As a hot issues in the field of information display technology, the current development of near-eye display equipment bears people's good vision for future information interaction. Meanwhile, people's demand for augmented reality display is also constantly improving, and augmented reality display in near-eye display has undoubtedly become a research hotspot in recent years. And with the continuous development of display technology, highly miniaturization and integration have become an important development trend in near-eye display. Micro Light-Emitting Diode (Micro-LED) display technology has great advantages over other technologies in brightness, resolution, contrast, energy consumption, service life, response speed, and stability, which is considered as an ideal light source in near-eye display equipment. This paper analyzes the research progress of Micro-LED from the aspects of structure, fabrication process, and challenges. The development of near-eye display is reviewed based on the visual characteristics of human eyes. Then, the advantages of Micro-LED in near-eye display are summarized, and the advancement and realizability of various technologies are illustrated. Finally, the future development of Micro-LED is prospected.
With the increase of the outgoing light angle of the micro spacing Mini LED direct display screen, there will be an angular color deviation from facing the white field to light red and then to light cyan. Through test and calculation, it is found that the inflection point of color coordinate appears at the position of 50°?~60°. Through the light type analysis, the color deviation on the surface of Mini LED screen is related to the light type mismatch and left-right asymmetry of RGB die chip. Due to the dispersion of RGB color in the medium, the escape angle of red light is greater than that of blue and green light, and the divergence of red light is stronger than that of blue and green light after passing through the medium. The difference in the intensity attenuation of red, green and blue light causes the angular color deviation of the outgoing light.
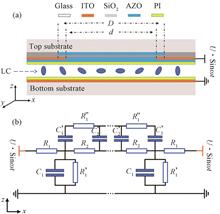
A thin film dielectric layer was used to separate the floating electrode and the mode control electrode. The floating electrode and the mode control electrode were on the same side of the substrate, which avoided the restriction of using a thin substrate. Comsol Multiphysics software was used to simulate the influence of the square resistance of floating electrode and the thickness of thin film on the wavefront error of liquid crystal lens. For the liquid crystal lens with a diameter of 2 mm, when the square resistance of floating electrode varies from 150 Ω·□-1 to 300 MΩ·□-1, the wavefront error of liquid crystal lens decreases first and then increases, and reaches a minimum value at 40 MΩ·□-1. When the thickness of the dielectric layer varies from 50 nm to 5 000 nm, the square resistance of the floating electrode with the smallest wavefront error decreases from 50 MΩ·□-1 to 2 MΩ·□-1, and the optimal square resistance parameters decrease monotonically. When the square resistance of floating electrode is 40 MΩ·□-1 and the thickness of dielectric layer is 250 nm, the focusing characteristics and wavefront error characteristics of liquid crystal lens are studied. When the focal length varies from 250 mm to infinity, the maximum root mean square error of wavefront at 589 nm is 0.041 2 μm, less than λ/14, which satisfy the Marechal criterion.
In order to obtain a silicon-based light source with high quantum efficiency, a micron-sized round hole cavity array was fabricated on monocrystalline silicon wafer in air by using nanosecond pulsed laser. The properties of the sample after annealing at high temperature were investigated. Firstly, the quantum dots formed in the cavity had a stronger emission near 710 nm in photoluminescence (PL) measurement. Then, annealing at 1 000 ℃, the PL spectra before and after annealing were compared by controlling the annealing time. The variation trends of spontaneous and stimulated emission were observed. Annealing for 20 min, the PL intensity was various at different positions in the cavity, and it is found that the PL emission at the cavity edge is the strongest, which may be related to a large number of quantum dots distributed on the edge of the cavity. Finally, adopting standard LED calibration, the maximum PL external quantum efficiency (PL-EQE) in the cavity was measured. Experimental results indicate that the external quantum efficiency in the cavity after annealing can reach 9.29%.
OLED technology is considered to have the following advantages with its self-emitting performance: light-thin,flexible,high contrast,fast response,high color gamut,wide view angle,low power consumption,and low cost, etc. After more than 10 years of large-scale application in mobile phones, although the scale has increased significantly, other applications have not made much progress. Through the performance analysis of mass production scheme and comparison with LCD, we find that on one hand, the expected OLED performance advantages have not been brought into full play in the product, on the other hand, the existing technical solutions have tended to be extreme in design and process. So there must be a big breakthrough in the design and process of OLED technology before it can be expanded to larger sizes and other applications.
In order to integrate the advantages of digital display and TFT-LCD, and further enrich the teaching cases of embedded system, a multi display terminal experimental device of embedded system based on FMSC bus is designed. The hardware design uses Bank1.Sector4 of FSMC bus to connect to LCD, FSMC interface is directly connected to LCD data, control signal, and the 8080 timing of LCD is generated by FSMC controller. The digital display multiplexes the data line with LCD through the latch, and the reverse phase of FSMC bus Bank1.Sector3 chip selection signal is used as the gating signal of the digital display. The software design completes FSMC initialization with the help of STM32CubeMX, realizes the digital display and LCD bottom driver, and transplants LCD basic display and high-level application. The running test shows that the system runs stably and reliably, the display effect is clear and smooth, and the software and hardware design is greatly simplified. It provides a classic case for the parallel expansion of multi display terminals in embedded system.
In order to solve the problem of poor accuracy of 3D palmprint feature representation, a 3D palmprint recognition method based on local orientation binary pattern (LOBP) and collaborative representation (CR) is proposed in this paper. The principal orientation coding and orientation confidence coding of palmprints are used to jointly characterize the directional features of 3D palmprints. This operation can effectively improve the accuracy of directional coding. The surface type coding is used to describe the structure of palmprint and fully express the geometric characteristics of palmprint. Finally, the features are combined by collaborative representation method to complete palmprint recognition in the classification and recognition. The experiment is carried out on the 3D palmprint database of Hong Kong Polytechnic University, and the results indicate that the average recognition rate is up to 99.55% and the average recognition time is 0.874 9 s. The proposed method can improve the recognition accuracy of 3D palmprints while maintaining a relatively low recognition time.
For the 3D key point pose estimation error caused by the high degree of freedom problem and structural similarity problem of the hand, this paper proposes a novel 3D hand skeleton pose regression framework for joint identification, detection, and pose estimation. The framework firstly adopts a YOLOv3-based detector to obtain the position of hands, then a cascade pose estimation network is designed to get initial hand poses with 2D and 3D pose supervisions. Finally, considering the natural constrains in hand graph connection, we present progressive GCN module to further refine the initial hand pose from coarse to fine. This paper compares PCK metrics and AUC metrics with the state-of-the-art approaches under different public benchmarks, and the proposed method achieves the highest AUC metrics on different test sets, with an average AUC accuracy of 92.9%. The experiments illustrate that the proposed method is able to effectively and robustly predict 3D hand pose from monocular image, performing well in both test sets and in the wild.
The existing image generation methods based on cycle generative adversarial network have achieved excellent results in unpaired image to image translation tasks by introducing a separate generic attention module, but they also increase the model complexity and training time, and it is difficult to focus on all the details of key regions in the image, and there is still room for improvement in image generation results. To solve these problems, this paper proposes a dual special attention-mechanism guided cycle generative adversarial network architecture for unpaired image transformation translation (Dual-SAG-CycleGAN). Firstly, to improve the quality of the generated images and reduce the complexity of the network, a special attention module called SAG (Special Attention-mechanism Guided) is proposed to guide the generator. Then, to suppress the generation of extraneous noise by the generator, a discriminator based on special attention mechanism of CAM (Class Activation Mapping)is introduced. Finally, a cyclic consistency loss function for the background mask is introduced to guide the network to generate a more accurate mask map, which can better aid for image translation. Experiments demonstrate that compared with similar existing models, our proposed method can reduce the maximum number of parameters by 32.8%, speed of train 34.5% faster, and generate higher quality images with a minimum KID and FID of 1.13 and 57.54, respectively.
Aiming at the optimization of speed and of final matching pairs for image mosaicing, this paper proposes an image mosaicing algorithm based on BRISK (Binary Robust Invariant Scalable Keypoints) keypoint detection algorithm and improved RANSAC (Random sample consensus) algorithm. The improved RANSAC algorithm aims to find more matching pairs through loops. The specific improvements are adding loops while calculating the number of inliers and changing the Euclidean distance used for inliers judgment to area. The experimental results show that the improved RANSAC algorithm increases the number of inliers, and the average back-projection error rate is reduced by about 10% compared with the original algorithm. Compared with the common mosaicking methods, the time cost of the mosaicking method proposed in this paper is reduced by about 50%. The method proposed in this paper can realize real-time and accurate image mosaic.
The propagation of light in water severely uates red light, this leads to green or blue color difference of the underwater image. Against this red light attenuation phenomenon, a method of improved conditional generation adversarial network is proposed to enhance the underwater images. Raw images are firstly corrected for preliminary color using a dynamic threshold. Then, the color recovery of the underwater image is achieved by generating confrontation network using the condition and introducing the link block to learn the mapping relationship between the underwater image and the normal image. The image denoising is performed using a two-sided filtering algorithm to improve image visibility. The combination of L1 with L2 loss is introduced to learn image color, and the focus loss is added to solve the high imbalance of the sample proportion. This method has an excellent enhancement in both color distortion and blur of underwater images, and good visual effects are obtained.
Aiming at the problem of reduced tracking accuracy caused by occlusion between targets in complex scenes, an improved multi-object trcking algorithm based on the Fairmot framework is proposed. The feature map of the backbone network is used for information interaction between dimensions through a triplet attention mechanism to generate an attention mask, which improves the positioning ability of the target. Person re-identification branch adopts Circle Loss to select the degree of optimization according to the current state, to extract more accurate appearance features and distinguish different target objects. The experimental results show that the tracking accuracy on the MOT15 data set is increased to 62%, the MT (Mostly Tracked) is increased to 358, and the identity switching is reduced by 68 times. It has a better tracking effect in the scene where occlusion occurs.