View fulltext
View fulltext
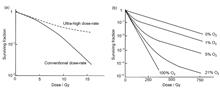
FLASH radiotherapy is a novel method that has the potential to improve the therapeutic gain ratio to a new level. FLASH radiotherapy technology is mainly characterized by irradiation at ultra-high dose rate, which can reduce radiation-induced injury to normal tissues during radiotherapy, while maintaining the ability of radiation damage to tumors. On the one hand, as a new radiotherapy technology, the radiobiological mechanisms of FLASH are unclear, which hinders its clinical transformation. On the other hand, there are many technical difficulties in the clinical application of ultra-high dose rate irradiation technology. This paper summarizes the research progress of radiobiological mechanisms underlying FLASH radiotherapy, as well as the challenges and possible solutions associated with FLASH radiotherapy treatment plans, to provide a reference for clinical translation of subsequent FLASH radiotherapy.
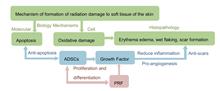
This article discusses the current research status of adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs) and platelet-rich fibrin (PRF) in the treatment of soft tissue radiation injury in the skin. ADSCs and PRF have unique advantages over conventional treatment modalities for improving cutaneous radiation injury. Radiation causes oxidative damage to skin and skin cells subsequently undergo apoptosis, which causes histopathological changes such as erythema edema and wet desquamation. The anti-apoptotic, paracrine growth factor and anti-scarring functions of ADSCs can concomitantly target the mechanism underlying skin radiation injury, reduce inflammation of radiation-injured wounds, increase microvascular density, and promote re-epithelialization of wounds, thereby effectively improving skin radiation injury. The high concentration of growth factors released from PRF can significantly increase the healing rate of wounds, and the biological properties of PRF can further optimize the activity of ADSCs in repairing skin damage. Future experimental research and clinical treatment directions may involve combining the current research status of ADSCs with PRF in the treatment of cutaneous radiation injury.
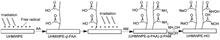
The secondary grafting of acrylic acid and acrylamide onto ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) fibers was accomplished through 60Co gamma-ray pre-irradiation, and UHMWPE fiber adsorbents containing hydroxamic, amide, and carboxyl groups were prepared through a hydroxamic reaction. The results of scanning electron microscope (SEM), attenuated total internal reflectance Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR), and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) all showed that acrylamide and acrylic acid were successfully grafted onto the fiber and that the hydroxamic reaction successfully converted the amide group into the hydroxamic group. Evaluation of the heavy metal ion adsorption performance indicated that the adsorption capacities of the UHMWPE fiber adsorbent for Cu(II), Co(II), and Ni(II) could reach 318 mg/g, 165 mg/g, and 140 mg/g, respectively (the adsorption concentration was 500 mg/L for 4 h). In the competitive adsorption of copper-cobalt-nickel mixed heavy metal ions, the removal rates of the copper, cobalt, and nickel ions were 99.5%, 43.5%, and 60.5%, respectively (the initial ion concentrations were all 200 mg/L and the amount of adsorbent used was 3 g/L).
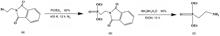
Glycidyl methacrylate (GMA) was grafted onto an ultrahigh-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) fiber through pre-irradiation grafting, and further modified with diethyl (2-aminoethyl) phosphonate. A novel type of phosphate-functionalized fiber (UHMWPE-g-DEPP) was successfully prepared for the separation and recovery of trace uranium in radioactive wastewater. The chemical structure, surface functional groups, stability, micro morphology, and other physical and chemical properties of the fiber materials were analyzed by X-ray diffraction, Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, thermogravimetric analysis, and scanning electron microscopy. The principal factors affecting the U(VI) adsorption performance of the UHMWPE-g-DEPP fiber were investigated, including pH of the aqueous solution, contact time, temperature, and coexisting ions. The experimental results showed that UHMWPE-g-DEPP can achieve an adsorption equilibrium at room temperature within 8 h and the maximum adsorption capacity (113.2 mg/g) at 25 °C, pH = 5.0, and m/V = 0.2 g/?L. The adsorption kinetic pattern was in good agreement with the pseudo-second-order model, and the adsorption equilibrium follows the Langmuir isotherm model well. The phosphate-functionalized fiber showed good recycling and adsorption selectivity.
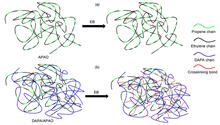
To broaden the application of amorphous poly-α-olefin copolymer in the heat shrinkable material industry, in this study, effects of absorbed dose on the softening point, gel content, DSC properties and rheological properties of dimer acid polyamide/amorphous α-olefin copolymer blends were studied. When the mass ratio of dimer acid polyamide was ≤25%, dimeric acid polyamide/amorphous α-olefin copolymer blends presented radiation degradation characteristics, the softening point, the corresponding temperature Tj of the intersection of the storage modulus G′ and loss modulus G″ with temperature change, and intrinsic viscosity |η*| decreased with absorbed dose increasing; during the oscillating temperature test, the phase angle increased obviously with absorbed dose increasing, which showed viscoelastic transition characteristics. When the mass ratio of dimer acid polyamide was ≥50%, the blends presented radiation crosslinking characteristics, the dependence of viscoelastic transition on temperature and the dependence of intrinsic viscosity on frequency were reduced with absorbed dose increasing.
To investigate the potential risk of electromagnetic exposure, systematic studies on the bioeffects caused by single-frequency electromagnetic fields have been carried out with plenty of achievements.However, the bioeffects caused by multiple-frequency fields still need to be further studied. In the resent work, we constructed a dual-sourced irradiation system to allow two microwaves simultaneously incident from two perpendicular directions. Subsequently, the influence of the number of pulses on the blood, brain, testis, heart, and liver tissues of rats under the simultaneous irradiation of S-band and C-band pulsed microwaves was studied, and compared to that caused by the single-sourced exposure with the same electromagnetic exposure dose. The results showed that when the amplitude of the space electric field intensity was 44.84 kV/m and the number of the pulses was 2, 5, 20 and 200, the blood routine, testosterone, alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase content of rats in the irradiation groups did not change significantly compared with the control group and sham group (p>0.05). The nuclear area in the brain, heart and liver of rats, as well as the Johnson score of the testis, has not significantly changed after the irradiation (p>0.05), and no pathological changes have been observed in these target tissues. The content of Bax in the above four tissues of rats in the irradiation groups increased nonlinearly with the increase of the number of pulses, which can be described as the non-thermal bioeffect that concerned the intensity of the electric field of the pulsed microwave. When the number of pulses is greater than 2, a significant apoptotic response was detected in the brain and testicle (p?0.05), while in the liver and heart the pulse number needs to be greater than 20 (p?0.05). This is mainly because the amplitude of the internal field of the brain and testicle (11.3 kV/m and 10 kV/m respectively) is higher than that of the liver and heart (5.73 kV/m and 5.33 kV/m respectively). Under the same electromagnetic exposure dose, there was no difference between the SC combined irradiation and the S or C individual-irradiation (p>0.05).
A Chinese medicinal formula was prepared by combining extracts from Astragalus, Siberian ginseng, wild Yam, grape seed, and wild Jujube and assessed for the protective effect of the Fangfu formula powder on the spleen of radiation-injured mice. The mice were irradiated with a one-time 60Co γ ray 6.5 Gy dose exposure. The experimental mice were randomized into five equal groups: the control, the model , and the low, middle, and high-dose group (500 mg/kg, 1 000 mg/kg, 2 000 mg/kg, respectively). Changes in the spleen index, pathomorphisms in the spleen tissues, Caspase-3, Caspase-9, cytochrome C, CD4+, CD8+, the apoptosis-related proteins Bax, Bcl-2, and P53 protein expression, and the cell DNA damage in each group were measured. Compared with the model group, there was an increase in the body weight and spleen index of the dosed mice, with the most significant (p<0.01 or p<0.05) increase occurring in the middle- and high-dose groups. Furthermore, the Fangfu formula significantly (p<0.01 or p<0.05) increased the CD4+, CD8+, CD4+/CD8+ percentages, and Bcl-2 protein expression and reduced the level of Caspase-3, Caspase-9, cytochrome C, Tail DNA%, Tail length, olive tail moment (OTM), Bax, and P53 protein expression in spleen tissue when compared with the model group. The histopathologic examination showed that the red and white pulp area of the spleen of the dosed mice was clear, and both lymphocyte necrosis and neutrophil infiltration were decreased significantly in the dosed mice as compared to that in the model group. The data suggest that the Fangfu Formula has a protective effect on the spleen of irradiated mice. These findings might be related to inhibition of DNA damage and apoptosis.
The study investigated the chemical composition, supramolecular structures, particle size distribution, and enzymatic efficiency of Phragmites australis lignocelluloses (PALs) with different moisture contents and treatment with 5 MeV electron beam irradiation. After irradiation, regardless of the moisture content, all PAL samples were degraded, their supramolecular structures were damaged, and the proportion of small PAL particles and the PAL enzymatic conversion rate increased significantly. There was no obvious difference in the apparent morphology, chemical structure, or crushed particle size distribution of PAL samples with different moisture contents when the absorbed dose was the same, but the enzymatic efficiency was negatively correlated with moisture content. The cellulose enzymatic conversion rates of PAL samples with 5%, 10%, and 50% moisture content were 22.24%, 19.76%, and 18.57%, respectively, and the enzymatic conversion rates of hemicellulose were 25.04%, 23.84%, and 19.56%, respectively, after 500 kGy electron beam irradiation. Meanwhile, the cellulose enzymatic conversion rates of PAL with 5%, 10%, and 50% moisture content were 54.09%, 47.27%, and 49.24%, respectively, and the enzymatic conversion rates of hemicellulose were 62.30%, 53.25%, and 47.83%, respectively, after 1 000 kGy electron beam irradiation. When the absorbed dose was 500 kGy, PAL cellulose and hemicellulose samples with 5% moisture content were severely degraded compared to samples with 10% and 50%. Meanwhile, when the absorbed dose was 1 000 kGy, the PAL cellulose and hemicellulose samples with 50% moisture content were severely degraded compared to those with 5% and 10% moisture content. Moreover, more cellulose and hemicellulose with 50% moisture content in PAL were degraded to non-carbohydrate substances compared to those with 5% and 10% moisture content.
In order to solve the problems of the nuclear accident emergency drill, such as invisible radiation field, potential radiation risk, and high labor costs, therefore, an adaptive ray-casting 3D nuclear radiation field visualization method based on feature importance was developed in this study. The nuclear accident emergency disposal drill training simulation system was developed based on the Unity3D simulation engine. The 3D visualization of a nuclear radiation field with millions of grids was realized using ShaderLab programming. Multi-job personnel collaborative operation exercise simulation was realized based on the finite state machine. The system frame rate was approximately 60 frames, which meets real-time interaction requirements. Considering an out-of-control radioactive source accident as a case, the operation modes and emergency disposal processes of the nuclear accident emergency drill could be rebuilt by the system. The proposed solution of the simulation system could be applied to ensure personnel radiation safety, enrich training methods, and reduce training costs.
An analytical method was developed for the rapid determination of 226Ra in water through liquid scintillation counting. The separation and purification of 226Ra from water were performed by co-precipitation using barium sulfate as the carrier; the direct measurement of 226Ra was realized by using a liquid scintillation spectrometer. Through sample analysis, a mathematical model for uncertainty evaluation was established and the sources of uncertainty were analyzed. The results showed that the overall counting efficiency of 226Ra is 91.3%-98.5%, the detection limit is 0.01 Bq/L, and the relative extended uncertainty is 7% (k=2), indicating that the proposed method is suitable for the rapid analysis of 226Ra in drinking water. The uncertainty of the method for the determination of 226Ra in water is mainly caused by the errors of sample counting rate and overall counting efficiency.