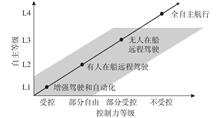
This paper introduces the development background of intelligent ships and their remote control. Based on introducing current applications of the remote control unmanned ship and analyzing the demands and scenarios of remote control cargo ships, this paper proposes a remote control framework for cargo ships based on man-machine integration. The corresponding technical levels and related key technologies of different remote control patterns are expounded upon. A review of the importance and development status of key technologies for the remote control of cargo ships is then conducted with reference to major ship network control system achievements. Moreover, regarding the operation and maintenance characteristics of shipping, three considerations are proposed for utilizing perception technologies in ways that can be beneficial for realizing the remote control of cargo ships.
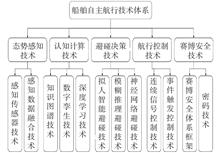
As a salient feature of smart ships, autonomous navigation has attracted the increasing attention of industrial and maritime enterprises. To grasp the status and development direction of autonomous navigation, this paper carries out an investigation and review of the relevant key technology by analyzing domestic and foreign state-of-the-art research into autonomous navigation technology over the past three years. Aiming at key technologies such as situational awareness of navigation , cognitive computing, collision avoidance decision-making, navigation control and cyber security, the technical connotations, research status and application situations are analyzed. Considering the current status and technical requirements of key technologies for intelligent navigation, this paper provides the future outlook of situational awareness, cognition, decision-making, control and security for the autonomous navigation of ships.
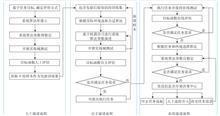
The core of the technology development for intelligent ships is to construct a complete software and hardware system from decision-making to autonomous control, which realizes the evolution from manual operation to intelligent navigation. The development of software and hardware systems are inseparable from comprehensive testing procedures and standards. This paper first reviews the latest in existing domestic and foreign technology test fields for intelligent ships. Afterward, ship performance, energy efficiency, information, and intelligence are proposed as objectives for intelligent navigation functional testing for intelligent ships. Finally, a system methodology of the virtual simulation tests, model-scale tests, and full-scale tests for the navigation function of intelligent ships is proposed.
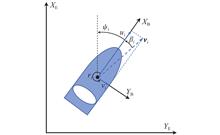
The future trends of marine operations will be intelligent, networked and swarmed marine vehicles. One of the main trends of future marine operations will be joint operations through the coordination of multiple unmanned surface vehicles (USVs). As an introduction to the mathematical model of USVs, this paper presents the key problems and fundamental challenges of motion controlling multiple USVs. Regarding different mission scenarios of USVs, the existing results will be classified into trajectory-guided, path-guided, and target-guided coordinated control. In conclusion, we discussed and summarized the future trends of the coordinated control of multiple USVs.
ObjectivesThe performance of unmanned surface vehicles (USVs) is defined as the ability to complete specific tasks in specific environments within a given time scale as a result of the cooperation of multiple technical aspects. However, the traditional optimization method that forcus on a single part in the system provides limited effect on improving the performance of USVs.MethodsBased on the features of autonomous system of USVs, two main forms of the intelligent evolution of USVs are conducted from the perspective of algorithms: the evolution of algorithm functions and evolution of algorithm parameters respectively. In this case, a machine learning-based intelligent evolution method is proposed. An automatic USV control system which satisfies the requirements of intelligent evolution is then designed and tested in a sea trial.ResultsThe obstacle-avoidance task in the sea trial proves the capability and feasibility of the proposed method.ConclusionThe machine learning-based intelligent evolution of USVs is an effective way to continuously improve the performance of USVs, making it a worthy research topic with high application value.
ObjectivesFor achieving navigational safety and continuous communication link between swarms of unmanned marine vehicle (UMV) during mission execution, the cooperative path planning of unmanned surface vehicle (USV) and unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) swarms is studied.MethodsKeep-in and keep-out geo-fences are used to carry out scene modelling, and the problems of threat and obstacle avoidance are transformed into geo-fence constraints. Aiming at collision avoidance and continuous communication link between vehicles, a judgment criterion for the constraints of collision avoidance and communication link via time sequence detection is proposed. The average travel time (ATT) of the swarm is taken as the path optimization function, and the multiple constraints are transformed into penalty functions. A self-adaptive differential evolution algorithm is adopted to solve the optimization problem.ResultsThe proposed method can ensure safe navigation and communication link between USV and UAV swarms in hostile and obstacle-filled environment, and achieve the shortest ATT under multiple constraints.ConclusionsThis method has practical value for the off-line path planning of UMV swarms in the hostile and obstacle-filled environment.
ObjectivesThere is now an increasing interest in deploying unmanned vehicles (USVs) to support complex oceanic operations. In order to perform these tasks more efficiently, a reliable track planning algorithm is required. Based on the research of existing path planning algorithms, a search scanning algorithm based on 2D scanning idea is proposed.MethodsFirst, establish an environmental space model. On the premise that there is an obstacle between the starting point and the end point, the surrounding obstacle information is acquired through the 360° scan of the starting point, and the child nodes are determined. The acquisition sub-node is determined by the cost function, and the optimal sub-node continuously scans and updates the next-generation sub-node to scan to the end point, and finally determines the planned route. Experiments were performed using the LabView2017 platform to write algorithm simulation software.ResultsThe results showed that the search scan algorithm is of a higher quality on the planned path than the ant colony algorithm. ConclusionsThe search algorithm reduces the problem that the result is not the optimal solution in the traditional algorithm planning path, and effectively improves the reliability of the algorithm applied to the two-dimensional space path planning.
Objective In order to realize the intelligent navigation and autonomous collision avoidance of unmanned ships in coastal areas, an intelligent collision avoidance decision-making method based on driving practice is proposed. Method First, the real-time rationality and uniqueness of the unmanned ship intelligent collision avoidance decision-making process is analyzed. The ontology conceptual model of the navigation situation is then designed and combined with the international regulations for preventing collisions at sea (COLREGS) and good seamanship practices, and the ship encounter scenarios are quantitatively divided into 12 types. An improved composite collision risk index assessment model is then proposed from the perspective of piloting practice to reflect collision risk more accurately. Finally, an intelligent collision avoidance decision-making model based on operator's perspective (BOP) is established, and the optimal collision avoidance strategy is solved by taking the shortest total collision avoidance path as the objective function under the constraints of ship maneuverability and rudder angle amplitude limit. Simulation experiments are then conducted in different obstacle environments. Results The simulation results show that this method can accurately determine the piloting situation, provide a reasonable steering strategy and achieve effective collision avoidance in different obstacle environments. Conclusion This study provides a theoretical basis and method for realizing the intelligent collision avoidance decision-making and dynamic local collision avoidance path planning of ships.
Objectives The tracking control of intelligent ships often faces the problem of low controller stability in complex control environments and manual algorithmic computing. In order to achieve precise tracking control, this paper proposes a controller based on deep reinforcement learning (DRL).MethodsGuided by the line-of-sight (LOS) algorithm and based on the maneuvering characteristics and control requirements of ships, this paper formulates a path of Markov decision processes by following the control problem, designing its state space, action space and reward by applying a deep deterministic policy gradient (DDPG) algorithm to implement the controller. An off-line learning method was used to train the controller. After the training, a comparison was made with BP-PID control to analyze the control effects.ResultsSimulation results show that the deep reinforcement learning (DRL) controller can rapidly converge from the training process to meet the control requirements, with the advantages of small yaw error, and a visible reduction in the frequency of changes of the rudder angle.Conclusions The study results can provide a reference for the tracking control of intelligent ships.
ObjectivesShip collision is one of the main factors threatening the navigation safety of intelligent ships. A calculation model of ship collision risk should identify potential collision risks in time and provide the basic information for the intelligent ship's autonomous collision avoidance decision-making.MethodsThis paper first analyzes the domain-based collision risk parameter calculation model according to the degree of domain violation and other parameters. The navigation scene is divided into a single-ship encounter situation and an encounter between a ship and target ship group, and a new collision risk parameter calculation model for multi-ship encounters is given. Second, based on the Wiener process, the uncertainty of ship position prediction is modeled and obtained according to the Chi-squared distribution. Finally, a calculation method for collision risk parameters which considers the uncertainty of ship position prediction is given.ResultsOn this basis, the influence of ship position prediction uncertainty on ship collision risk is considered. ConclusionsThis method can further guarantee the safety of intelligent ships at sea.
ObjectivesUnder complex environmental conditions, unmanned surface vehicles (USVs) may deviate from the target course. In order to improve the anti-jamming ability and actual navigation stability, and achieve accurate track control, an improved USV track control method is proposed.MethodsAccording to the influence on navigation signals caused by the environment, track control is analyzed in two cases of GPS signal: effective and invalid. A track control method based on a fuzzy control variable ship length ratio line-of-sight (LOS) algorithm and active disturbance rejection control (ADRC) algorithm is then realized on an autonomous controllable platform, and a lake test is carried out using a USV with dual propellers and dual rudders.ResultsThe simulation results show that this method can meet the requirements of track control, and the heading can be stabilized quickly without frequent rudder swinging after turning. The proposed method can complete track control in real environments with an average track error of about 0.1 m and variance of about 0.03.ConclusionsThe lake test results verify the feasibility and effectiveness of the proposed algorithm in practical engineering applications.
ObjectivesFocusing on the model uncertainties of unmanned surface vehicles (USVs) and unknown marine environmental disturbances, an anti-disturbance target-tracking control algorithm, based on extended state observer (ESO), is proposed for twin-screw unmanned surface vehicles.MethodsAt the kinematic level, a guidance law based on the principle of constant bearing is presented for USVs. At the kinetic level, aiming at model uncertainties and unknown disturbances, surge velocity and yaw angular velocity anti-disturbance control laws based on ESOs are designed to eliminate the problems caused by model uncertainties and unknown marine environmental disturbances. Finally, the proposed controllers' stabilities are analyzed via in-put-to-state stability and cascade theory.ResultsThe results show that such a USV can effectively track the virtual target point using the proposed anti-disturbance target tracking controller. ConclusionsThe effectiveness of the proposed control algorithm is verified via experimental results.
ObjectiveIn order to solve the remotely operated vehicle (ROV) motion control being easily influenced by the environment and model uncertainty factors, as it is difficult to achieve the desired control effect, a sliding mode control method of ROV based on a parameter disturbance model is proposed. MethodsOn the base of standard ROV model, taking the external environmental disturbance, and the uncertainty parameter of the model as the model disturbance parameters, the ROV model with parameter disturbance is established, and the depth direction control model is obtained by decoupling the model. Under the new model, the sliding mode controller is designed for the depth determination motion of ROV. The sliding mode controller is designed based on the new model.ResultsThe simulation results show that the sliding mode controller based on the ROV model can control the ROV depth stabily, effectively and efficiently, and the control method can improve the influence of external disturbance and model parameter uncertainty.ConclusionThe design method of the controller can provide a solution to the problem of disturbance and model uncertainty in the ROV control process.
ObjectivesIn order to expand the application of NMEA2000 communication protocol standard and optimize and improve its transmission efficiency, an NMEA2000 data acquisition and transmission system based on an autonomous and controllable platform is developed. Non-NMEA2000 devices can be connected to the NMEA2000-based network and improve the transmission efficiency. MethodsThe autonomous and controllable platform consists of a GD32F207 microcontroller and RT-Thread embedded real-time operating system. The protocol format conversion is accomplished by data mapping according to the original device protocol and NMEA2000 standards. Further, it uses unused identifier fields in the NMEA2000's data frames and a priority dynamic adjustment method to improve the transmission efficiency of NMEA2000-based network.ResultsThe NMEA2000 board based on the platform achieves non-NMEA2000 device access. The optimized network's transmission efficiency is improved to some extent with the number of bytes transferred. The real-time and reliability are also improved.ConclusionsThe NMEA2000 data acquisition and transmission system based on the proposed platform has a variety of interfaces, can help non-NMEA2000 devices access the network. The data transmission efficiency, real-time operation and reliability can fulfil the needs of data transmission among shipborne devices.
ObjectivesIn order to increase safety, reduce maintenance support costs and implement an efficient maintenance support mode for unmanned surface vehicle (USV) navigation, this study conducts an analysis of the integrated vehicle health management (IVHM) system of USVs.MethodsAccording to the functional structure composition of a type of USV, several key pieces of equipment and hull structure are analyzed in terms of failure mode, effect and criticality. Based on the operation and maintenance requirements, the functional requirements, system framework and key technologies of the IVHM system are analyzed and designed, and its software architecture devised. An agent-based simulation model is then used to evaluate the mission success and resource requirements of the USV. ResultsTaking equipment failure and functional parameters as the input, an agent-based IVHM model is established, providing a theoretical basis for the mission success evaluation and supporting resource requirement analysis of USVs.ConclusionsThe results of this study can provide valuable references for the construction of IVHM systems.
ObjectiveIn light of problems such as the untimely condition monitoring and alarm, excessively large threshold bandwidth and inaccurate condition evaluation parameters of intelligent ship power system equipment, an adaptive threshold method is proposed to monitor, alarm and evaluate the conditions of such equipment.MethodFirst, a simulated annealing algorithm is used to optimize the support vector regression (SVR) machine prediction model to simulate the general state characteristic parameters of the power system equipment. Then, after the normal transformation of the modeling residual, combined with the sliding time window, the adaptive threshold model is constructed. Finally, the exhaust gas temperature of the ship's main propulsion diesel engine is selected as the research object for example verification.ResultsThe results show that compared with the traditional fixed threshold, the adaptive threshold model has more compact bandwidth and good adaptability, and can identify abnormal phenomena in power system equipment in advance.ConclusionThis method improves the efficiency and threshold accuracy of monitoring and alarm systems, and provides an effective means of early fault diagnosis and a more accurate basis for system status evaluation.
ObjectivesIn view of the development demand of intelligent engine room of ships, in order to uncover the potential failure factors of equipment in advance, a new AEC health state evaluation model suitable for the ship's system and equipment is proposed.Methods This model combines the improved analytic hierarchy process (AHP) and entropy weight method (EWM) to form a combined weight method to determine the comprehensive weight of each evaluation index, and then the cloud gravity center evaluation method (CGCEM) is used to evaluate the health status of the research object based on the weight of each evaluation index.ResultsThe proposed model is verified by the actual operation data of the fuel supply system on the ship, and the calculation results show that the weighted deviation degree of the actual operation data is 0.181 5, which belongs to the interval (0, 0.33) and is in a healthy state, which is consistent with the facts.Conclusions It indicates that the AEC evaluation model can accurately evaluate the health status of the fuel supply system and has certain practical application values in the intelligent ship status evaluation and maintenance decision-making .
The swarm operation of unmanned marine vehicle (UMV) has been developed and evolved from concept to practical application. In view of the mission requirements of UMV swarms, this paper summarizes the development of the UMV swarm concepts of unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV), unmanned surface vehicle (USV) and unmanned underwater vehicle (UUV), and cross-domain swarm operations of UMV in naval warfare. It then analyzes the key technologies of UMV swarm cooperative engagement, including self-organizing communication, collaborative situational awareness, tasking, path planning, formation control and virtual testing. Finally, the main research ideas, representative algorithms and development trends of the related algorithms are summarized systematically. This study can provide valuable references for research on UMV swarm operation technology.
Intelligent energy efficiency management, as an important part of the development of intelligent ships, can realize the automatic monitoring, analysis and autonomous decision-making of ship energy efficiency. Therefore, improving the level of ship energy efficiency and intelligence is of great significance. Based on the analysis of the rules and inspection guidelines of ship intelligent energy efficiency management, the current research status of ship energy efficiency optimization methods is systematically analyzed by focusing on the core issues of ship intelligent energy efficiency, including intelligent monitoring and system design, the application of big data on ship intelligent energy efficiency, intelligent optimization algorithms and models of ship energy efficiency. The shortcomings and challenges in the development of ship intelligent energy efficiency are proposed based on the research status, and the future development and research contents of intelligent energy efficiency optimization are prospected to provide reference for the development of the energy efficiency management of intelligent ships.
ObjectivesIn order to realize the intelligent condition monitoring of marine engine room equipment, machine learning algorithms are introduced and a condition monitoring method based on manifold learning and an isolation forest is proposed.MethodsAs condition-monitoring data is multi-dimensional, the proposed method extracts useful features through manifold learning, thereby reducing the dimensions and complexity of the raw data. An isolation forest algrithm is introduced to utilize the normal condition data to train and construct multiple sub forest detectors, realizing the fault monitoring of the target equipment. To validate the proposed scheme, a two-stroke marine diesel engine was developed in Matlab/Simulink to simulate reliable normal and fault condition datasets.ResultsComparisons of the simulated datasets of the different fault monitoring schemes demonstrate that the proposed method has a highest fault detection rate of 98.5% and lowest false alarm rate of 3%.ConclusionsThe method proposed in this study improves the fault monitoring performance of marine equipment.
ObjectivesCurrently, how to plan the safe and efficient movement trajectory of an unmanned surface vehicle (USV) in local waters with multiple known obstacle positions is a research hotspot.MethodsFirst, the obstacle areas are treated with simple and effective circular and convex quadrilateral envelopes, and the obstacle avoidance problem is transformed into the state inequality constraint of a time optimal control problem. The time optimal control problem is then transformed into an optimal parameter selection problem by control parameterization and time scale transformation. Finally, for multiple continuous state inequality constraints caused by multiple obstacles, the exact penalty function method is used to append all state constraints to the cost function. The final form of the problem is suitable for solving any effective optimization technique as a nonlinear optimization problem.ResultsThe numerical simulation results show that the planned trajectory successfully avoids the obstacles in the water and conforms to the motion characteristics of USVs.ConclusionsThe results of this study can provide valuable references for the obstacle avoidance problem in USV trajectory planning.
Intelligent cargo ships are a research field involving ship design, power composition, state perception, information processing, communication control, risk identification, artificial intelligence, and so on. Its development seeks to make water transportation safer, greener, and more economical. Firstly, the characteristics and difficulties of the autonomous control and decision-making of cargo ships are analyzed, and the research status of intelligent cargo ships at home and abroad is expounded. Secondly, from the three aspects of intelligent navigation technology, intelligent engine room technology, and remote driving technology, the future development directions of intelligent cargo ships have prospected. Finally, some thoughts on the development of intelligent cargo ships are proposed in this paper.