Image defocus clues are widely used for generating corresponding depth images because of their speed and convenience. However, when the defocus degree of the defocused image is exceptionally high or low, the depth information of the image is often lost, making the generated depth images unable to satisfy the actual user requirements. It is necessary to distinguish and separate these images. However, existing methods are not sufficiently accurate for distinguishing the blur degree of the defocused images in different scenes, and lack the unified standards. Hence, they cannot distinguish and separate the defocused image effectively. In this study, an automatic discrimination method for the defocused image based on the image gray ratio is proposed to solve this problem. First, by analyzing and using the gradient and frequency-domain features of different regions of the out-of-focus image, it can effectively distinguish the blurred and clear areas of the image. Second, the feature images are fused to obtain a fusion image. Because the defocus degrees of the blurred and clear regions of the out-of-focus image are somewhat different, the contrast between the gray values of the two parts in the fusion image is evident. The ratio is used as a criterion to assess the degree of defocusing. When the ratio of the defocused image exceeds the set threshold standard, the image does not satisfy the depth image generation conditions, and separation is performed automatically. Finally, by comparing the existing definition evaluation function with the results obtained using the proposed method for discriminating the degrees of blurring of different defocused blurred images in the same and different scenes, the proposed method can more accurately and rapidly distinguish the degrees of blurring of defocused images in the same and different scenes, effectively separate the unqualified defocused images, and improve the generation efficiency of depth images.
Owing to the increasing severity of garbage pollution, automatic garbage detection has become significantly important in practice. The detection mechanism of YOLOv5 is improved in this study to achieve better performance in outdoor garbage detection against a complicated background. Moreover, here, a garbage dataset is constructed comprising six garbage image types collected in a complex background; subsequently, a simple yet efficient method is proposed to generate ground truth heat maps of garbage objects presented in the images. We treat the corresponding heat maps as a quantization standard and then obtain a branch structure based on YOLOv5 by conducting experiments to generate predicted heat maps. Subsequently, the predicted heat maps are sent back to the backbone structure of YOLOv5 to increase the spatial attention weights of the feature maps in the training process to improve the performance of the entire target detection network. Only a few parameters are added to the improved network, which generates proper predicted heat maps and the performance of garbage detection has been greatly improved.
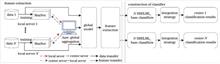
The field of medical imaging currently faces the problems of data island and non-independent and independently distributed (Non-IID) variables in multi-center data. In this study, a federated learning algorithm based on adaptive aggregate weight (FedAaw) is proposed. Using a global model polymerization process, this study utilized the accuracy threshold to filter out the local model; the model accuracy is calculated by the center server. The corresponding weights of polymerization, which are updated in the global model, yielded models with better classification performances that are used to construct a global model, which helps address the problems associated with Non-IID multicenter data. Furthermore, to improve the applicability of the model to mining the information between the long and short distance of the image, the multi head self-attention mechanism is introduced to the local and global models. In addition, to address the problem of model overfitting caused by end-to-end redundant features, the convolution kernel features in the global model are extracted. The learning of sparse Bayesian extreme learning machine based on L1 norm (SBELML1) framework is used for the feature classification of the data obtained from each center. Finally, the anti-interference ability of the FedAaw algorithm is verified by shuffling the data distribution of different centers several times. The AUC ranges of the test sets used in the five centers are as follows: center 1: (0.7947?0.8037), center 2: (0.8105?0.8405), center 3: (0.6768?0.7758), center 4: (0.8496?0.9063), and center 5: (0.8913?0.9348). These results indicate that FedAaw has good classification performance on multi-center data and a strong anti-interference ability.
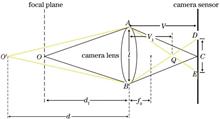
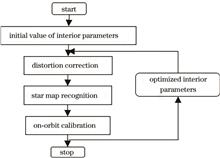
It is necessary to calibrate the internal and external parameters of a camera with a large field of view in real time to measure the antenna profile of spacecraft with high accuracy in orbit via photogrammetry. In this paper, a fast recognition method for star map captured using a camera with a large viewing angle is presented. First, a star map recognition strategy combining calibration results is proposed to improve the matching accuracy. Next, a tag search and matching method based on the angular distance between four stars is proposed, which reduces the complexity to linearity and achieves fast and accurate matching. Finally, a matching test method based on back-casting error analysis is proposed to prevent false identification. The experimental results show that compared with the traditional algorithm, the method reflects both the recognition speed and recognition rate. The recognition rate reaches 99.5%, and the recognition time is reduced by 75%. This study demonstrates that the proposed method is reasonable and effective, can save storage space, improve the recognition speed and rate of star maps, and has a good practical value.
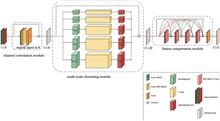
Due to the interference of thermal noise of the instrument, sample surface characteristics, and sample staining preparation conditions during microscopic imaging with Cell microdissection, the imaging quality is easily impaired. Aiming at this problem, a denoising network model based on multi-module combination (DNMMC) is proposed. The model processes the input images using channel correlation module, multi-scale denoising module and fusion compression module, then outputs the denoised image. Furthermore, by comparing the proposed method with the current mainstream denoising methods in terms of quantitative measurement and visual quality perception, the experimental results show that DNMMC has higher robustness in denoising biological microscopic images. It can be seen that the method will significantly improve the imaging quality of biological microscopes.
This study proposes a two-stage progressive image deraining algorithm for vehicle detection in rainy days. The proposed algorithm aims to improve the accuracy of vehicle detection in rainy days and solve the problem of accuracy degradation caused by rain streak interference in the vehicle detection system of intelligent and connected vehicles. For the algorithm, a two-stage progressive deraining network was developed with light feature extraction and weighting block along with efficient feature transfer and fuse block as the core to realize the mining and capture of rain streak information and achieve accurate deraining. The deraining images were input to benchmark vehicle detector YOLOv5 for verifying the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm. Furthermore, a mix vehicle dataset was constructed based on the working environment of intelligent and connected vehicles. The gains of the proposed deraining algorithm on the precision, recall, and mAP@0.5 of the benchmark vehicle detector YOLOv5 are 3.0 percentage points, 8.9 percentage points, and 7.6 percentage points, respectively, under a rainy traffic scenario compared with other algorithms. The results prove that the proposed deraining algorithm considerably improves the accuracy of vehicle detection in rainy days and can be used in practice.
A point cloud registration algorithm based on structured light and CT images is proposed to address model sensitivity to noise and low accuracy issues in medical image registration using existing deep learning algorithms. The primary aim is to improve registration accuracy and algorithm robustness whilst avoiding radiation caused by X-rays during image acquisition. First, project encoded structured light onto the body surface of an intraoperative patient, and principal component analysis is used to obtain the point cloud for the body surface after spindle correction. Second, CT scans are performed on preoperative patients and three-dimensional reconstruction and sampling are conducted to obtain their body surface point clouds. Finally, a dynamic graph convolutional network model based on feature reuse and attention mechanisms is constructed, combined with an image iterative registration algorithm for point cloud registration on the back of the human body. The entire process effectively integrates the information from the two modes, with the advantages of no radiation, high accuracy, and short time consumption.
In order to address the issues of missing and leaking instance masks caused by redundant semantic information in mainstream single-stage instance segmentation algorithms, this paper proposes an instance segmentation algorithm based on semantic alignment and graph node interaction. In the global mask generation stage, a semantic alignment module was designed to evaluate the influence of semantic information on global and local semantic integrity through global mapping and Gaussian mapping, thereby suppressing redundant semantic information. In addition, a graph node interaction module was designed in the instance mask assembly stage that extracts spatial features of the topological graph by transforming the feature map into graph-structured data and interacting with graph node information, supplementing the mask assembly information and further improving the accuracy of the instance masks. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm achieves a mean average accuracy (mAP) of 38.3% on the MS COCO dataset, exhibiting strong competitiveness against other state-of-the-art algorithms.
With the aim to solve surface-quality detection of liquor bottle-cap packaging and the difficulty of deploying algorithms owing to large parameters, this study proposes a more lightweight and high-precision detection algorithm, named SEGC-YOLO, which is based on YOLOv5s. First, the ShuffleNet V2 is used to replace the original backbone network to effectively simplify the parameters, and the backbone network is enhanced using efficient channel attention mechanism. Next, the improved GhostConv and C3-Ghost modules, based on GhostNet, are used to improve the neck network and reduce the neck parameters. In addition, the CARAFE operator is introduced to replace the nearest neighbor interpolation upsampling operator. The upsampling prediction kernel with adaptive content awareness can improve the information-expression ability of the neck network and thereby the detection accuracy. The Adam gradient optimizer is used for training. Experimental results show that the proposed SEGC-YOLO algorithm achieves the mean accuracy precision mAP @0.5 of 84.1% and mAP@0.5∶0.95 of 49.0% at different intersection over union (IoU) thresholds, which are 1.2 and 0.5 percentage points higher than the original YOLOv5s algorithm, respectively. The overall floating-point operations (FLOPs), parameter volume, and model file size are also reduced by 69.94%, 71.15%, and 69.66%, respectively, indicating higher accuracy and lighter weight compared with that of the original algorithm. Therefore, SEGC-YOLO can quickly and accurately identify the surface defects of bottle caps, providing data and algorithm support for rapid detection and equipment deployment in related fields.
Renal tumors pose great harm to and seriously affect human health. Early detection and diagnosis of renal tumors can help patients' treatment and recovery. To efficiently segment kidneys and tumors from abdominal computed tomography (CT) images, this paper proposes a method based on 3D U2-Net. First, we upgrade the 2D U2-Net, adjust loss function, depth of network, and supervision strategy. To improve the feature expression ability of the decoder, we propose a residual feature enhancement module, which enhances the channel and spatial domain of the feature map at the decoder. To further improve the model's ability to extract global information, we propose a multi-head self-attention module based on global features, which calculates the long-term dependencies between all voxel points in the feature map and obtains more contextual information of 3D medical images. The method is tested on the official KiTS19 dataset and the results show that the average Dice value is 0.9008 and the parameter quantity is 4.60 MB. Compared with existing methods, our method can achieve better segmentation accuracy with small parameter quantity, and has great application value for small memory embedded system used for kidneys and tumors image segmentation.
The calibration process for a line-scan camera is typically complicated, often requiring external auxiliary devices. This paper proposes a static calibration method for line-scan cameras built in 2D space to address this problem. First, from the application point of view, the line-scan camera imaging model in 3D space is adapted to derive an equivalent model in 2D space, and a new line-scan camera calibration plate is designed. Next, the line-scan camera imaging model in 2D space is solved using the principle of the invariance of the cross-ratio. Finally, an aberration correction fitting strategy is proposed, using the amount of aberration change to overcome excessive aberration correction errors, which can occur when trying to correct small aberrations. The aberration correction fitting strategy is effective, achieving a good aberration correction effect. The proposed static calibration method for line-scan cameras in 2D space is simple, is not limited by the field environment, and has a high calibration accuracy. The proposed calibration method has a mean absolute error of 0.06 mm (equivalent to ~ 1.5 pixels) and a maximum stable error standard variance of 0.068. As a result, the proposed calibration method meets the application requirements for low and medium calibration accuracy, and is extremely promising for practical applications.
Binary fringe projection profilometry has experienced significant growth in recent years to eliminate the gamma effect of projectors. Determining the appropriate defocus amount is crucial for three-dimensional measurement in binary fringe defocus projection. Insufficient defocusing can result in fringes containing higher-order harmonics, while excessive defocusing can reduce fringe contrast, decrease phase resolution, and relatively increase noise impact. Both insufficient and excessive defocusing can affect the phase measurements accuracy. To address this problem, a method for determining the optimal defocus amount based on digital correlation is proposed. This method utilizes the correlation between fringes and their second-order derivatives to determine the optimal defocus amount and achieve quasi-sinusoidal fringes. In both under-defocus and over-defocus situations, the correlation coefficient is small, and it reaches its maximum value only when the fringes are quasi sinusoidal. The method was numerically simulated and experimentally validated. The experimental results show that the proposed method offers fast speed and high accuracy, enabling real-time tracking of the correlation coefficient during the binary fringe projection process and determining the optimal defocus amount.
Herein, a differential modulation computational ghost imaging method based on discrete W transform is proposed. The light source is differentially modulated by two sets of discrete W transform basic patterns: positive and negative, and the spectrum of the target object is obtained according to the light intensity measured by the barrel detector. The target image is reconstructed by inverse discrete W transform in matrix form. The proposed method is verified by both computational simulations and laboratory experiments. The results show that the method can obtain an image from compressive measurements. The background noise can be removed by differential measurement to realize excellent image quality, and the image can be reconstructed quickly by applying the inverse discrete W transform. Compared with other methods, this method offers more advantages in terms of imaging quality.
The facial structure information of a person includes a high degree of uniqueness. Data obtained from 3D measurements and reconstruction of the face is useful in facial recognition and medical plastic surgery. In this study, structured light projection technology is used to project a specially coded near-infrared grating stripe onto the face to facilitate the calculation of a 3D appearance of the face. Simultaneously, the facial feature points are detected using 2D texture images, and the distribution of key facial feature points is obtained. Finally, accurate acquisition and understanding of key facial feature information is achieved by combining 2D distributed feature points and 3D point cloud information. This provides reference for future applications of 3D facial detection, such as medical treatment, facial recognition detection, and virtual human data input.
To achieve quantitative detection of unlabeled samples, a miniaturized phase microscope is independently designed using NX12.0 and related devices. Compared to the expensive phase microscopes currently on the market, the newly designed microscope has an approximately 60% smaller volume while achieving the same system resolution, significantly improving portability; it does not require coherent devices, and the cost is only approximately 5000 yuan. The system also incorporates an autofocus algorithm and a field of view correction algorithm, based on transform domain techniques, to accelerate the detection speed and accuracy of phase recovery. After testing, the resolution of the system reached the resolution board limit of 2.19 μm using a 10× objective lens. Further, the detection of random phase plates indicates that the accuracy of phase recovery also meets the basic requirements. Additionally, defects in the structure of living cells and flat glass are also tested. The results indicate that the proposed system can quantitatively measure living cells and play an important role in detecting transparent/semitransparent plane defects. They also prove the feasibility of this low-cost and portable unlabeled-sample quantification system design scheme.
This paper proposes an improved point cloud guided filtering algorithm to address the difficulties in separating and removing noise close to the model surface in point cloud denoising, as well as the problem of losing valid points during noise removal. First, the statistical filtering method is used to screen out difficult-to-smooth noise and perform initial guided filtering, thereby reducing the impact of difficult-to-smooth noise on the overall filtering effect. Then, based on the geometric features of each point in the point cloud, the weight parameters are adaptively adjusted and incorporated into the improved guided filtering algorithm for the second round of point cloud guided filtering. Finally, a smoother point cloud is obtained by adaptively adjusting the weight parameters while preserving valid points. According to experimental results, the proposed algorithm shows substantial smoothing effects on noisy point clouds. Moreover, the processed point cloud model has more prominent edge lines, and difficult-to-smooth noise can be well handled using the proposed algorithm.
Laser line scanning technology is primarily used for surface inspection of mechanical parts and three-dimensional (3D) reconstruction of objects. Many relief artifacts cannot be reconstructed owing to the absence of digital models; however, laser line scanning can perform relief reversal and generate a 3D model for the processing of these relief artifacts. In this study, a robot and line laser are combined to obtain point cloud data and reconstruct a 3D digital model of reliefs. To calculate the scanning path of a robot, a 3D reconstruction system based on the size of the reference model is constructed, and the robot is combined with the laser line scan to obtain the point cloud data of the relief. The point cloud data is preprocessed, and then the point cloud data with robot error is compensated according to the reference plane. Based on the derived iterative closest point (GICP) algorithm, the point cloud is automatically stitched and postprocessed. The 3D model is then reconstructed according to the Delaunay triangulation and surface reconstruction algorithms. The experiments were performed with an eagle relief as the reconstruction object. The experimental results show that implementing path scanning in point cloud stitching provides an easy to execute process, with 40.48% improvement in the accuracy after data rectification and significant error compensation. Additionally, the average standard deviation between the reconstructed relief and reference model is 0.0576 mm, meeting the requirements of the reconstruction effort.
In this study, a Canny-Cauchy edge detection algorithm is proposed to address the issues of unsatisfactory object contour detection performance, high false detection rate, and high missed detection rate of traditional edge detection methods caused by factors, such as Gaussian noise, salt and pepper noise pollution, and small edge gradient changes. The proposed algorithm is an improved Canny algorithm that performs adaptive median filtering preprocessing on salt and pepper noise images to remove salt and pepper noise while protecting edges from blurring. For designing the filter, the algorithm uses the first derivative of the Cauchy distribution function as the edge detection function and obtains the edge detection filter by sampling the function. Theoretical analysis is conducted on the proposed edge detection function according to the three design criteria of edge detection algorithms, and comparative experiments are conducted with other edge detection algorithms on the BSDS500 dataset. The experimental results show that this algorithm can ensure that the peak signal-to-noise ratio of the processed image is greater than 30 dB and the structural similarity is greater than 0.9 under 20% density salt and pepper noise. In addition, this algorithm has a stronger ability to suppress white noise and respond to real edges than the traditional Canny algorithm. Moreover, regarding the BSDS500 dataset, the proposed algorithm exhibites an increase in F1 score and average accuracy by 7.5% and 10.2%, respectively.
Aiming at the problem that some artificial intelligence-based subway vehicle train inspection products in the current rail transit market have low detection accuracy when the vehicle is shifting, a computer vision-based subway speed measurement method is proposed. First, the corrected subway image is obtained through image perspective transformation, and on the basis of the corrected image, the deep learning target detection method is used to locate the subway area. Second, feature point detection is performed on the subway area located in the adjacent two frames of images, and the matching point pair is obtained by using the strongest feature point matching method in the region. Then, the average pixel distance of the subway movement is calculated according to the matching point pair, and the actual moving distance is converted by combining the pixel size. Then, the current real-time speed of the subway can be obtained through the known time difference between two adjacent frames of images. Finally, according to the speed information detected in real time, the line frequency of the line scan camera is adjusted in real time, so as to reduce the image distortion caused by the speed change or parking of the subway vehicle as much as possible. Further improve the detection accuracy of subway train inspection products when the vehicle is shifting. The actual test results at Zhujiajiao Station of Shanghai Metro Line 17 show that the line scan images of subway vehicles obtained by this technology will not be significantly distorted due to changes in vehicle speed. Moreover, the speed measurement frequency is high, and the test error is within 1.2 km/h.
During the production and processing of pineapple peeling line, inner thorns remain on the pineapple surface, which require manual secondary removal. To address this, an image processing method is adopted to extract features and spatially locate the inner thorns of pineapple, to determine their precise location for automatic removal of the thorns. Accordingly, a pineapple image acquisition system and a corresponding pineapple inner thorn detection algorithm are designed. The pineapple image is preprocessed to separate the inner thorn features from the background, eliminating the interfering features, and the contour of the inner thorn is used as the extracted feature. The area of the contour and the roundness of the contour are used as descriptors, and the center coordinates of the smallest outer rectangle of the pineapple inner thorn contour are used as the position of the pineapple inner thorn in the image, while the outer contour of the pineapple is used to convert the two-dimensional coordinates of the inner thorn into three-dimensional coordinates to precisely locate the pineapple inner thorn. The comparison experiments show that the accuracy of the pineapple inner thorn detection algorithm is significantly higher than that of the traditional speckle detection algorithm. In addition, the accuracy of fitting the center of the inner thorn is higher, with the maximum detection error of 0.63 mm and average detection error of 0.33 mm. The study shows that the average detection speed and accuracy can meet the needs of the pineapple inner thorn removal process, which provides a certain technical basis for the inner thorn removal in pineapple assembly line processing.
An improved Lidar odometer based on continuous-time spline constraints is proposed to address the problem of motion trajectory drift caused by sudden turning and swaying of the laser radar owing to road bumps and other road conditions. By assuming motion discontinuity, the accuracy of point cloud matching is improved by scanning keyframes and spline segmentation, and then adding spline constraints. By using the improved iterative nearest neighbor (ICP) algorithm for frame-to-map matching, the drift of motion trajectories can be effectively suppressed. The experimental results of using the KITTI mileage and laboratory-collected mileage datasets show that the proposed Lidar odometer algorithm reduces the global average error of the motion trajectory by 12.43% and 29.40%, respectively. Compared with existing methods that are based on geometric features, the proposed Lidar odometer is stable and effectively suppresses motion trajectory drift, improving the performance of the Lidar odometer.
To address the issue of inadequate accuracy and real-time performance of infrared ship target detection methods on coastal defense scenarios, a novel lightweight ship detection algorithm based on improved YOLOv7 framework is proposed. This framework incorporates several enhancements to augment its capabilities. First, to achieve model lightweight processing, the algorithm integrates the MobileNetv3 network into the architecture of the Backbone network. This addition contributes to efficient computation and model size reduction.Second, an attention mechanism is introduced within the Neck network to mitigate noise and interference, thereby improving the network's feature extraction capability. In addition, we employ a bidirectional weighted feature pyramid to enhance feature fusion within the network, promoting more effective information integration. Finally, the algorithm incorporates Wise IoU to optimize the loss function, improving convergence speed and model accuracy. Experimental evaluations on the Arrow dataset demonstrate noteworthy improvements over the standard YOLOv7 approach. Specifically, the proposed enhanced algorithm exhibits a 0.9 percentage points increase in accuracy, 2.5 percentage points increase in recall, and 1.2 percentage points increase in mean average precision (mAP) at IoU thresholds of 0.5 and 0.5∶0.95. In addition, it achieves approximately 38.4% reduction in model parameters and a 65.5% reduction in floating point operations per second (FLOPs). This enhanced algorithm delivers superior inspection accuracy while meeting the speed requirements for efficient ship inspection. Consequently, it effectively enables high-speed and high-precision ship detection.
This study proposes a new method for multiline laser classification and optical plane calibration to overcome the limitations of the existing on-line laser calibration methods used for three-dimensional (3D) measurement systems. These limitations include difficulties in multiline calibration and low accuracy in extracting feature points. The proposed method utilizes the steger algorithm to extract the laser center line and classifies it using a method based on contour judgment. The key points on the calibration board are detected, and the corresponding relationship matrix between the camera and calibration board is obtained using singular value decomposition. Using this relationship matrix, the 3D coordinates of the key points in the camera coordinate system can be determined. Subsequently, the plane equation of the calibration plate in the camera coordinate system is obtained via fitting, allowing for the determination of the 3D point of the laser line on the calibration plate plane. This process can be repeated several times by changing the position and attitude of the calibration plate till multiline laser plane calibration is achieved. Experimental results on the standard block demonstrate that the proposed method is effective and meets the industrial accuracy parameters, achieving an average size accuracy of 0.02 mm after repeated measurements.
Existing point cloud registration algorithms are not effective for cross-source point cloud registration. To address this issue, this paper proposes a cross-source point cloud registration algorithm that uses angle constraints. The algorithm redefines the weight coefficients of the fast point feature histogram (FPFH) algorithm to adapt it to point cloud data with different scales and improve the inlier rate of matching point pairs. Additionally, the algorithm uses angle constraints to filter the matching point pairs and reserves those with good compatibility to estimate scale, thus unifying the scale of two point clouds. In the coarse registration phase, the compatibility triangles satisfying the distance constraint are filtered to calculate the coarse registration matrix, thus completing the preliminary transformation. Finally, the iterative closest point (ICP) algorithm is used for fine registration to improve the overall registration accuracy. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm has a good registration effect on point cloud data with same and different scales and can quickly register point clouds.
Herein, an improved YOLOx algorithm is proposed to address the challenges concerning false and missing detection of metal gear surface defects in an industrial interference environment. First, by utilizing the adaptive spatial feature fusion (ASFF) to fully utilize the differences between the features of defects and interference items at different scales, the model’s anti-interference ability is improved. Second, through the effective channel attention (ECA) module, the network’s feature extraction capability is increased. Finally, the confidence loss function is modified to the Varifocal loss function, which reduces the interference of complex samples in the network. Experimental results indicate that the improved YOLOx network outperforms the original network. Particularly, the recall rate, accuracy, and mean average precision indexes of the improved YOLOx network are improved by 6.1, 4.6, and 9.4 percentage points, respectively, as compared with the original network.
The basis of using 3D LiDAR in engineering application is to calibrate the external parameters of LiDAR, and the external parameters of LiDAR usually need to calibrate the data of other sensors jointly, and the calibration method is complicated and the process is long.In this paper, a simple automatic calibration algorithm is proposed.The algorithm first uses RANSAC algorithm to draw up a number of planes, and through the angle of the normal vector of the adjacent points for the secondary screening plane equation, then according to the plane equation to get the coordinates of the intersection point between the planes, using the antisymmetric matrix to construct the rotation matrix, further using the intersection point coordinates in the radar coordinate system and the world coordinate system under the difference, to obtain the approximate transformation relationship.Finally, the approximation matrix is optimized by the least square method, and a more accurate rotation displacement matrix is obtained.In the absence of feature points and corner clouds, the proposed algorithm can be used to fit more accurate corner points by plane equation. The simulation results show that the proposed calibration algorithm is feasible.
An optical neural network (ONN) based on fast Fourier transform (FFT) is constructed for digital image recognition in optical devices. Herein, ONN uses Mach-Zehnder interferometer (MZI) as its linear optical processing unit. These MZIs are connected in a grid-like layout and modulate the passing optical signals to achieve multiplication and addition. Subsequently, MZIs achieve classification and recognition for images. In this study, the influence of main hyperparameters (e.g., momentum coefficient and learning rate of the training algorithm) on the performance of ONN in recognizing handwritten digital images is investigated. First, the performance of ONN with four training algorithms in recognizing handwritten digital images under different learning rates is compared. These algorithms connect with different nonlinear functions and different number of hidden layers, namely, stochastic gradient descent (SGD), root mean square prop (RMSprop), adaptive moment estimation (Adam), and adaptive gradient (Adagrad). Additionally, the accuracy, running memory, and training time of ONN with the SGD algorithm connected with different nonlinear functions and different number of hidden layers are analyzed under different momentum coefficients. The recognition performance of ONN with SGD and RMSprop training algorithms is also compared after the introduction of momentum, where the learning rate is 0.05 and 0.005. The experimental results show that when the learning rate changes from 0.5 to 5 × 10-5, the FFT-typed ONN with the RMSprop training algorithm, two hidden layers, and the nonlinear function of Softplus has the highest recognition accuracy, reaching 97.4%. Furthermore, for the momentum coefficient of 0, the ONN with two hidden layers and the nonlinear function of Softplus trained by the SGD algorithm exhibits the highest recognition accuracy of 96%, when the momentum coefficient increases to 0.9, the accuracy of ONN is improved to 96.9%. However, the RMSprop algorithm with momentum leads to nonconvergence or slow convergence of network recognition accuracy.
In this study, we propose a ground-segmentation algorithm based on a two-stage coarse-fine processing approach to address the limitations of traditional LiDAR ground-segmentation algorithms, such as poor real-time performance and threshold dependence for complex slope roads. First, the point cloud was divided into fan-shaped regions, with the local slope threshold of each area being adaptively determined to complete the first stage of rough segmentation. Subsequently, the point cloud was projected onto the RGB image, and "unknown classification points" were obtained using an image expansion algorithm. Finally, effective points were screened out to perform convolution filtering on the "unknown classification points" to achieve fine segmentation and to determine the distance threshold by dividing multiple regions. The results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm achieves a ground-point segmentation accuracy exceeding 96% for both flat roads and complex slope roads. In addition, the recall rates consistently maintain a high level of over 95%. Moreover, the local slope threshold can be adjusted to achieve excellent robustness, and the average processing time is 16.57 ms, which satisfies the real-time requirements of unmanned vehicles.
The presence of clouds affects a wide application of remote-sensing images. Based on the high spatial resolution and wide band range of the visual and infrared multispectral imager (VIMI) of the hyper-spectral observation satellite, an improved multichannel-threshold cloud-detection algorithm applicable to the VIMI data is proposed. First, potential cloud pixels and clear pixels are separated according to various characteristics of clouds in the visible-thermal infrared channels. Then, the probabilities of temperature, variability, and brightness are combined to generate a cloud mask over land and water. Finally, clear-sky restoration tests are applied to the potential cloud layers to reduce the misclassification of clouds over land, water, and snow/ice scenes. The results of the improved multichannel-threshold cloud-detection algorithm are quantitatively compared with those of the conventional cloud-detection algorithm. The results show that the improved algorithm can be applied to different surface scenes to obtain better detection results with an average overall accuracy of 92.0%, and the overall difference is reduced by 3%. Furthermore, the average cloud-pixel accuracy and clear-sky pixel accuracy are obtained as 92.4% and 91.8%, respectively. The results show substantial reduction in misclassification and omission errors; especially, on the bright surface, the average cloud-pixel accuracy over a city and snow surfaces improves by 4% and 5% and the difference decreases by 4% and 2%, respectively. The improved cloud-detection algorithm outperforms the conventional algorithm in terms of high efficiency operation.
Remote sensing scene classification aims to assign specific semantic labels to aerial images, which is a fundamental and important task in remote sensing image interpretation. Existing studies have used convolutional neural networks (CNN) to learn global and local features and improve the discriminative representation of networks. However, the perceptual wilderness of CNN-based approaches has limitations in modeling the remote dependence of local features. In recent years, Vision Transformer (ViT) has shown powerful performances in traditional classification tasks. Its self-attention mechanism connects each Patch with a classification token and captures the contextual relationship between image pixels by considering global information in the spatial domain. In this paper, we propose a remote sensing scene classification network based on local selection ViT, in which an input image is first segmented into small chunks of Patch that are unfolded and converted into sequences with position encoding; thereafter, the obtained sequences are fed into an encoder. In addition, a local selection module is added before the last layer of input in order to learn the local discriminative features, and Token with discriminative properties are selected as input to obtain the final classification output. The experimental results show that the proposed method achieves good results on two large remote sensing scene classification datasets (AID and NWPU).
This study proposes a semi-supervised method using multimodality data with contrastive learning to improve the classification accuracy for hyperspectral images (HSI) and light and detection ranging (LiDAR) data in the case of a few labeled samples. The proposed method conducts contrastive learning using HSI and LiDAR data without labels, which helps to build the relationship between the spatial features of the two data. Thereafter, their spatial features can be extracted by the model. We designed a network combining the convolution and Transformer modules, which allows the model to extract the local features for establishing a global interaction relationship. We conducted experiments on contrastive learning on the Houston 2013 and Trento datasets. The results show that the classification accuracy of the proposed method is higher than that of other multisource data fusion classification methods. On the Houston 2013 dataset, the classification accuracy of the proposed method is 20.73 percentage points higher than that of the comparison method when the number of labeled samples is five. On the Trento dataset, the classification accuracy of the proposed method is 8.35 percentage points higher than that of the comparison method when the number of labeled samples is two.
The FY_3D satellite medium-resolution imager (MERSI-II) has been primarily used for meteorological observation, environmental monitoring, disaster prevention, and mitigation. As the observation angle of FY_3D satellite transit is expected to affect the calibration accuracy, this study proposes a site calibration method based on bidirectional reflectance distribution function (BRDF) model. In July 2022, a satellite-ground synchronous measurement experiment was conducted in the Dunhuang calibration field, and 42 BRDF models were established based on six kernel-function combinations which included seven sets of unmanned aerial vehicle multiangle observation data at different moments in 2020. Consequently, the applicability of the constructed BRDF model for the FY_3D images obtained from different observation angles was analyzed. The relative deviation between the apparent reflectance of each band of the sensor based on the BRDF model and that measured by the satellite was calculated. The results show that the difference between the corrected surface reflectance of different models is not more than 1% affected by the time and sun angle, and not more than 3% affected by the different combinations of the kernel functions of FY_3D. Furthermore, the average relative deviation of apparent reflectance from satellite observations calculated by the B1-B12 band model of MERSI-II in 2021 was less than 5.22%, whereas that from satellite observations calculated by the B1 and B2 band models in 2022 was more than 8%; the remaining bands were less than 5.74%.
Super-resolution optical imaging technology has significant implications for biology, life science, and materials science. The mainstream technology to achieve super-resolution optical imaging relies on fluorescence imaging, but fluorescence-based super-resolution imaging cannot reveal molecular-specific information and causes cytotoxicity to living cells. In contrast, photothermal microscopy is a promising analytical technique that allows noninvasive imaging of molecular bonds. Therefore, photothermal microscopy can overcome the inherent limitations of super-resolution fluorescence imaging, making it an attractive option with excellent application prospects. This review discusses the theoretical basis of photothermal microscopy, development of the imaging technique, and the methodological developments that improve the detection limit and spatial resolution. We further provide future perspectives for promoting the development of high-sensitivity and super-resolution photothermal imaging technology.
High dynamic range imaging images are images that truly represent the high dynamic range brightness of natural scenes, and can reflect more information about natural scenes. Multi-exposure fusion has become one of the important means to reconstruct high dynamic range images due to its advantages of no need to improve hardware and simple algorithm process, and has been widely used in mobile phone cameras, industrial cameras, and other fields. In this paper, the multi-exposure image fusion methods for static scenes and dynamic scenes were classified and summarized according to the fusion level and motion pixel processing methods, and the methods based on deep learning were analyzed and summarized separately. Secondly, the relevant datasets and performance evaluation indicators of multi-exposure image fusion were reviewed, and the performance evaluation indicators used in the fusion method were summarized. Finally, the issues worthy of attention in multi-exposure image fusion research were prospected, and ideas for follow-up related research were provided.
Smoke screening is an effective passive interference countermeasure that is extensively used to counter various types of electro-optical reconnaissance and guided weapons. Evaluating smoke screening and its interference effects is crucial for assessing photoelectric countermeasures and tactical deployment, which constitutes the main focus of research within the context of smoke screen technology. Current evaluation methods are complex and lack a solid foundation; therefore, we proposed evaluation methods to better describe the smoke screening and interfering effects, based on a review of existing evaluation methodologies. These methods focus on the shielding performance of the smoke screening, the operational states of the interfered targets, and the changes in the image quality before and after smoke screening. Moreover, we discussed the proposed method's advantages and disadvantages, application occasions, and limitations. Finally, this paper outlines future research directions and emerging trends concerning the effects of smoke screening.
Hydrogen possesses highly reactive physical properties, which may lead to fire and explosion accidents in cases of leakage. Based on the arrangement of point-type hydrogen sensors, employing Raman-Lidar telemetry technology can enhance noncontact, remote, and large-coverage detection of hydrogen leakage, thereby facilitating the rapid development of diversified hydrogen energy utilization scenarios and ensuring the safe and efficient utilization of hydrogen energy. First, an overview of the fundamental principles of gas Raman scattering is provided. Second, the research progress in Raman-lidar telemetry technology for hydrogen leakage is examined, both domestically and internationally, from two aspects: system structure and detection effect. Finally, the prospective applications of Raman-lidar telemetry technology in hydrogen leakage monitoring and detection are studied.