View fulltext
View fulltext
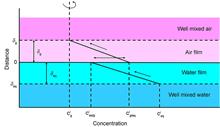
Copper and copper alloys are widely used in the field of nuclear materials. The effects of aqueous solutions that have undergone copper ion radiolysis on the generation of H2O2, O2, and H2 must be considered for material corrosion control and hydrogen explosion risk assessment. In this study, a γ-radiolysis experiment of an aqueous solution containing copper ions was conducted to explore the effects of different absorbed doses, absorption dose rates, and Cu2+ concentrations on the generation of H2O2, O2, and H2. The results showed that with an increase in the absorbed dose (0-1.80 kGy), the concentrations of H2O2 and H2(g) firstly increased and then tended to stabilize under steady-state concentrations of 5.41×10-6 and 7.91×10-5 mol/L, respectively, whereas the concentration of O2(g) remained at 9.04×10-4 mol/L. The presence of Cu2+ enhanced the equilibrium concentrations of H2 and H2O2 by one and two orders of magnitude, respectively, which in turn promoted the generation of H2O2 and H2; however, it had a negligible effect on O2 generation. The equilibrium concentrations of H2O2 and H2 increased with an increase in the absorption dose rate. Specifically, when the absorption dose rate was increased from 1.40 to 46.93 Gy/min, the equilibrium concentrations of H2O2 and H2 increased from 4.56×10-6 and 1.78×10-5 mol/L to 2.46×10-5 and 3.81×10-4 mol/L, respectively, whereas O2 remained essentially unaffected within this absorption dose rate range. In addition, based on the kinetics of water radiolysis and two-film theory of gas-liquid mass transfer, we constructed a calculation model for the radiolysis of aqueous solutions containing copper ions. Compared with the experimental data, the absolute values of the normalized mean bias in the simulation results were mostly between 1% and 7%, with a maximum of approximately 24%, thereby demonstrating the effectiveness and correctness of the calculation model. Accordingly, the model was used to calculate the radiolytic behavior of an aqueous solution containing copper ions under C6+ ion irradiation, and the simulation results matched well with the experimental data reported in the literature, indicating that the model can be expanded to other applications.
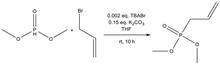
Reactive flame-retardant dimethly allylphosphonate (DA) was prepared using dimethyl phosphite and 3-bromopropy and was grafted onto cotton fabric via ultraviolet (UV) irradiation using N,N'-Methylenebis (2-propenamide) (MBA) as a crosslinker and benzoin dimethyl ether as an initiator. The effects of DA and MBA mass concentrations on the flame retardancy of the cotton fabric were studied. The results indicated that the flame retardancy of the cotton fabric was proportionate to the mass concentrations of DA and MBA. The limiting oxygen index (LOI) of the cotton fabric could reach 27.2%, and the afterburning time and smoldering time were both 0 s. After 20 washing turns, the LOI could still reach 24.5%. The final cotton fabric exhibited better thermal stability, and the flame-retardant finishing demonstrated no significant effect on the tensile property of the cotton fabric.
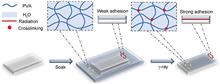
In this study, polyvinyl alcohol (PVA)-modified polyethylene glycol terephthalate (PET) films were prepared using γ-radiation crosslinking. The PVA molecules formed a crosslinking network after γ-irradiation and were loaded onto the surfaces of the PET films. The samples were analyzed by Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy and scanning electron microscopy to demonstrate that the PVA was successfully anchored to the PET film surfaces. Light transmission tests revealed that the modified films maintained good optical properties with a light transmission of 89%. Whether under high-temperature, high-humidity, or low-temperature freezing conditions, the tests revealed that the samples exhibited good anti-fogging performance. Saturated water absorption tests revealed that the anti-fogging properties of the modified PET films were derived from the water absorption of the PVA crosslinking network, where the PET film under 12.43% loading showed a saturated water absorption of 50%.
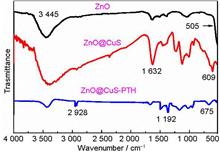
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC), which is used as one of the most widely polymer, the general purpose plastic in industry, agriculture, household items and many other fields because of abrasion resistance, thermal insulation, and low cost, etc. Nevertheless, PVC can easily change color, degrade under heating or ultraviolet (UV) light radiation because of its structural features and inherent composition, finally limited the application range of the materialist. To overcome these, the zinc- copper -sulphur composite was prepared with ZnO nanoparticle, copper chloride, thiourea and thiophene, then added to PVC solution, composite films were prepared by a casting method. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray powder diffraction spectra (XRD), Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) and ultraviolet (UV) spectrophotometr were applied to study the structure and optical performance. The results showed that the functionalized ZnO NPs could endow the PVC composite films with excellent UV shielding capability.
The degradation of simulated methyl red dye wastewater in a concentric tubular reactor using dielectric barrier discharge low-temperature plasma technology was studied. The effects of discharge power, initial solution concentration, initial pH, treatment time, and atmospheric conditions on the degradation efficiency were studied. The color, pH, and absorbance of methyl red at 521 nm were used to detect the dye concentration, analyze the degradation process, and propose a degradation mechanism for methyl red. The results indicate that (1) in this experiment, the discharge power affects the degradation of methyl red but is limited by temperature and humidity, such that there is no positive correlation between the discharge power and the treatment effect. Therefore, the treatment of the solution at a low discharge power of 115 W is preferable; (2) the higher the initial concentration, the longer the time needed to achieve the same degradation rate as that achieved at lower concentrations; and (3) under the same conditions, a low pH is conducive to the degradation of methyl red, and acidic conditions are conducive to the bond breaking of methyl red.
The purpose of this study was to explore the ameliorative effect of CpG-ODN on spleen damage after carbon ion radiation (CIR). In the experiment, C57BL/6L mice were irradiated with 5 Gy of CIR and the index of spleen was calculated. Changes in spleen tissue structure were observed by histological examination (HE). Double-strand break (DSB) of DNA and apoptosis were detected by γ-H2AX immunohistochemistry and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick and labeling (TUNEL) assay, respectively. The number of B cells in the peripheral blood was examined using CD19 antibody labeling. These results showed that CpG-ODN improved the index of spleen, relieved red pulp atrophy, and increased the area of white pulp, in which the number of γ-H2AX foci and TUNEL-positive cells were decreased after CIR. In addition, CpG-OND increased the number of CD19+ B cells in peripheral blood after CIR. These results indicated that CpG-ODN ameliorates spleen damage induced by CIR, possibly by inhibiting the rate of DSB and apoptosis.
This study aimed to evaluate the effects of multi-leaf collimator angle change on the dosimetric parameters of the medial, central, and lateral tumor bed boost in hypofractionated left whole-breast irradiation with dynamic multi-leaf collimator technology. Sixty patients with early breast cancer following conservative surgery who underwent hypofractionated radiotherapy with tumor bed boost were enrolled from The First People’s Hospital of Zunyi between January 2018 and January 2023. All patients were classified into three groups according to the location of the tumor bed: medial, central, and lateral. The differences in target volume and cardiopulmonary dosimetric parameters between the plan of multi-leaf collimator angle change (labeled as Plan-A) and the original plan of 0° multi-leaf collimator angle (labeled as Plan-O) were compared in each group. The results did not show any significant differences in the coverage of the target prescription, conformability index, and homogeneity index between Plan-A and Plan-O of the three groups. In the medial group, the left lung V5, V10, and Dmean; heart V8 and Dmean; and left anterior descending artery (LAD) Dmax and Dmean of Plan-A were significantly lower than those of Plan-O (p<0.05). Meanwhile, in the central and lateral groups, only the LAD Dmax and Dmean of Plan-A decreased significantly in the lateral group, and no differences were observed in other cardiopulmonary parameters compared to those in Plan-O (p<0.05). In conclusion, the change in collimator angle did not have a significant effect on the target dosimetric parameters of hypofractionated radiotherapy with tumor bed boost for the left breast. On the contrary, it could significantly reduce the cardiopulmonary dose in the medial group compared to the original radiotherapy plan. Given this information, it is recommended to change the multi-leaf collimator angle for the radiotherapy plan of the medial tumor bed group in left whole-breast hypofractionated radiotherapy.
Gamma (γ) analysis is the most important method for dose verification and dose distribution comparison. Because of the inconsistency of the coordinate system definitions and directions of different dose distributions and the inconsistent reference point settings, in γ analysis, the dose distributions should often be aligned for comparison. However, the alignment method of the current commonly used γ analysis software is extremely simple, and there are significant errors in processing the dose distribution of the large radiation field, which seriously affect the accuracy of the dose analysis and comparison. Aligning the two-dimensional dose distribution requires performing spatial transformations such as translation and rotation to achieve the same spatial position of the corresponding dose points on the two dose maps. Because the distance between different points must be constant during this alignment process, in this study, the alignment problem is transformed into a rigid registration problem. A rigid registration method based on normalized cross-correlation is used to register the dose distribution map calculated using a treatment planning system with the actually measured dose distribution map and output the corresponding translation amount after registration. 36 groups of static intensity-modulated quality assurance data designed using the pinnacle3 treatment planning system, whose planning system is consistent with the measured center point, are selected; 18 groups are small irradiation fields, and the other 18 groups are large irradiation fields. PTW VeriSoft software is used to calculate the γ passing rate under 3%/3 mm, 3%/2 mm, and 2%/2 mm pass standards separately. For small irradiation fields, the results of the direct calculation of different standard γ passing rates after alignment with VeriSoft and rigid registration are identical. Among them, under the 3%/3 mm pass standard, the results of VeriSoft alignment and rigid registration are compared with those directly calculated,the average differences in γ passing rate are 0.5% and 0.3%, respectively. For the large irradiation field, compared with the directly calculated γ passing rate results, the average differences of the γ passing rate under 3%/3 mm, 3%/2 mm, and 2%/2 mm pass standards after VeriSoft alignment are 17.1%, 23.3%, and 28.3%, respectively, with ten groups of cases all exhibiting great differences. The average differences of the γ passing rate under the 3%/3 mm, 3%/2 mm, and 2%/2 mm standards after rigid registration and direct calculation are 0.4%, 1.1%, and 2.3%, respectively, and the average difference is small. Rigid registration solves the problem of significant errors in VeriSoft’s handling of large-field dose distributions. It can be used as a method for the alignment of dose distributions in different fields when verifying the dose of radiation treatment plans.
During the transportation of components related to nuclear materials, accidental chemical explosions may occur, resulting in the release of radionuclides. Effective decision-making during nuclear transport accidents, especially in cases with incomplete source information and a complex terrain, requires the rapid prediction of changes in radionuclide concentration. This paper proposes a method for predicting the concentration of radionuclides resulting from nuclear transport explosion accidents based on stacked long short-term memory (LSTM) networks. Specifically, this study considered plutonium-containing explosive transport and chemical explosion accidents under the pad surface of a hill as a research scenario. The diffusion data of radionuclide Pu-239 were simulated using the computational fluid dynamics (CFD) software OpenFOAM. Nuclide concentration and meteorological time series data of a specific area were selected for stacked LSTM network training and prediction based on geographical characteristics and population density. The proposed model, optimized using grid search, can stably achieve a mean absolute percentage error (MAPE) of less than 5% within 150 iterations for Pu-239 nuclide concentration prediction. The model is highly efficient and has significant practical value for use in nuclear emergencies.
Through questionnaire analysis, the cognitive situation and behavioral characteristics of different people around the nuclear power plant for nuclear emergency evacuation were obtained, and the possible behaviors of people during evacuation were predicted by Logistic model. Chi-square test and Logistic regression model were used to make correlation analysis and influence judgment on the evacuation psychology and evacuation behavior of different people in the area, and the optimal allocation algorithm was used to judge the prediction correctness of the model. The results showed that the factors such as whether to purchase nuclear safety-related insurance, the number of nuclear emergency evacuation drills, the understanding of nuclear emergency evacuation, and the presence of non-nuclear emergency protective measures at home had significant effects on the evacuation consciousness and psychology of the population. Gender, knowledge of nuclear emergency evacuation, the number of nuclear emergency evacuation drills participated, whether there are nuclear emergency protection measures at home and whether nuclear safety insurance has been purchased, and other factors have significant influence on crowd evacuation behavior. The simulation shows that people with certain nuclear evacuation experience can make relatively correct evacuation behavior and reduce evacuation time.
This study was conducted to assess the levels and trends of environmental radiation in Shenzhen between 2011 and 2020. The monitoring encompassed dose rate, radon concentration in the air, water radioactivity, and natural radioactivity content in soil. Results indicated that the dose rate ranged from 69.3 to 131.0 nGy/h, while radon concentration was between 6.23 and 18.60 Bq/m3. The activity concentration in water, for total alpha and total beta, ranged from 0.016 to 0.225 Bq/L and 0.028 to 0.826 Bq/L, respectively. The natural radioactivity content in soil was found to be within background levels. Overall, the environmental radiation levels in Shenzhen fluctuated within the background range. To enhance the comprehensiveness of the data, it is recommended that marine radiation monitoring projects be increased and the basic data on radiation levels in Shenzhen be further refined.
Taking six typical associated ore waste samples as the research object, the thorium content in the samples was determined by spectrophotometry and the factors affecting the test results were analyzed. Three factors that may obviously affect the accuracy of the results were selected and optimized the experimental conditions by controlling variates, and the results were compared with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry and gamma spectrometry to prove the reliability of the optimization method. The results showed that the main affecting factors in the sample were the digestion frequency, colorimetric time, and residual extractant. The detection accuracy and efficiency of thorium in the six typical associated ore residues were improved by increasing the digestion frequency to 3 times, ensuring a colorimetric time of 3 min to 5 min, and adding hydrogen peroxide and perchloric acid to remove the extractant.