View fulltext
View fulltext
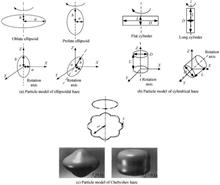
In order to distinguish the non-spherical haze particles with different physical characteristics, the haze detection model of "solar-blind" ultraviolet backscatter is established to simulate the process of UV backscatter under the condition of non-spherical haze, based on T-matrix theory and Monte Carlo method. The peak power and the full width at half maximum of UV pulse with different widths are analyzed. The simulation results show that when the haze concentration is less than 500 μg/m3, the peak power of backscatter echo of UV pulse increases with the increase of haze concentration, and there is a linear relationship between the peak power of pulse echo of different concentrations of haze, and the full width at half maximum of pulse echo decrease with the increase of haze concentration. For ellipsoidal and cylindrical haze particles, under the same concentration, the smaller the shape variable of particles is, the larger the peak power and the full width at half maximum of pulse echo are. For chebyshev haze particles, under the same concentration, the larger the deformation parameters and ripple parameters are, the larger the peak power and the full width at half maximum of pulse echo are. The results of this study can provide a basis for the detection of haze concentration and the discrimination of non-spherical haze particles by ultraviolet light.
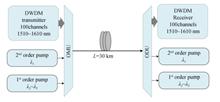
In order to achieve a larger amplification bandwidth, while increasing the output gain and maintaining a small gain flatness, a second-order Raman fiber amplifier is designed, which used a second-order pump and four first-order pumps to perform distributed Raman amplification on 100 channels of signal light. First, numerically solve the second-order Raman coupled wave equation. Simultaneously, in order to further improve the output performance, the performance parameters of the second-order Raman fiber amplifier are optimized by using particle swarm optimization algorithm. Then, under the same pump parameter configuration, compare the first-order RFA with the second-order RFA. Finally, the factors affecting the output gain of the second-order Raman amplifier are analyzed. Through experimental simulation, within the 1 510~1 610 nm gain bandwidth range, the designed second-order Raman fiber amplifier has an average output gain of 23.768 0 dB, a maximum output gain of 24.124 4 dB and the gain flatness is 0.911 2 dB.
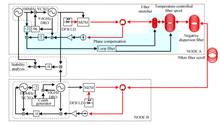
An experimentally study on microwave frequency transfer over a 50 km long fiber was reported, which frequency instabilities reach 4.38×10-15@1 s and 2.80×10-18@65.5×103 s. By using the well-known Doppler noise cancellation method, the fiber noise was measured by comparing the phase of the signal double-passed fiber and the reference one at local site, and compensate the fiber noise with a home-made fiber-based variable delay line, which includes a fiber stretcher driven by a piezo-transducer for fast action with 1 kHz bandwidth and a temperature controlled fiber spool with a delay adjustment range of 5 ns. Compared with electronic phase compensation technique, this approach is insensitive to microwave leakages which is difficult to avoid in such a case, consequently, enables a better instability for long terms. In addition, we synthesized the back and forward transferred signals into two different frequencies to avoid effect introduced by stray optical reflections, and employ dispersion-compensation fiber to reduce the penalty due to the chromatic dispersion.
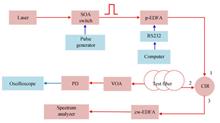
The limitation of peak power caused by two kind of nonlinear effect, self-phase modulation and stimulated Brillouin scattering, in G.652 single-mode fiber is studied. It shows that dispersion and self-phase modulation lead to distortion of optical pulse waveform and its effect is determined by optical pulse peak power.Stimulated Brillouin scattering results in fast decay of pulse power in fiber and further shorter sensing distance, and its effect is determined by optical pulse energy. Experiment data shows that self-phase modulation puts more stringent limit on optical pulse lauch power. Based on the analysis of experimental data, empirical formulas for power upper limit are given, which can be used to estimate the maximum optical pulse incident power in distributed fiber sensing systems. For a typical distributed fiber sensing system with range of 25 km, the incident power upper limit of optical pulse peak is about 1 W.
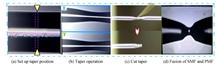
In this paper, a dual optimized down taper structure based on fiber Mach-Zehnder interferometer is designed. This structure is manufactured by using insufficient arc discharge splicing between single-mode fiber and polarization-maintaining fiber method, achieving simultaneous measurement of strain and temperature. The spherical core which located at the middle of the down taper can further regulate the light power distribution in the core and cladding area. The optimized structure can obtain a larger interference fringe extinction ratio of 16 dB, which is greater than the dual-down taper structure under the same parameters. Sensing experiments show that the proposed structure has high resolutions of ±1.616 με and ±0.79℃ in the range of 0~244.35 με and 25~50℃, respectively. The measurement error of both parameters is less than 1×10-3% due to cross-sensitivity. This structure provides a promising method for simultaneous measurement of strain and temperature, which can be applied to precision instrument measurement.
There is an error between the measured strain of the fiber Bragg grating sensor bonded on the surface of bending host material and the real strain of the host material. As a result, the issues of the deformation mechanism and the relationship between measured strain and real strain of the fiber Bragg grating sensor received considerable critical attention. First of all, the interaction mechanism between the fiber Bragg grating sensor and the host material was studied. Then, finite element solution, experimental value and theoretical solution were used for comparison and verification. Also, the causes of the errors were analyzed. Finally, the influence of the parameters (e.g., Young's modulus, thickness, bonding length) on the measurement effect of fiber Bragg grating sensor was studied. The results reveal that finite element solution, experimental value and theoretical solution exhibit the same variation trend. The error between finite element solution and theoretical solution is controlled within 2%, while the error between experimental value and theoretical solution is controlled within 7%. The average strain transfer rate increase with an increase of both the Young's modulus of the host material and the bonding length. Opposite conclusion held for the decreasing elastic modulus of the adhesive and increasing thickness of the adhesive. This theory has a certain guiding significance for the design of fiber Bragg grating sensors used for the strain measurement of the bending host material.
Aiming at the ill posed problem of motion blurred image restoration in traditional exposure mode, a method of motion blurred image restoration based on complementary sequence pairs of fluttering shutter is proposed. The imaging principle of fluttering shutter and the correlation characteristics of code sequence in frequency domain are analyzed. Combined with the information complementarity characteristics between coding sequence pairs, the Golay complementary sequence generation theory is introduced to construct binary fluttering shutter complementary sequence pairs with moderate length. The joint modulation transfer function of complementary sequence pair realizes information complementarity in frequency domain, its curve has a larger minimum value and a lower variance value than the modulation function of the single code word, and it forms peak valley correspondence, which ensures that complementary image sequence can compensate each other for spatial information loss caused by motion blur. The total variation regularization model is introduced to construct an integrated multi frame image deblurring restoration algorithm framework to achieve effective acquisition of clear images. A real-time simulation imaging platform for moving objects is built, and experiments of simulation and real-time motion blur restoration are carried out. The experimental results show that the proposed method can better retain the details of the scene, obtain high-quality motion blur restoration results, and effectively improve the negative effects in the restoration process. Compared with other acquisition methods of moving target imaging, the proposed method has better subjective and objective evaluation results.
In order to improve the accuracy and real-time performance of infrared image target detection, an infrared target fusion detection algorithm based on pseudo modal transformation is proposed. First, the pseudo visible image corresponding to the infrared image is obtained by using the advantage of dual cycle generation confrontation without training image scene matching; then, the residual network is constructed to extract the features of the dual-mode image, and the feature vector is fused by the add superposition method, and the rich semantic information of the visible image is used to make up for the lack of the target information of the infrared image, so as to improve detection accuracy. Finally, considering the target detection efficiency, three scales of dual-mode targets are predicted by using the YOLOv3 single-stage detection network, and the targets are classified by using the logistic expression model. Experimental results show that the algorithm can effectively improve the accuracy of target detection.
High-precision image registration is the key to ensure the in-flight data validity of the Directional Polarimetric Camera (DPC). This paper introduces the polarization image registration method based on optical wedge and the multi-angle, multi-spectral image registration method based on earth reference grid. The error of the registration performance of the multi-angle and multi-spectral image of DPC are fully investigated, and the use of relative geometric calibration is applied to correct the error and improve the registration performance. To verify the effectiveness of this relative geometric calibration method, we compare the registration effects before and after error correction. The results reveal that the accuracies of DPC in flight multi-angle, multi-spectral and polarized image registration are better than 0.26 pixel, 0.14 pixel and 0.1 pixel respectively, which show an improvement of the registration performance.
A light field camera is used to collect particle images, and the tomographic inversion algorithm is improved to obtain the three-dimensional spatial position of particles faster and more accurately. Based on imaging principle of the light field camera, a forward tracing model of light emitted by particles is established. On the basis of this model, a tomographic inversion model is constructed to reversely trace rays emitted from non-zero pixels and realize the mapping between non-zero pixels and spatial voxels. A descending dimension method is proposed to calculate the weighting matrix. The depth accuracy of MART algorithm is improved by combined with the similar triangle principle. According to the Gaussian Blob model, center position of voxel with the strongest intensity is taken as the three-dimensional position of particles. Experiments indicate that the improved MART algorithm can significantly reduce calculation time and memory size while meeting the accuracy requirement. The x-axis coordinate error is ±0.16 mm. The y-axis coordinate error is ±0.18 mm. The z-axis coordinate error is ±1.8 mm. It is more suitable for occasions that demand higher calculation speed and has better practical application value.
In the galvo scanning laser drilling systems, the depth of processing is usually limited due to the short focal length. To solve this problem, a method based on high damage threshold spatial light modulator loading Fresnel lens phase is proposed. The focal length of the Fresnel lens is adjusted to change the position of the focus. As the machining depth increases, the focus position moves downward. Then the experiment processing and testing were carried out. The experimental results show that a high quality microhole with a diameter of about 330 microns was machined on stainless steel sample by using the method. The new method uses galvo scanning laser drilling systems and spatial light modulator to process microhole, which has a good application prospect in the field of laser processing.
A gradient-index lens with a diameter of 1.8 mm, a cylindrical lens with a diameter of 2.5 mm and a volume Bragg grating are designed and fabricated as an optical system for a commercial blue single-tube semiconductor laser with a fast axis full width at half maxima of 23°. The experimental results show that this scheme can achieve a beam width of 0.48 mm at a distance of 5.5 m from the system, and the beam width is less than 0.60 mm in 5.5±0.5 m nearly, which can provide a new solution for the selection of the measurement scheme of line structured light.
An artificial neural network method is proposed for estimating reduced scattering coefficient μs' and phase function parameter γ of biological tissues from spatially resolved reflectance profiles in the sub-diffusive regime. Monte Carlo simulation method is used to obtain data samples of diffuse reflection from biological tissues. These data samples are used to train back-propagation neural network get the information of γ predicted from the sub-diffused scattered light. Since there is a large error occurs when predicting μs' and γ simultaneously, the segmenting data train of two back-propagation networks is performed to identify the μs' and γ in turn. It is found that 3.64lth (lth representing the average transport free path) is an insensitive points of γ. The network trained with data samples near this point is used for predicting μs', while the network trained with data samples in the 2lth is used for predicting γ. Monte Carlo simulation result show that within the range 1.3 ≤ γ ≤ 1.9, the relative root mean square error between the predicted result and the true value is within 1%. Compared with the existing measurement methods, the proposed method is simpler and has improved accuracy.
Trace detection of genetic tumor marker microRNA (miRNA) has important application value for early diagnosis of cancer. According to the Surface-enhanced Raman Scattering characteristics of hollow sea urchin gold nanoparticles and Ag/ZnO nanostructures, and based on the principle of complementary base pairing, a "sandwich" structure of probe-nucleic acid-substrate is constructed and a highly sensitive quantitative detection scheme for genetic tumor marker miRNA is proposed. First, the captured DNA is linked to the hollow sea urchin gold nanoparticles modified with 4-mercaptobenzoic acid (4-MBA) as a probe. At the same time, the target DNA is modified on the Ag/ZnO nanostructure, and the SERS signal is detected to obtain the corresponding dose-response curve after complementary hybridization with miRNA-106a. The experimental results show that the detection limit of miRNA-106a reached 1.84 fmol·L-1 within the detection range of 1 fmol·L-1~1 nmol·L-1. Meanwhile, the reliability of the miRNA detection scheme based on the hollow sea urchin gold nanoparticles and Ag/ZnO nano-structure SERS characteristics was verified by the Real-time quantitative Polynucleotide Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR) method.
Active cooling must be utilized to meet the need for the space-based telescope which need very low detector noise level. The precise thermal control measures based on thermo-electric cooling technique are utilized and especially the package system and heat rejection system of thermo-electric coolers and its cotroller system are designed respectively. The parasitic heat load to the detector and the heat path resistances are optimized to reduce the input power and the radiator size. Based on the Peltier effect and Joule effect and Frourie effect, the relations between the enviroments parameters and working parameters are analyzed. The enviroments parameters include the heat pumped requirements, the thermal resistance between the hot side and the sink and the hot side sink temperature, while the working parameters include the current, voltage and input power of coolers. The sensitivity between the heat loads, thermal resistance and the input power are especially researched. The qualification model of the telescope is developed and the thermal vaccum and balance test are accomplished. The test results show that the system design are appropriate and effective, the detector temperature is controlled at -75±0.2℃. Based on the test environments conditions and the cooler's working parameters, the thermal analysis model are discussed and corrected.These lessons can provide some reference for the development of thermo-electric cooling system of the similar space based telescope.
The mathematical model of fundus imaging under the non-coaxial array illumination is established. A micro optical system of fundus camera is proposed by using the independent design method of illumination light path and imaging light path, which avoids the interference of human cornea and omental objective reflected light on the retina image in the traditional fundus camera. The design of 6-array ring light source illumination system is completed, which is only 17.9 mm in length and the effective illumination line field of fundus retina is not less than 12 mm. The secondary imaging design is adopted in the imaging optical system.The modulation transfer function is better than 0.2@91 lp/mm and the distortion is less than 5% with 75 mm length. The simulation and design results show that the optical system of the proposed fundus camera can effectively suppress the stray light in the optical path which is conducive to obtaining high contrast retinal image. The results can provide a design reference for the development of high image quality, miniaturization and low stray light fundus camera.
The effects of different optical window positions and different optical window areas on the optical response characteristics of SiGe/Si Heterojunction Phototransistor (HPT) are analyzed. HPTs with emitter optical window can generate more photo-generated carriers due to the longer absorption region, and then bring out a larger optical-generated voltage at emitter junction interface, which is beneficial for electronsto inject from the emitter into the base. Therefore, a larger collector current and optical gain are obtained. When the optical window area is 10 μm×10 μm, the maximum optical gain of SiGe/Si HPT can reach 9.24 with 650 nm incident light wavelength and 2.0 V collector voltage. HPTs with base optical window get larger photo-generated carrier density in the absorption region when incident power become larger, then the possibility of rapid relaxation for photo-generated holes increases, which relieves the limitation of the operating speed from hole's low mobility to some extent, so the optical characteristic frequency is increased. When the optical window area is 10 μm×10 μm, the optical characteristics frequency of SiGe/Si HPT can reach 16.75 GHz with 650 nm incident light wavelength and 2.0 V collector voltage. For the SiGe/Si HPTs with emitter optical window that can achieve higher optical gain and optical characteristic frequency merit, when the optical window area gradually increases from 3 μm×10 μm to 50 μm×10 μm, the effective injection area of electrons at emitter junction interface gradually increases. However, at the same time the emitter junction capacitance and collector junction capacitance increase and results the RC delay time increasing, so the optical characteristic frequency gradually decreases. The optical gain and optical characteristic frequency merit increase gradually with the increase of the optical window area, but the rate of increase slows down and the optical gain and optical characteristic frequency merit tends to become saturated.
Dy3+ and Eu3+ ions with different doses were implanted into AlN thin films grown by hydride vapor phase epitaxy method. For Dy doped AlN, results of X-ray diffraction and Raman scattering show that the compressive stress of the sample increases with the increase of Dy3+ dose. When the Dy3+ dose increases from 5×1014 at/cm2 to 1×1015 at/cm2, the compressive stress of samples is close to saturation. For Dy3+ and Eu3+ co-doped AlN, according to the cathodoluminescence spectra, a possible energy transfer process between Dy3+ and Eu3+ is proposed. In addition, through changing the dose ratio of Dy3+ respect to Eu3+ ions, the chromaticity coordinates and color temperatures of Dy3+ and Eu3+ co-doped AlN can be effectively regulated.
SiO2/YF3 and TiO2/YF3 composite films were prepared by SiO2, YF3, TiO2 single-component materials respectively, the changes of optical, mechanical and laser damage resistance properties of the composite films were explored. Two kinds of fluorine-oxide composite films with a mixing molar ratio of 1:1 were prepared by controlling the deposition rate of the materials during evaporation through dual-source co-evaporation technique, the refractive index, extinction coefficient, transmission characteristics, surface morphology and roughness of the composite films were investigated, and laser damage resistance performance was studied. The results show that the refractive indexes of SiO2/YF3 and TiO2/YF3 composite films are 1.478 7 and 1.864 6(wavelength 550 nm) respectively, which are between the single-component materials(YF3 1.493 6, SiO2 1.465 1, TiO2 2.048 3), and all present normal dispersion distribution; the results of ZYGO interference measurement show that the stress value of SiO2/YF3 film is 1.9 GPa, which is larger than the 0.4 GPa of the single-component materials SiO2 and YF3 but less roughness; the stress value of TiO2/YF3 film is 0.8 GPa, which is smaller than the 3.9 GPa stress of TiO2 but larger than YF3, both of them show a more obvious stress adjustment effect. The laser-induced damage threshold of SiO2/YF3 composite film is 9.2 J/cm2, which is 2.2% higher than single-component SiO2 and 39.2% higher than YF3; the laser-induced damage threshold of TiO2/YF3 is 7.8 J/cm2, for the single-component TiO2 film, it increases by 85.6%, compared with YF3 by 17.4%. The fluorine-oxide composite films are deposited by dual-source co-evaporation technology with small absorption and adjustable film refractive index; SiO2/YF3 and TiO2/YF3 composite films are better than single-component materials in resisting laser damage; the doping of YF3 can significantly reduce the stress of the single TiO2 material, but the stress of SiO2/YF3 is larger than that of single-component SiO2 and YF3 films.
In order to study the semi-transparent thin film solar cell with better material stability, use direct current magnetron sputtering technique to deposit cuprous oxide(Cu2O) thin film and zinc oxide(ZnO) thin film, forming the Cu2O/ZnO heterojunction. By using scanning electron microscope, X-ray diffractometer, raman spectrometer, thin film measurement instrument and solar simulator, the influence caused by Cu2O layer prepared under different Ar/O2 gas flow ratio on material properties, optical properties and photoelectric properties of heterojunction is studied. Results show that the Cu2O/ZnO heterojunctions produced under the certain Ar/O2 gas flow ratios have certain photoelectric conversion ability under the standard simulated sunlight of AM1.5, which can be used as the energy conversion unit of the semi-transparent solar cell.