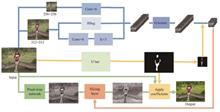
Deep learning based high dynamic range (HDR) image processing algorithms has the problem of skin color deviation when processing images containing human figures. In response to this issue, this article proposes a portrait HDR image processing algorithm based on multi feature fusion-U2HDRnet. This algorithm consists of three parts: skin feature extraction module, trilateral feature extraction module and color reconstruction module. Firstly, the skin feature extraction module separates the color and position information of the skin region. Secondly, the trilateral feature extraction module extracts local features, global features and semantic features of the image, and fuses them with skin features. Finally, the color reconstruction module interpolates the grid in terms of space and color depth. In addition, this article adds an improved fusion module of self attention and convolution to improve the processing performance of HDR. At the same time, this article also produces the PortraitHDR dataset for portraits, filling the gap in the dataset in this field. The test results show that the PSNR of U2HDRnet reaches 31.42 dB, and the SSIM reaches 0.985, both of which are superior to the commonly used HDR algorithms. They obtain high-quality portrait HDR images while avoiding skin distortion.
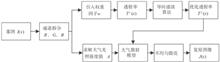
This paper addresses the issue of hazy stray light in fundus retinal images, which leads to unclear blood vessel details. The proposed dehazing algorithm for fundus retinal images is based on the dark channel theory and incorporates Gamma transformation. The algorithm enhances the clarity of the image while preserving blood vessel information. This algorithm aims to defog images by processing the R, G and B channels separately. Firstly, the algorithm calculates the dark channel image using adaptive window minimum filtering and takes the average value of the top 0.1% pixels as the atmospheric illumination intensity value. Secondly, the algorithm solves the rough transmittance of the image and improves it using the guided filtering algorithm. Finally, the algorithm restores the haze-free image using the atmospheric scattering model and applies Gamma transformation. The experimental results show that the information entropy and average gradient of the restored image increase by an average of about 6.8% and 11.6%, respectively. The algorithm in this paper can quickly and effectively remove hazy stray light in the fundus retinal image, restore the image to be clear and natural, and retain the details information of retinal blood vessels.
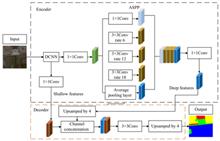
A lightweight network based DeepLabV3+ remote sensing image land feature segmentation method is proposed to address the errors caused by the loss of detail information and imbalanced categories in remote sensing image segmentation. Firstly, MobileNetV2 is adopted to replace the backbone network in original baseline network to improve training efficiency and reduce model complexity. Secondly, the dilation rate of atrous convolutions within ASPP structure is increased and max-pooling in final ASPP layer is incorporated to effectively capture context information at different scales. At the same time, SE attention mechanism is introduced into each branch of ASPP, and ECA attention mechanism is introduced after extracting shallow features to improve the model’s perception ability for different categories and details. Finally, the weighted Dice-Local joint loss function is used for optimization to address class imbalance issues. The improved model is validated on both the CCF and Huawei Ascend Cup competition datasets. Experimental results show that the proposed method outperforms original DeepLabV3+ model on both test sets, with various metrics showing different degrees of improvement. Among them, mIoU reaches 73.47% and 63.43%, representing improvements of 3.24% and 15.11%, respectively. The accuracy reaches 88.28% and 86.47%, showing enhancements of 1.47% and 7.83%, respectively. The F1 index reaches 84.29% and 77.04%, increasing by 3.86% and 13.46%, respectively. The improved DeepLabV3+ model can better solve the problems of loss of detail information and class imbalance, which improves the performance and accuracy of remote sensing image feature segmentation.
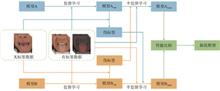
Accurate tongue image segmentation is a crucial prerequisite for objective analysis in tongue diagnosis in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM). At present, the widely-used full-supervised segmentation methods require a large number of pixel-level annotated samples for training, and the single-model-based semi-supervised segmentation methods lack the ability to self-correct the learned error knowledge. To address this issue, a novel semi-supervised tongue image segmentation method based on mutual learning with dual models is proposed. Firstly, model A and B undergo supervised training on the labeled datasets. Subsequently, model A and B enter the mutual learning phase, utilizing a designed mutual learning loss function, in which different weights are assigned based on the disagreement between predictions of the two models on the unlabeled data. Model A generates the pseudo-labels for the unlabeled dataset, and model B fine-tunes on both the labeled dataset and the pseudo-labeled dataset. Then, model B generates the pseudo-labels for the unlabeled dataset, and model A fine-tunes in the same manner. After the dual-model fine-tuning process, the model with better performance is selected as the final tongue image segmentation model. Experimental results show that with labeled data proportions of 1/100, 1/50, 1/25, and 1/8, the mean intersection over union (mIoU) achieved by the proposed method is 96.67%, 97.92%, 98.52%, and 98.85%, respectively, outperforming other typical semi-supervised methods compared. The proposed method achieves high precision in tongue image segmentation with only a small number of labeled data, laying a solid foundation for subsequent applications in TCM such as tongue color, tongue shape and other tongue image analysis, which can promote the digitization of TCM diagnosis and treatment.
To meet the demand of green prevention and control of crop diseases and pests for the detection of disease and pest severity, an improved U-Net network model is designed for the detection of crop leaf disease and pest severity. First, the ResNet50 network is selected as the backbone network of the model, and transfer learning is used to improve the training convergence speed and reduce the computational cost. Second, the attention mechanism is introduced to optimize the feature extraction and fusion of each layer of the U-Net network, so as to improve the ability of the network model to receive key information. The experimental results show that the improved U-Net512 network model has the best detection performance, with an average detection accuracy of 90.14% and an average absolute error of 276.3. By analyzing the feature maps of each layer of the model under different sampling depths, it is found that the introduction of attention mechanism enables the network model to obtain and fuse two dimensions of information: the overall feature of the leaf and the disease area feature, which further improves the model detection performance. This method can not only effectively detect the disease and pest severity of crop leaves, but also has high accuracy and reliability, which is conducive to achieving green prevention and control of crop diseases and pests.
In response to the issue of inadequate discrimination capability in the D3S algorithm for tracking target,a video object tracking algorithm based on dual-branch online optimization and feature fusion is proposed. Firstly, a dual-branch online optimization classifier is constructed, which achieves secondary location of the target, resulting in a more accurate target position response map. Secondly, the fusion of the response map and search features is realized on the feature layer, and the encoder module promotes the fusion process, further highlighting the features of tracking target. Finally, by updating the template features with the encoder module, the differences between features are fitted, thereby enhancing the discriminative capability of the segmentation module. Experimental evaluations are conducted on the VOT2018 and UAV123 datasets. Compared with the original algorithm, the improved algorithm improves EAO by 2.9% on the VOT2018 dataset, increases success rate by 2.4% and accuracy by 2.9% on the UAV123 dataset. The experimental results demonstrate that the method in this paper improves the algorithm's discriminative ability and further improves accuracy and robustness.
Image registration plays an important role in computer-aided diagnosis of brain diseases and remote surgery. The U-Net and its variants have been widely used in the field of medical image registration, achieving good results in registration accuracy and time. However, existing registration models have difficulty in learning the edge features of small structures in complex image deformations and ignore the correlation of contextual information at different scales. To address these issues, a registration model is proposed based on cross-scale point matching combined with multi-scale feature fusion. Firstly, a cross-scale point matching module is introduced into encoding structure of the model to enhance the representation of prominent region features and grasp the edge details of small structure features. Then, multi-scale features are fused in the decoding structure to form a more comprehensive feature description. Finally, an attention module is integrated into the multi-scale feature fusion module to highlight spatial and channel information. The experimental results on three brain Magnetic Resonance (MR) datasets show that, taking the OASIS-3 dataset as an example, the registration accuracy has been improved by 23.5%, 12.4%, 0.9%, and 2.1% compared to methods such as Affine, SyN, VoxelMorph and CycleMorph, respectively. The corresponding ASD values for each method have decreased by 1.074, 0.434, 0.043, and 0.076. The proposed model can better grasp the feature information of images, which improves registration accuracy and has important implications for the development of medical image registration.