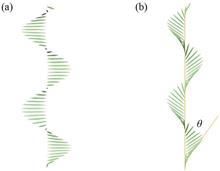
Dynamic control of selective reflection of chiral liquid crystals (LCs) through the external field is one of the important research directions. In recent years, a special nematic phase, twist-bend nematic (Ntb), has been discovered, and a new type of oblique heliconical cholesteric phase (ChOH) can be formed by mixing Ntb mixture with chiral molecules under electric field induction. Different from the electric-field modulation performance of ordinary cholesteric phase, the pitch of ChOH decreases in a certain range with increasing electric field intensity, thus realizing the wide range switching of selective reflection from ultraviolet to near infrared spectra. This phenomenon caused the wide attention of the researchers, and it also makes the ChOH LCs material have great potential in reflective display, smart windows, tunable filters, holograms and other applications. On the basis of a brief introduction of the characteristics of ChOH LCs, this review paper focuses on the recent research progress of field-controlled ChOH LCs and polymer/ChOH LCs composites, and prospects their future development trends.
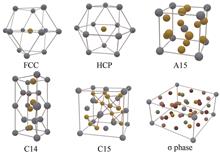
Man’s exploration of the microstructure of matter has never stopped, and understanding how particles stack up in space is still remaining a great challenge for scientists and technicians. The soft matter often shows abundant self-assembly morphologies and phase topological structures due to the drive of weak intermolecular interactions and the competition of entropic enthalpies. Among them, Frank-Kasper phases are the most fascinating, which have complex topologically dense stacking structures. As a transition state between crystal and quasicrystal, the Frank-Kasper phase has a kind of complex spherical phase structure with a dense icosahedral shell and a high coordination number (CN=14,15,16). The soft matter offers novel molecular and self-assembled structures for study of Frank-Kasper phase. This paper presents a brief review of the research process on soft matters such as small molecule surfactants, block copolymers, dendritic macromolecules and giant amphiphilic molecules that can form Frank-Kasper phases. These soft matters can be used as a material for studying the spatial accumulation of non-homogeneous and deformable soft spheres. The Frank-Kasper phase plays a crucial role in the mechanism of soft matter self-assembling into complex topological close-packing structures, which should contribute to understanding the growth mechanism of quasicrystals.
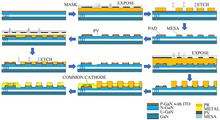
The fabrication of a high-resolution 1 920×1 080 active matrix GaN-based micro-display chip was presented in this paper. The patterning of the current spreading layer and mesa were completed with ICP (Inductively Coupled Plasma) dry etching in a single step, resulting in the so-called self-alignment processing. At the same time, HMDS (Hexamethyldisiloxane) was used to improve the adhesion of photoresist, that significantly improve the consistency and integrity of small-size mesa etching. Furthermore, the problem of unequal height of P-electrode and N-electrode in traditional flip-chip was solved by padding the N-electrode, which was beneficial to the bonding of display chip and driver chip. This chip had a size of 17.78 mm (0.7 in), a mesa size of 6 μm and a pixel pitch of 8 μm, and a high density of 3 129 PPI. The I-V curve of a single Micro-LED pixel was measured and illustrated, which showed a turn-on voltage of 3.5 V.
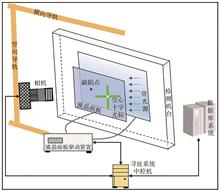
In order to solve the problems of low efficiency and poor accuracy of traditional small size LCD panel defect addressing method applied to high resolution and large size LCD panel, a full automatic accurate defect addressing system was established, and its hardware and software architecture, implementation and defect addressing logic were studied. Firstly, an addressing central control system was constructed by adding a movable optical camera mechanism and corresponding software architecture on the basis of detection equipment. Then, the system can accurately detect the defect by comparing the pictures taken by camera before and after the hollow cross cursor displayed by the LCD panel coincided with defect. Finally, the defect coordinates were output through the LCD panel driving device. After five types of defects test, the results show that the system is stable and easy to use, as well as fully automatic, faster recognition and 100% accurate addressing. After the application of the system in the defect coordinates addressing process of H company, the accuracy of defect coordinates increases by more than 30%, which brings significant improvement in repair benefits. The system has great application value in the field of defect coordinates addressing of large size LCD panel.
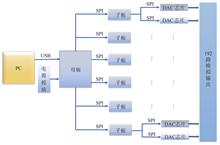
In order to realize the driving of multi-channel passive liquid crystal optical devices, the driving circuit with low cost, low complexity and adjustable amplitude and frequency is designed and developed. Firstly, to facilitate the control of the liquid crystal device, the USB data transmission method is used to transmit the control signal between the PC and the driver board. Secondly, the driver board adopts the combination of the mother board and daughter board, and each daughter board can output 32 driving signals, which can flexibly select the number of daughter board according to actual needs, thereby reducing the cost. The mother board and the daughter board both use STM32 as the main control chip, and the daughter board communicates with the mother board through the SPI interface. Each daughter board distributes data packets to the DAC chip through 2 SPI interfaces, and each DAC chip can control 16 channels of digital-to-analog conversion, realize the output of 192 channels of analog signals eventually. Finally, the board is made and tested. The results show that the output analog voltage is in linear proportional relationship to the gray value, and its absolute error is about 0.010 V, which is in line with the modulation accuracy of 10 bit, 1 024-level voltage gray value. The driver board can realize the output of multi-channel driving signals and meet the requirements of driving control of multi-channel passive liquid crystal optical devices.
Aiming at the problems of low contrast, unclear details and poor visualization in non-uniform illumination images due to over-dark or over-bright local regions, an image enhancement method via symmetric brightness mapping and virtual multi-exposure fusion is proposed. A color space conversion is used to retain the hue and saturation components and separate the brightness component of the input image for enhancement processing. According to the camera response model, the principle of image information entropy and average gradient maximization is adopted to estimate the optimal exposure ratio. A pair of symmetrical brightness mapping functions are designed to generate virtually corresponding images with the enhanced exposure and reduced exposure, forming an image sequence with different exposures together with the original brightness component. Then, a multi-exposure fusion method with detail enhancement is applied to the image sequence to reconstruct the enhanced result. Experimental results indicate that the average values of evaluation indices such as image information entropy, average gradient, image contrast, and color consistency of the proposed method are 7.644, 9.209, 450.683 and 0.962 on seven public datasets respectively, which are superior to those of the contrast method and achieve enhanced results with high dynamic range, strong contrast, clear details and good visualization.
In view of the problem that the commonly used registration algorithms cannot meet the high-precision process requirements in the manufacturing industry, this paper proposes an improved 3DSC point cloud registration based on the 3D point cloud. Firstly, the threshold value is set to collect the contour point cloud by the improved down-sampling method, and the collected point cloud is divided into 3D mesh in turn to form a 3D shape context. Then, the improved 3DSC coarse registration is performed, and the ICP fine registration is used to realize the rotation and translation transformation between the source point cloud and the target point cloud. In order to verify the effectiveness of the improved algorithm, the traditional 3DSC, FPFH-ICP, PFH-ICP and the improved algorithm in this paper are used to compare the registration experiments. The experiment results show that the accuracy of the improved algorithm can reach 2.253 55e-05 m and 9.969 02e-06 m respectively for the bunny point cloud and the flowerpot point cloud, which is obviously better than the registration accuracy of other algorithms. Compared with the traditional 3DSC registration algorithm, the improved 3DSC registration algorithm can save 75%~85% of the registration time. The improved 3DSC point cloud registration method is beneficial to improve the registration accuracy, optimize the registration time, and improve the registration efficiency.
In order to efficiently segment and analyze complex scenes such as urban landscapes, this paper combines the high-resolution network (HRNet) and supplements the global context information through the pyramid pooling module, and proposes a high-resolution scene analysis network. Firstly, HRNet was used as the backbone feature extraction network, and the atrous separable convolution was used to improve its widely used residual module, so as to reduce the amount of parameters and improve the segmentation ability of multi-scale targets. Secondly, the mixed cavity convolution framework was used to design the multi-level cavity rate, which can dense the receptive field and reduce the influence of the grid problem. Then, a multi-stage continuous up-sampling structure was designed to improve the simple post fusion mechanism of HRNetV2. Finally, the improved pyramid pooling module which can adapt to different image resolutions was used to aggregate the context information of different regions to obtain high-quality segmentation images. The accuracy of 83.3% MIOU is achieved with only 16.4 Mbit parameters on the CityScapes urban landscape dataset, and good results are also achieved on the Camvid dataset. A more reliable, accurate, and low-computing scene analysis method based on semantic segmentation has realized.
Anomaly detection in video is one of the challenging computer vision problems. The existing state-of-the-art video anomaly detection methods mainly focus on the structural design of deep neural networks to obtain performance improvements. Different from the main research trend, this article focuses on the combination of ensemble learning and deep neural network, and proposes a method based on ensemble generative adversarial networks (GAN). In the proposed method, a set of generators and discriminators are trained together, so each generator gets feedback from multiple discriminators, and vice versa. Compared with a single GAN, an ensemble GAN can better model the distribution of normal data, thereby better detecting anomalies. The performance of the proposed method is tested on two public data sets. The results show that ensemble learning significantly improves the performance of a single detection model, and the performance of ensemble GAN exceeds the frame-level AUC of 0.4% and 0.3% on the two data sets compared with the existing recent methods, respectively.
Aiming at the problems of insufficient feature extraction, incompleteness and low recognition accuracy in action recognition based on human skeleton sequence, a action recognition model based on multi-branch feature and multi-scale spatio-temporal feature is proposed in this paper. Firstly, the original data are enhanced by the combination of various algorithms. Secondly, the multi-branch feature input form is improved to multi-branch fusion feature information, which is input into the network, respectively. After a certain depth of network modules, it is fused together. Then, a multi-scale spatio-temporal convolution module is constructed as the basic module of the network to extract multi-scale spatio-temporal features. Finally, the overall network model is constructed to output action categories. The experimental results show that the recognition accuracy on Cross-subject and Cross-view of NTU RGB-D 60 data set is 89.6% and 95.1%, and the recognition accuracy on Cross-subject and Cross-setup of NTU RGB-D 120 data set is 84.1% and 86.0%, respectively. Compared with other algorithms,the more diversified and multi-scale action features are extracted, and the recognition accuracy of action categories is improved to a certain extent.
Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is a common complication of diabetes and one of the major diseases leading to blindness in the world. It is difficult to detect DR in the early clinical stage. A computer aided diagnosis method based on convolution neural network is proposed, which can automatically classify the severity of DR according to the fundus images. Various preprocessing methods are used to improve the quality of the input images and various data enhancement methods are used to improve the balance of datasets. Cost-sensitive regularization is used to expand the standard classification loss function based on EfficientNet network architecture. Depending on the degree of difference between the predicted label and the ground truth label, they are applied different penalties. In addition, pre-training on ImageNet dataset is carried on to introduce transfer learning, and the full connection layer of Softmax activation functions are used to achieve better performance of the model. According to the experimental results of two datasets, compared with the recent research results, the model can achieve an improvement of about 5% in quadratic weighted kappa score and 3% in AUC. The introduction of cost-sensitive regularization into the EfficientNet network model can improve the accuracy of diabetic retinopathy classification task and obtain a good model performance.