy, and LMR before and after radiotherapy were independent prognostic factors in patients with middle and advanced lung and esophageal cancer following radiotherapy (p<0.05). LMR before and after radiotherapy was associated with the prognosis of patients with middle and advanced thoracic tumors. Patients who accepted radiotherapy for middle and advanced lung and esophageal cancer with high LMR had a better prognosis.
Multi-modal imaging technology was used to screen the cervical microlymph nodes of patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Based on the pathological results, radiotherapy was optimized to improve the quality of life of patients. CT or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) examination before radiotherapy was performed in 36 patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Fifty-one microlymph nodes with ≤1 cm diameter were selected. Following the ultrasonic detection of relevant indicators, ultrasound-guided puncture biopsy was performed to confirm the pathology. Based on the multi-modal evaluation results, the target area and plan of radiotherapy was confirmed. We evaluated the dose to organs at risk before and after target optimization. The difference in the detection results was compared, and the 3-year local control rate of the lymph node region of interest was observed. The Dmean and V30 of the parotid (left and right) and submandibular gland (left and right) and the V50 of the mandibular gland (left and right) had significant differences before and after optimization in the microlymph node target area of the neck (p<0.05). After 3 years of follow-up, four patients had cervical lymph node recurrence in the high-dose irradiated field. The recurrence rate was 11.11%, and no local recurrence was observed in the microlymph node area of interest. Thus, multi-modal imaging technology is a safe and reliable method to further optimize radiotherapy target planning to distinguish between benign and malignant cervical microlymph nodes of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.
The study aimed to analyze and compare dosimetric differences with various thicknesses and frequencies of bolus in post-mastectomy intensity-modulated radiotherapy. Based on the Oncentra4.1 treatment planning system, Thirty-eight post-mastectomy patients were selected randomly between 2017 and 2021. Three sets of simulated treatment planning with 5~~mm all, 5~~mm half, and 10~~mm half virtual boluses were formed. A total prescribed dose of 50 Gy regimen was delivered in 25 fractions over 5 weeks, in which half-time bolus was used for 15 out of 25 fractions. The dosimetric parameters of target areas, skin, and organs at risk were compared. Furthermore, normal tissue complication probability (NTCP) was evaluated for the skin. Regarding the D2, D50, V90, V95, and V115 of the clinical target volume, the 5~~mm all bolus group was prominently better than other groups, and the D50 and V90 of the clinical target volumes were statistically significant (p < 0.05). Regarding the D2, D50, D95, D98, Dmax, V90, V95, V115, homogeneity index (HI), and conformity index of the planning target volume, the 5~~mm thick bolus group was prominently better than other groups, and the D50, D95, D98, V90, V95, and HI of the clinical target volumes were statistically significant (p < 0.05). For organs at risk, there was no statistical significance for the three planning groups, but the 5~~mm all bolus group was prominently better than other groups in the V45 of the esophagus, V30, V40, and Dmax of the heart, V50, Dmax, and Dmean of the humerus head, V20, V30, and Dmax of the left lung, Dmax and Dmean of the thyroid, and Dmean of the trachea. Calculated with the 5~~mm all bolus, the mean dose, V40, V45, and V50 for the skin structure, were all higher than other bolus regimens, while the dose maxima (Skinmax and V55) were all lower than others. Regarding the skin radiobiological evaluation, the NTCP of the 5~~mm all bolus group was prominently better than other groups and was statistically significant (p < 0.05). Besides, the monitor unit of 5~~mm all bolus regimen was the minimum compared with other groups and was statistically significant (p < 0.05). Therefore, the 5~~mm all bolus group can not only improve the dose but also reduce the hot dose of skin and target volume, as well as reduce the NTCP. Our study provides a clinical reference in the delivery of post-mastectomy radiotherapy.
We used 60Co-γ ray and electron beam irradiation to mutate Bacillus velezensis to breed genetically stable mutant strains. The mutant strains were screened and re-screened by plate confrontation and the four-point method to study their antibacterial effects on Colletotrichum gloeosporioides. The results demonstrated that the D10 value of Bacillus velezensis suspension irradiated by 60Co-γ ray was 2 366 Gy, and the lethality rate increased with an increase in the irradiation coefficient dose in the range of 100-2 000 Gy. The lethality rate of Bacillus velezensis was 81.8% at 2 000 Gy irradiation coefficient dose, and five mutants (B004, B112, B114, B117, and B118) were screened. The inhibition rate against Colletotrichum gloeosporioides increased from 51.2% of the original strain to 57.5%, 58.0%, 57.0%, 57.7%, and 59.9%, respectively. The Bacillus velezensis suspension was irradiated by an electron beam (10 MeV), the D10 value was 499 Gy, and the lethality rate increased with an increase in the irradiation coefficient dose in the range of 100-600 Gy. The lethality rate of Bacillus velezensis was 91.8% at 400 Gy irradiation coefficient dose. Two mutant strains (D115 and D243) were screened, and their inhibition rates against Colletotrichum gloeosporioides increased from 55.2% of the emitted strains to 58.4 and 58.1%, respectively. The inhibitory effects of B004, B112, B117, and B118 mutants on Colletotrichum gloeosporioides were genetically stable within six generations. In conclusion, γ-ray and electron beam irradiation have potential application value in the mutation breeding of Bacillus velezensis. The results provide a basis for Bacillus velezensis mutation breeding and a theoretical reference for the biological control of Colletotrichum gloeosporioides.
The foreign materials in primary of nuclear power plant are activated with the coolant into the core, and the activated foreign materials are highly radioactive, while these highly radioactive foreign materials are often easily deposited in the primary related equipment. Hence, operators are frequently overexposed to radiation during foreign body salvage work in primary systems. Special transfer shielding devices, high discharge waste storage containers, and transfer area isolation control are designed to effectively reduce the impact of foreign body transfer and storage on the radiation level of the surrounding area and to ensure the radiation safety of the staff. Theoretical calculations of foreign body activation are consistent with the measured on-site radiation levels and can be used to guide the radiation protection work plan and personnel protection measures during foreign body salvage work.
Bremsstrahlung radiation can produce pulsed X-ray, and the energy spectra and conversion efficiencies of X-ray produced by such radiation are related to the electron beam energy, target material, and structure of this material. In this study, electron beam spectra were obtained from the voltage and current waveforms of diodes, and the particle transport Monte Carlo calculation model of a composite target was established. Using the resulting model, the transport laws of electrons and photons in different materials were simulated, and the influence of composite targets was studied. The results were found to be useful in the design of composite anode targets to achieve low energy, high fluence, high conversion efficiency, and low transmission electron energy. The results also revealed that an organic glass softened the electron spectrum and attenuated transmission electrons in the composite anode target. The X-ray energy spectrum produced by the same thickness of a moderated target was found to be much harder than that produced by a thin target with the same thickness. Decreasing the thickness of tantalum was deemed to be good for reducing the average photon energy, while increasing the thickness was found to be good for improving the energy conversion efficiency. When a thin target with 2 cm organic glass and 10 μm tantalum was chosen, the average energy of the X-ray was 133.22 keV, and the conversion efficiency of the photon energy was 0.055%.