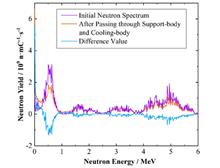
BackgroundBoron Neutron Capture Therapy (BNCT) is a binary radiation therapy with strong targeting and high energy transfer line density at the cellular scale. It has the advantages of short treatment cycle and minimal damage to surrounding healthy tissues, making it a promising cancer treatment method.PurposeThis study aims to design beam shaping assembly (BSA) to make the neutron beam of D-Be neutron source suitable for BNCT and ensure neutron directionality.MethodsThe Monte Carlo simulation programs GEANT4 and FLUKA were employed to simulate the generation of 9Be(d,n)10B reaction neutron sources and subsequent neutron moderation. Then, a scheme design for BSA was carried out using a 1.45 MeV, 30 mA deuterium beam to bombard a 9 μm thin beryllium target, and set a basis BSA model with a cylindrical structure as a whole.ResultsThe simulation results show that using a 20 cm thick BiF3 and 30 cm thick MgF2 combined slowing layer, a 30 cm thick Pb reflector layer, a 9 cm thick MgF2 supplementary slowing layer, and a 0.2 mm thick Cd thermal neutron absorption layer, the outlet is ensured to γ and fast neutron composition, Φepi/Φth, Φepi/Φfast meets the recommended values of the IAEA (International Atomic Energy Agency).ConclusionsThis study obtained the neutron spectra and BSA specific design scheme of low-energy deuterium beams and thin beryllium targets, providing data reference for the slowing shaping of neutrons in D-Be neutron sources and supporting subsequent research on D-Be sources.
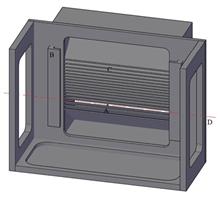
BackgroundCompared with commercial X-ray tubes, Betatron can emit MeV-level X-rays and its penetration capability is better than that of keV-level X-rays, which can be used for non-destructive testing (NDT) of large workpieces.PurposeThis study aims to design and build a 2D/3D X-ray imaging platform for NDT of large workpieces by using a compact Betatron as the X-ray source.MethodsFirstly, the hardware of the imaging platform was designed. It consisted of the compact Betatron with X-ray energy of 2.50/7.50 MeV, a high-energy X-ray line array detector with GGAG(Gd3Ga2Al3O12) scintillator and a two-axis mobile platform. Then, based on the principle and image correction algorithm of the 2D imaging system, the stripe noise characteristics in both the pixel direction and time direction were analyzed, and the blank pixel correction method was employed to correct the two-dimensional image. Its two-dimensional imaging performance test was conducted on a 6 cm square steel workpiece. Finally, three-dimensional image reconstruction of the workpiece was achieved by rotating the workpiece to obtain projection values at different angles, and the spatial resolution of 3D imaging was calculated using logistic function fitting method. Results of different tomographic reconstruction algorithms were compared and analyzed to obtain important 3D imaging system parameters.ResultsMeasurement results show that the thickness of the stainless-steel half-value layer of the system is 24.94 mm, the 2D imaging spatial resolution is 2.12 mm, and the tomographic reconstruction image spatial resolution is 1.00 mm.ConclusionsCompared with the keV-level X-ray imaging system, this system can complete the non-destructive testing of larger workpieces.
BackgroundShanghai HIgh repetitioN rate XFEL and Extreme light facility (SHINE) is a large-scale scientific facility under construction in China. Due to 1 MHz repetition rate and thousands of kilometers length of SHINE, the accelerator interlock system should be a large system with response speed in microsecond magnitude and capable of processing tens of thousands of signals simultaneously.PurposeThis study aims to design and implement fast interlock system integrated with the conventional slow interlock system for SHINE accelerator.MethodThrough the analysis of SHINE requirements, FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) technology, distributed control technology, and network communication technology were adopted to complete the design of the fast interlock system. The integration of fast interlock system and slow interlock system on the same platform was achieved through programmable control technology and interface program development. The interface development software for the control system was designed and developed using PyDM, and the massive data exchange between large-scale interlock system was solved by using FL-net technology. Finally, based on Experimental Physics and Industrial Control System (EPICS), the design of operation mode, system architecture and data transmission were implemented and deployed.ResultsThe accelerator interlocking system developed in this study enables data exchange and expansion between fast and slow interlocks, as well as between any station. The average response time for multiple sites connected by a 1 m cable is 903.32 ns, and the average response time for multiple sites connected by an 800 m cable is 5.33 μs.ConclusionsAll the functions of fast interlock system are implemented and verified, and the system have been put into online operation for SHINE injector. The response time test results meet the SHINE operation requirements, and remote control of the system has been implemented based on the EPICS.
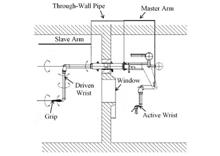
BackgroundReprocessing technology is recognized internationally as one of the most promising technologies to realize the closed cycle of nuclear fuel. Shanghai Institute of Applied Physics (SINAP) of Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) has been focusing on the development of this technology, as well as the corresponding support systems engineering in the past decade. The hot cell is an important guarantee for the practical application of nuclear fuel reprocessing technology, therefore, a remote operation system suitable for reprocessing post-treatment process equipment is developed so that the pyroprocessing experiments of molten salt can be conducted in hot cell.PurposeThis study aims to evaluate equipment remote operation and pyroprocessing verification in hot cell.MethodsMain focus of this study was the fluoride volatility and vacuum distillation process of molten salt reactor fuel salts, and the remote operation evaluation of hot cell equipments and pyroprocessing verification experiments were carried out using multi-view coordination. The workload of the operation of the fluoride volatility and vacuum distillation process units was analyzed and evaluated, and the operation efficiency was obtained based on the frequency and time spent on the basic movements of the manipulator in pyroprocessing verification experiments. On this basis, experiments were conducted on the uranium fluoride volatility in the LiF-BeF2-ZrF4-UF4 salt, and vacuum distillation process in LiCl-KCl, LiF-NaF-KF molten salts. Then, before and after the fluoride volatility experiments, inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) was used to determine the uranium content in molten salt, and the conversion rate and reaction rate of uranium were calculated. The uranium content in the base solution downstream of adsorption column was analyzed to obtain the recovery rate of uranium product. Finally, the molten salts evaporation was calculated by the residual mass after the vacuum distillation experiments. The evaporated salts were collected through the condensing cover, and the collection rate was calculated.ResultsThe results of reprocessing validation experiments in hot cell show that the workload of feed and discharge in the operation unit is large than 2.0 on the basis of reasonable arrangement of process equipments in hot cell. The load values for the on/off operation are relatively small, with values of 0.07 and 0.14, respectively. In the operations of processes, due to the various types and frequency of the manipulator operation, the feed and discharge units take a long time with a time-consuming of 20 min and 19 min respectively. The operational efficiency of the pyroprocessing in the hot cell can be improved by optimizing processes and reducing unnecessary operations. A uranium conversion rate of 99.8% and recovery rate of over 99% in molten salt are achieved in he uranium fluoride separation experiment. By improving distillation temperature and sealing of components, a higher evaporation rate and a 100% recovery rate of molten salt distillation are achieved in the vacuum distillation experiments.ConclusionsThe designed small-scale fluoride volatility and vacuum distillation devices can be used for remote operation and process experimental research in the hot cell, and the experimental results meet the key process targets. The research work can provide a reference basis for the pyroprocessing of real spent fuel in hot cell.
BackgroundThe gas ionization chamber is a kind of intensity monitoring detector widely used in Synchrotron Radiation Facility. Lytle detector is often used to measure the fluorescence signal from the element of interest in the fluorescent mode XAFS (X-ray absorption fine structure), it is one of the important fluorescence detectors for the X-ray absorption spectrum study and used in XAFS beamline station of Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility (SSRF). However, this type detector is predominantly manufactured by foreign company (The EXAFS Company).PurposeThis study aims to develop a domestic fluorescent gas detector according to the operating conditions and technical requirements of fluorescent mode XAFS.MethodsFirstly, a filter and a slit assembly were designed and optimized with Geant4 toolkit. Subsequently, a multilayer grid ionization chamber for fluorescence detection was designed, and the supporting electronics circuit with both high voltage and amplification gain functions was designed. Secondly, all components were manufactured and assembled into a complete detector, and the digital noise, response time, response intensity, and linearity of self-developed detector were tested at BL11B beamline of SSRF. Finally, the actual measured performance of self-developed detector was tested and compared with Lytle detector at BL11B beamline.ResultsThe test results indicate that the digital noise level is approximately ~3.2×10-9 V, which is superior to the (9~10)×10-9 V observed in the Lytle detector. Additionally, the response time is less than 2.1 ms, significantly outperforming the Lytle detector's response time of approximately 150 ms. The linearity of the detector's response also exceeds 0.999 6.ConclusionsThe self-developed detector with shorter response times and better performance than Lytle detector has been achieved, and the localization replacement of the Lytle type detector is realized. Meanwhile, it has been used in the fluorescent mode XAFS of BL11B beamline at SSRF.
BackgroundGaussian pulses have good time and frequency domain characteristics, and perform well in terms of signal-to-noise ratio, ballistic loss, and other aspects of the synthesis. When performing Gaussian pulse shaping, errors introduced by hardware limitations may lead to differences in shaping results. Compared to infinite impulse response (IIR) filters, finite impulse response (FIR) filters have the advantage of being less affected by errors and more stable.PurposeThis study aims to propose a FIR filter-based Gaussian pulse shaping algorithm using impulse response functions, and realize a FPGA-based hardware implementation of this algorithm to evaluate the impact of hardware limitations on it.MethodsFirst of all, the discrete impulse response of Gaussian pulse shaping (GPS) was derived by means of impulse response invariant transformation, and shaped pulse waveforms under different quantization accuracies and truncation intervals were obtained using a computer simulation, so did that under Gaussian pulse shaping with or without additional truncation were assessed. Then, X-ray fluorescence signals emitted by Mn sample was acquired using fast silicon drift detector (FAST-SDD) to assess shaping performance on the spectrum, and processed by a digital multichannel analyzer utilizing FIR GPS algorithm implemented in a field programmable gate array (FPGA) processing board. Finally, peak area and energy resolution of the spectrum were used to compare performances of GPS under different quantization accuracies and truncation intervals, as well as performances of three methods of trapezoidal pulse shaping, Gaussian pulse shaping with additional truncation method and normal GPS.Results & ConclusionsFor comparisons of quantization accuracy, when the quantization accuracy is greater than 4 bits, the shaping performance of GPS remains consistently stable within the peaking time ranging from 120 ns to 1 140 ns when the quantization accuracy is greater than 4 bits. Otherwise, the influence of low quantization accuracy on GPS is minimized ranging from 420 ns to 780 ns. For inter-method comparisons, GPS with or without additional truncation outperform trapezoidal pulse shaping. The truncated GPS algorithm has better energy resolution and saves more hardware resources, whilest the normal GPS algorithm owns better pulse pile-up rejection capability for the same peaking time.
BackgroundMultisphere neutron spectrometers are pivotal in accurately measuring neutron flux across various fields. The inherent complexities and non-linearities in their calculation processes, such as correlated variables, make traditional uncertainty analysis methods based on theoretical models and empirical formulas (e.g., the GUM (Guide to the Uncertainty in Measurement) method) unsuitable.PurposeThis study aims to demonstrate the application of the Monte Carlo (MC) method as an effective tool for evaluating measurement uncertainty in multi-sphere spectrometers, addressing the challenges posed by complex systems and non-linear problems.MethodsFirst of all, the MC method was employed to conduct probability density sampling of input variables to obtain the probability density distribution of the output variables. Detailed statistical characterization of the calculation results was allowed to provide a more comprehensive understanding compared to conventional methods. Then, numerous simulations were performed to take into account of variability and uncertainty in the input parameters, hence the robustness of the analysis was enhanced. Consequently, this technique overcome the limitations of traditional deterministic approaches, offering more reliable and nuanced insights into the system's behavior. Finally, experiments were carried out using multisphere neutron spectrometers and neutron field standard device (including 4 neutron sources), and the measurement results of neutron flux spectrum under 30 cm iron ball shielding were evaluated using above-mentioned method.ResultsThe spectrum unfolding results obtained by this method have a total uncertainty of 5% in the energy group of interest after being passed by the spectrum unscrambling program.ConclusionsThe application of the MC method offers a robust framework for the assessment of measurement uncertainties in multi-sphere neutron spectrometers. This study not only enhances the accuracy and reliability of spectrometer measurements, but also contributes to the broader field of neutron measurement techniques by providing a reference for the evaluation of complex systems.
BackgroundSevere accident is complex coupling processes involving multiple components, phases, and physical fields, and related research is a complex and challenging systematic engineering project. In recent years, relevant scientific research institutions have placed greater emphasis on the development of integrated analysis codes for severe accident in order to address the issue of program autonomy, and modular severe accident analysis program (MOSAP) is one of them independently developed by Xi'an Jiaotong University, China.PurposeThis study aims to validate the early in-vessel phenomenon analysis model of the self-developed integrated analysis code MOSAP for severe accident.MethodsThe MOSAP code and the internationally recognized severe accident analysis code were used to model and calculate experiments on international standard questions ISP31 and ISP46. The calculation results of fuel and control rod temperature, hydrogen production, and major radioactive nuclide release rates obtained by the MOSAP were compared and analyzed with experimental and internationally recognized code calculation results.ResultsThe results show that the MOSAP calculation results are in good agreement with the experimental and internationally recognized code calculation results, and the deviation between the main parameter calculation values and the experimental values is within 20%.ConclusionsThe self-developed code MOSAP can simulate the early in-vessel phenomena of severe accident such as core overheating, fuel, cladding, and control rod oxidation, as well as fission product release.
BackgroundAfter the steam generator tube rupture accident (SGTR) in the lead-based reactor, water will jet into the molten pool with a lot of steam generated, and bubbles may enter the reactor core affecting the safe operation of the reactor.PurposeThis study aims to observe the penetration depth of water jet into high-temperature liquid pool by visualization technique for the evaluation of this process.MethodsFirstly, a novel experimental system was designed for injecting subcooled water jets into a high-temperature silicone oil pool, and a high-speed video-camera was employed to capture the dynamic process of water jets into the oil pool. Then, a series of visualization experiments were conducted to analyze the penetration behavior of the jets in the pool by manipulating the pressure and nozzle diameter.ResultsA new correlation for dimensionless penetration depth is developed based on the form of model analysis. The discrepancy between predicted results and present experiment results is within ±30%. It is also found that the spatiotemporal inhomogeneity of momentum change and boiling heat transfer has an important effect on the penetration depth.ConclusionsThis study contributes to a deeper understanding of CCI (Coolant-Coolant Interaction) type jets and can be further applied to studying the phenomena when water jets into molten heavy metals.
BackgroundMolten salt reactor (MSR) is one of the six internationally recognized and recommended fourth generation reactors, which is different from conventional solid-state nuclear fuel reactors. It is necessary to analyze the relationship between 7Li abundance and nuclear critical parameters in order to manage MSR core design and nuclear safety supervision.PurposeThis study aims to model a molten salt reactor with reference to engineering practice, and analyze the impact of different 7Li abundance fuel salts on the reactivity of the MSR, as well as the changes in nuclear critical parameters by simulation.MethodsFirstly, a MSR with engineering practice, i.e. the Molten Salt Reactor Experiment (MSRE) designed by Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL), USA, was referenced to establish MSR model with mass abundance of nuclear fuel salt 235U assigned to 20% (enrichment of 20.2%) instead of the 33% enrichment designed by MSRE. Then, based on the established model, Standardized Computer Analyses for Licensing Evaluation (SCALE) code was applied to iterative calculation for quick and accurate obtaining of the 7Li abundance value at the critical state of the MSR core. Finally, in-depth exploration of calculation results was conducted from the perspective of applicable laws and regulations for the safety analysis of MSR.ResultsSimulation results show that the reactivity of the MSR increases with the increase of fuel salt 7Li abundance, and the rate of reactivity variation of the MSR is also related to 7Li abundance. At the critical 7Li abundance (i.e. around 99.98%), for every 0.001% change in 7Li abundance, the reactivity changes by more than 0.05%.ConclusionsBased on the analysis results of this study, the abundance of 7Li has a significant impact on the keff of MSR, hence it is necessary to choose an appropriate 7Li abundance for safety analysis of MSR criticality.
BackgroundHigh-temperature heat pipes, as heat transfer components with high efficiency, safety, and the advantage of not requiring additional power, have broad applications in space nuclear power and small, mobile nuclear power sources. Due to the complexity of the internal mechanisms of high-temperature heat pipes, steady state performance analysis is important for design and operation of lithium heat pipe.PurposeThis study aims to develop an improved lumped parameter numerical heat pipe model with a more complete physical model and a simpler solution for steady state performance analysis of lithium heat pipe.MethodFirst of all, the physical operation of the high-temperature heat pipe was considered to be composed of heat transfer cycles and fluid flow cycles, and the influence of different flow forms, compressibility, and Mach numbers on steam flow, as well as the variation of the liquid core working fluid, were taken into account into the fluid flow cycle. Then, the high-temperature heat pipe was divided into the evaporation section, adiabatic section, and condensation section, each consisting of solid, liquid, and vapor regions, and each part was treated as a node, with physical parameters concentrated on the nodes. Subsequently, thermal conduction differential equations, fluid flow differential equations, and thermodynamic differential equations were established for each node as needed, combining all the differential equations to form a system of differential equations based on the lumped parameter heat pipe with a combined annular and mesh wick. Thereafter, the finite difference method was employed to discretize the system of differential equations, and a Python program was used for solving these equations. Finally, the above-mentioned model was employed to analyze the flow and heat transfer characteristics of the ultra-long lithium heat pipe in the HP-STMC space reactor, and simulate the variations in operating parameters of the lithium heat pipe under fixed heat sink and working temperature conditions.ResultsThe research results indicate that: 1) The program demonstrates good predictive accuracy when compared with literature data. 2) Under fixed heat sink condition, with increasing heating power, thermal resistance, steam velocity, and the dryness of the liquid core decrease. 3) Under fixed working temperature of 1 600 K, the steam does not reach turbulent flow when the heat transfer power is below 8.5 kW, resulting in minimal changes in both total thermal resistance and steam thermal resistance. However, when the heat transfer power exceeds 8.5 kW, steam enters turbulent flow, causing a rapid increase in both total thermal resistance and steam thermal resistance. Simultaneously, steam velocity and the dryness of the liquid core also increase. In contrast, the liquid working fluid does not enter turbulent flow and maintains an extremely low velocity, with a maximum Reynolds number and velocity of approximately 260 m·s-1 and 0.12 m·s-1, respectively. 4) For ultra-long lithium heat pipes operating at 1 800 K and below, the steam thermal resistance accounts for about 3.9% of the total thermal resistance.ConclusionsThe findings of this study enhance our understanding of the complex dynamics within high-temperature heat pipes, providing a theoretical foundation and guidance for the design and engineering application of alkali metal heat pipes, represented by lithium heat pipes. This study may also serves as a technological basis for the design and operation of heat transfer systems in space nuclear power and portable nuclear power sources.
BackgroundThe molten salt pump (MSP) is a crucial component in thorium-based molten salt reactor (TMSR) loop systems, driving the circulation of molten salt in the primary loop. The safety and economy of reactor operation relies on the safety and reliability of MSP operation. State monitoring of MSP is an effective method for ensuring the safe operation of the system.PurposeThis study aims to design and develop a real-time monitoring system for timely detection of abnormalities in MSP and system operation, providing a basis for condition-based maintenance, the state monitoring and abnormal signal localization of a MSP system.MethodsBased on the Windows Presentation Foundation (WPF) and Model-View-ViewModel (MVVM), a desktop application for the real-time monitoring system of MSP was developed. The system comprised various modules, including monitoring model management, real-time monitoring and alarm, abnormal signal localization, and log query. Based on Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and contribution analysis, a method for state monitoring and anomaly signal localization was implemented.ResultsThe relevant operating parameters of MSP are centrally monitored by this proposed system, and the current operating status of the equipment is displayed in real time. Signal parameters that may cause abnormalities can be quickly identified after an abnormality occurs.ConclusionsThe monitoring system of this study provides necessary information to operators and is thus helpful for operators in making operational decisions. Compared with traditional distributed control system (DCS) threshold alarms, the timeliness and effectiveness of monitoring are improved. This study lays the foundation for the implementation of intelligent operational support applications.
BackgroundTetragonal BaTiO3 exhibits temperature-dependent surface wettability as a pyroelectric material, hence is expected to be exploited to improve boiling and heat transfer efficiency on the surface of nuclear-reactor heat exchange components.PurposeThis study aims to prepare BaTiO3 pyroelectric thin films and explore their properties.MethodsFirstly, TiO2 nanotubes were prepared by anodic oxidation, and a controllable preparation of BaTiO3 nanotube array films was achieved using hydrothermal synthesis. Then, the X-ray Diffraction (XRD) and Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) were employed to observe characteristics and analyze the growth mechanism of TiO2 nanotube and BaTiO3 nanotube array film. Finally, the surface morphology and phase structure changes of the nanotubes were investigated by adjusting the voltage, NH4F concentration, and oxidation time.ResultsThe results show that the size of the generated oxygen bubbles increase with the increase of electron current caused by high voltage, and the diameter of the nanotubes increases with the oxidation voltage. The tube diameter distribution ranges within 60~140 nm, and the tube wall thickness is 10 nm. Increasing the concentration of NH4F and oxidation time are beneficial for the formation of TiO2 nanotubes. Polishing the titanium sheet can considerably improve the flatness of the nanotube array generated by oxidation. By extending the hydrothermal time and increasing the high-temperature annealing treatment, the cubic phase of BaTiO3 is successfully converted into a tetragonal phase with pyroelectric effects. Compared with the sample prepared over longer hydrothermal time, the annealed sample exhibits better pyroelectric properties.ConclusionsThe results of this study provide a valuable reference for further analyzing the growth mechanism of anodized TiO2 nanotubes and exploiting the spontaneous polarization intensity change of pyroelectric materials to change the surface wettability and improve the boiling heat transfer.
BackgroundTransparent protective materials are an important component of nuclear radiation protection equipment and a key factor in reducing radiation damage to the eye lenses of radiation workers.PurposeThis study aims to prepare polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) doped with gadolinium element and explore its shielding properties against neutron and gamma rays.MethodsFirstly, samples of PMMA doped with gadolinium element were prepared by intrinsic polymerization of gadolinium-containing PMMA, and the PMMA samples with different Gd(MA)3 content were applied to both experimental test and simulation calculation. Then, the 252Cf neutron source (moderated by 12 cm polyethylene) and 3He counting tube detector were employed to test the effect of Gd(MA)3 content on the neutron shielding performance of samples whilst the 241Am gamma source and high-purity germanium (HPGe) detector were used to explore the effect of different Gd(MA)3 content on the 59.5 keV γ ray shielding performance of samples. Simultaneously, the MCNP software was applied to the validation of gadolinium-containing PMMA neutron shielding performance experiments, and analyze the effect of different Gd(MA)3 content on the neutron shielding performance of PMMA against 252Cf. Finally, both thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) curves and tensile properties of PMMA doped with different Gd(MA)3 contents were compared and analyzed.ResultsThe results show that the shielding properties of the PMMA against 252Cf neutrons (moderated by 12 cm polyethylene) are continuously improved with the increase of Gd(MA)3 content. However, when the Gd(MA)3 content exceeds 10%, no obvious improvement in shielding performance is observed whereas the shielding performance against gamma rays is improved continuously. The PMMA containing 10% Gd(MA)3 has absorption cross-section of for 252Cf neutrons whilst linear attenuation coefficient of PMMA containing 30% Gd(MA)3 for 59.5 keV (241Am) gamma ray is 2.10 cm-1. With the increase of the thickness of PMMA, its neutron shielding performance increases exponentially, 90.2% of 252Cf fast neutrons are shielded by PMMA with a thickness of 10 cm and a Gd(MA)3 content of 10%.ConclusionsPMMA doped with gadolinium can effectively enhances its shielding properties against thermal neutrons and gamma rays while maintaining good visible light transmittance and improving the heat resistance of the material, but its mechanical strength is reduced. The results of this study provide valuable information for the development of apparent neutron/gamma shielding equipment.
BackgroundComplex lithology well sections require high precision in density well logging data whilst traditional computational models are difficult to meet this high precision requirement.PurposeThis study aims to improve the precision of density logging curves utilizing machine learning regression prediction models.MethodsFirstly, Monte Carlo N-Particle transport code (MCNP) was utilized to obtain stratigraphic data of varying density of dual-detector density logging tool instrument to validate the predictive effectiveness of the model. Then, sparrow search algorithm (SSA) was adopted to enhance XGBoost model, resulting in the development of the SSA-XGBoost density prediction model. Subsequently, the parameters of support vector regression (SVR), random forest regression (RFR), and long short-term memory (LSTM) were optimized by employing the SSA to construct the SSA-SVR, SSA-RFR, and SSA-LSTM models to predict the simulated formation density, and quantitative evaluation metrics and Taylor diagram models were applied to the comparison and analysis of the predictive performance of each model. Finally, the performance of different prediction models was evaluated on actual density logging data.ResultsResults of the comparative analysis and processing of actual well density logging data with various models show that the SSA-XGBoost model exhibits smaller errors between predicted and actual density and its error in predicting formation density is 0.017 4 g?cm-3, which is much lower than the traditional spine-ribs plots error of 0.028 4 g?cm-3.ConclusionsThe SSA-XGBoost model demonstrates higher predictive accuracy than traditional spine-ribs plots and other models, showing great potential for applications in the processing of actual density logging data.
BackgroundGaN-based high electron mobility transistor (HEMT) has been widely used in satellite communication, space station and other fields due to its high thermal conductance, high breakdown voltage and radiation resistance. However, the existence of a large number of high-energy particles in space will induce defects in the device, resulting in the performance degradation or even failure of the device, which seriously threatens the reliability of the device.PurposeThis study aims to investigate the anti-proton irradiation damage ability of enhancement mode gallium nitride devices with different structures, analyze the degradation rule of the devices' electrical characteristics after proton irradiation, and clarify the damage mechanism of proton irradiation.MethodsFirst of all, the enhancement mode Cascode structure devices manufactured by Transphorm corporation and P-GaN gate structure GaN HEMTs manufactured by Innoscience corporation were taken as irradiation samples. Then, a 5 MeV proton irradiation experiment with irradiation dose of 2×1012 p?cm-2, 1×1013 p?cm-2, 1×1014 p?cm-2 was carried out using the EN-18 serial electrostatic accelerator at Peking university for Cascode structure samples whilst only 1×1013 p?cm-2 for P-GaN gate structure samples. The irradiation was carried out at room temperature, and the devices were not biased during the experiment. After each irradiation dose, drain current (Ids), threshold voltage (Vth), and gate leakage current (Igs) were electrically characterized in all the samples. Finally, Kesight B1500A semiconductor parameter tester and LFN-1000 low-frequency noise testing system were employed to test the electrical characteristics and low-frequency noise of these samples before and after irradiation.ResultsThe experimental results show that the threshold voltage negative drift of the Cascode device becomes more serious with the increase of proton irradiation dose, and the saturation drain current increases significantly. When the irradiation dose reaches 1×1013 p?cm-2, the degradation of the electrical characteristics of the device begins to slow down. For P-GaN gate structure HEMT devices, the degradation law of electrical properties after irradiation is completely opposite to that of Cascode structure devices, and the degradation degree is significantly smaller than that of Cascode structure devices, indicating that Cascode structure devices are more sensitive to proton irradiation. Low-frequency noise test results show that the noise power spectral density of the device increases first and then tends to be stable with the increase of the irradiation dose, and its change law is consistent with the degradation of electrical characteristics.ConclusionsResults of this study demonstrate that the ionization damage effect induced by 5 MeV proton irradiation produces more oxide trap charges and interfacial trap charges in the cascade Si MOSFET gate oxide layer of Cascode structure device, which is the main reason for its sensitivity to proton irradiation. This study provides a certain reference value for the reinforcement design of GaN power devices and the selection of aerospace devices.
BackgroundA superconducting undulator prototype with the length of 4 m, the period length of 16 mm, and the gap of 5 mm for the Shanghai High Repetition Rate XFEL and Extreme light facility (SHINE) has been successfully integrated and delivered for acceptance test.PurposeThis study aims to propose a magnetic field measurement method tailored for small gap superconducting undulators and to optimize the phase error associated with the magnetic field.MethodsA magnetic field measurement technique based on dual Hall probes without fixed guiding rails was put forward based on the calculating formulas derived for the position of the magnetic neutral plane and the magnetic field distribution on this plane using data from the dual Hall probes. Then, a phase error optimization method based on segmented powering of the superconducting undulator magnet was proposed. These methods were applied to measuring and optimizing the magnetic field in the middle section of the prototype, which was 2 m long and divided into two 1-m sections, each powered by separate power supplies.ResultsThe measurement results show that the repeatability of the effective peak magnetic field between two measurements at 100 A excitation current is better than 1.5 Gs, and the phase error repeatability is better than 0.2°. After fine-tuning the excitation current, the phase error of the 2 m segment is reduced to 4.6°, meeting the design requirements.ConclusionsThe results confirm that the magnetic field measurement and optimization method proposed of this study is practical and effective.