View fulltext
View fulltext
Under the opportunity of "Made in China 2025", in the field of ultra-precision, China has broken through many key bottleneck technologies, achieved many remarkable scientific research results, built a number of high-level ultra-precision processing technology innovation platforms, talent growth platforms and application demonstration bases, and created an independent ultra-precision industry in China. This paper mainly introduces the research progress of optical ultra-precision processing technology and equipment in the Precision Engineering Laboratory of Xiamen University. Focusing on the grinding and polishing processing of large-diameter optical aspherical components, the processing technology, grinding and polishing equipment, equipment monitoring and control software and related unit technologies developed by the group are described. These research results can provide manufacturing and processing technology support and equipment solutions for the ultra-precision processing of high-end optical components.
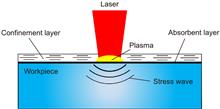
Laser shock peening uses the force effect of the laser to strengthen the surface. The traditional laser shock peening technology is a single-sided shock. When applied to thin-walled parts with complex profiles, it is difficult to achieve shape control and fatigue performance control coordination. The new double-sided laser shock peening technology is ideal for solving the surface strengthening challenges of thin-walled parts with complex profiles. On the basis of introducing the characteristics and deficiencies of single-sided laser shock peening technology, the principle and technical characteristics of two double-sided laser shock peening technologies are summarized. The application of simulation research in analyzing the physical mechanism of stress wave propagation and stress field distribution of double-sided laser shock peening is expounded. The mechanism and application of double-sided laser shock peening in the application of shape control and fatigue performance control are introduced, and the future development of double-sided laser shock peening is prospected.
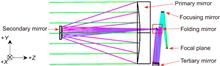
How to further improve the lightweight ratio of high-performance meter-level space mirrors is one of the core issues in the field of large aperture optomechanical structure design. In this paper, a primary mirror with a clear aperture of Φ1200 mm was developed for a high-resolution space camera, which achieves the goal of designing area density below 40 kg/m2. The SiC mirror blank was prepared by gel injection molding and reaction sintering process. The state of the optical axis being horizontal was taken as the testing state to simplify the supporting structure. Novel lightweight measures such as an alternate arrangement of main and auxiliary stiffeners and the addition of lightweight holes on vertical walls were used inside the semi-closed mirror blank. The distributed datums were used to replace traditional datum settings, which reduces the machining area of datums by more than 80% and improves machining efficiency. Through parametric modeling and integrated optimization, the optimal structural parameter combination of the mirror blank was determined, with the final design weight of 46.9 kg. The RMS value of self-weight deformation of the mirror blank is only 2.87 nm under the state of the optical axis being horizontal, and its free fundamental frequency is 602 Hz, indicating that the primary mirror proposed in this paper has good dynamic and static characteristics. After machining, the measured weight of the mirror blank is 51.3 kg, about 9.4% overweight, and the facesheet is about 1-mm thicker than the design. At present, the mirror has already been polished to RMS λ/8 (λ=632.8 nm) of surface shape accuracy, with no obvious print-through effect observed.
Aiming at the problems of color distortion, noise amplification, and loss of detailed information in the process of low illumination image enhancement, a progressive fusion of parallel hybrid attention (PFA) is proposed. First, a multi-scale weighted aggregation (MWA) network is designed to aggregate multi-scale features learned from different receptive fields, promote the global representation of local features, and strengthen the retention of original image details; Secondly, a parallel hybrid attention module (PHA) is proposed. Pixel attention and channel attention are combined in parallel to alleviate the color difference caused by the distribution lag of different branches of attention, and the information between adjacent attention is used to complement each other to effectively improve the color representation of images and reduce noise; Finally, a progressive feature fusion module (PFM) is designed to reprocess the input features of the previous stage from coarse to fine in three stages, supplement the shallow feature loss caused by the increase of network depth, and avoid the information redundancy caused by single stage feature stacking. The experimental results on LOL, DICM, MEF, and LIME datasets show that the performance of the method in this paper is better than that of the comparison methods on multiple evaluation indicators.
Learning with limited data is a challenging field for computer visual recognition. Prototypes calculated by the metric learning method are inaccurate when samples are limited. In addition, the generalization ability of the model is poor. To improve the performance of few-shot image classification, the following measures are adopted. Firstly, to tackle the problem of limited samples, the masked autoencoder is used to enhance data. Secondly, prototypes are calculated by task-specific features, which are obtained by the multi-scale attention mechanism. The attention mechanism makes prototypes more accurate. Thirdly, the domain adaptation module is added with a margin loss function. The margin loss pushes different prototypes away from each other in the feature space. Sufficient margin space improves the generalization performance of the method. The experimental results show the proposed method achieves better performance on few-shot classification.
Feature extraction in the CNN-based stereo matching models has the problem that it is difficult to learn global and long-range context information. To solve this problem, an improved model STransMNet stereo matching network based on the Swin Transformer is proposed in this paper. We analyze the necessity of the aggregated local and global context information. Then the difference in matching features during the stereo matching process is discussed. The feature extraction module is improved by replacing the CNN-based algorithm with the Transformer-based Swin Transformer algorithm to enhance the model's ability to capture remote context information. The multi-scale fusion module is added in Swin Transformer to make the output features contain shallow and deep semantic information. The loss function is improved by introducing the feature differentiation loss to enhance the model's attention to details. Finally, the comparative experiments with the STTR-light model are conducted on multiple public datasets, showing that the End-Point-Error (EPE) and the matching error rate of 3 px error are significantly reduced.
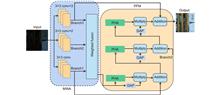
As a kind of high-quality factor thermo-electromechanical coupling device composed of isotropic elastic-optical crystal and piezoelectric crystal, photoelastic modulator (PEM) is widely applied for polarization measurement, spectrum measurement, and many other purposes. However, the resonant frequency tends to drift with temperature changes in the high-voltage resonant state, which destabilizes the phase modulation amplitude of the photoelastic modulator and reduces the driving efficiency. To solve this problem, the resonant frequency characteristics of the photoelastic modulator are analyzed at first. Then, a compound resonant network model of the photoelastic modulator and its high voltage resonant driving circuit is established, and a solution to frequency tracking based on the amplitude-frequency characteristics of the resonant network is proposed. Besides, a control test system based on field programmable gate array (FPGA) is developed to achieve resonant frequency tracking and modulation amplitude measurement. The test results show that this method is applicable to track the resonant frequency effectively and improve the stability and driving efficiency of the elastic light modulator. The duration of the test exceeds 90 min, and the standard deviation of the phase modulation amplitude is 0.83% rad.
The voice coil motor-driven fast steering mirror is an important part of a high-precision photoelectric tracking system. In the photoelectric tracking system of the moving platform, the fast steering mirror system will suffer more complex and intense internal and external interference. The traditional passive interference suppression methods and the active interference suppression methods that treat the interference as lumped interference will not be enough to ensure the high-precision stability of boresight. Therefore, this paper proposes a sliding mode composite layered interference observation and compensation control strategy which combines harmonic interference observation and extended state observation. Firstly, the harmonic disturbance observer is used to observe the harmonic disturbance with a priori frequency information. Then the extended state observer is used to observe other unknown disturbances. Finally, based on the observed multi-source interference, the sliding mode nonlinear method with anti-interference ability is used to design a composite controller to maximize the suppression of multi-source disturbances suffered by the system. The experiment shows that the sliding mode composite layered interference observation compensation method proposed in this paper can significantly improve the LOS stability accuracy of the fast steering mirror compared with the traditional single interference observation compensation method.
In order to realize the rapid measurement of composite surfaces with diffuse and mirror reflection, the composite surface measurement system based on fringe projection and fringe reflection can obtain the absolute phase rapidly through the multi-color channel of the camera. Aiming at the crosstalk and chromatic aberration between the color channels introduced by the camera, projector, and display in the composite surface topography measurement, this paper studies the crosstalk elimination method based on the matrix and the chromatic aberration elimination method of the absolute phase corresponding pixel deviation. Based on the crosstalk matrix, the crosstalk matrix of the projector and display screen is established. The crosstalk intensity from other channels in the desired color channel is eliminated to complete the crosstalk elimination between color channels. The absolute phase in the horizontal and vertical directions of each color channel is obtained by color orthogonal stripes. The relationship between phase difference and pixel deviation is established to realize the pixel deviation correction of each pixel point and eliminate the influence of color difference. The experimental results show that the proposed method reduces the average measurement error of the composite step from 0.479 mm to 0.030 mm, and improves the efficiency and accuracy of measurement.