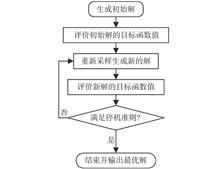
The optimal design of complex engineering equipment usually faces high-complexity, high-dimensional optimization problems – the so-called "large-scale black-box optimization problems (LBOPs)" – which are characterized by unavailable mathematical expressions of objective functions and/or constraint functions, and high dimensionality of design variables. The LBOPs have attracted the interest of scholars in various fields in recent years, and meta-heuristic algorithms are considered effective methods for solving these problems. This paper comprehensively summarizes recent research progress in meta-heuristic algorithms for solving LBOPs, including meta-heuristic algorithms with and without decomposition strategies, and meta-heuristic algorithms for handling computationally expensive large-scale optimization problems. Finally, possible future research directions of meta-heuristic methods for solving LBOPs are proposed.
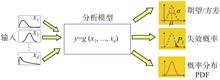
Uncertainty exists widely in engineering design. As one of the key components of engineering design, uncertainty propagation and quantification has always been an important research topic. Polynomial chaos (PC) is a highly efficient uncertainty propagation method which has been widely studied and applied. Therefore, this paper reviews recent advances in the PC method. First, the fundamentals of PC are introduced, including the construction of an orthogonal polynomial basis and the calculation of PC coefficients. Second, strategies such as basis truncation, sparse reconstruction, sparse grid and multi-fidelity modeling are described to address the "curse of dimensionality" issue of PC. Local and global sensitivity analyses based on PC are then introduced. Finally, the research prospects of PC are given.
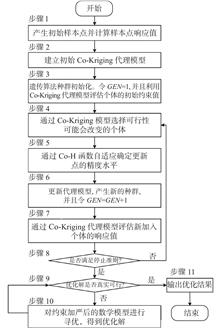
Objectives This study addresses the problem of time-consuming simulation in the optimization design of underwater structures. Focusing on time-consuming and non-time-consuming targets and constraints, it proposes an optimization method for constrained sequential surrogate models in the case of multi-fidelity data sources.Methods A multi-fidelity sequential constraint updating optimization approach based on confidence intervals and the Co-Kriging surrogate model (MF-SCU-CI) is proposed. The Co-H function is established to take into consideration the uncertainty of the surrogate model and the correlation degree and time consumption ratio of the high/low fidelity model. Three typical numerical test functions and an engineering example of longitudinal and transverse stiffened conical shell structure for vibration optimization are then tested.Results The results demonstrate that the feasibility ratio and effectiveness of the MF-SCU-CI method are better than those of the existing SCU-CI method. In addition, the MF-SCU-CI method can further reduce the number of simulation runs.ConclusionsThe proposed MF-SCU-CI method shows great potential for practical simulation-based engineering design optimization.
ObjectivesThe optimization design of a ship strong frame structure under the requirements of the common structural rules (CSR) is a complex and time-consuming problem. Moreover, its tremendous constraints make it difficult to judge the feasibility of any design scheme. As the approach aims at global accuracy, when adopting the static surrogate-assisted evolutionary algorithm to solve this problem, the prediction of key areas will be distorted in the case of small size samples. Aiming at the above problem, a strong ship frame optimization method based on a sequential surrogate-assisted genetic algorithm is proposed.MethodsFirst, the constraints of a strong frame structure based on CSR are analyzed, and all 675 constraints are reduced to 2 positive constraints according to constraint type. Then, surrogates for objective functions and constraint functions are constructed, and a genetic algorithm based on the feasibility principle is adopted to find the optimized solution. The true response of the solution is then calculated and the surrogates updated. In addition, the expected feasibility function (EFF) criterion is applied to update the constraint surrogates in order to refine the prediction accuracy at the constraint boundaries. The above procedures are iterated several times, and the optimized global feasible solution is finally obtained.ResultsThe proposed method can obtain a better solution than the static surrogate-based algorithm with a lower computational burden, and the weight of the design area is finally reduced by 15.55%.ConclusionsThe proposed sequential surrogate-based algorithm is superior to the static surrogate-based algorithm, and possesses good application value in the optimization of ship strong frame structures under complex constraints.
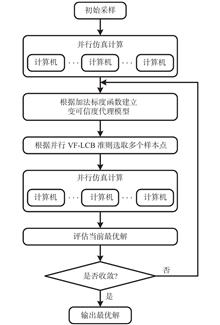
ObjectivesIn order to reduce the weight while maintaining the performance of the antenna cover of a deeply submerged body, a parallel variable-fidelity lower confidence bound (PVF-LCB) approach is proposed to optimize the structure of the antenna cover.MethodsThe proposed algorithm adaptively allocates computational resources of different fidelities through a variable-fidelity LCB (VF-LCB) function, allowing it to select several candidate samples based on influence functions (IFs) constructed by the variable-fidelity Kriging model. Moreover, the proposed method is assisted with widely used constraint-handling methods to solve the structural optimization problem.ResultsThe proposed approach obtains an optimized antenna cover structure which satisfies all constraints. Compared with the well-known variable-fidelity optimization method, the optimized structure is about 50% lower in weight. Additionally, the proposed approach reduces the weight of the antenna cover by about 30% compared with the results of single-fidelity parallel optimization methods.ConclusionsThe proposed method can not only reduce the design cycle of engineering optimization, but improve the quality of the optimal solution, giving it certain development prospects and guiding significance for engineering applications.
ObjectivesUnderwater structures have strict requirements for intensity, mass, vibration, noise and so on. From a multidisciplinary perspective, realizing the design optimization of such structures to improve their overall performance is of great significance.MethodsThe enhanced analytical target cascading method and surrogate model are employed for the design optimization of underwater structure vibration and acoustic radiation: an enhanced target cascading (ATC) method based on the Lagrange duality theory and traditional ATC method is established to achieve the classification of problems and parallel optimization of the performance of different disciplines; and the Kriging surrogate model is used to solve the time-consuming problem in the calculation of the vibration and acoustic radiation of underwater structures. Underwater non-uniform stiffened cylindrical shells (i.e., underwater unmanned vehicles) are selected for multidisciplinary design optimization (MDO): six design variables are selected, and the structural mass, stress components, resonant frequency and corresponding radiated power level are regarded as objectives for establishing the parallel optimization model when considering the vibration and acoustic radiation characteristics and lightweight requirements.ResultsThe results show that the Kriging surrogate model can accurately predict the response in the design space, while the enhanced ATC method can obtain effective multidisciplinary optimization results with a 30% increase in convergence properties.ConclusionsThis study shows that multidisciplinary design optimization based on the enhanced ATC method and surrogate model not only obtains effective results but also has better convergence properties.
ObjectivesThe cabin-skeleton coupling structure of a blended-wing-body underwater glider is optimized using a data-driven discrete optimization concept.MethodsFirst, a Kriging-assisted discrete global optimization algorithm (KDGO) is proposed for computationally expensive black-box problems. The KDGO uses a novel infill-sampling strategy to capture discrete sample points with better performance, and introduces a multi-start method with a data mining strategy, including multi-start optimization, projection, sampling and selection. Second, a parametric cabin-skeleton coupling structure model is established using the finite element analysis method under lifting deformation and deep-water pressure conditions. The float-to-weight ratio and strength and stability of the cabin-skeleton structure are taken as the goal and constraints respectively. Considering the interference between shape and cabin, and the coupling relationship between cabin and skeleton, a discrete optimization mathematical model of the overall coupling structure is established. Finally, the discrete optimization algorithm and coupling structure simulation are combined to build an overall optimization framework.ResultsBy using KDGO to conduct 200 function evaluations and comparing the optimal feasible points in design of experiments (DoE) with the global optimal feasible points after optimization, it is found that the optimized float-to-weight ratio of the coupling structure is increased by nearly 40%, representing satisfactory results.ConclusionThe results of this study can provide valuable references for the cabin-skeleton coupling structure design of blended-wing-body underwater gliders.
ObjectivesThe structural optimization of ships usually involves the use of high-fidelity numerical simulations which are time-consuming and thus difficult to evaluated frequently, and this intrinsic property hinders the optimization process. To promote efficient design optimization, this paper explores the use of Gradient-enhanced Kriging (GEK) surrogate mode in order to shorten the design loop and save design cost. A reduced GEK-based infill criterion is proposed to decrease the number of simulations by calculating the gradients only for sample locations where improvement occurs.MethodsA multi-start local optimization algorithm is employed to search the local optima of the "expected improvement" function and locate candidate infill points. The associated "approximate probability of stationary point (APSP)" values are also evaluated, and infill decisions are made according to the extent of consistency between these two quantities, thereby improving optimization efficiency. The proposed method is then applied to the structural optimization of an underwater vehicle to increase the seventh-order natural frequency under unconstrained free vibration in an underwater environment, and the validity is verifed.ResultsThe result shows that, compared with the baseline, the optimized design achieves a 14.6% improvement.ConclusionsThe proposed GEK-based optimization method can be generalized to cases when gradients can only be evaluated by finite difference.
ObjectivesDue to the functional requirements of structures, a large number of thin-walled structures with cutouts are adopted in the structural design of aviation, aerospace, shipbuilding and other fields, leading to a significant reduction in the bearing capacity of such structures. Although the curved stiffening method has great potential in improving the load-bearing performance of open structures, the sharp increase in design variables presents a challenge for structural optimization.The data-driven deep learning method is used to optimize the design of hierarchical stiffened thin-walled structures with cutouts reinforced by curvilinear stiffeners. MethodsFor structures with cutouts, the hierarchical curvilinearly stiffened method is designed, and the image representation method of structural parameters is proposed. The deep learning network model for structural response feature-learning is established to realize structural optimization design under data-driven conditions.ResultsThe results show that compared with the classical surrogate models constructed by structural numerical parameters, the prediction accuracy of the proposed structural response feature-learning model based on image recognition is improved roughly twofold. In the optimization design of structures based on the learning model, the bearing capacity of hierarchical orthogonal stiffened structures increased by 10.78%, and the bearing capacity of hierarchical curvilinearly stiffened structures increased by 18.19%.ConclusionsThe results show that this deep learning-based structural optimization method is more effective for hierarchical stiffened structures with large numbers of design variables and dynamic changes in the number of design variables. Compared with traditional straightly stiffened panels, the curvilinearly stiffened panel is more effective in strengthening the bearing capacity of thin-walled structures with cutouts.
ObjectivesIn order to provide the basis for accurate control of diesel engine fuel injection quantity, a method was proposed to establish the main injection quantity prediction model with input parameters as dwell time, common rail pressure and main injection pulse width for the pre-main injection mode.MethodsAMESim simulation model was used to conduct simulation experiments and then collect data. Based on the data, the relationship between the dwell time and the main injection volume under single working condition was obtained. On this basis, the influence of common rail pressure and main injection pulse width on the model coefficient was introduced to build a complete multi-working condition main injection quantity prediction model. Multiple input parameter combinations were used to verify the accuracy and reliability of the prediction model of main injection quantity fluctuation.ResultsThe results show that the root-mean-square error (RMSE) of the scheme of multi-working condition main injection quantity prediction model is 1.443 mm3. It can reduce the experiment amount required for modeling from n3 orders of magnitude to n2 orders of magnitude.ConclusionsThe proposed prediction model has sufficient accuracy, which is of great significance for engineering application of model-based fuel injection control.
ObjectivesTo improve the vibration and noise of an air purifier employed in enclosed cabinet, the flow field and vibration are analyzed for the prototype and improved air purifier.MethodsFirst, theoretical research is used to analyze the intrinsic vibration mechanism of the prototype air purifier, then improved schemes are proposed which satisfy the requirements of six properties (i.e. reliability, maintainability, supportability, testability, safety and environmental adaptability) and type tests based on the guaranteed service, design and manufacturing experience. Finally, the air purifier is redesigned according to simulations in ANSYS Fluent and ABAQUS software. ResultsIt is demonstrated that under the premise of the same power consumption, aerodynamic characteristics, purification effects and size, the improved air purifier has significant advantages. The flow field becomes more stable with significantly fewer backflows; the natural frequencies and specific stiffness are increased remarkably; the vibration is reduced dramatically in the low frequency range (operating region); and the energy in the high frequency area is absorbed by the damping layer. The total energy is decreased by approximately 9 dB (10 Hz-10 kHz).ConclusionsThe improved scheme is reasonable and evidently improves the vibration and noise of the device. This study has practical significance for the control of compartment environments and research on innocuous gas purification with high efficiency, low noise and low power consumption.
ObjectivesIn view of the problem of multi-parameter setting and strategy complexity under the traditional control strategy, a modular multi-level converter (MMC) model predictive control method for the electric propulsion drive system of a ship is proposed.MethodsFirst, the complexity of driving system design under the traditional control strategy is analyzed. Next, based on the advantages of model predictive control, a corresponding MMC model predictive control strategy is designed for the electric propulsion drive system of a ship. Finally, in a Matlab/Simulink environment, a 3.3 kV/20 MW permanent magnet synchronous motor (PMSM) driving system model with propeller load is built, and the control strategy is simulated and verified.ResultsThrough simulation, the designed MMC model predictive control method can maintain the static difference of the motor speed within 1% and reduce torque ripple by 6.1%, indicating that the proposed control method is feasible and has certain advantages.ConclusionsThe results of this study can provide valuable references for the MMC design of medium-voltage DC electric propulsion systems of ships.
ObjectiveAiming at the problems of the power quality degradation of the power grid and the power distribution of energy storage devices when the load power of a ship power system fluctuates sharply, a power fluctuation control strategy based on the hybrid energy storage of batteries and supercapacitors is proposed.MethodsFirst, based on the low-pass filtering algorithm, the power fluctuation of the ship's power system is initially allocated to the corresponding energy storage unit according to its fluctuation frequency. Then, based on the droop control strategy, the output current of each energy storage unit is adjusted according to the allocated power. Finally, based on the state of charge of each energy storage unit, the charge and discharge control of the hybrid energy storage system is conducted to smooth out the power fluctuations.ResultsThe simulation results show that this power distribution strategy realizes the reasonable distribution of power between energy storage units and the charge and discharge power control of the energy storage system, which can effectively smooth out the load power fluctuations of the ship's power system.ConclusionThe results of this study can provide valuable references for the optimal power quality design of a ship's power grid.
ObjectivesIn order to realize the rapid data exchange of the monitoring module in a grid-connected control system, the fault tolerance rate of communication data is improved and the extra CPU occupancy is saved by using Direct Memory Access (DMA) and interrupt communication technology to solve the problem of variable length transmission.MethodsThis paper is based on the communication protocol between the configuration software of the monitoring module and the microcontroller in a grid-connected control system. It designs a communication handshake flow between configuration and main controller, taking STM32F417 as the main controller, with the help of a serial interface hardware circuit. The use of DMA and interrupt communication technology is proposed to overcome the shortcomings of the traditional serial communication data fixed-length transceiver.ResultsOn the grid-connected control device of a ship's integrated power system, DMA and interrupt communication technology is adopted to realize the variable-length transmission function of the monitoring data, thereby improving the serial communication data transmission capacity and data tolerance.ConclusionsThe results of this study have certain practical guiding significance and reference value for the development of monitoring modules for ship grid control systems.
ObjectiveIn order to improve the charging efficiency, safety and speed of mobile online photovoltaic (PV) charging devices, a type of mobile online PV charging maximum power point tracking (MPPT) technology based on the variable step size disturbance approximation method is proposed.MethodsBy combining a high-frequency inverter and isolation transformer as the MPPT carrier, the former DC/DC structure of traditional PV charging topology devices is removed, charging control is combined with the pulse modulation of the high-frequency inverter, and the three functions of high-frequency isolation, MPPT tracking and charging control are finally integrated into one. At the same time, according to the different states of the remaining power battery, a three-stage charging control strategy is proposed.ResultsSimulation analysis and field test results show that this device can track the maximum power points of PV panels stably when their illumination intensity changes, and the battery can be charged efficiently in the three stages according to the set charging scheme. The measured overall charging efficiency can be maintained above 92%.ConclusionThis device and control strategy can improve PV panel-to-battery charging efficiency and meet the requirements of fast and safe charging.
ObjectivesIn order to determine the control method and recovery strategy for submarines falling deep underwater, a six-degrees-of-freedom motion model was established for an X-rudder submarine.MethodsFirst, the control rules of the X-rudder and the drainage capacity of the submarine were analyzed, and a recovery control system was designed using the fuzzy method. Second, recovery control in different degrees of depth scenarios was simulated in the course of large depth navigation, and the recovery control system was improved in both controller and control strategy. Finally, the recovery ability under different speed conditions was compared.Results The results show that, on the controller side, the intelligent fuzzy integral link was introduced, improving the recovery efficiency and depth control effect. On the recovery strategy side, the original control strategy was optimized using pitch assisted and acceleration, improving the deep recovery ability.ConclusionsThe results of this study show that the X-rudder fuzzy control system combined with the pitch assisted and acceleration recovery control strategy has a good recovery effect for dangerous situations at depth.
ObjectivesIn order to obtain a simplified mathematical model of ship motion for intelligent control, this paper takes a Mariner-class vessel as the research object and proposes a sensitivity analysis method combining the standard maneuverability test and PID (proportion-integral-differential) heading control test.Methods Compound analysis of the control index, maneuverability index and squared loss of typical motion state variables throughout the entire process is performed to obtain a dataset containing multi-dimensional sensitivity coefficients. A K-means machine learning algorithm is introduced to perform cluster analysis on the dataset. The sensitivity division of hydrodynamic derivatives is completed and the model is simplified.ResultsContrastive simulation tests of heading control and track control are carried out among the simplified model, former simplified model and complete model, and the results show that the sensitivity analysis method proposed in this paper is effective and the model proposed in this paper has higher control prediction accuracy.ConclusionsThe method proposed in this paper has certain significance for guiding ship motion modeling for intelligent control.
ObjectivesIn order to realize the automatic collection of general ship layout data, a new 3D data collection method based on 2D graphic analysis is proposed.MethodsIn light of the inherent defects of drawings, a complete cabin boundary recognition algorithm is developed to achieve accurate cabin boundary information. Efficient matching between cabin attributes and cabin boundaries is realized using cabin and point serial numbers, and cabin 3D automatic modeling is realized through hierarchical Boolean operation technology.ResultsThis reliable and feasible method reduces the general layout work of 3D cabin modeling, data analysis and unsinkability raw data consolidation, as well as improving design efficiency.ConclusionsThe above technology allows automatic modeling from a 2D layout to a 3D cabin. The development and testing of the relevant layout information collection software is carried out, and the test results verify the feasibility and applicability of the proposed data collection method.
ObjectivesIn order to solve the problem of ship nonlinear rolling control, a fractional order adaptive sliding mode control (FOASMC) algorithm is proposed.MethodsFirst, the spectral density of random waves, spectral density of wave inclination and spectrum of waves acting on ships are calculated using a random wave model with long peak waves. The rolling angle tracking error of the system is then verified on the basis of Lyapunov stability theory. Moreover, the switching function is designed to make the system robust to uncertainties and external disturbances. Finally, the effects of fractional order, control law gain and sliding surface mode gain are analyzed.ResultsThe results show that the mean rolling angle and standard deviation of FOASMC are smaller than those of basic sliding mode control (SMC) for various speeds and wave directions. For example, when the ship's speed is 10 m/s and the encountering wave direction is five degrees, the average rolling angle is 25.89% of the basic SMC, and the mean square deviation is 14.32% of the basic SMC.ConclusionsIt is proven that the proposed control algorithm has good stabilization effectiveness at various navigation speeds and encountering wave directions, as well as such advantages as strong robustness, continuous control input and no high gain.
ObjectivesConsidering the large motions of heave and pitch of high-speed mult-hull ship with the strict input constraints of installed anti-pitching appendages, a predictive control method is proposed for vertical stabilization based on Kalman filtering.MethodsA high-speed multi-hull vertical control model is established with T-foils and flaps serving as anti-pitching appendages, and the motion couplings of heave and pitch are analyzed. In order to obtain an anti-pitching control signal, the wave-induced colored noise is whitened and an adaptive extended Kalman filter is adopted for the online estimate of heave velocity and pitch angular velocity. On this basis, predictive control is proposed for vertical stabilization with input constraints. Defining the error between actual state and predicted state, a predictive control model with linear varying error correction is obtained. Error feedback correction is used to improve the robustness of the anti-pitching control, the problem of anti-pitching control is transformed into a quadratic programming (QP) problem with input constraints, and a rolling optimization solution of predictive control is realized through numerical solution.ResultsThe simulation results show that under the effects of predictive control considering feedback correction, hull heave is reduced by about 40% and pitch angle is reduced by about 50%.ConclusionsPredictive anti-pitching control with feedback correction can improve the control accuracy and robustness of the system, which is of great significance for practical engineering applications.
ObjectivesAiming at the characteristics of semi-submersible vessels with large roll period changes under different working conditions, a passive controllable anti-roll tank with an adjustable harmonic period is designed. The harmonic period is changed by controlling the height of the T-shaped baffle in the tank, generating a better anti-roll effect that matches the ship's roll period.MethodsFirst, the influence of the T-shaped baffle arrangement on the harmonic period of the tank is analyzed though Computational Fluid Dynamics software, and the design of the tank is optimized. Second, in order to adapt to semi-submersible vessels under different working conditions or encountering waves of different frequencies, the auto-regressive (AR) model is used to predict the ship's roll period and adjust the number of raised baffles according to the prediction, on the basis of which the designed water tank is simulated.ResultsThe simulation results show that the designed anti-roll tank can adapt to the different working conditions of semi-submersible vessels with positive effects.ConclusionsChanging the number of T-shaped baffles can increase the harmonic period of the tank to a certain extent, and it can be set to match the roll period of the semi-submersible vessel by controlling the baffles, thereby better adapting to ships with large roll period changes and providing strong anti-roll ability.
ObjectivesTo improve the efficiency of the ballast water allocation of crane vessels and reduce energy consumption in this process, an optimization method following a multiobjective evolutionary algorithm based on decomposition (MOEA/D) is proposed.MethodsTaking the water volume of each ballast tank after allocation as the decision variable, and the minimum total volume of allocated ballast water as the optimization objective, and introducing the constraint of floating state, a mathematical model for the ballast water allocation optimization of crane vessels is built. Aiming at the problems of slow solution speed and poor solution quality caused by the high dimensions of decision variables, an adaptive selection method for ballast tanks is proposed which greatly reduces the number of tanks involved in the adjustment. In light of the complex handling of constraint conditions, the single objective optimization is transformed into a multiobjective optimization problem, and the MOEA/D algorithm is then applied. The final results are selected from the Pareto solution set.ResultsAn example of ballast water allocation in the process of the crane slewing of a crane vessel is put forward. The calculation results show that the number of cabins involved in ballast adjustment is reduced by 27%, and compared with the NSGA-II algorithm and genetic algorithm (GA) algorithm, the total volume of allocated ballast water is reduced by 24% and 38% respectively, which verifies the feasibility and effectiveness of the MOEA/D algorithm.ConclusionsThe proposed method based on MOEA/D provides a new solution for the optimization of the ballast water allocation of crane vessels. It has certain engineering application value by offering a better ballast water allocation scheme.
ObjectivesAiming at the difficulty of ensuring the fitting accuracy and optimization efficiency of surrogate models due to the high nonlinearity in ship structure reliability-based optimization design, a reliability-based ship structure optimization method based on the interest subdomain dynamic surrogate model is proposed.MethodsThis method puts forward the concept of the interest subdomain based on the sequential optimization and reliability assessment (SORA) method, determines the range of interest subdomains and formulates adaptive spatial reduction rules based on information entropy function H, then proposes an adaptive spatial reduction sequential sampling strategy based on interest subdomains, thereby constructing a dynamic Kriging surrogate model that highly fits the subdomain of interest locally with as few sample points as possible, and embedding the surrogate model and multi-island genetic algorithm (MIGA) in the SORA method to undertake reliability-based optimization.This study proposes a probability constraint feasibility checking method to reduce unnecessary reliability assessment processes. A mathematical example is given to verify the reliability-based optimization method.ResultsThe relative error between the optimal solution and theoretical solution is 0.066 8%, and the number of function calls is 40.6% less than those of the optimal method in the references, which proves the accuracy and efficiency of this method.ConclusionsWhen the proposed method is applied to the reliability optimization design of a cabin structure, the total cabin mass is reduced by 0.511% compared with the references, and 94 fewer finite element calculations are required, proving the efficiency and applicability of this method.
ObjectivesDesigning the hardware resources of the whole warship from the top level and making comprehensive use of the information resources among different equipment is the inevitable requirement of information design. Under this trend, the integrated information service system for warships was proposed.MethodsFirst of all, the design objectives and general plan are analyzed. The information infrastructure is used for planning the overall hardware resources. The software structure is composed of a system management module and an information service module. Then it discusses the software design and implementation ideas from the aspects of the application integration platform design and information application design. In the application integration platform design, the integrated design concept about B/S applications and C/S applications involves using Docker technology and software integrated management warehouses which were analyzed respectively. In information application, the design of the functional module of the message push service was mainly discussed to realize "information for the crew and pushing on demand".ResultsBased on the above design ideas, the system design is completed, which has realized functions such as integrated management for various applications and message pushing, etc.ConclusionsThe operation of the system meets the design objectives, improves the information level of the whole warship, and also helps to improve the efficiency of the crew.
Objectives The purpose of this paper is to explore the feasibility of applying heterogeneous network and internet of things (IoT) technology to the remote monitoring of offshore facilities.MethodsTherefore, this study proposes an experimental platform for the corrosion acceleration of IoT based on a heterogeneous network composed of a perception layer, network layer and application layer. The salt spray experiment method is adopted to realize the simulation of marine atmospheric corrosion on land, and the perception layer collects simulated corrosion environment data and corrosion effect data. Taking the characteristics of the offshore production environment and existing network transmission technology into consideration, the network layer completes the task of data transmission through the heterogeneous network composed by ZigBee, LoRa, WiFi and Ethernet. Finally, the corrosion information is completed via a web application in the application layer.ResultsThis experimental platform effectively simulates the acceleration of salt spray corrosion in an ocean atmosphere, as well as data transmission and remote monitoring in complex environments.ConclusionsThe construction of a heterogeneous network-based corrosion acceleration experiment platform can provide a basis for follow-up research on corrosion laws based on big data and artificial intelligence technology in order to predict the corrosion failure of marine structures.
ObjectiveWith the increasingly complex electromagnetic environment, it is more and more difficult to separate signals. In order to solve the problem that the performance of the existing efficient sorting algorithm depends heavily on external input parameters, a non-parametric radar signal clustering algorithm based on Dominant Sets (DSets) and Dempster-Shafer(D-S) evidence theory is proposed.MethodThe algorithm is applied to radar signal sorting; a non-parametric radar signal pulse clustering algorithm is then given and combined with D-S evidence theory to solve the problem of excessive DSets algorithm segmentation.ResultsIn the absence of any prior information, this algorithm can complete the precise clustering of mixed pulse radar signals. In addition, its sorting accuracy rate is more than 93.13% when the false pulse ratio is less than 50%.ConclusionThe combination of the DSets algorithm and D-S evidence theory can effectively complete the clustering of radar signal pulses without prior information, and achieves good clustering performance.