View fulltext
View fulltext
Images captured under low-light conditions are often characterized by low brightness and contrast, color distortion, and high noise, which seriously affect the subjective vision of human eyes and greatly limit the performance of higher-order vision tasks. Low illuminance image enhancement (LIIE) aims to improve the visual effect of such images and provide favorable conditions for subsequent processing. Among many low-illuminance image enhancement algorithms, the LIIE based on deep learning has become the latest solution. Firstly, the representative methods for LIIE based on deep learning were reviewed. Secondly, the existing low-illuminance image datasets, loss functions, and evaluation indicators were introduced. Thirdly, the existing LIIE algorithms based on deep learning were comprehensively evaluated through benchmark testing and experimental analysis. Finally, a summary of current research was provided, and the development direction of LIIE was discussed and prospected.
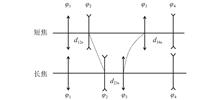
In order to meet the needs of high-definition imaging of atmospheric sulfur dioxide remote sensing monitoring at different distances, a continuous zoom ultraviolet lens was designed. Based on the theoretical analysis of Gaussian optical solution of zoom system, four groups of positive compensation mechanical zoom initial structure were selected, three intervals of zoom group solution of two-group mechanical compensation zoom system were calculated, and the power distribution of zoom group and compensation group was obtained. According to the absorption characteristics of atmospheric sulfur dioxide to ultraviolet light, the working band was determined to be 250 nm~340 nm. An ultraviolet continuous zoom optical system with zoom ratio of 10, F number of 4 and total length of 431.5 mm was designed by using Zemax optical design software, and the motion curves of zoom group and compensation group were drawn by using Matlab software. The focal length range of the system is 25 mm~250 mm, the short focal field range is 0°~7.67°, the medium focal field range is 0°~1.45°, and the telephoto field range is 0°~0.77°. During zoom process, the transfer function is greater than 0.3 at 107 lp/mm, the distortion is less than 1%, and the radius of the speckle is less than 5.5 μm. This system is suitable for monitoring sulfur dioxide in various scenarios, such as ship exhaust, industrial production chimney exhaust and so on.
In view of the problems of low target surface illumination uniformity and insufficient energy utilization rate in the current machine vision detection, the use of LED free-surface reflective cups to replace ordinary diodes for array arrangement was proposed for the first time, and the optimal spacing was optimized to realize the compensation of the center illumination of target surface, reduce the loss of large-angle light source, and improve the illumination uniformity and energy utilization rate in the light source array system. In the free-surface reflective cups light source array, the relationship between the optimal spacing in light sources and the half-light intensity angle and the target surface distance was first theoretically analyzed, respectively. Then, the optimal spacing was calculated when the free-surface reflective cup arrays were rectangular, circular and triangular, respectively, and the corresponding array experiments were compared and analyzed by using ordinary diodes. The results show that under three array forms, the energy utilization rate of the system is higher than 70%, and the illumination uniformity is higher than 89%. Compared with the ordinary diode array, the energy utilization rate is improved by at least 58.6%, and the illumination uniformity is improved by at least 12.8%. Among them, the overall light source of the free-surface rectangular array light source has the highest illumination, and the optimal energy utilization rate is 74.2%, which is 61.9% higher compared with the ordinary diode array. The free-surface circular array light source has the optimal illumination uniformity of 94.1%, which is 15% higher compared with the traditional diode array. The final experimental results show that using the LED free-surface reflective cup light source for array combination, the overall light source effect can be significantly improved.
For an unmanned helicopter optoelectronic system, the external passive vibration isolation platform was designed and verified based on the Hexapod configuration. The dynamic model of the Hexapod vibration isolation platform was established, the parametric modeling of the platform was completed, and the theoretical analysis and simulation comparison of the digital prototype were carried out based on Adams and Simulink co-simulation to verify the accuracy of the modeling. The sweep frequency test and the line/angle coupling response test of the developed prototype were conducted. The results show that the natural frequency of the three-direction linear excitation of the vibration isolation platform is less than 8 Hz, which can realize the vibration attenuation of the main vibration frequency of the helicopter platform, and the RMS value of coupling angle swing response is less than 200 μrad. Finally, the field hanging flight test was completed, which verified that the engineering prototype of the vibration isolation platform met the operational requirements.
Liquid particle measurement technology is based on light scattering method or photo resistance method to analyze and detect the particle size and quantity of the particles contained in the liquid. Aiming at requirements of the measurement accuracy of liquid particle measurement technology, based on the hydrodynamic focusing principle, the sheath flow system model for the measurement of particles in the liquid was designed by SolidWorks software. Through the fluid calculation module of COMSOL, the fluid simulation calculation of the model was carried out, and the change of the focusing flow width and the focusing performance of the system on the particles were simulated. The simulation results show that the focusing performance of the sheath flow system on the sample flow is consistent with the theoretical derivation, and it can be focused to 0.24 mm width when the sample flow speed is 0.1 m/s. Meanwhile, the COMSOL particle tracking module was used to simulate the particle trajectory at this width, and the effective focusing of particles was realized. On this basis, the state of particles flowing through the detection area was analyzed, and the influencing factors of coincidence errors were obtained, which had certain theoretical guiding significance for the practical design of the sheath flow system of liquid particle measurement technology.
The multispectral spectral imager equipped with a long-wave infrared detector can provide spatially high-resolution surface temperature information, and the study of surface temperature is of great significance in the global energy balance and climate change. A 10 μm~11 μm filter was used as the window of the infrared detector for surface temperature detection, and a wide-cutoff and high-transmission long-wave infrared bandpass filter film was designed on a Ge substrate using Ge and ZnS as the high and low refractive index materials, respectively. Vacuum coating technology was used to prepare long-wavelength pass and short-wavelength pass filter films on both sides of the Ge plate to realize the bandpass, in which Ge and ZnS films were deposited by electron beam and resistive thermal evaporation, respectively, and the film thickness was controlled by a crystal controller. The mathematical model of film thickness deposition was established by Matlab software, which simulated and corrected the tooling of the multilayered film in order to reduce the thickness error. The test results show that the average transmittance of 10 μm~11 μm reaches 94.3%, and the ripple amplitude of the transmittance area is 1.6%, of which the average transmittance of 4 μm~9.5 μm and 11.5 μm~16 μm is less than 0.1%, and the filter meets the requirements of the use through various environmental tests.
The correlated imaging represented by ghost imaging has novel physical phenomenon and potential application values, which has attracted the research interests of many scholars, among which the measurement of the correlation characteristics of the light source is particularly important. However, the coherence time of thermal light sources (sunlight, tungsten light) is too short to be directly measured with existing detectors, preventing the development of passive correlated imaging. Based on the two-photon absorption with ultrafast time resolution ability due to short lifetime of virtual level, a photon-counting photomultiplier tube detector was used to measure the correlation of super-continuum laser with spectrum band of 150 nm by Michelson interferometer. The results show that the coherence time of super-continuum laser is 60 fs, and the ratio of peak to background is 2.6:1, which is consistent with the theoretical prediction. Besides, compared with the second-order correlated function of spontaneous radiation light source (ratio of peak to background of 4:1) and the pulsed light (ratio of peak to background of 8:1), the ratio of peak to background of the correlated function of super-continuum laser exhibits different results, which gives the new method to recognize the different light sources. The experimental device of this method is more simple and compact, which provides a new idea for ghost imaging by direct use of sunlight.
The infrared radiation calibration method was introduced, the field calibration of infrared warning equipment was carried out by short-range direct extended source method and long-distance small source method, and the verification and error analysis were carried out. The results show that the relative calibration errors of the short-range direct extended source method is between 5.67% to 15.73% at the temperature range of 10 ℃~50 ℃. The relative calibration errors of the long-distance small source method at 37 m ranging from 1.38% to 5.72%, and those at 63 m ranging from 10.34% to 29.66%, indicating that the long-distance small source method at an appropriate distance is an effective method for field calibration of infrared warning equipment operating in the mode of circular scanning.
In order to solve the problems of missed alarm and slow response speed in the existing laser alarm system due to untimely data processing, a rapid extraction algorithm of spot center based on projection segmentation was proposed. According to the characteristics of the horizontal uniform distribution of spots at all levels in the diffraction images, a method of rapid extraction was proposed by projecting to the coordinate axis and calculating the center coordinates of light spot respectively. The proposed algorithm was deployed to the FPGA hardware system, so as to enable the alarm system to complete the task of extracting the center coordinates of the spot within a frame image transmission cycle, which improved the image processing efficiency and realized the efficient alarming. Experiments show that the maximum error of spot center coordinate extraction is 1 pixel, and the response time of the alarm system is 17.453 ms. By optimizing the image processing algorithm, the response time of the alarm equipment is shortened, and the rapid and accurate alarm of the incoming laser is realized.
Currently, the microscopic 3D observation primarily relies on specific fluorescence staining, which will cause irreversible damage to samples and presents issues such as high cost and phototoxicity. A novel method for mesoscopic high-resolution 3D reconstruction without fluorescence was proposed, known as RGB-MesoLFM. First, a fluorescence-free labeled white-light mesoscopic circuit was constructed, where the RGB three-band light field data were decoupled. Subsequently, based on fluctuating optics point spread function, the point impulse response of the system at any depth within the three bands was computed. Finally, an objective function was developed using convex optimization theory, considering the RGB three-band light field data and point impulse response as input for 3D deconvolution iteration, which can reconstruct the slice image of the high-resolution target object at any depth. The 3D reconstruction experiment was based on the light field sampling results of egg embryo slices, and could obtain slice images in the range of 0~?20 μm with a sequence interval of 4 μm. Compared with the traditional fluorescence reconstruction method, the proposed method does not require fluorescence, but uses white light for imaging. The reconstructed peak signal to noise ratio (PSNR) value of arbitrary depth slices is about 10% higher than that of traditional methods.
The optical attenuation and absorption effects in turbid water often lead to a significant decrease in imaging quality, which has an undeniable impact on many applications based on underwater visual images. A polarization imaging method for underwater scattering suppression was proposed, the crucial idea of which was to maximize the degree of polarization of backscattered light through active illumination modulation, thus the backscattered light was suppressed to the greatest extent. Through the measurement of the Mueller matrix of the target scene, the given Stokes vector of the backscattered light, the determination of the Stokes vector of the incident active illumination, and the calculation of the polarization feature vectors, the images in the scattering medium were finally recovered by combining above information. Experimental results show that the method performs well in dealing with the imaging problems under turbid water. Compared with other methods, it significantly improves image quality and provides a powerful solution for imaging applications in underwater environments. The uniqueness of this method lies in its active illumination modulation technique, which achieves the modulation of the polarization characteristics of the backscattered light through active illumination control, thereby effectively reducing the imaging degradation caused by scattering, and bringing new research ideas to the field of underwater polarization imaging.
In the practical application of Moire tomography, the intelligent recognition of effective Moire fringe areas is a crucial step. To address the cumbersome and inaccurate process of manually determining effective areas, a method for intelligent recognition of effective Moire fringe areas was proposed. First, the Moire fringes were preprocessed using a combination of the Otsu algorithm and mathematical morphology. Then, the difference values of light intensity images of straight and curved fringes with and without the measured flow field were obtained. Finally, the coordinates of the effective areas were determined based on Gaussian fitting. To verify the feasibility and universality of this method, it was applied to practically effective areas recognition of Moire fringes with different flow field structures, contrasts and fringe widths, and the automatic and accurate extraction of effective Moire fringe areas was successfully achieved. In summary, this method significantly simplifies the algorithm structure, achieving precise and reliable recognition of effective Moire fringe areas with lower computational costs.
Recognition of smoke emission behavior in industrial environments is of vital importance for regulating and monitoring companies in real time, as well as for environmental protection. However, it is highly challenging. On the one hand, industrial emission smoke is characterized by high transparency and high dynamics, and on the other hand, the shape and size of smoke may change due to the environment, lighting, and other factors. Currently, the mainstream smoke recognition methods are deep learning models based on images and videos, but the image-based models cannot effectively model the dynamic characteristics of the smoke in the video in a time-series manner, while the video-based models do not take into account the characteristics of the variable shape of the smoke. The random patch shift (RPS) and deformable attention (DA) was introduced into the Swin Transformer. The traditional 2D spatial attention was transformed into spatio-temporal attention by RPS, thereby modeling the dynamic smoke using 2D self-attention computations. By means of adaptive deformation, DA enabled the network to adapt to different smoke shapes and appearance changes, thereby improving the robustness and generalization ability of the network. Experimental results on the RISE dataset show that the proposed method can achieve F1 scores of 0.85, 0.86, and 0.84 in the three subsets, respectively, with an improvement of 0.01~0.06 compared to other methods.
Based on the Muller matrix and Stokes vector measurement principles, a stress measurement and online error correction method using circularly polarized light and no rotating elements was proposed. The phase delay of the sample to be tested was calculated by the light intensity information captured by polarization camera, and the stress distribution of the sample could be obtained by tracing the phase delay. By analyzing the effect of the phase delay of standard quarter wave plate and the extinction ratio of polarization camera on the measurement results, the corresponding online measurement and calibration method was proposed. To verify the feasibility of the proposed approach, a stress measurement system was constructed. A quarter wave plate with 633 nm wavelength assigned by the metrological service was measured by this system, and the measurement results were corrected by the proposed error correction method. The results show that the relative errors of the wave plate phase delay before and after correction are 11.5% and 1.73%, respectively, and the corrected relative errors are primarily caused by the linear polarizer. The proposed method exhibits characteristics such as simple measurement process and high accuracy.
In the scenario of hydrogen leakage, personnel may be exposed to great dangers such as fire, explosion and asphyxiation. In order to effectively reduce the risk of personnel exposure during detection and to monitor hydrogen concentrations in real time, a hydrogen telemetry system based on tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy (TDLAS) technology under an open light path combined with wavelength modulation system (WMS) technology was developed, in which the simulation modeling was realized by using MATLAB visual modeling and simulation software Simulink. To further improve the detection accuracy and signal-to-noise ratio of the system, the influence of laser scanning parameters on the second-harmonic signal waveform and the influence of different Fresnel lens F numbers on the light intensity received by the detector were comparatively analyzed, and the optimal parameter value was obtained by combining the peak value, peak width, signal-to-noise ratio and signal integrity of the waveform. The results show that the waveform is optimal with the scanning amplitude of 1 V and the scanning frequency of 10 Hz. After parameters optimization, the maximum detection distance of wood board, lime, plastic, and aluminum plate as non-cooperative targets is increased from 1.8 m, 2.4 m, 4 m and 6 m to 2 m, 2.8 m, 5.1 m and 10 m respectively, and the laser-echo incident power of the system is also significantly improved. The hydrogen detection system has the characteristics of wider operating environment, safer detection environment and higher detection accuracy. This research serves as a theoretical foundation for the selection of relevant parameters in practical measurement, and provides theoretical guidance for enhancing the accuracy of system measurement in practical applications.
In the infrared spectroscopic transmittance testing system based on the retro-reflective method, the position of the components such as aperture will affect the measurement of spectral transmittance of the infrared lens during measurement. To address this issue, a vignetting model was established to analyze the vignetting of the measurement beam in the testing system, and the vignetting formula generated by aperture and other components placing at different positions was derived. Experimental results show that maintaining the consistency in relative vignetting between the aerial and actual measurements can effectively reduce the effect of vignetting variations on the measurement of spectral transmittance of the infrared lens.
In large numerical aperture (NA) spherical surface shape detection, the defocusing errors introduced by the measured sphere deviating from the ideal confocal position will seriously affect the detection accuracy. In order to accurately extract and effectively correct defocusing errors and improve the efficiency of adjusting the final inspection position of components, a defocusing error correction method based on the error extraction algorithm assisted installation and adjustment was designed. The defocusing error extraction algorithm was used to quantitatively extract the defocusing amount and determine the direction of adjustment, so that the large NA spherical surface could be adjusted to zero fringe position quickly and accurately, and the defocusing errors could be greatly reduced. After auxiliary installation and adjustment, Zernike wavefront fitting algorithm was used to eliminate the defocusing term and the spherical difference term introduced by the large NA spherical surface for fine adjustment. The experimental results show that the defocusing extraction errors is within 3% by using the proposed method to correct large NA spherical surface. This method increases the range of defocusing errors extraction and compensation for components, and can extend the upper limit of defocusing amount to ±25 μm, which ultimately achieves the sub-nanometer correction accuracy.
In structured light 3D measurement technology, the system calibration is the basis of measurement. A method was introduced that projected a coding grating onto a checkerboard calibration plate and calculated its projected pixel coordinates from the phase values at the corner points. Considering the problems of phase missing and phase anomalies in the corner neighborhood, a fitting algorithm based on local random sample consensus (RANSAC) was proposed to eliminate phase outliers and surface fitting interpolation, thereby calculating the sub-pixel level projected pixel coordinates of the feature points for calibration. This method does not rely on the calibration results of the camera and is also applicable to the dot calibration plate, effectively filtering the anomalies and noise of the phase values near the feature points. Experimental results show that this method has good robustness to outliers, and the reprojection error reaches 0.09 pixels, which has lower requirements on the type and cost of calibration plates, and has certain practical values.
The simulated dynamic light scattering data of particles with different distribution widths were inverted using the methods of removing and retaining the non-Gaussian term. The distribution of the particle size information in the light intensity autocorrelation function (ACF) with different distribution widths was calculated by the differences between the light intensity ACF and the light intensity ACF corresponding to the average particle size. The results show that for narrow distribution particle systems, the removal and retention of non-Gaussian term have no obvious effect on the inverted particle size distribution at lower noise levels. As the noise level increases, the performance indices of inversion results by removing non-Gaussian term are better than that of by retaining non-Gaussian term. For wide distribution particle systems (coefficients of variation typically greater than 3%), retaining the non-Gaussian term can yield more accurate inversion results. The reason for the above results is that the content of particle size information in the non-Gaussian term corresponding to particles with different distribution widths is different. Compared with narrow distribution particle systems, the non-Gaussian term corresponding to wide distribution particle systems contains more particle size information. The removal of non-Gaussian term can lead to the loss of some particle size information, thereby reducing the accuracy of the inversion results. Since the long-delay period of the intensity ACF contains more noise, the inversion of narrow distribution particles not only cannot benefit from retaining non-Gaussian term, but also reduces the accuracy of inversion results due to the increase of noise.
Ultra-wideband spectroscope is an indispensable optical component in spectral analysis system, and its performance directly affects the measurement accuracy of Fourier infrared spectrometer. Based on the optical film theory, the Ge, ZnSe and YbF3 were selected as coating materials. The film system design was completed combined with the actual spectrum curves of the substrate, through the spectral compensation design method, and combined with TFC software. The electron beam evaporation and ion beam assisted deposition technology was used to prepare the thin film. Through the optimization of the deposition process, the problem of poor spectrum caused by large film thickness control error during the preparation of the spectroscope was solved. The Spectrum Two Fourier infrared spectrometer was used to detect that the average spectral ratio of 2.5 μm~20 μm band was 52:45.5 at 45° incidence. Through the environmental test, the spectroscope has good stability.
The preparation process of porous thin films is an important part of their optical properties. The porous TiO2 films were prepared by sol-gel method and quartz glass substrate under different process conditions, the optical properties of the films were characterized and analyzed by ellipsometer, spectrophotometer and white light interferometer, and the effects of raw material ratio, hydrochloric acid concentration, the addition of porous agent (polyethylene glycol, PEG) and other process parameters on the refractive index, porosity, transmittance and surface morphology of porous TiO2 films were studied. Finally, the optimal process parameters for the preparation of porous TiO2 films were determined. The results show that in the spectral range of 300 nm~700 nm, the refractive index of TiO2 film can be reduced to 1.496 0 (wavelength 550 nm) when butyl titanate, hydrochloric acid (20%), deionized water and absolute ethanol are used in the ratio of 3∶1∶10∶8, the amount of PEG in the solution is 0.03 g·ml?1, and the film is coated twice. The pores of the film layer are evenly distributed, and the porosity is 48.3%. The optical bandgap value of the thin film is 3.77 eV.
Aiming at the issue of low efficiency in random noise injection in a mechanically dithered laser gyroscope, the effect of random noise on the elimination of dynamic lock-in region in laser gyroscope was intensively studied, and a functional relationship between noise frequency components and dynamic lock-in region was obtained. Based on the pseudo-random sequence and combined with the analysis of noise injection transfer function for the laser gyroscope, a polymorphic random noise enhancement injection technology was proposed, and an algorithm for polymorphic random noise enhancement injection was developed in field programmable gate array (FPGA), followed by experimental verification of the technique. The results show that, in comparison to conventional random noise injection methods, polymorphic enhanced random noise injection notably enriches the frequency components of random noise and boosts the noise amplitude in the high-frequency range. Consequently, the noise injection efficiency of the laser gyroscope rises by around 50.57%, the gyroscope accuracy is increased by about 33.62%, and the angular random walk coefficient is reduced by approximately 17.62%. The polymorphic enhanced random noise injection technology offers important reference for improving the performance of mechanically dithered laser gyroscopes.
Aiming at the problems of low resolution of wavelength and angle, and low angle range of field of view of incoming laser measurement in two-dimensional laser alarm, a scheme of laser alarm using binocular image sensor was proposed. The optical system was mainly composed of grating, lens group and two COMS image sensors. Based on the grating diffraction principle, binocular detection was carried out to improve the angular resolution of measurement. The wavelength of the incoming laser was obtained by measuring the pixel distance of the diffraction spot of two adjacent levels on CMOS~~1, and the two-dimensional direction angle of the incoming laser was obtained by measuring the center position of the spot of the incident laser in the CMOS~~2 image sensor. The measurement feasibility was verified by experiments. The experimental results show that the improved wavelength resolution is better than 6 nm, the angle resolution is 0.1°, the angle of field is ±50°, and the accuracy of angle measurement is 0.1°.
A numerical calculation model of laser light field considering thermal distribution and gain distribution was constructed to evaluate the beam pointing angle instability of high-power solid-state lasers. The influence of the detuning degree of the resonant cavity output mirror and the mirror on the beam pointing stability was analyzed. The cavity mirror rotation perturbation factor and the cavity mirror movement perturbation factor were defined to describe the degree of parallel detuning and coaxial detuning of the cavity mirror, respectively, and the perturbation factor, thermal effect modulation and gain modulation were introduced in the calculation of the resonant cavity light field. The influence of resonant cavity parameters on the beam pointing stability of high-power Nd:YAG solid-state laser under the condition of cavity mirror detuning was studied. When the pump power is 10 000 W, and the cavity mirror rotation perturbation factor and the cavity mirror movement perturbation factor changing in the range of 1×10?4~50×10?4 and 1×10?7~50×10?7, respectively, the fluctuation range of the root mean square value of laser beam pointing offset angle in the pump pulse time is 1×10?6 rad~5×10?3 rad.
Single-longitudinal-mode (SLM) lasers, characterized by their superior output laser beam quality, narrow linewidth, stable frequency, and compact size, find extensive applications in coherent optical communication, lidar, nonlinear optics, gravitational wave detection, and high-precision spectral measurement. A short cavity scheme in conjunction with Fabry-Perot etalon mode selection was employed, and a theoretical analysis of the longitudinal mode within the cavity was carried out. A laser diode single end-pumped acousto-optic Q-switched Nd:YVO4 laser with a cavity length of 90 mm was involved, into which a 5 mm thick Fabry-Perot etalon with a reflectivity of 90% was inserted. A SLM laser output was realized with an adjustable repetition frequency of 1 Hz~10 Hz, a pulse duration of 10 ns, a single pulse energy of 133 μJ, and an energy instability of 3.39%. The output SLM laser was further amplified by two stages, and a single-pulse energy output of 40 mJ was obtained.
According to the characteristics of non-axisymmetric optical fiber, the optical path system was built by using digital holographic microtomography. Based on the phase information of the measured sample carried by the object light wave, the information of the object light wave on the CCD was extracted. Due to the characteristics of non-axisymmetric optical fiber, a 360° digital hologram was collected. The phase distribution information of object light wave of each hologram was extracted by the reconstruction algorithm of angular spectrum theory, and the three-dimensional refractive index distribution was obtained by the reconstruction algorithm of tomography. Then, the Changying Tong and Corning fibers were used as test samples, the difference in refractive indices between the fiber core and cladding was measured to be 0.005 and 0.006, respectively, which was basically consistent with the parameters provided by the manufacturer. In order to further verify the effectiveness of the proposed testing method, the refractive index measurements were conducted at the solder joints. The experimental results show that the accuracy of the proposed measurement method is superior to previous fiber optic measurement methods, and it has advantages such as non-destructive testing of fiber optic samples, simple measurement methods, and fast measurement speed.
Aiming at the problems of low indoor positioning accuracy and large boundary area positioning error, an indoor visible light positioning method based on the bald eagle search-extreme learning machine (BES-ELM) neural network and weighted dual-mode edge (WDME) positioning model was proposed. In this method, a visible light system structure with a single LED and five photodetectors was proposed, and the room was divided by fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm. The BES was used to optimize the ELM neural network, and the BES-ELM positioning model was established in different regions. Aiming at the boundary area, a weighted dual-mode edge (WDME) positioning model was constructed to achieve accurate edge location. Based on the indoor environment simulation of 3.2 m×3.2 m×3 m, the results show that using the BES-ELM algorithm to locate the center area, the average positioning error is 0.011 7 m, and the minimum positioning error is 0.001 9 m. Using the WDME positioning model to locate the edge area, the average positioning error is 0.013 3 m, which is 84%, 27%, and 26% higher than that of ELM, Elman and BES-ELM models, respectively. Therefore, the proposed visible light positioning method reduces the overall area positioning errors, especially improving the positioning accuracy of edge area.
The single-layer coating and Fabry-Parot resonant cavity (FP cavity) were analyzed in principle, and the tap coating and FP cavity were modeled using the coatings tool of Zemax software. The reflectance and transmittance of single-layer coating with different refractive index materials were analyzed with respect to wavelength. The model of FP cavity was simplified and analyzed, and the reflectance and transmittance were preliminarily verified with an air-gap FP cavity with 3 mm gap. A fiber optical etalon of 50 GHz commonly used in communication was designed, and a production scheme of in-line optical etalon based on Glens collimator was introduced. Through the design, the transmittance and reflectance of the spectral ratio film of the Glens plane were controlled, and the distance between two Glens collimators was adjusted to achieve the control of the peak value, valley value transmittance and free spectral range (FSR) parameters of the FP cavity. Through the simulation, the parameters of the simulation and samples were obtained to be basically the same. The inter-sample differences, differences in spectral peak transmittance and spectral phase differences were also analyzed. Analysis of FP etalon by Zemax is convenient and intuitive, which provides a new method for FP design and analysis.