BackgroundThere are a large number of Cloisonné enamel in the Palace Museum, among which there are many problems in the screening of the manufacture process and background information of the enamel with "Jingtai". X-ray technology can be applied to non-destructive test of the structure and composition of enamel, and help researchers to acquire the information behind cultural relics.PurposeThis study aims to apply X-ray techniques to the investigation of Cloisonné enamel in the Palace Museum for analyzing their period, glaze and structure.MethodsFirstly, two pieces of enamel inscribed with "Jingtai" in the Palace Museum were selected as the research object. Then, the X-ray Computed Tomography (CT), X-ray Fluorescence (XRF) and Raman spectroscopy techniques were applied to investigating the period, glaze, structure and composition of these two Cloisonné enamels. Finally, comparative analysis of these identified characteristics was conducted to infer the differences in different parts of Cloisonné enamels.ResultsAnalysis results indicate that both of two Cloisonné enamels are old utensils made by changing their shapes with recombination of the old pieces, thus forming a new piece of enamel with "Jingtai" engraved on the bottom.ConclusionsThrough the mutual verification between the results of scientific and technical means, a clear conclusion is obtained, which provides a new idea and solution for the subsequent research on the modified enamel.
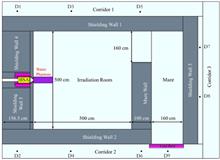
BackgroundBoron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) is a new type of binary targeted radiotherapy that is gradually entering the commercial stage. The accelerator-based boron neutron capture therapy (AB-BNCT) neutron sources used in hospitals are inevitably accompanied by neutron leakage and gamma-ray contamination during equipment operation and patient treatment.PurposeThis study aims to analyze the radiation safety of public during the operation of BNCT using Monte Carlo geometric splitting variance reduction technique.MethodsFirstly, based on a 10 mA 2.8 MeV proton accelerator neutron source, the International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP) and the basic standard for ionizing radiation protection and radiation source safety in China, GB 18871?2002 was taken as the reference standard for the annual effective dose limit of 1 mSv for the public. This dose limit was conservatively estimated to be equivalent to a dose rate limit of 0.5 μSv·h-1. Then, a water model with the size of 100 cm×30 cm×80 cm was placed at the outlet of beam shaping assembly (BSA) after neutron beam moderation and collimation, and the shielding calculations of AB-BNCT treatment room were conducted by Monte Carlo programs with various techniques. Finally, these results were comparatively analyzed to give shielding scheme design of the AB-BNCT treatment room, and the optimization design was carried out according to the weak link of the shielding.ResultsThe simulation results indicate that the variance reduction techniques of geometric splitting and Russian roulette for shielding simulation calculations has higher efficiency and achieve more accurate calculation results. After optimizing the shielding design of the BNCT treatment room, the conservative calculation results prove that the total dose rate at the corridor outside the treatment room is less than 0.5 μSv·h-1 when the shielding body is 60 cm thick boron containing heavy concrete, which meets the design requirements. In addition, the thickness range of the boron containing heavy concrete shielding wall required for radioactive workers is given to be 45~50 cm when the dose rate limit is less than 2.5 μSv·h-1.ConclusionsThe shielding design of BNCT treatment room using Monte Carlo geometric splitting variance reduction technique in this study is safe and reliable, providing a theoretical basis for the commercial development of BNCT.
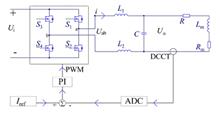
BackgroundBipolar magnet power supplies using switching techniques are commonly used to provide stable excitation current for correction magnet coils. Specification of the Shenzhen Superconductive Soft-X-ray Free Electron Laser (S3FEL) project requires enhanced magnetic field stability of correction magnets. However, when switching power supplies are used for correction magnets at low currents, the very narrow pulse width of the power switch leads to poor stability in the output current.PurposeThis study aims to propose a method involving a series controllable bidirectional impedance circuit to improve the stability of low current output from the correction magnet power supply.MethodsFirstly, the characteristics of a controllable bidirectional impedance was identified when connected in series from the power supply to the correction magnet, and a Bode diagram was applied to analyzing its features. Then, a controllable bidirectional impedance circuit was designed on the basis of simulation analysis. Finally, experimental validation was conducted using the correction magnet and power supply from Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility (SSRF).ResultsThe experimental results demonstrate that serially connecting controllable bidirectional impedances not only improves low current stability but also allows for smooth switching between MOSFETs and controllable bidirectional impedances.ConclusionsThe circuit design proposed in this study is simple and proves to be effective to improve the stability of bipolar magnet power supply under low current condition.
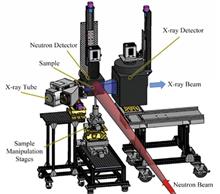
In multiple important fields such as industry and homeland security, traditional single ray imaging technology often only provides limited image information and material analysis, making it difficult to meet the growing demand for non destructive detection. With the continuous advancement of technology, various ray fusion imaging techniques have emerged, which can comprehensively obtain richer detection information, thus gradually attracting widespread attention from scientists around the world. This article first provides a detailed introduction to the basic principles of X-ray and neutron fusion imaging technology, and elucidates its advantages in material identification and structural analysis. Secondly, by reviewing the development history and application status of X-ray and neutron fusion imaging technology in China and other countries, the research progress and application examples of different countries in this field are comparatively analyzed. Subsequently, the main achievements of the current research are summarized, and some issues in the existing research plan are pointed out, such as the complexity of data processing and limitations in imaging accuracy. Finally, the future development of X-ray and neutron fusion imaging technology is discussed, and possible technological innovation directions and application prospects are discussed.
Since the ion cyclotron resonance isotope separation (ICR-IS) method was proposed in 1970s, it has received widespread attention from researchers and industries around the world. Based on the published results on the ICR-IS in the past few decades, a review is presented in this paper including the fundamental theories of ICR-IS, basic structures of the devices, major criteria for obtaining significant isotope separation effects; and in particular, the recent progress in the theoretical and experimental research fields for obtaining different isotopes using the ICR-IS approach is summarized and discussed. And finally, the key scientific and technological issues in future research for promoting industrial applications of the ICR-IS method are discussed briefly.
Indium phosphide (InP)-based high electron mobility transistors (HEMTs) have been widely adopted in space communication systems such as satellites, manned spaceflight, and deep space exploration due to their high frequency and gain, and low noise. However, high-energy particles such as protons, electrons, and neutrons in a space environment affect the performance of InP-based HEMTs and reduce the reliability of space communication systems. This paper mainly discusses the influence and degradation mechanism of defects induced by high-energy particle irradiation on the direct current (DC) and radio frequency (RF) performance of InP-based HEMTs, as well as the transconductance and kink effect in the irradiation environment. Subsequently, the research progress of radiation-hardening measures for InP-based HEMT devices is summarized and analyzed so as to provide the theoretical guidance for studying damage mechanism of InP based HEMT irradiation effect and improving its radiation-hardening technology. Finally, based on current challenges in the field, future research directions are proposed for radiation effects and radiation-hardening technologies of InP-based HEMTs.
BackgroundIn order to ensure the accuracy of the dose received by the patient in radiotherapy, it is usually necessary to verify the plan before treatment, and the water tank is widely used to achieve this purpose. However, the existing dose validation tanks can only be used for beam therapy terminals with horizontal, vertical and 45° angles, which cannot meet the multi-angle dose validation requirements of the advanced rotary Gantry beamline treatment rooms.PurposeThis study aims to develop a three-dimensional (3D) water tank for multi-angle beam dose verification, so as to meet the beam detection requirements of multi-direction beam irradiation of gantry beam line.MethodsThe water tank box was constructed from Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) and driven by the motor to rotate around the isocenter. Solidworks Simulation software package was employed to simulate the structure of the water tank, and the motion accuracy of the 3D motion mechanism was evaluated. The lateral profile dose distribution of the beam at different depths in the water was measured by a multi-strip ionization chamber (MSIC), and a 3D dose distribution of the pencil beam was obtained by stacking the profile dose distribution measured at different depths. The measurement results were compared with data obtained from commercial PTW water tank.ResultsEvaluation results show that, the maximum position error of the probe is 0.132 mm when the probe is moving in the depth direction, the maximum position error of the probe is 0.24 mm in the Y and Z directions for the probe position adjustment, and the dose measurement deviation is 0.5%±1.18%.ConclusionsThe water tank proposed in this study can quickly and accurately provide the 3D dose distribution of a pencil beam, hence, provide basic data for treatment planning systems and improve the efficiency of regular quality assurance practice. The whole measuring device can be rotated around the isocenter of the treatment head, meeting the beam detection requirements of multi-directional irradiation in the Gantry treatment rooms.
BackgroundIn order to apply in different scenarios of silicon photomultiplier (SiPM) coupled scintillator detector, preamplifiers need to fulfill different requirements.PurposeThis study aims to design high-bandwidth, low-noise preamplifiers to adapt for different output modes of SiPM-coupled scintillator detector.MethodsBased on OPA855 chip and consideration of bandwidth and noise, a transimpedance amplifier (TIA) and a voltage feedback amplifier (VFB) were designed. The amplifier circuits were simulated and analyzed using PSpice for TI software to obtain circuit parameters. Then, the signal response and noise baseline level were measured and analyzed by experimental test using 241Am radioactive source and a sSiPM-coupled Cerium-doped Gadolinium Aluminum Gallium Garnet (GAGG(Ce)) detector.ResultsExperimental results show that these preamplifiers have good gain stability, high-bandwidth and low-noise. TIA's bandwidth is 101 MHz, lower than VFB's 381 MHz, but its baseline noise level (σnoise≈448.32 μV) is better than that of the VFB's ( σnoise≈680.96 μV).ConclusionsFor GAGG(Ce) detector ,both VFB and TIA meet the bandwidth design requirements of 2 ns for fast output pulse and 20 ns for standard output pulse, respectively. Limited by the inherent noise of circuits and the input capacitance of SiPM,TIA is suitable for energy measurements and small-area SiPM applications, while VFB is more suitable for time measurements and large-area SiPM arrays.
BackgroundElectroporation technology can be used in biomedicine, food safety, sewage treatment and other fields. The pulse waveform is an important parameter affecting electroporation efficiency.PurposeThis study aims to propose a distributed arbitrary waveform high-voltage pulse generator composed of multiple standard pulse power modules to meet the needs of controllable electroporation.MethodsFirstly, based on full bridge inverter structure, the framework of the distributed generator with bipolar all solid state Marx topology was designed, and the basic working principle of the main circuit of standard module was elaborated. Then, the power and load parameters were simulated and analyzed using Simulink module of MATLAB software. Based on the simulation results, a prototype generator composed of two standard modules in series was built, and the resistance load test was carried out. Finally, under the condition of the same pulse amplitude and pulse energy, the electroporation experiment of microalgae was carried out to verify the correctness and feasibility of high-voltage pulse generator.ResultsThe generator can output arbitrary pulse waveform of ±8 kV with 33 electrical levels. Under the condition of pulse amplitude 8 kV and pulse energy 0.4 J, the electroporation efficiencies of positive square wave and exponential attenuation wave are 65.25% and 46.15%, respectively.ConclusionsThe applicability of the generator proposed in this study is demonstrated in the controllable electroporation experiment, and the electroporation efficiency of square wave with constant amplitude and energy is higher than that of exponential attenuation wave.
BackgroundAppropriate fast detection method for radionuclides is necessary for customs radioactive security inspection with high flow rates and low counting rate levels. Compared with the traditional uncertainty analysis method, the Bayesian method and the Sequential Probability Ratio Test can fully utilize all the information of measured physical quantities and reduce the required sample size.PurposeThis study aims to develop a new method to solve the problem of the fast and accurate detection of radionuclides at low radioactive counting rate scenarios.MethodsA new Sequential Bayesian fast detection method for radionuclides was proposed on the basis of binary hypothesis H0 (no radionuclides) and H1 (radionuclides). Based on the principle that the time interval between adjacent two rays was exponential distributed, the decision was caculated by collecting a series of ray time samples in chronological sequence, and decisions were made by comparing the decision function with the preset upper and lower thresholds. Finally, experimental verifications were conducted on the feasibility, detection performance, and universality of the method by placing a set of standard point sources at different distances from the front of a LaBr3(Ce) detection system in both low and natural radiation background environments. The effects of the key parameters of the method on the detection performance were investigated.ResultsUnder the absence of radionuclides in two type of background radiation environments, the average detection time for background radiation by this method is 24.08 s and 10.54 s, with an average detection sample size of 1 427 and 1 742, respectively. Under the presence of radionuclides in two type of background radiation environments, the lower limits of detection sensitivity of experimental measurements are 8.2% and 6.1%, respectively, the corresponding average detection times were only 8.59 s and 6.61 s respectively, and the experimental measurement false negative rates were all zero.ConclusionsResults of this study verify that above proposed method is very suitable for fast detection of low-level radionuclides.
BackgroundAccurate prediction of the coefficient of heat transfer (HTC) under extremely high parameter conditions in nuclear reactors is crucial for the design and operation of reactors, but the HTC is influenced by many factors, and there are issues such as unclear physical model and lack of experimental data. Traditional empirical relations often struggle to meet the demands of high-precision numerical calculations. Machine learning algorithms can effectively address the complex nonlinear problems, but some results do not conform to physical laws.PurposeThis study aims to propose a physical information machine learning (PIML) algorithm model that can calculate thermal parameters more accurately.MethodsFirstly, HTC experimental data were collected from a circular tube and subjected to preprocessing. Then, the HTC model was developed by combining the Jens-Lottes formula and the Thom formula with Multi-layer Perceptron (MLP), Backpropagation Neural Network (BPNN), and Random Forest (RF). Following this, the preprocessed data were partitioned into training and testing sets, with the training set utilized for model training and the testing set employed for model validation. Finally, six algorithms in the HTC models were evaluated and compared against empirical correlations.ResultsEvaluation results show that the calculation accuracy of Jens-Lottes formula combined with RF in the HTC model is the highest, with average relative error of predicting experimental data of 3.17%. The expandable range of the model accounts for 63.6% of the total applicable range, demonstrating good extrapolation capabilities. At the same time, using the PIML algorithm significantly enhances the computational accuracy of the physical model. The model based on the Jens-Lottes relationship combined with RF reduces the relative error of evaluation by 24.5% compared to the empirical relationship.ConclusionsThe PIML algorithm proposed in this study provides a framework for a high precision calculation model for HTC. It also provides a reference for expanding the scope of application.
BackgroundIn a series of startup physics tests, measuring the control rod worth is a critical means to determine whether the actual worth of the control rods matches the design values. This test ensures that the reactivity of the reactor can be precisely controlled through the control rods, thereby ensuring the safe operation of the reactor. Traditional methods for this measurement include the boron dilution method and the dynamic rod worth measurement method. Although these methods are now widely used in nuclear power plants (NPP), there is still potential for further improvement in both safety and economic performance. Subcritical control rod worth measurement does not require equipment transformation and on-site operations, which makes it easier to implement whilst control rod worth measurement under deep subcritical conditions is totally a different technique with respect to traditional control rod worth measurements, which changes the reactor condition from the Low Power Physics Test (LPPT) window after reaching criticality to the Criticality Approach Test (CAT) window before reaching criticality. The test conditions vary from near-critical condition to deep subcritical condition, making the core much safer.PurposeThis study aims to minimize the risk of core re-criticality during control rod withdrawal by measuring control rod worth within existing test windows without occupying the critical path.MethodsSubcritical control rod worth measurement was implemented within the window of startup physics tests, saving outage time and improving the economic efficiency of the power plant, hence no additional work was required for subcritical control rod worth measurement test, except for collecting relevant data while measuring the worth of control rods during the test. Two functional modules, namely the spatial correction factor calculation module and the data processing and display module were developed for subcritical control rod calibrating system. Under deep subcritical conditions, the traditional point reactor model was no longer applicable due to the significant impact on neutron flux distribution caused by the external neutron sources, therefore, a different approach was adopted to calculate the effects of external neutron sources on neutron flux distribution under deep subcriticality by carrying out a spatial correction of count rate to ensure a linear relationship between the corrected count rate and the subcriticality. Finally, two verification tests of subcritical control rod worth measurement were conducted on the AP1000 reactors at Sanmen Nuclear Power Plant (NPP), the count rate of the source range detector and reactor condition data were collected, and processed for quality improvement and spatial correction of count rate.ResultsVerification results show the linearity of the corrected count rate achieved is above 0.999, and the maximum subcriticality provided is approximately 0.1, indicating that the experimental conditions are in a deep subcritical state. All sets of control rod worth values meet the acceptance criteria requirement of a relative deviation of 10% or an absolute deviation of 75 pcm.ConclusionsThe results met the acceptance criteria of control rod worth, providing preliminary verification of the accuracy and reliability of calculation system under deep subcritical conditions.
BackgroundWith the development of nuclear-thermal coupling technology, it is essential to consider the strong coupling effects between multiple physics fields and achieve high precision and large-scale parallel computing. Simultaneous solutions to the conservation equations of multiple physics fields need to be pursued, providing a unified approach to modeling, discretization, and iterative computation processes.PurposeThis study aims to achieve discrete and iterative solutions for multigroup neutron diffusion equations and neutron transport equations, considering the strong coupling between neutronics and thermal-hydraulics.MethodsFirstly, based on the open-source computational fluid dynamics (CFD) platform OpenFOAM, the finite volume method (FVM) was employed to discretize the control equations for neutron diffusion and neutron transport using the Gauss theorem. Then, the discrete ordinates method was applied to the discretization of the neutron transport equation for spatial angular discretization, and FVM was used to discretize both neutron diffusion and neutron transport equations spatial variables whilst the multigroup method was employed for discretizing energy variables, and implicit Euler method was utilized for discretizing time variables. Finally, neutron diffusion was verified using three benchmark cases, i.e., two-dimensional International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), three-dimensional IAEA, and three-dimensional LMW, to validate the effectiveness of the developed program, and neutron transport was verified using various benchmark cases including IAEA, TAKEDA, and C5G7.ResultsThe verification results for the two-dimensional IAEA benchmark show excellent agreement, with a maximum error of 1.1% in normalized power. The three-dimensional IAEA benchmark results align closely with reference values, showing a maximum error of 3.4%. For the three-dimensional LMW benchmark, the total power at 20 s is slightly underestimated, with a maximum error below 2%. The IAEA criticality benchmark results show region-averaged flux and effective multiplication factor deviations of 6.9% and 22×10-?, respectively. The TAKEDA benchmark confirms the program's accuracy in three-dimensional problems, with effective multiplication factor, neutron flux, and control rod worth matching reference values. The C5G7 benchmark validates the FVM-based transport algorithm's strong geometric adaptability and ability to solve both uniform and non-uniform neutron physics problems accurately.ConclusionsFVM-based neutron diffusion and transport algorithms developed in this study lay the foundation for the future simultaneous solution of conservation equations for physical and thermal multi-physics fields under a unified programming framework. The integrated verification of neutron diffusion and transport programs underscores the reliability and flexibility of the FVM in accurately solving complex neutron transport and diffusion scenarios, providing a pathway for enhancing precision and computational efficiency in nuclear engineering simulations under a unified programming framework.
BackgroundGas-cooled fast reactor (GFR) is one of the six recommended nuclear reactor types of Generation IV Forum (GIF) with the lowest technical maturity. Cooled by inert gas like helium and super critical carbon dioxide which performs not so good as water or liquid metal in heat transfer, GFR has been challenged by safety issues especially in Loss-Of-Coolant-Accident (LOCA) events. It has been considered to be an effective way to improve the core inherent safety of GFR by strengthening the temperature feedback on reactivity in the core. However, with no moderating materials and low neutron reaction rates which cause a harder neutron spectrum than other reactor types, GFR has very weak negative temperature feedback.PurposeThis study aims to optimize nuclear design of GFR core by increasing the negative temperature feedback.MethodsFirstly, moderating materials were utilized in the fuel assemblies (FAs) in order to get a softer neutron spectrum in the core and increase both the doppler effect of the fuel and the temperature feedback on reactivity. Four moderators including graphite, beryllium oxide, zirconium carbide and zirconium hydride were used in the FA with different geometric structures such as uniformly mixing in the fuel pellets, separate rods distributed in the fuel rod bundles and thick layer outside the fuel rod bundles. Then, Monte Carlo (MC) calculation software RMC was employed to carry out neutronics analysis of the GFR core. Neutronics characteristics of these FA models was comparatively analyzed in details to find the best performance FA model. Finally, a 10-megawatt-power micro GFR core design was given based on the selected FA structure. Effects of the High-to-Diameter ratio (H/D) value as well as the uranium enrichment of fuel on the temperature feedback of the core were thoroughly studied and optimization of the GFR nuclear design was conducted.ResultsThe MC simulation results show that the optimized GFR core has a more than twice larger reactivity temperature coefficient value compared to the general core design, which greatly enhances the inherent safety of GFR core. Meanwhile, flat power distribution of the core has been demonstrated with the axial and radial power peaking factor of 1.14 and 1.23, respectively. Results of temperature field around the hottest fuel rod show sufficient safety margin of and that the core has the ability to automatically shutdown by negative temperature feedback solely.ConclusionsFA model with a layer of beryllium oxide moderator has shown the best performance, and the effectiveness of the optimization methods for reactivity temperature feedback and core design of GFR is verified in this study, providing design experience for the future GFR nuclear design and optimization.
BackgroundThe neutral beam injection system (NBI) has the highest heating efficiency and the clearest physical mechanism, so it has become one of the main auxiliary heating methods used in the world's large magnetic confinement controlled thermonuclear fusion devices. The application of NBI system based on negative ion source is increasingly demanding and urgent. Cavity ring-down spectroscopy (CRDS) is a highly sensitive absorption spectrum measurement technique with relatively simple principle, and the measurement results are not limited by electromagnetic field interference and other plasma parameters.PurposeThis study aims to explore the characteristics of negative ion generation in negative ion source based on CRDS, and measure negative ion density produced by NBI.MethodsFirst of all, a CRDS diagnostic system was developed on a large area negative ion source. Then the related characteristics of negative ion production was investigated by sequentially measuring the decay time of pulsed laser in front of the plasma electrode plate under different experimental parameters. Finally, developed CRDS diagnostic system was employed to study the characteristics of hydrogen anion generation under different experimental parameters, such as radio-frequency (RF) power, source pressure and bias voltage.ResultsExperimental results show that produced negative hydrogen ions increase with the increase of RF power and pressure in the source cavity. Due to the different effects of the two changes on the electron temperature, the growth rate of negative hydrogen ions changes opposite under the influence of different power and pressure. There is an optimal value of bias voltage that is conducive to the generation of negative hydrogen ions because of the plasma potential.ConclusionsApplication of CRDS-based measurement approach in this study provides valuable experience for further research on the generation of negative hydrogen ions and the beam quality.
BackgroundThe operation of marine reactors and floating nuclear power plants is challenged by the thermal fluctuation of heat transfer surfaces caused by oceanic motion. The pyroelectric effect of lithium tantalate (LiTaO3, LT), a material with high Curie temperature and low relative dielectric constant that changes its spontaneous polarization with temperature variations, has the potential to influence the wettability of surfaces, thereby improving heat transfer performance.PurposeThis study aims to prepare LT coatings with controlled pyroelectric properties and to investigate the mechanism of temperature-dependent wettability of LT, thereby enhancing heat transfer efficiency in two-phase systems.MethodsFirst of all, the sol-gel method was used to achieve the controlled synthesis of LT. Subsequently, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was employed to characterize micro surface morphology of coatings whilst the crystal phases and crystallinity in LT coatings were analyzed by X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns. Then, the effects of synthesis parameters on the crystallinity, coating quality, particle size and pyroelectric properties of LT coatings were explored by systematically changing the curing time, sol settling time and annealing temperature in the sol-gel method. Finally, the pyroelectric effect and mechanism of wettability modulation were investigated by evaluating the hydroxyl radicals generated during temperature changes.ResultsThe results indicate that the particle size of LT increases with increasing annealing temperature. The pyroelectric characteristics are significantly influenced by the thickness and particle size of the coatings, pyroelectric performance is enhanced by increasing the coating thickness and decreasing the particle size. Fluorescence spectroscopy analysis shows that the hydroxyl radical concentration of LT increases during the heating process, confirming that LT has the ability to regulate the hydroxyl radical concentration when undergoing heating and cooling cycles.ConclusionsResults of this study demonstrate that LT coatings have temperature-dependent surface wettability of heat transfer in two-phase system with variable temperature.
BackgroundTritium permeation leakage exists in fusion reactor such as International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER), which leads to a series of problems such as fuel loss and environmental pollution, etc. Al2O3 coating is a hot research topic for preventing tritium permeation. The preparation of Al2O3 coatings on the surface of materials is an effective way to solve this problem. Electrodeposition of Al and heat treatment diffusion technology is a common method to prepare tritium-resistant coatings. The relevant parameters during the preparation process have important effects on the microstructure and tritium-resistant performance of Al coatings.PurposeThis study aims to analyse the mechanism of the effect of different electrodeposition process parameters on the phase structure and internal micro-morphology of aluminium coatings, and to obtain good quality aluminum coatings.MethodsFirstly, the aluminum coating was prepared on the surface of 316L stainless steel substrate at room temperature with 316L stainless steel as cathode, aluminum wire (99.99% purity) as anode, and AlCl3-1-Ethyl-3-methylimidazolium Chloride (EMIC) ionic liquid as plating solution. Then, the changes of surface and cross section morphology of aluminum coating were observed by changing the current density under direct current mode whilst the plating time (60 min) was fixed, and the difference of the microstructure of the aluminum coating prepared under the three current modes, i.e., direct current (15 mA·cm-2), unidirectional pulse and bidirectional pulse current, was compared. Both the X-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) were employed to characterize the phase structure and internal microstructure of aluminum coatings.ResultsThe experimental results show that the coatings are all composed of Al element and have a face-centered cubic structure, in which the preferred orientation of the crystal faces of the direct current and bidirectional pulsed electrodeposition coatings is different. In the direct current mode, some grains on the coating surface increase with the increase of direct current density, and the optimal current density of direct current electrodeposition ranges from 10~20 mA·cm-2. Compared with the direct current electrodeposition process with similar parameters, under the condition of the same current density and electroplating time, the grain size of the coating microstructure obtained by pulsed current and bidirectional pulse electrodeposition is more uniform, and the grain size after bidirectional pulse electrodeposition is smaller, and the thickness of the aluminum coating obtained by unidirectional pulse current waveform electrodeposition is the largest. The grain and thickness of aluminum coating formed by bidirectional pulse current are the smallest and the grain size is uniform.ConclusionsThe introduction of pulse current has a significant effect on the size and uniformity of particles on the surface of aluminum coating. The coating obtained by pulse current is relatively dense, the grain thinning phenomenon is obvious, and the grain size is relatively uniform. The reason is that the large instantaneous peak current can inhibit the excessive growth of the grain and play a leveling role, so as to further improve the micro-morphology of the coating and improve the quality of the coating.
BackgroundIn electron spin resonance dating (ESR) of old fossils, the double saturation exponential (DSE) function is often used for the equivalent dose (DE) determination, it generally requires more than 15 dose points and the maximum irradiation dose (Dmax) greater than 20 kGy to ensure the fitting accuracy, which limit the practical application of dating old fossils by ESR method with insufficient sample size.PurposeThis study aims to explore the feasibility and reliability of using the single saturation exponential (SSE) fitting function to fit fewer dose points with lower Dmax to obtain the DE values of the fossil teeth from the late Miocene to the early Pleistocene, and compared with the ones determined by DSE function.MethodsFirstly, 17 fossil samples were taken from seven fossil sites in different regions of China and Myanmar, and their ages covered the late Miocene to early Pleistocene. Then, three fitting functions, i.e., DSE, SSE and EPL-exponential plus linear, were employed to obtain the DE values of ESR using the additional dose method. Finally, the influence of different Dmax on the DE results of three fitting functions was investigated by comparative analysis.ResultsComparison results show that: (1) The SSE and DSE function are used to fit the 15 dose points with Dmax=50 kGy, and the DE-SSE results of 11 samples are basically consistent with the DE-DSE results, meanwhile the precision of the fitting results of SSE function is generally higher than DSE cases. (2) For samples with DE>4 500 Gy and 2 000 Gy<DE<4 500 Gy, the results of SSE and DSE are basically consistent within the error range under the conditions of Dmax≥6.5×DE and 1.9×DE<Dmax<3.5×DE, respectively, which can provide the recommended dose value of Dmax for samples with DE>2 000 Gy when using SSE function. (3) For fossil samples with 2 000 Gy<DE<4 500 Gy, the SSE function can be used to fit the 11 dose points with Dmax≤10 kGy, and the DE results are generally consistent with the DSE function within the error range.ConclusionsBased on above results, it is viable to use SSE function to perform DE fitting on old fossil samples under certain Dmax/DE conditions, and establishing the standardized growth curve of old fossils and the fragmental analysis of the fossil teeth for DE determination will be explored in the future study.
BackgroundBetavoltaic nuclear batteries, leveraging beta-emitting radioisotopes, offer inherent advantages such as long-term reliability, high energy density, compact form factors, and robust resistance to interference, positioning them as promising power sources for self-powered portable or embedded microdevices.PurposeThis study aims to enhance the conversion efficiency and output power of betavoltaic batteries with comprehensive consideration of the effects of backscattering, depletion region width, diffusion length, and electrode structure on charge collection efficiency, conversion efficiency, and output power.MethodsBy optimizing the device and electrode structure, i.e., introducing a PIN structure with "concentration gradient I- layer", optimizing the depletion region width, doping concentration and electrode materials, and increasing the spacing between electrode grid lines, 63Ni-SiC-based PIN junction betavoltaic batteries were successfully fabricated with higher overall conversion efficiency and output power. Both the Monte Carlo simulations and numerical computations were employed to obtain characteristic parameters of these developed batteries, and their performances were measured by experiments.ResultsThe fabricated batteries exhibit short-circuit currents, open-circuit voltages, output powers, and total conversion efficiencies ranging from 10.29 nA·cm-2 to 13.43 nA·cm-2, 1.32 V to 1.44 V, 11.66 nW·cm-2 to 14.69 nW·cm-2, and 2.24% to 2.82%, respectively. Compared with previous reported work, the open-circuit voltage, fill factor, and overall conversion efficiency increase by an average of 127.50%, 114.47%, and 512.10%, respectively. Moreover, the overall conversion efficiency is higher than those reported in the literature (0.5% to 1.99%).ConclusionsThese results indicate that the conversion efficiency and output power of betavoltaic batteries can be significantly improved by taking above-mentioned optimization measures, providing important theoretical guidance and experimental evidence for the design and fabrication of betavoltaic batteries.
BackgroundSolid-state amplifiers of synchrotron radiation high-frequency cavity equipment may sustain unrecoverable damage due to the excessive reflected power resulting from load detuning, a high-power circulator is used to guide the reflected power to the absorbing load and thus protect the power source. In this case, if the reflected power suddenly increases during device operation, the temperature of the circulator cavity will be risen and the parameter characteristics of the gyromagnetic ferrite will be changed in the circulator, and eventually lead to poor absorption of the reflected power by the load.PurposeThis study aims to design and develop a circulator with a temperature compensation control unit, capable of functioning at 499.654 MHz with a 160 kW continuous wave radiofrequency power.MethodsFirstly, the circulator was simulated and optimized using the HFSS software. Thermal simulation shows that the temperature rise of ferrite sheets under 160 kW continuous wave is less than 13 °C. Then, impedance matching was performed on the circulator using tuners arranged at each of the three ports, and feedforward control was used to compensate for the temperature changes. Finally, a constant temperature water tank was employed to simulate the change in water temperature during actual operation, the reliability of temperature compensation function of the control unit was verified by the performance of the circulator restoring to the best condition.ResultsThe insertion loss is better than -29 dB under the worst case of a complete short circuit at the output port, the circulator loss is less than 0.1 dB in the bandwidth of ±5 MHz, and this loss reaches 0.06 dB at the center frequency.ConclusionsThe S parameters of the circulator meet the design requirements, and the reliability of the temperature control compensation unit of circulator is verified by constant temperature water tank simulation test in this study.